Abstract
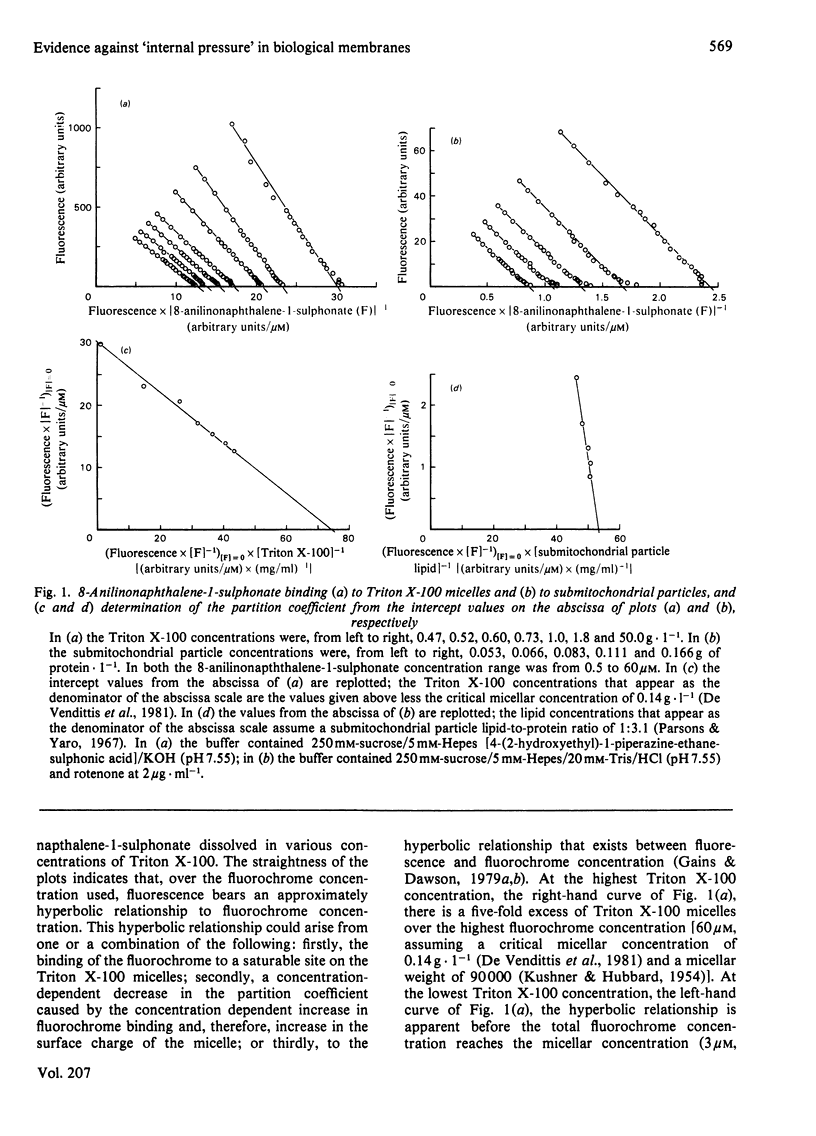
It has recently been proposed that although small amphiphilic molecules partition into phospholipid vesicles this partition is reduced by a factor of 103–104-fold by the presence of proteins in biological membranes [Conrad & Singer (1979) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 5202–5206 and (1981) Biochemistry 20, 808–818]. However, the affinity with which 8-anilinonaphthalene-1-sulphonate partitions into, or binds to, Triton X-100 micelles and submitochondrial particles is very similar and therefore does not support this proposal.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conrad M. J., Singer S. J. Evidence for a large internal pressure in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5202–5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. J., Singer S. J. The solubility of amphipathic molecules in biological membranes and lipid bilayers and its implications for membrane structure. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):808–818. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser A. F., Lanyi J. K. Structure of the lipid phase in cell envelope vesicles from Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochemistry. 1973 May 8;12(10):1933–1939. doi: 10.1021/bi00734a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretten P., Morris S. J., Watts A., Marsh D. Lipid-lipid and lipid-protein interactions in chromaffin granule membranes. A spin label ESR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gains N., Dawson A. P. A kinetic analysis of the changes in fluorescence on the interaction of 8-anilinonaphthalene-1-sulphonate with submitochondrial particles. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):295–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1580295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gains N., Dawson A. P. Transmembrane electrophoresis of 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonate through egg lecithin liposome membranes. J Membr Biol. 1975 Dec 4;24(3-4):237–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01868625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gains N. The limitations of chlorotetracycline as a fluorescent probe of divalent cations associated with membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):199–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. S., Pringle M. J., Miller K. W. Correlation of general anesthetic potency with solubility in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 20;649(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moules I. K., Rooney E. K., Lee A. G. Binding of amphipathic drugs and probes to biological membranes. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 8;138(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons D. F., Yano Y. The cholesterol content of the outer and inner membranes of guinea-pig liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 2;135(2):362–364. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Seeman P. The membrane concentrations of neutral and positive anesthetics (alcohols, chlorpromazine, morphine) fit the Meyer-Overton rule of anesthesia; negative narcotics do not. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



