Abstract
N-Methylprotoporphyrin IX strongly inhibits synthesis of phycocyanobilin, but not chlorophyll a, in the dark. In the light, both phycocyanin and chlorophyll a synthesis are inhibited in parallel. These results are consistent with the intermediacy of haem in algal bilin synthesis and suggest a control mechanism for chlorophyll a synthesis, previously unknown.
Full text
PDF

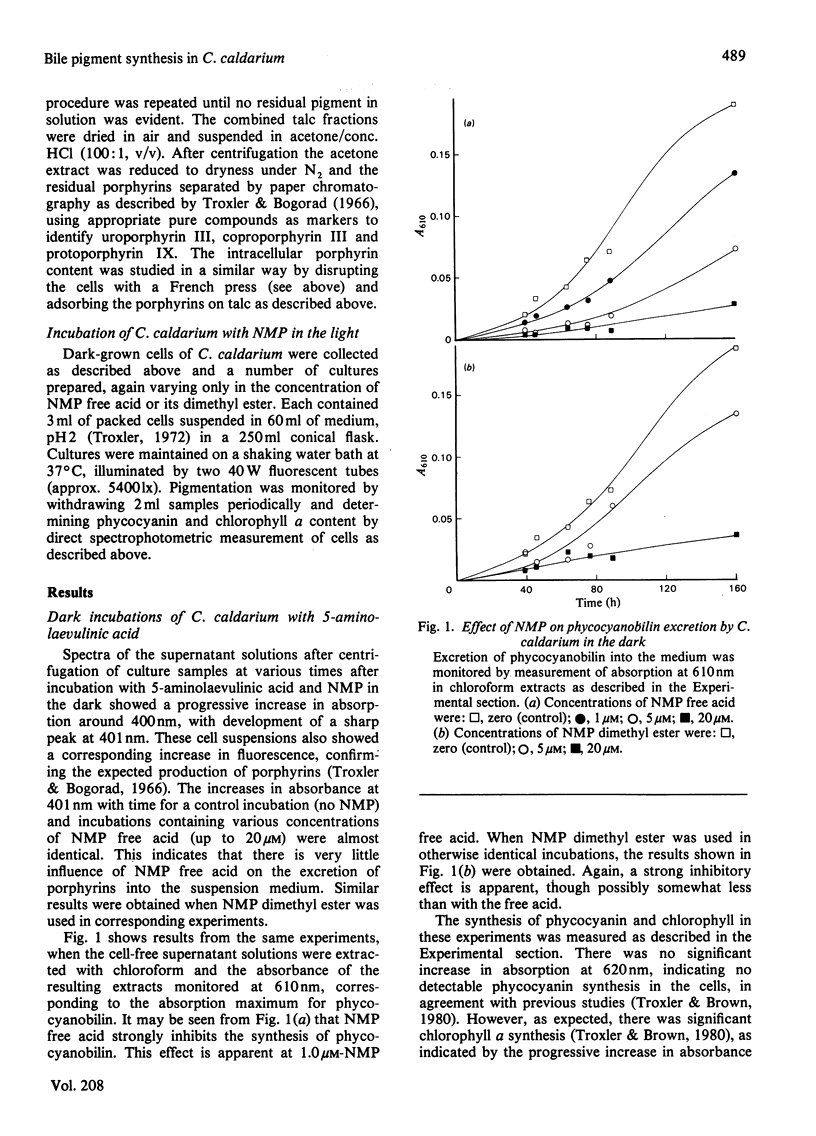
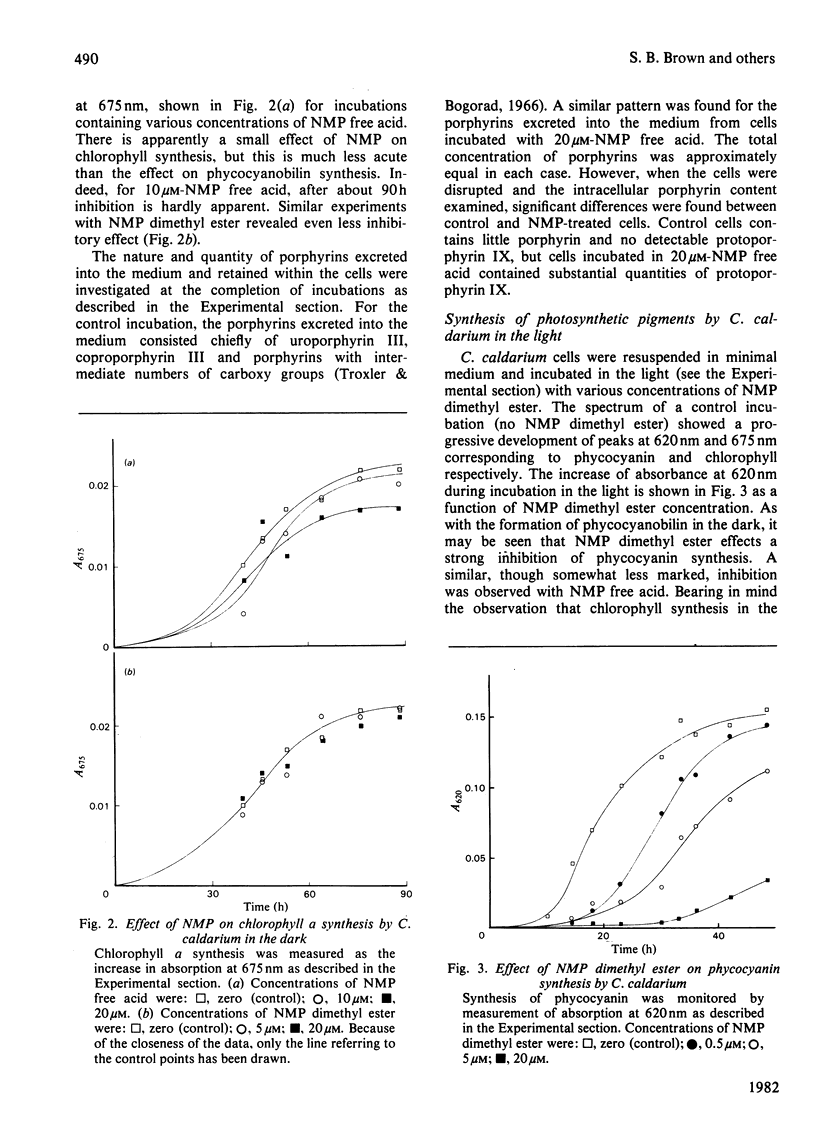

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN M. B. Studies with Cyanidium caldarium, an anomalously pigmented chlorophyte. Arch Mikrobiol. 1959;32(3):270–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00409348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. B., Holroyd A. J., Troxler R. F. Mechanism of bile-pigment synthesis in algae. 18O incorporation into phycocyanobilin in the unicellular rhodophyte, Cyanidium caldarium. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 15;190(2):445–449. doi: 10.1042/bj1900445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F., Gibbs A. H., Smith A. G. Inhibition of protohaem ferro-lyase by N-substituted porphyrins. Structural requirements for the inhibitory effect. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):645–648. doi: 10.1042/bj1890645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F., Jackson A. H., Gibbs A. H., Rao K. R., Atton J., Weerasinghe S., Hollands C. Structural isomerism and chirality of N-monosubstituted protoporphyrins. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 1;142(1):44–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton J. D., Honeybourne C. L., Smith K. M., Tabba H. D., Jones O. T. The use of N-methylprotoporphyrin dimethyl ester to inhibit ferrochelatase in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides and its effect in promoting biosynthesis of magnesium tetrapyrroles. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 15;208(2):479–486. doi: 10.1042/bj2080479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R., McDonagh A. F. The enzymatic formation of bilirubin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:533–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tephly T. R., Coffman B. L., Ingall G., Ziet-Har M. S., Goff H. M., Tabba H. D., Smith K. M. Identification of N-methylprotoporphyrin IX in livers of untreated mice and mice treated with 3, 5-diethoxycarbonyl- 1, 4-dihydrocollidine: source of the methyl group. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler R. F., Bogorad L. Studies on the formation of phycocyanin, porphyrins, and a blue phycobilin by wild-type and mutant strains of Cyanidium caldarium. Plant Physiol. 1966 Mar;41(3):491–499. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler R. F., Brown A. S., Brown S. B. Bile pigment synthesis in plants. Mechanism of 18O incorporation into phycocyanobilin in the unicellular rhodophyte. Cyanidium caldarium. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3411–3418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler R. F. Synthesis of bile pigments in plants. Formation of carbon monoxide and phycocyanobilin in wild-type and mutant strains of the alga, Cyanidium caldarium. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4235–4242. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


