Abstract
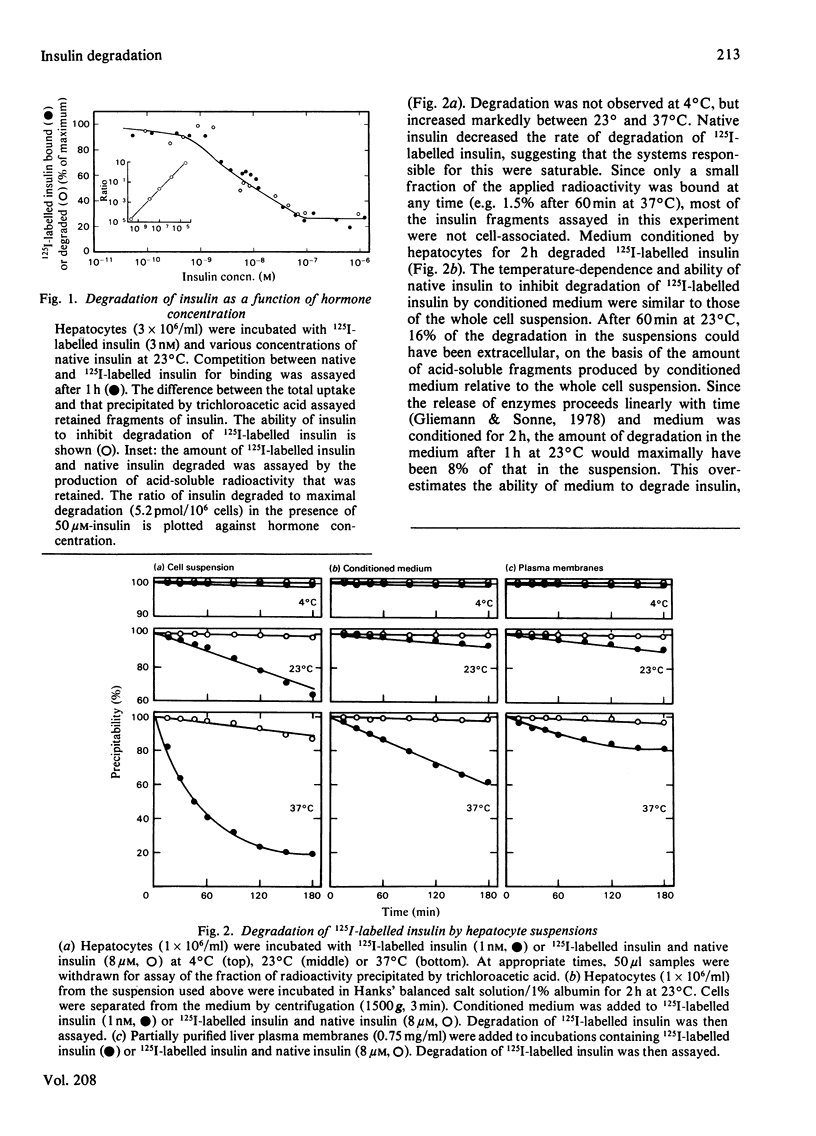
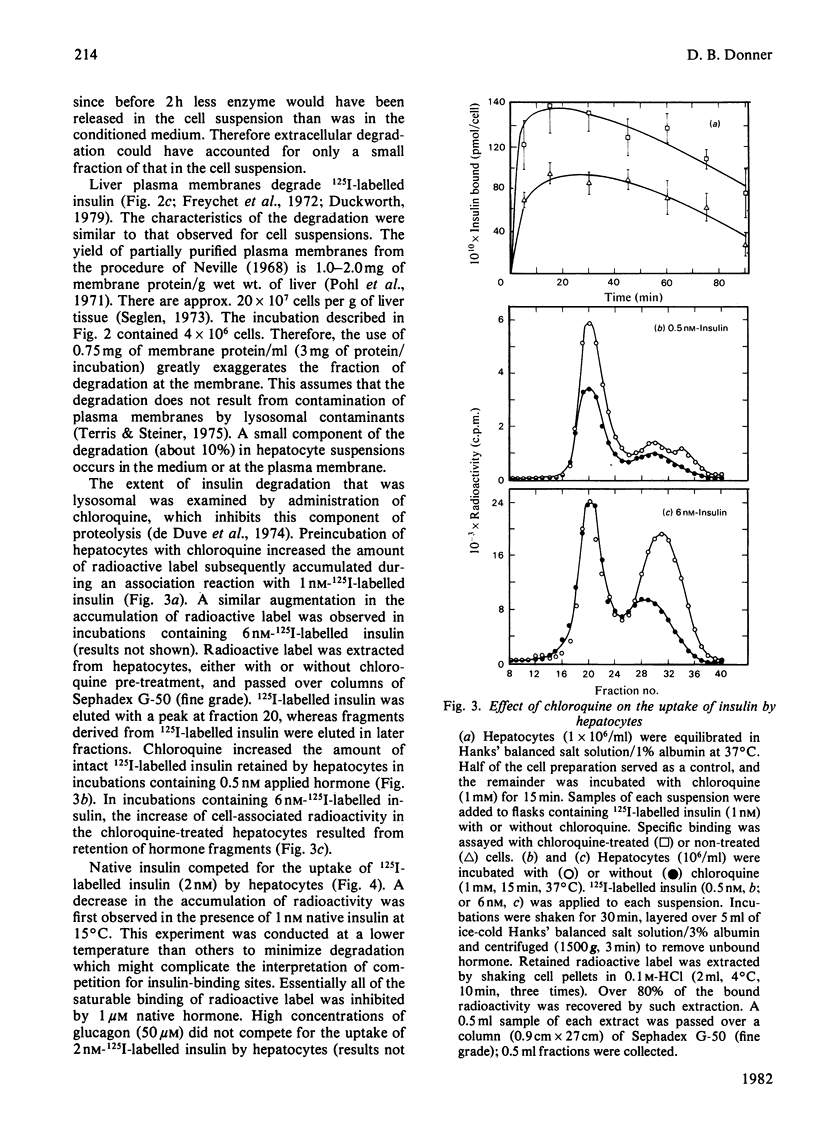
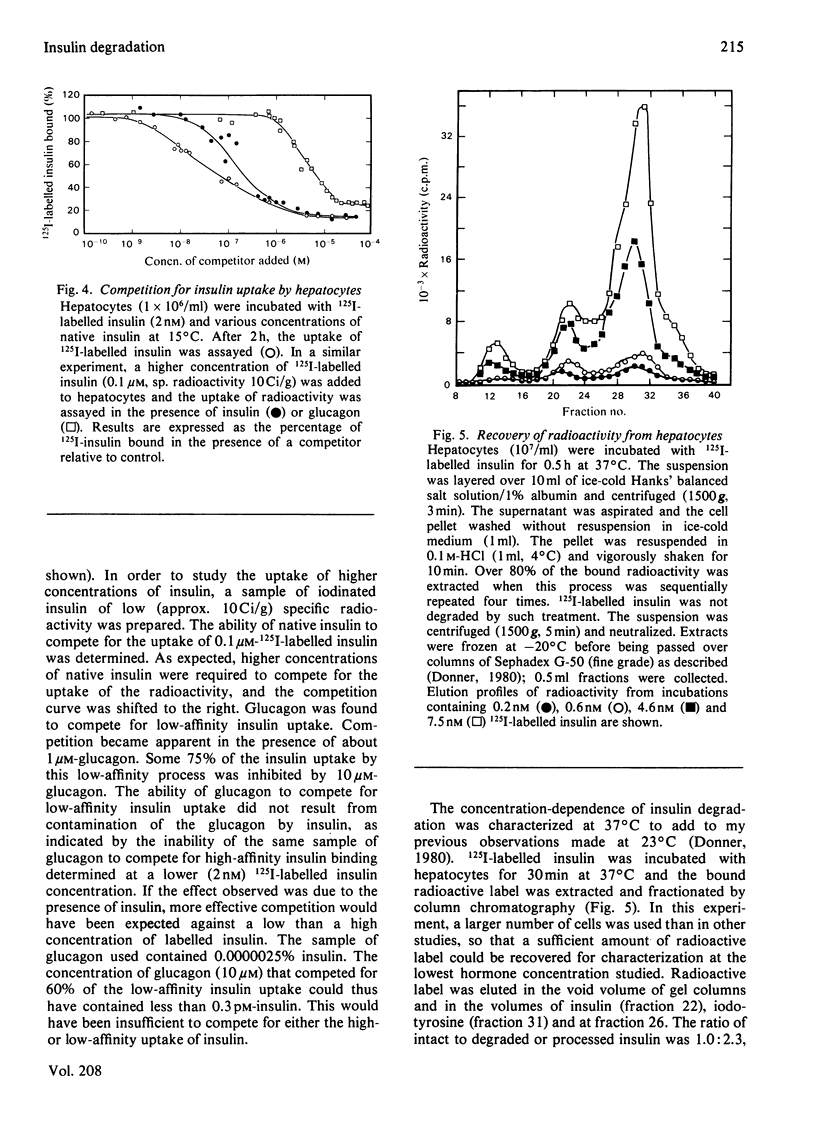
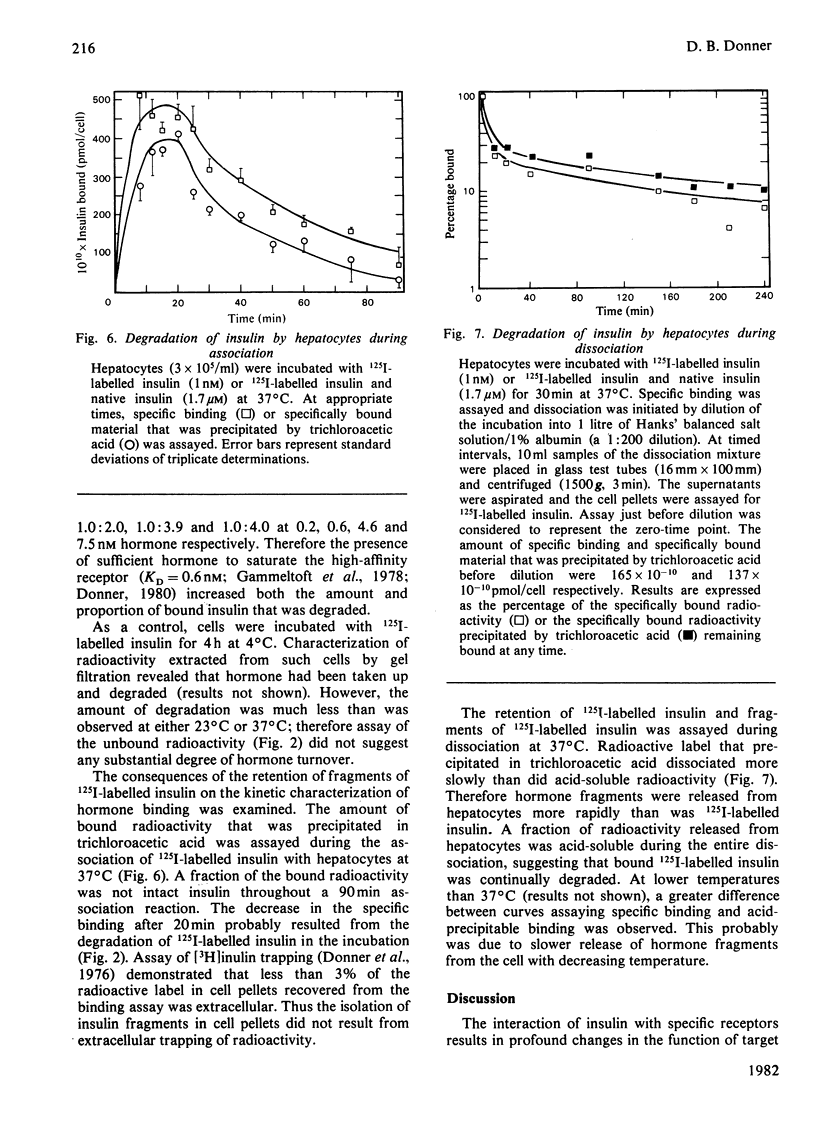
Native insulin inhibits the binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin in parallel. Half-maximal inhibition of degradation occurs with 10nm-insulin, a hormone concentration sufficient to saturate the insulin receptor. The proportion of bound hormone that is degraded increases as the insulin concentration is increased, suggesting that low-affinity uptake is functionally related to degradation. Since only a small fraction (approx. 10%) of the overall degradation occurs at the plasma membrane, or in the extracellular medium, translocation of bound hormone into the cell is the predominant mechanism mediating the degradation of insulin. In the presence of 0.6nm-insulin, a concentration at which most cell-associated hormone is receptor-bound, chloroquine increases the amount of 125I-labelled insulin retained by hepatocytes. However, chloroquine increases the retention of degradation products of insulin in incubations containing sufficient hormone (6nm) to saturate the receptor and permit occupancy of low-affinity sites. Glucagon does not compete for the interaction of 125I-labelled insulin (1nm) with the insulin receptor. In contrast, 20μm-glucagon inhibits 75% of the uptake of insulin (0.1μm) by low-affinity sites. A fraction of the cell-bound radioactivity is not intact insulin throughout a 90min association reaction at 37°C. During dissociation, fragments of 125I-labelled insulin are released to the medium more rapidly than is intact hormone. The production and transient retention of degradation products of the hormone complicates the characterization of the insulin receptor by equilibrium or kinetic methods of assay. It is proposed that insulin degradation occurs by receptor- and non-receptor-mediated pathways. The latter may be related to the action of glutathione–insulin transhydrogenase, with which both insulin and glucagon interact.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Inefficient internalization of receptor-bound low density lipoprotein in human carcinoma A-431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):441–452. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorge S., Bohley P., Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Hanson H. Metabolism of insulin and glucagon. Glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase from microsomes of rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 3;32(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brush J. S., Jering H. The importance of proteolysis as the initial step of insulin degradation in rat liver homogenates. Endocrinology. 