Full text
PDF
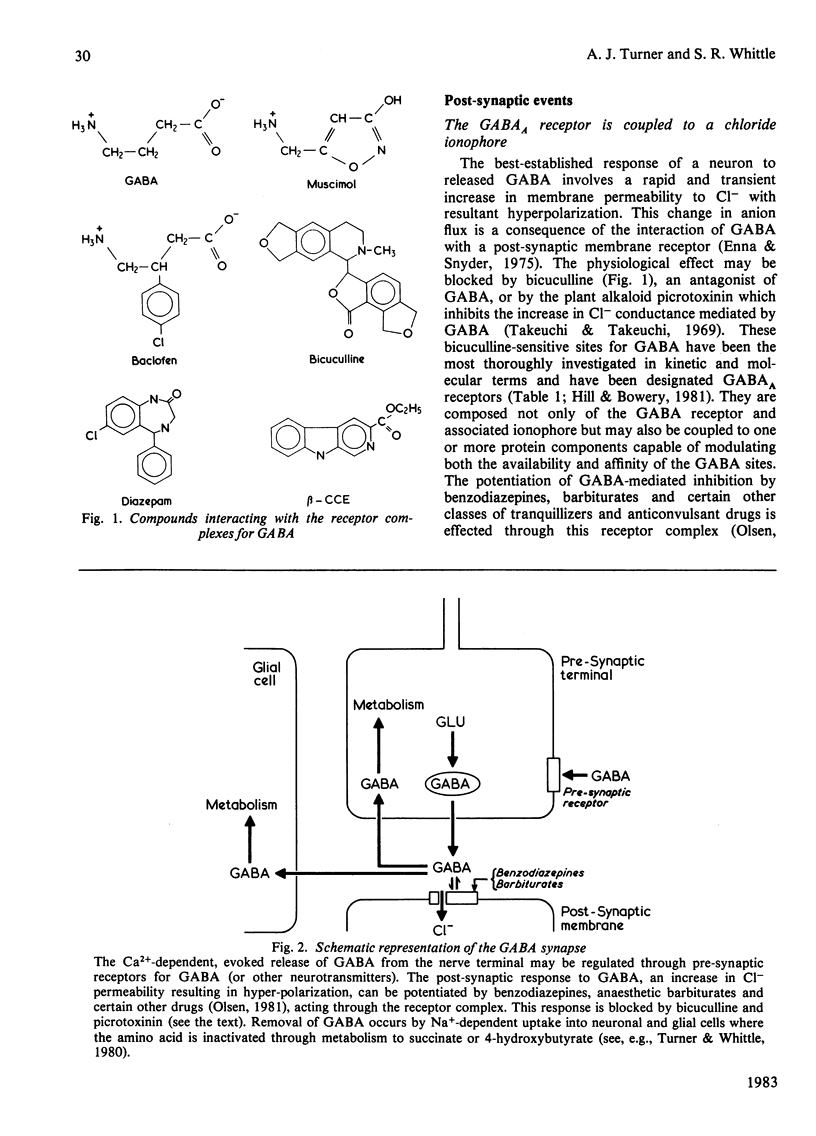

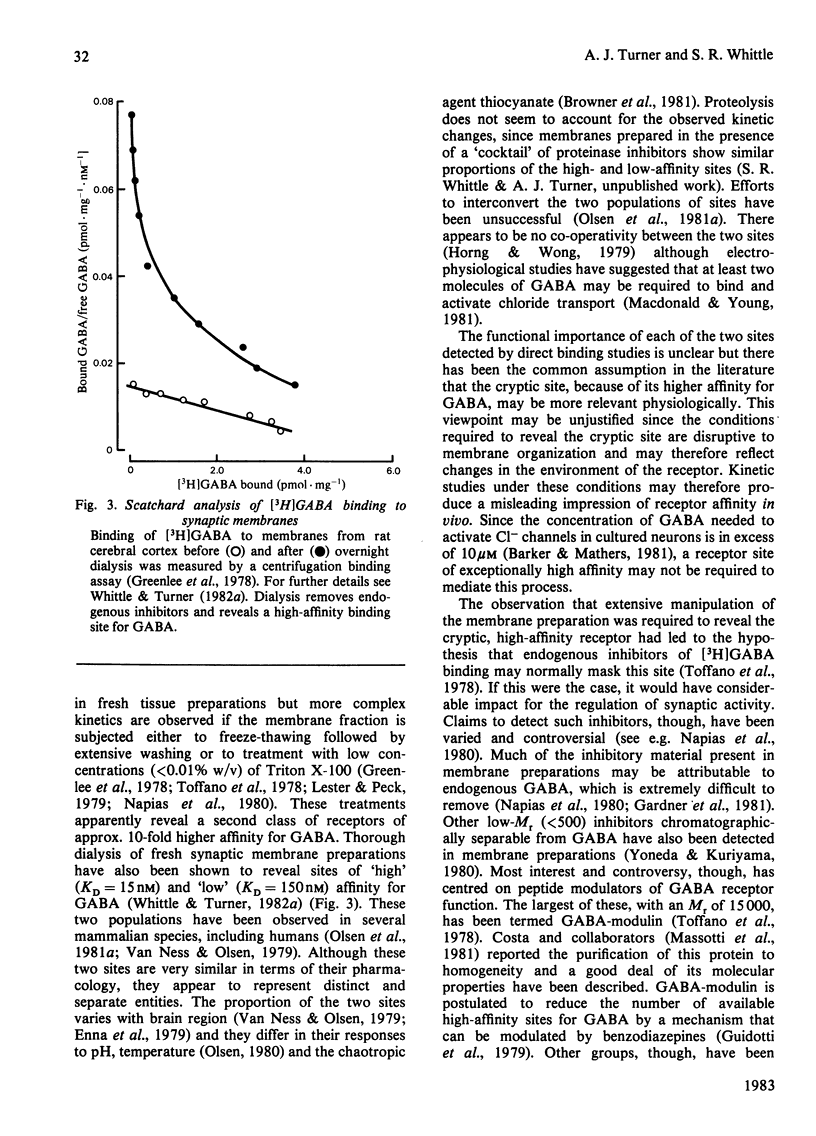









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. R., Johnston G. A. GABA agonists and antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 15;28(18):2697–2702. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90549-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Ogasawara N. Chloride-dependent stimulation of GABA and benzodiazepine receptor binding by pentobarbital. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90333-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H. The depressant action of baclofen on the isolated spinal cord of the neonatal rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 May 22;71(4):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BASEMORE A. W., ELLIOT K. A., FLOREY E. Isolation of factor I. J Neurochem. 1957;1(4):334–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balázs R., Machiyama Y., Hammond B. J., Julian T., Richter D. The operation of the gamma-aminobutyrate bypath of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in brain tissue in vitro. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):445–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1160445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber R. P., Vaughn J. E., Saito K., McLaughlin B. J., Roberts E. GABAergic terminals are presynaptic to primary afferent terminals in the substantia gelatinosa of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 3;141(1):35–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benavides J., Rumigny J. F., Bourguignon J. J., Cash C., Wermuth C. G., Mandel P., Vincendon G., Maitre M. High affinity binding sites for gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in rat brain. Life Sci. 1982 Mar 15;30(11):953–961. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90624-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benavides J., Rumigny J. F., Bourguignon J. J., Wermuth C. G., Mandel P., Maitre M. A high-affinity, Na+-dependent uptake system for gamma-hydroxybutyrate in membrane vesicles prepared from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1982 Jun;38(6):1570–1575. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb06634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A. Depolarizing actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related compounds on rat superior cervical ganglia in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):205–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Doble A., Middlemiss D. N., Shaw J., Turnbull M. (-)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):92–94. doi: 10.1038/283092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M., Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Falch E. Partial agonists for brain GABA/benzodiazepine receptor complex. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):331–333. doi: 10.1038/280331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M., Olsen C. E. Urinary and brain beta-carboline-3-carboxylates as potent inhibitors of brain benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2288–2292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Brain specific benzodiazepine receptors. Br J Psychiatry. 1978 Sep;133:249–260. doi: 10.1192/bjp.133.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., Cantrill R. C. Delta-aminolaevulinic acid is a potent agonist for GABA autoreceptors. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):514–515. doi: 10.1038/280514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J. GABA autoreceptors are not coupled to benzodiazepine receptors in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1982 Jan;38(1):264–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb10879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briley M. S., Langer S. Z. Influence of GABA receptor agonists and antagonists on the binding of 3H-diazepam to the benzodiazepine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov 1;52(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Marsh S. Axonal GABA-receptors in mammalian peripheral nerve trunks. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 3;156(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browner M., Ferkany J. W., Enna S. J. Biochemical identification of pharmacologically and functionally distinct GABA receptors in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1981 May;1(5):514–518. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-05-00514.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Autoradiographic localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors in the rat central nervous system by using [3H]muscimol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):1024–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. R., Barnard E. A., Lo M. M., Dolly J. O. Molecular sizes of benzodiazepine receptors and the interacting GABA receptors in the membrane are identical. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 20;126(2):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Rodbard D., Pert C. B. Is the benzodiazepine receptor coupled to a chloride anion channel? Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):315–317. doi: 10.1038/277315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. G., Cohen R. K. Identification of an endogenous peptide-ligand for the benzodiazepine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doble A., Iversen L. L. Molecular size of benzodiazepine receptor in rat brain in situ: evidence for a functional dimer? Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):522–523. doi: 10.1038/295522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudai Y. Modulation of benzodiazepine binding sites in calf cortex by an endogenous factor and GABAergic ligands. Brain Res. 1979 May 11;167(2):422–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90839-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K. Two types of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor on embryonic sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):579–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert F. J., Roeske W. R., Yamamura H. I. Multiple benzodiazepine receptors and their regulation by gamma-aminobutyric acid. Life Sci. 1981 Jul 20;29(3):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. A simple, sensitive and specific radioreceptor assay for endogenous GABA in brain tissue. J Neurochem. 1976 Jan;26(1):221–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb04465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding in rat brain synaptic membrane fractions. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):81–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdö S. L., Rosdy B., Szporny L. Higher GABA concentrations in fallopian tube than in brain of the rat. J Neurochem. 1982 Apr;38(4):1174–1176. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb05368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOREY E. An inhibitory and an excitatory factor of mammalian central nervous system, and their action of a single sensory neuron. Arch Int Physiol. 1954 Feb;62(1):33–53. doi: 10.3109/13813455409145367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falch E., Krogsgaard-Larsen P. The binding of the GABA agonist [3H]THIP to rat brain synaptic membranes. J Neurochem. 1982 Apr;38(4):1123–1129. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb05357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner C. R., Klein J., Grove J. Endogenous GABA determines the characteristics of [3H]GABA-binding. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct 22;75(2-3):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish M., Snyder S. H. Benzodiazepine recognition sites on GABA receptors. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):651–652. doi: 10.1038/287651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giambalvo C. T., Rosenberg P. The effect of phospholipases and proteases on the binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid to junctional complexes of rat cerebellum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 15;436(4):741–756. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorguieff M. F., Kemel M. L., Glowinski J., Besson M. J. Stimulation of dopamine release by GABA in rat striatal slices. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 6;139(1):115–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind J. M., Krnjević K., Pumain R. Doubtful value of bicuculline as a specific antagonist of GABA. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):675–676. doi: 10.1038/228675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. B., Chin J. H., Lyon R. C. Ethanol disordering of spin-labeled mouse brain membranes: correlation with genetically determined ethanol sensitivity of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4231–4233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee D. V., Olsen R. W. Solubilization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor protein from mammalian brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):380–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee D. V., Van Ness P. C., Olsen R. W. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding in mammalian brain: receptor-like specificity of sodium-independent sites. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):933–938. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Konkel D. R., Ebstein B., Corda M. G., Wise B. C., Krutzsch H., Meek J. L., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of a rat brain protein (GABA-modulin). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6084–6088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J. D., Kochman R. L., Sumner P. R. Heterogeneity of brain benzodiazepine receptors demonstrated by [3H]propyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):618–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. L., Wermuth B., von Wartburg J. P. Human brain aldehyde reductases: relationship to succinic semialdehyde reductase and aldose reductase. J Neurochem. 1980 Aug;35(2):354–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horng J. S., Wong D. T. gamma-Aminobutyric acid receptors in cerebellar membranes of rat brain after a treatment with Triton X-100. J Neurochem. 1979 May;32(5):1379–1386. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Dipple I., Gordon L. M. Phenobarbital selectively modulates the glucagon-stimulated activity of adenylate cyclase by depressing the lipid phase separation occurring in the outer half of the bilayer of liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):675–681. doi: 10.1042/bj1970675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Ellory J. C., Smith G. A., Hesketh T. R., Stein J. M., Warren G. B., Metcalfe J. C. Exchange of partners in glucagon receptor-adenylate cyclase complexes. Physical evidence for the independent, mobile receptor model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 2;467(2):208–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Barker J. L. Pentobarbital: stereospecific actions of (+) and (-) isomers revealed on cultured mammalian neurons. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):195–197. doi: 10.1126/science.7350656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyttel J. Characterization of 3H-GABA receptor binding to rat brain synaptosomal membranes: effect of non GABAergic compounds. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 Oct;65(2):211–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00433051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iloyd K. G., Shemen L., Hornykiewicz O. Distribution of high affinity sodium-independent [3H]gamma-aminobutyric acid [3H]GABA binding in the human brain: alterations in Parkinson's disease. Brain Res. 1977 May 27;127(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. W., Yamamura H. I. Photoaffinity labeling of the benzodiazepine receptor in bovine cerebral cortex. Life Sci. 1979 Oct 29;25(18):1613–1620. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karobath M., Placheta P., Lippitsch M., Krogsgaard-Larsen P. Is stimulation of benzodiazepine receptor binding mediated by a novel GABA receptor? Nature. 1979 Apr 19;278(5706):748–749. doi: 10.1038/278748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karobath M., Sperk G. Stimulation of benzodiazepine receptor binding by gamma-aminobutyric acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):1004–1006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karobath M., Supavilai P. Distinction of benzodiazepine agonists from antagonists by photoaffinity labelling of benzodiazepine receptors in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Jul 20;31(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempner E. S., Schlegel W. Size determination of enzymes by radiation inactivation. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):2–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90617-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg F., Snowman A., Olsen R. W. Barbiturate receptor sites are coupled to benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7468–7472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester B. R., Peck E. J., Jr Kinetic and pharmacologic characterization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptive sites from mammalian brain. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 26;161(1):79–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. G., Dreksler S. An analysis of [3H]gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) binding in the human brain. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 9;163(1):77–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. G., Dreksler S., Bird E. D. Alterations in 3H-GABA binding in Huntington's chorea. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):747–753. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo M. M., Strittmatter S. M., Snyder S. H. Physical separation and characterization of two types of benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):680–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Young A. B. Pharmacology of GABA-mediated inhibition of spinal cord neurons in vivo and in primary dissociated cell culture. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Aug 11;38(Spec No)(Pt 1):147–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00235693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R., Barker J. L. Benzodiazepines specifically modulate GABA-mediated postsynaptic inhibition in cultured mammalian neurones. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):563–564. doi: 10.1038/271563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallorga P., Hamburg M., Tallman J. F., Gallager D. W. Ontogenetic changes in GABA modulation of brain benzodiazepine binding. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Apr;19(4):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Martino A. M. Studies on the relationship of gamma-aminobutyric acid-stimulated diazepam binding and the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;20(1):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R. J., Winters W. D., Mori K., Spooner C. E. EEG and behavioral comparison of the effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate, gamma-butyrolactone and short chain fatty acids in the rat. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1967 May;6(3):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(67)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini C., Lucacchini A., Ronca G., Hrelia S., Rossi C. A. Isolation of putative benzodiazepine receptors from rat brain membranes by affinity chromatography. J Neurochem. 1982 Jan;38(1):15–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb10848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massotti M., Guidotti A., Costa E. Characterization of benzodiazepine and gamma-aminobutyric recognition sites and their endogenous modulators. J Neurosci. 1981 Apr;1(4):409–418. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-04-00409.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. R., Martin I. L. Is GABA release modulated by presynaptic receptors? Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):904–905. doi: 10.1038/274904a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. A novel GABA receptor modulates stimulus-induced glutamate release from cortico-striatal terminals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 3;67(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. Benzodiazepines modify the agonist responses at a presynaptic GABA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Dec 5;68(3):369–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90535-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. Interactions of agonists and antagonists with a novel type of GABA receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 15;31(16):2684–2686. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90720-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenroth V. H., 3rd, Walters J. R., Roth R. H. Dopaminergic neurons--alteration in the kinetic properties of tyrosine hydroxylase after cessation of impulse flow. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Mar 15;25(6):655–661. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhyaddin M., Roberts P. J., Woodruff G. N. Presynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors in the rat anococcygeus muscle and their antagonism by 5-aminovaleric acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):163–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Battersby M. K., Richards J. G. Benzodiazepine receptor protein identified and visualized in brain tissue by a photoaffinity label. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1666–1670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding with (+)-[3H]bicuculline methiodide in rat cerebellum. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Mar;14(2):256–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Richards J. G., Wu J. Y. Autoradiographic localization of benzodiazepine receptors in immunocytochemically identified gamma-aminobutyrergic synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1935–1938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napias C., Bergman M. O., Van Ness P. C., Greenlee D. V., Olsen R. W. GABA binding in mammalian brain: inhibition by endogenous GABA. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 15;27(11):1001–1011. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Schou H., Braestrup C. [3H]propyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate binds specifically to brain benzodiazepine receptors. J Neurochem. 1981 Jan;36(1):276–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb02404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Koella W. P. Inhibition of nigral and neocortical cells by gamma-hydroxybutyrate: a microiontophoretic investigation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb 1;53(4):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90460-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Mikoshiba K. Localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding in the mammalian cerebellum: high levels in granule layer and depletion in agranular cerebella of mutant mice. J Neurochem. 1978 Jun;30(6):1633–1636. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Ticku M. K., Van Ness P. C., Greenlee D. Effects of drugs on gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors, uptake, release and synthesis in vitro. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 13;139(2):277–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90929-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Van Ness P., Napias C., Bergman M., Tourtellotte W. W. GABA receptor binding and endogenous inhibitors in normal human brain and Huntington's disease. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1980;21:451–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Iversen L. L., Hall Z. W., Kravitz E. A. Release of gamma-aminobutyric acid from inhibitory nerves of lobster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1110–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J. Ontogeny of GABA and benzodiazepine receptors: effects of Triton X-100, bromide and muscimol. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90456-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the rat cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):670–674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Marangos P. J. Differential effects of GABA on peripheral and central type benzodiazepine binding sites in brain. Neurosci Lett. 1982 May 28;30(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Marangos P. J., Goodwin F. K. [3H] Ethyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate binding to the benzodiazepine receptor is not affected by GABA. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):419–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90590-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson A. G., Turner A. J. Folate-dependent 1-carbon transfer to biogenic amines mediated by methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):173–174. doi: 10.1038/258173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson A. G., Turner A. J. The formation of beta-carboline alkaloids mediated by serine hydroxymethyltransferase. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 1;98(1):96–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck E. J., Jr, Schaeffer J. M., Clark J. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid, bicuculline, and post-synaptic binding sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):394–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90724-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck E. J., Miller A. L., Lester B. R. Pentobarbital and synaptic high-affinity receptive sites for gamma-aminobutyric acid. Brain Res Bull. 1976 Nov-Dec;1(6):595–597. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(76)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J., Smith I. L., Tipton K. F. The enzymes catalysing succinic semialdehyde reduction in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 1;30(7):741–747. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. H., Doherty J. D., Walters J. R. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate: a role in the regulation of central dopaminergic neurons? Brain Res. 1980 May 12;189(2):556–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. H., Nowycky M. C. Dopaminergic neurons: effects elicited by gamma-hydroxybutyrate are reversed by picrotoxin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Nov 1;26(21):2079–2082. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumigny J. F., Maitre M., Cash C., Mandel P. Specific and non-specific succinic semialdehyde reductases from rat brain: isolation and properties. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryle C. M., Tipton K. F. Subcellular localization of aldehyde reductase activities in ox brain. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1970715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W., Karobath M. Molecular heterogeneity of benzodiazepine receptors. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):285–287. doi: 10.1038/286285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Oster-Granite M. L., Herndon R. M., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding selectively depleted by viral induced granule cell loss in hamster cerebellum. Brain Res. 1976 Mar 26;105(2):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A. A site for the potentiation of GABA-mediated responses by benzodiazepines. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):558–560. doi: 10.1038/284558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A. Evidence that bicuculline and picrotoxin act at separate sites to antagonize gamma-aminobutyric acid in rat cuneate nucleus. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Jan;19(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerritt J. H., Willow M., Johnston G. A. Diazepam enhancement of low affinity GABA binding to rat brain membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Mar 17;29(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick P., Moncada V., Barker J. L., Paul S. M. Pentobarbital: dual actions to increase brain benzodiazepine receptor affinity. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1448–1450. doi: 10.1126/science.6258230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Goodman R. R. Multiple neurotransmitter receptors. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):5–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Benson D. I., Braestrup C., Coupet J., Klepner C. A., Myers V., Beer B. Some properties of brain specific benzodiazepine receptors: new evidence for multiple receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 May;10(5):825–830. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Saederup E. gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors modulate cation binding sites coupled to independent benzodiazepine, picrotoxin, and anion binding sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson F. A., Watkins A. E., Olsen R. W. Physicochemical characterization of detergent-solubilized gamma-aminobutyric acid and benzodiazepine receptor proteins from bovine brain. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):291–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock G., Magnusson T., Andén N. E. Increase in brain dopamine after axotomy or treatment with gammahydroxybutyric acid due to elimination of the nerve impulse flow. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;278(4):347–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00501479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockton J. M., Turner A. J. Characterization of adenylate cyclase purified from rat brain by hydrophobic chromatography. J Neurochem. 1981 May;36(5):1722–1730. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Study R. E., Barker J. L. Diazepam and (--)-pentobarbital: fluctuation analysis reveals different mechanisms for potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric acid responses in cultured central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7180–7184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Takeuchi N. A study of the action of picrotoxin on the inhibitory neuromuscular junction of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(2):377–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Paul S. M., Skolnick P., Gallager D. W. Receptors for the age of anxiety: pharmacology of the benzodiazepines. Science. 1980 Jan 18;207(4428):274–281. doi: 10.1126/science.6101294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Thomas J. W., Gallager D. W. GABAergic modulation of benzodiazepine binding site sensitivity. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):383–385. doi: 10.1038/274383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Ban M., Olsen R. W. Binding of [3H]alpha-dihydropicrotoxinin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid synaptic antagonist, to rat brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 May;14(3):391–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Olsen R. W. Interaction of barbiturates with dihydropicrotoxinin binding sites related to the GABA receptor-ionophore system. Life Sci. 1978 May 8;22(18):1643–1651. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Van Ness P. C., Haycock J. W., Levy W. B., Olsen R. W. Dihydropicrotoxinin binding sites in rat brain: comparison to GABA receptors. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 21;150(3):642–647. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90830-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toffano G., Guidotti A., Costa E. Purification of an endogenous protein inhibitor of the high affinity binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid to synaptic membranes of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4024–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. J., Whittle S. R., Hryszko J., Guha S. R. Biogenic aldehyde metabolism in rat brain: subcellular distribution of aldose reductase and valproate-sensitive aldehyde reductase. J Neurochem. 1982 Aug;39(2):306–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb03947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Pizzi W. J. Muscimol and gamma-hydroxybutyrate: similar interactions with convulsant agents. Life Sci. 1981 Jul 27;29(4):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness P. C., Olsen R. W. Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding in human brain regions. J Neurochem. 1979 Aug;33(2):593–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle S. R., Turner A. J. Differential effects of sedative and anticonvulsant barbiturates on specific [3H]GABA binding to membrane preparations from rat brain cortex. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Sep 15;31(18):2891–2895. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle S. R., Turner A. J. Effects of anticonvulsants on the formation of gamma-hydroxybutyrate from gamma-aminobutyrate in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1982 Mar;38(3):848–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin G. P., Hudson A. L., Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. Autoradiographic localization of GABAB receptors in rat cerebellum. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):584–587. doi: 10.1038/294584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willow M., Johnston G. A. Enhancement by anesthetic and convulsant barbiturates of GABA binding to rat brain synaptosomal membranes. J Neurosci. 1981 Apr;1(4):364–367. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-04-00364.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willow M., Johnston G. A. Enhancement of GABA binding by pentobarbitone. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jul;18(3):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willow M., Morgan I. G., Johnston G. A. Phenobarbitone binding sites in rat brain synaptosomal membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jul 17;24(3):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D. The role of gamma-aminobutyric acid in the mechanism of seizures. Prog Neurobiol. 1975;5(1):77–95. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(75)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf J. H., Nixon J. C. Endogenous effector of the benzodiazepine binding site: purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4263–4269. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda Y., Kuriyama K. Presence of a low molecular weight endogenous inhibitor on 3H-muscimol binding in synaptic membranes. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):670–673. doi: 10.1038/285670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



