Abstract
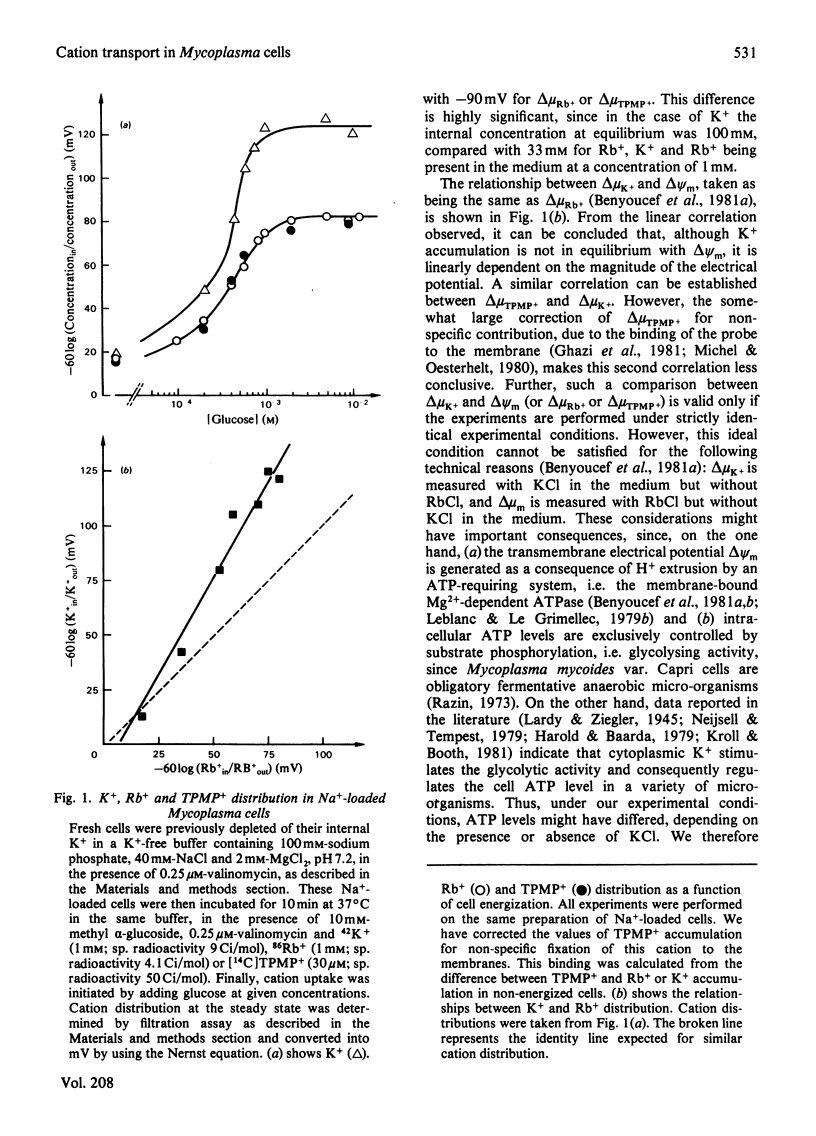
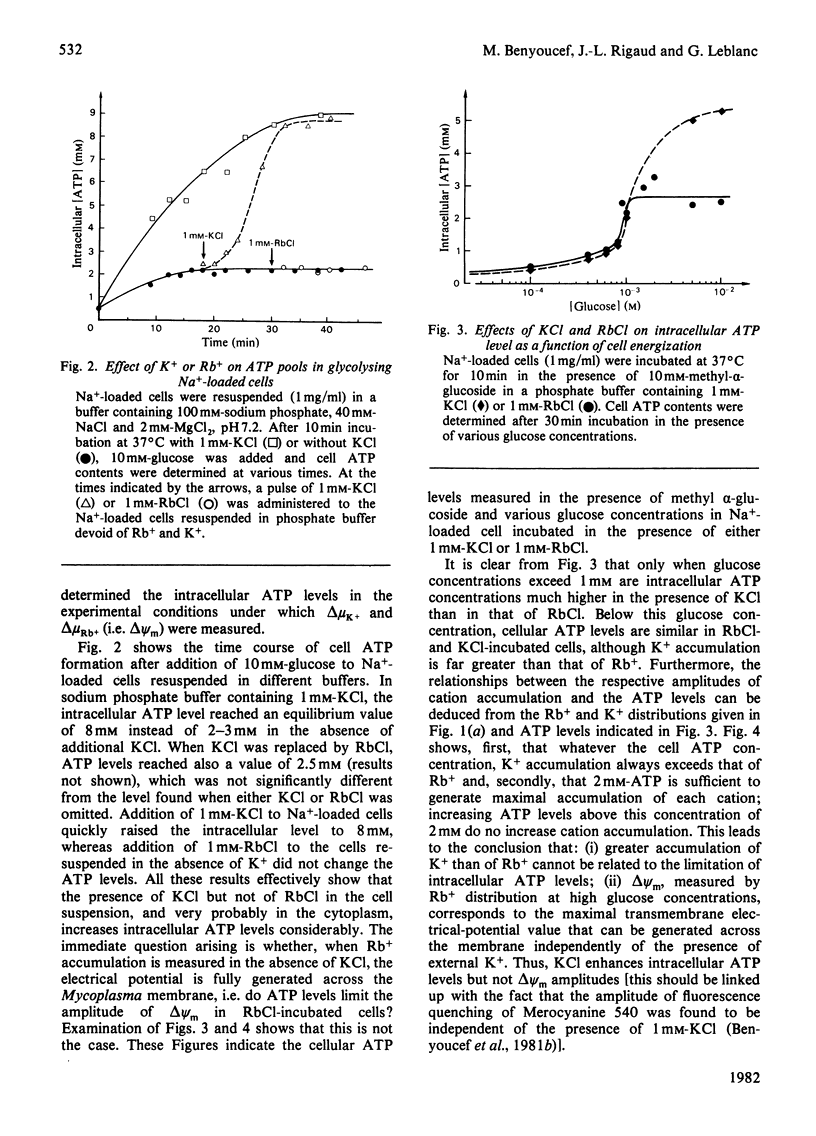
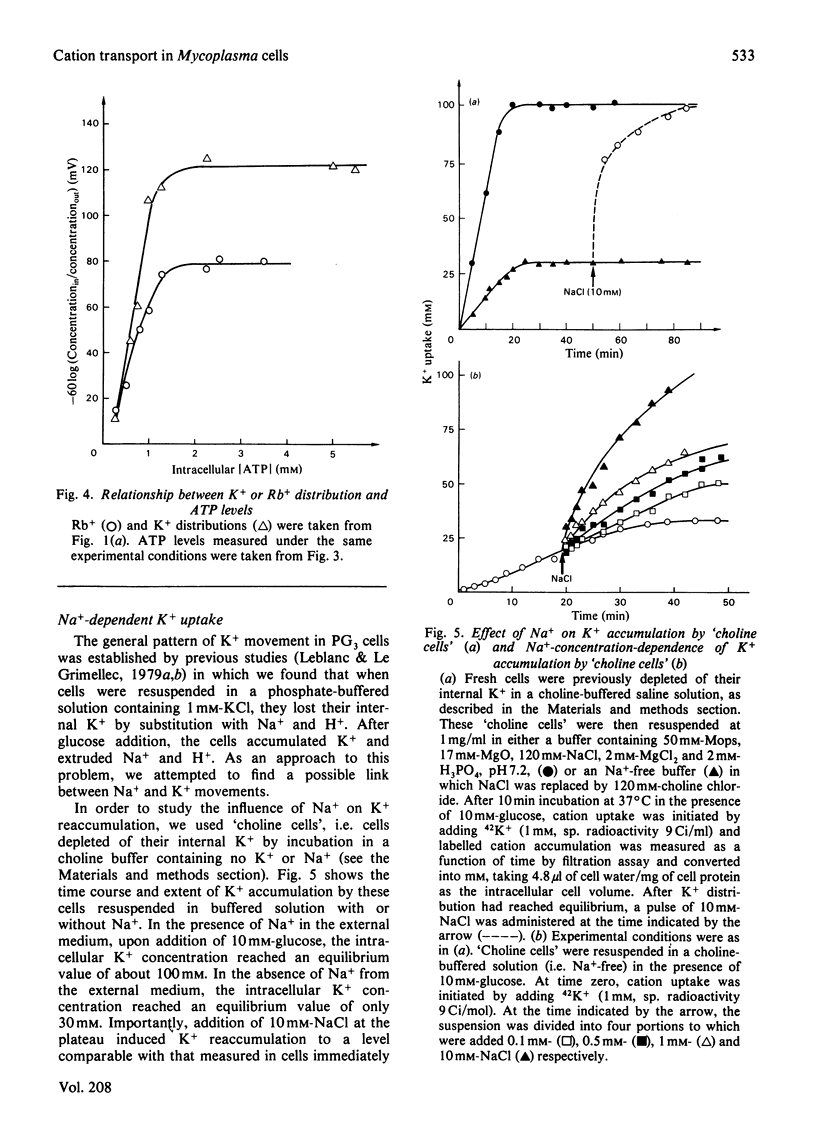
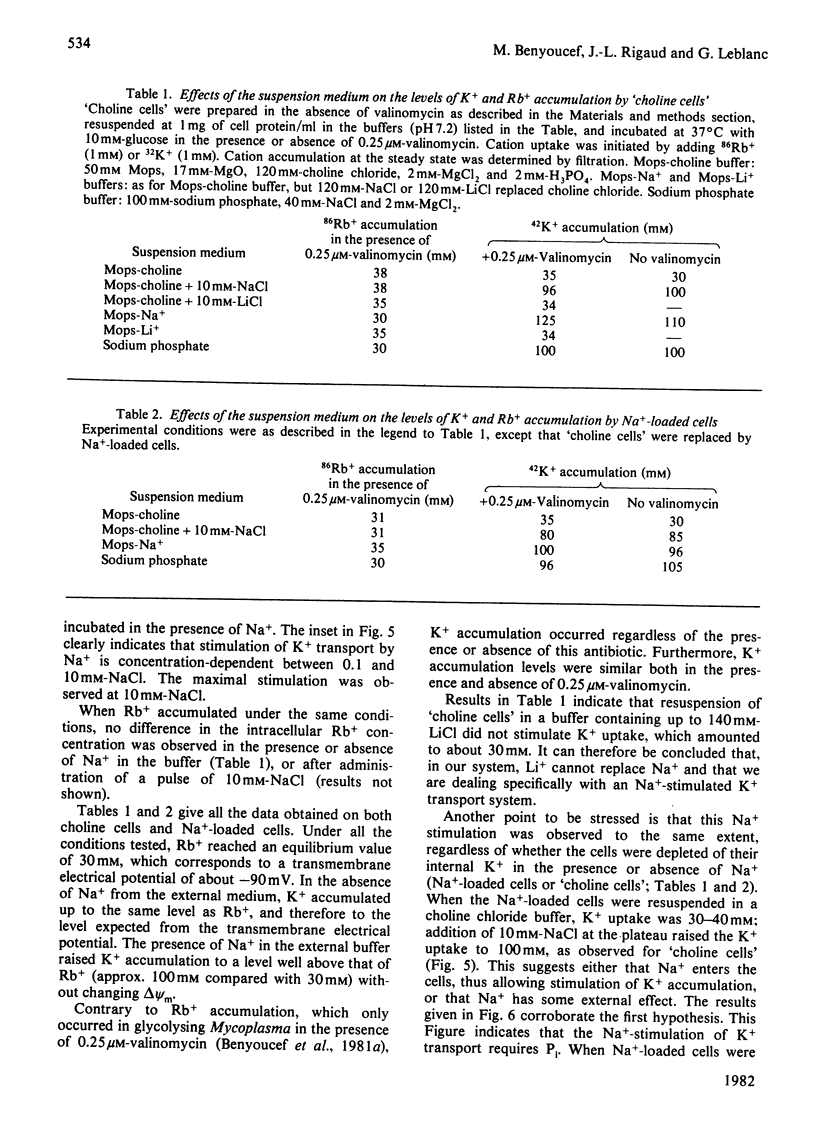
We have studied some features of K+ accumulation by glycolysing Mycoplasma mycoides var. Capri cells. We report that when Na+ is absent from the external medium, K+ accumulates up to the level predicted by the amplitude of the transmembrane electrical potential, delta psi m, measured by Rb+ and methyltriphenylphosphonium cation (TPMP+) distribution. Therefore, under these experimental conditions, the coupling mechanism of K+ uptake consists of a delta psi m-driven uniport. More important, when Na+ is present in the external medium, the level of K+ accumulation by glycolysing Mycoplasma cells is far too steep to be equilibrium with delta psi m (-120 mV for delta muK+ compared with -90mV for delta muRb+ or delta muTPMP+). Our results clearly indicate the presence in Mycoplasma of an active K+-transport system specifically stimulated by Na+. Furthermore, by controlling the amplitude of the energy-dependent delta muH+, we obtain strong evidence that this specific Na+-stimulated K+ transport is modulated by the transmembrane electrical potential. Finally, we show that ATP is consumed when such a transport system is in activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Whitelaw V., Hesse J. A K+ transport ATPase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6666–6668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORREST W. W., WALKER D. J. SYNTHESIS OF RESERVE MATERIALS FOR ENDOGENOUS METABOLISM IN STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1448–1452. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1448-1452.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazi A., Schechter E., Letellier L., Labedan B. Probes of membrane potential in Escherichia coli cells. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80717-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R., Baron C., Abrams A. Inhibition of membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase and of cation transport in Streptococcus faecalis by N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2261–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heefner D. L., Kobayashi H., Harold F. M. ATP-linked sodium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. II. Energy coupling in everted membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11403–11407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Active transport of thallous ions by Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8129–8131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The role of potassium transport in the generation of a pH gradient in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):691–698. doi: 10.1042/bj1980691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. The role of Na+ in transport processes of bacterial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):377–397. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc G., Le Grimellec C. Active K+ transport in Mycoplasma mycoides var. Capri. Net and unidirectional K+ movements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 13;554(1):156–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc G., Le Grimellec C. Active K+ transport in Mycoplasms mycoides var. Capri. Relationships between K+ distribution, electrical potential and ATPase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 13;554(1):168–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H., Oesterhelt D. Electrochemical proton gradient across the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium: effect of N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, relation to intracellular adenosine triphosphate, adenosine diphosphate, and phosphate concentration, and influence of the potassium gradient. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 30;19(20):4607–4614. doi: 10.1021/bi00561a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Performance and conservation of osmotic work by proton-coupled solute porter systems. J Bioenerg. 1973 Jan;4(1):63–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01516051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Physiology of mycoplasmas. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;10:1–80. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen E. N., Rosen B. P. Effects of sodium and lithium ions on the potassium ion transport systems of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1458–1462. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