1979 Jun;104(6):1639–1643. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-6-1639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghen G. A., Kitabchi A. E., Brush J. S. Characterization of a rat liver protease with specificity for insulin. Endocrinology. 1972 Sep;91(3):633–642. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-3-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Amatruda J. M. Functional relationships between insulin binding, action, and degradation. A reassessment. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10052–10055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Freychet P., Le Cam A., Orci L. Lysosomal association of internalized 125I-insulin in isolated rat hepatocytes. Direct demonstration by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1249–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI109420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corin R. E., Donner D. B. Insulin receptors convert to a higher affinity state subsequent to hormone binding. A two-state model for the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Insulin action and the regulation of hexose transport. Diabetes. 1980 May;29(5):399–409. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.5.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner D. B., Casadei J., Hartstein L., Martin D., Sonenberg M. Characterization of the slowly dissociable human growth hormone binding component of isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3293–3300. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner D. B., Corin R. E. Formation of a receptor state from which insulin dissociates slowly in hepatic cells and plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9005–9008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner D. B., Fu J. J., Hess G. P. Equilibrium dialysis of the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor: a simple method to avoid common errors. Anal Biochem. 1976 Oct;75(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner D. B., Nakayama K., Lutz U., Sonenberg M. The effects of bioregulators upon amino acid transport and protein synthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 21;507(2):322–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner D. B. REgulation of insulin binding to isolated hepatocytes: correction for bound hormone fragments linearizes Scatchard plots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3176–3180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C. Insulin degradation by liver cell membranes. Endocrinology. 