Abstract
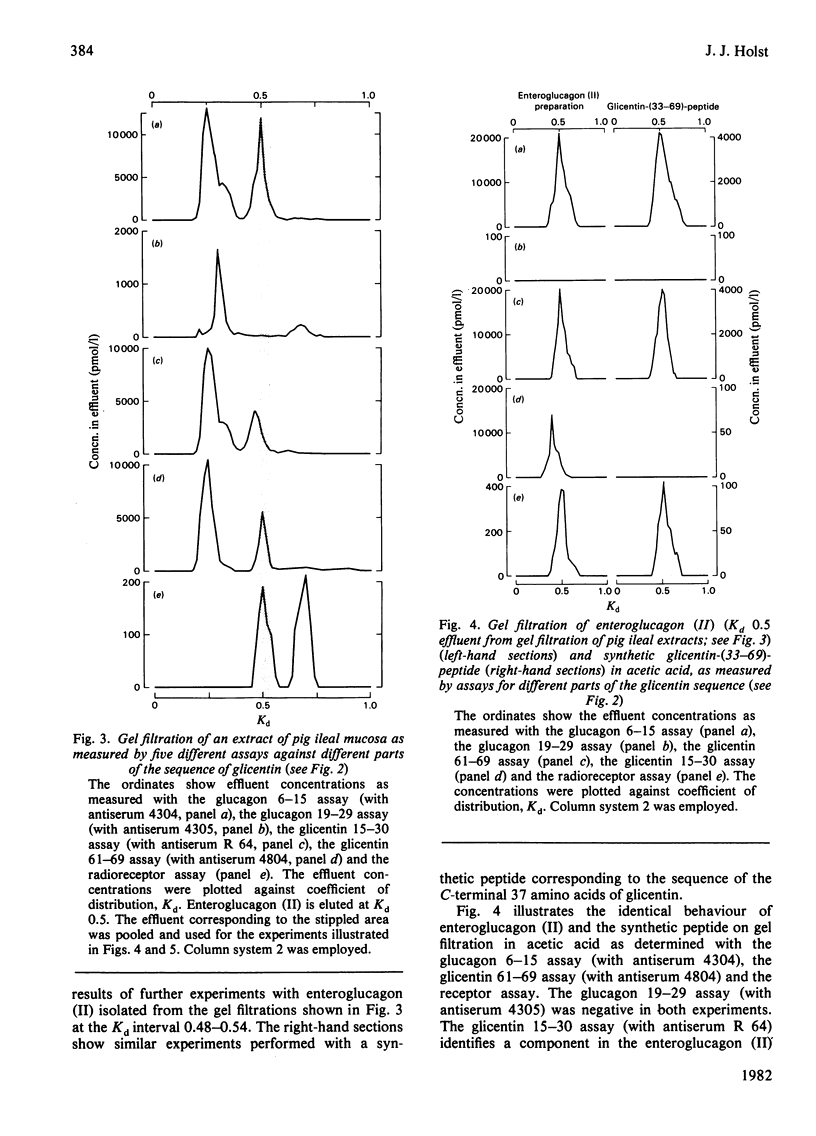
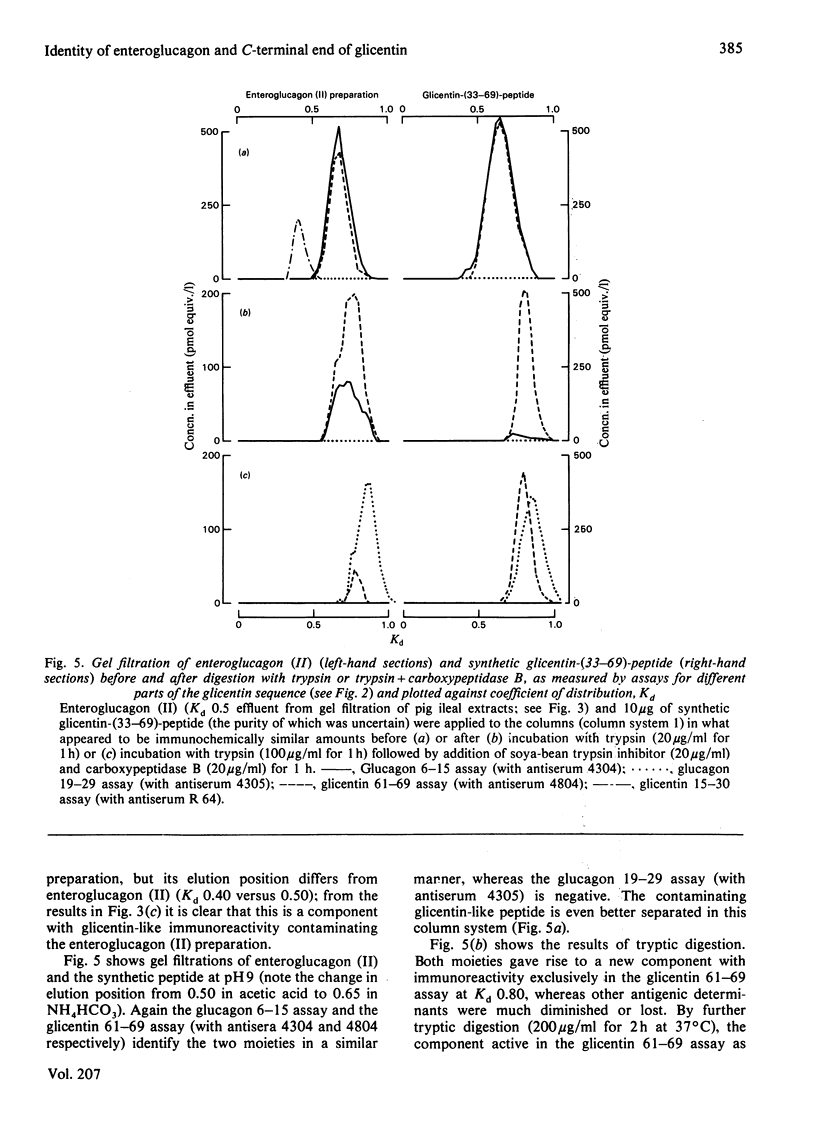
Enteroglucagon (II) was isolated from extracts of pig ileum mucosa by repeated gel filtrations, and its immunochemical and chromatographic characteristics were compared with those of a synthetic peptide corresponding to the 33-69 sequence of pig glicentin, before and after digestion with trypsin or trypsin followed by carboxypeptidase B, by using five region-specific assays covering most of the glicentin sequence. Enteroglucagon (II) and the synthetic peptide behave identically under three different conditions of chromatography as determined with all five assays (including a highly specific radioreceptor assay), and gave rise to similar fragments after enzyme digestion. It was therefore concluded that enteroglucagon (II) and the 33-69 sequence of glicentin are most probably identical.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Holst J. J. A radioreceptor-assay for glucagon: binding of enteroglucagon to liver plasma membranes. Diabetologia. 1975 Jun;11(3):211–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00422324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