1979 Jun;104(6):1758–1764. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-6-1758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Kitabchi A. E. Insulin and glucagon degradation by the same enzyme. Diabetes. 1974 Jun;23(6):536–543. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.6.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Runyan K. R., Wright R. K., Halban P. A., Solomon S. S. Insulin degradation by hepatocytes in primary culture. Endocrinology. 1981 Apr;108(4):1142–1147. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-4-1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Kristensen L. O., Sestoft L. Insulin receptors in isolated rat hepatocytes. Reassessment of binding properties and observations of the inactivation of insulin at 37 degrees C. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8406–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Sonne O. Binding and receptor-mediated degradation of insulin in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7857–7863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Livingston J. N. Insulin degradation by insulin target cells. Metabolism. 1981 Aug;30(8):825–835. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Freychet P. O., Orci L. Internalization of polypeptide hormones: mechanism, intracellular localization and significance. Diabetologia. 1980 Apr;18(4):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00251003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammons G. T., Jarett L. Lysosomal degradation of receptor-bound 125I-labeled insulin by rat adipocytes: its characterization and dissociation from the short-term biologic effects of insulin. Diabetes. 1980 Jun;29(6):475–486. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.6.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hern E. P., Varandani P. T. Turnover of hepatic glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase (disulfide interchange enzyme) in normal and diabetic rats utilizing a new simplified isolation procedure. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):697–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber C. T., Solomon S. S., Duckworth W. C. Time-course of insulin degradation in perifused isolated rat adipose cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):461–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI109689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZEN H. M., STETTEN D., Jr Hepatic glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Diabetes. 1962 Jul-Aug;11:271–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. L., Flier J. S., Grunfeld C., Harmon J. T., Harrison L. C., Karlsson F. A., Kasuga M., King G. L., Lang U. C. Insulin receptors, receptor antibodies, and the mechanism of insulin action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1981;37:477–538. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571137-1.50015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Peptide hormone-induced receptor mobility, aggregation, and internalization. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 9;305(2):77–88. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107093050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Lane M. D. Evidence for different pathways for the degradation of insulin and insulin receptor in the chick liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1372–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Livingston J. N. The binding and degradation of insulin by rat liver membranes: demonstration of three distinct insulin-binding components in detergent-solubilized material from liver plasma membrane. Endocrinology. 1980 Jan;106(1):179–184. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesniak M. A., Roth J., Gorden P., Gavin J. R., 3rd Human growth hormone radioreceptor assay using cultured human lymphocytes. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 3;241(105):20–22. doi: 10.1038/newbio241020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY I. A. THE METABOLISM OF INSULIN. Diabetes. 1964 May-Jun;13:225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Olefsky J. M. Effects of lysosomotropic agents on insulin interactions with adipocytes. Evidence for a lysosomal pathway for insulin processing and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10153–10160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaleb M. L., Donner D. B. Affinity of the hepatic insulin receptor is influenced by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11051–11057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaleb M., Donner D. B. Consequences of 125I-labeled insulin degradation by hepatocytes on the interpretation of receptor binding studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 29;720(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Kobayashi M., Chang H. Interactions between insulin and its receptors after the initial binding event. Functional heterogeneity and relationships to insulin degradation. Diabetes. 