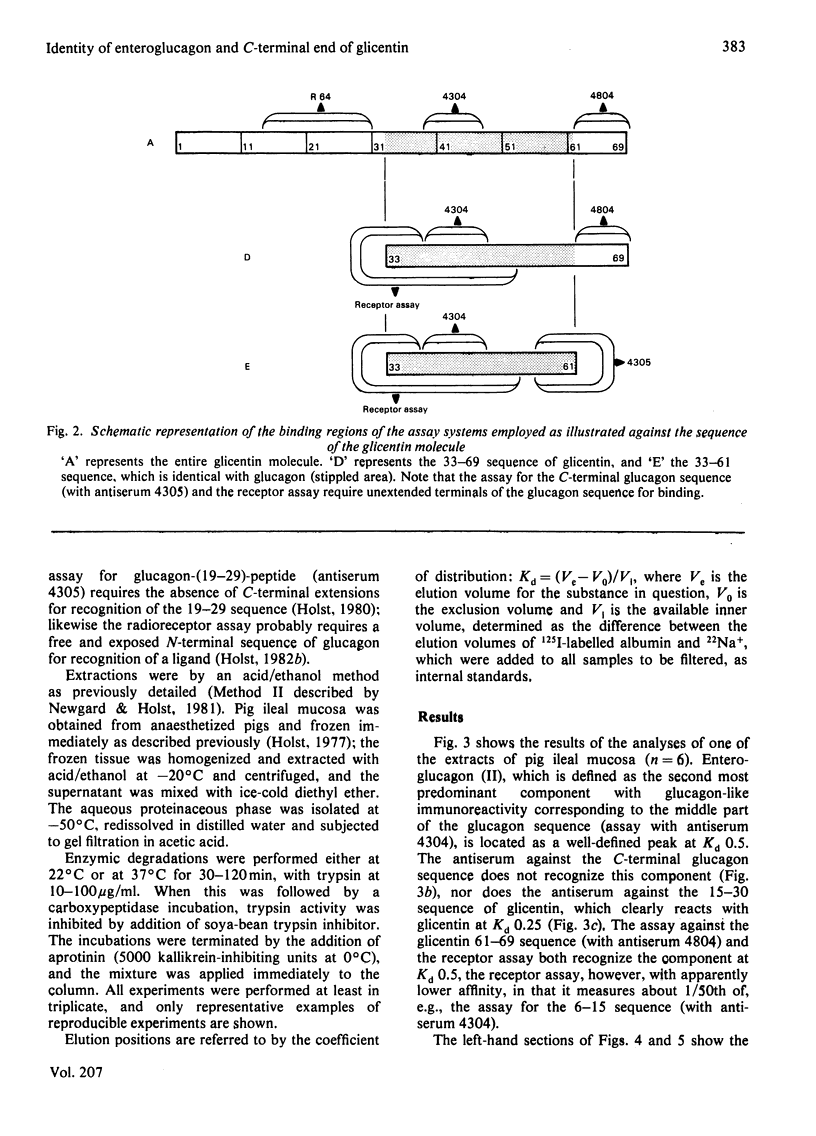
- Holst J. J. Evidence that glicentin contains the entire sequence of glucagon. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj1870337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J. Extraction, gel filtration pattern, and receptor binding of porcine gastrointestinal glucagon-like immunoreactivity. Diabetologia. 1977 Apr;13(2):159–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00745145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J. Extrapancreatic glucagons. Digestion. 1978;17(2):168–190. doi: 10.1159/000198107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen K. H., Larsen U. D. Purification of 125 I-glucagon by anion exchange chromatography. Horm Metab Res. 1972 May;4(3):223–224. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1097092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korányi L., Péterfy F., Szabó J., Török A., Guóth M., Tamás G., Jr Evidence for transformation of glucagon-like immunoreactivity of gut into pancreatic glucagon in vivo. Diabetes. 1981 Sep;30(9):792–794. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.9.