1979 May;28(5):460–471. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.5.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ose L., Ose T., Reinertsen R., Berg T. Fluid endocytosis in isolated rat parenchymal and non-parenchymal liver cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Mar;126(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90475-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papachristodoulou D. K., Birbeck M. S., Scott G. S., Thomas J. H. Subcellular distribution of intravenously injected 125I-labelled insulin in rat liver. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(3):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Halban P. A., Gjinovci A., Duckworth W. C., Estreicher J., Renold A. E. Increased clearance and degradation of [3H]insulin in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI110082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. IV. Effects of guanylnucleotides on binding of 125I-glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1872–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of rat liver cells. 3. Enzymatic requirements for tissue dispersion. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Dec;82(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uete T., Shimano N., Shimizu S., Morikawa M. Autoregulatory system of insulin degradation in liver. II. Relationship between blood insulin levels and GSH-dependent insulin degrading activity in liver and blood. Metabolism. 1976 Apr;25(4):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. I. Purification and properties of glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):126–135. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. VI. Feedback control by insulin of liver glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase in rat. Diabetes. 1974 Feb;23(2):117–125. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. X. Identification of insulin degrading activity of rat liver plasma membrane as glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T., Nafz M. A., Chandler M. L. Interaction of insulin analogs, glucagon, growth hormone, vasopressin, oxytocin, and scrambled forms of ribonuclease and lysozyme with glytathione-insulin transhydrogenase (thiol: protein-disulfide oxidoreductase): dependence upon conformation. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2115–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