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody A. J., Holst J. J., Thim L., Jensen S. L. Relationship of glicentin to proglucagon and glucagon in the porcine pancreas. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):514–516. doi: 10.1038/289514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Holst J. J. Heterogeneity of somatostatin like immunoreactivity (SLI) in extracts of porcine, canine and human pancreas. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Dec;98(4):564–572. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0980564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundby F., Jacobsen H., Moody A. J. Purification and characterization of a protein from porcine gut with glucagon-like immunoreactivity. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Sep;8(5):366–371. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
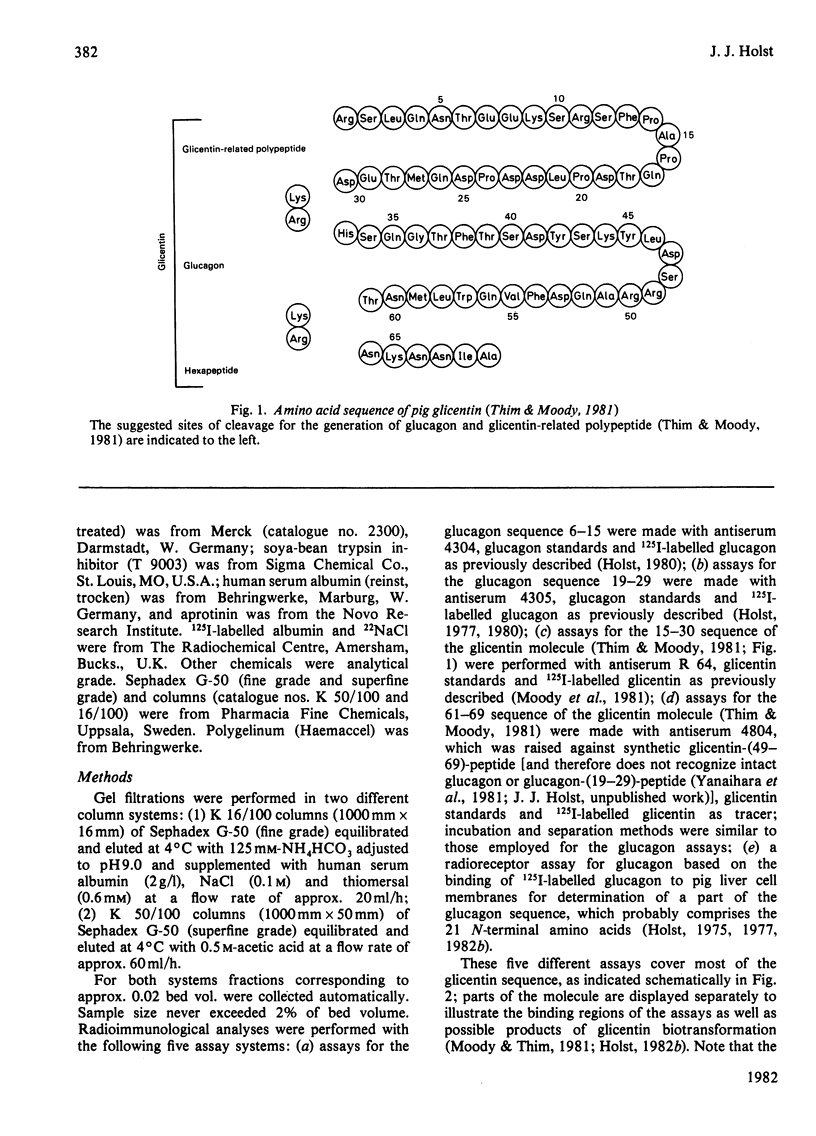
- Thim L., Moody A. J. The primary structure of porcine glicentin (proglucagon). Regul Pept. 1981 May;2(2):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(81)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



