Abstract
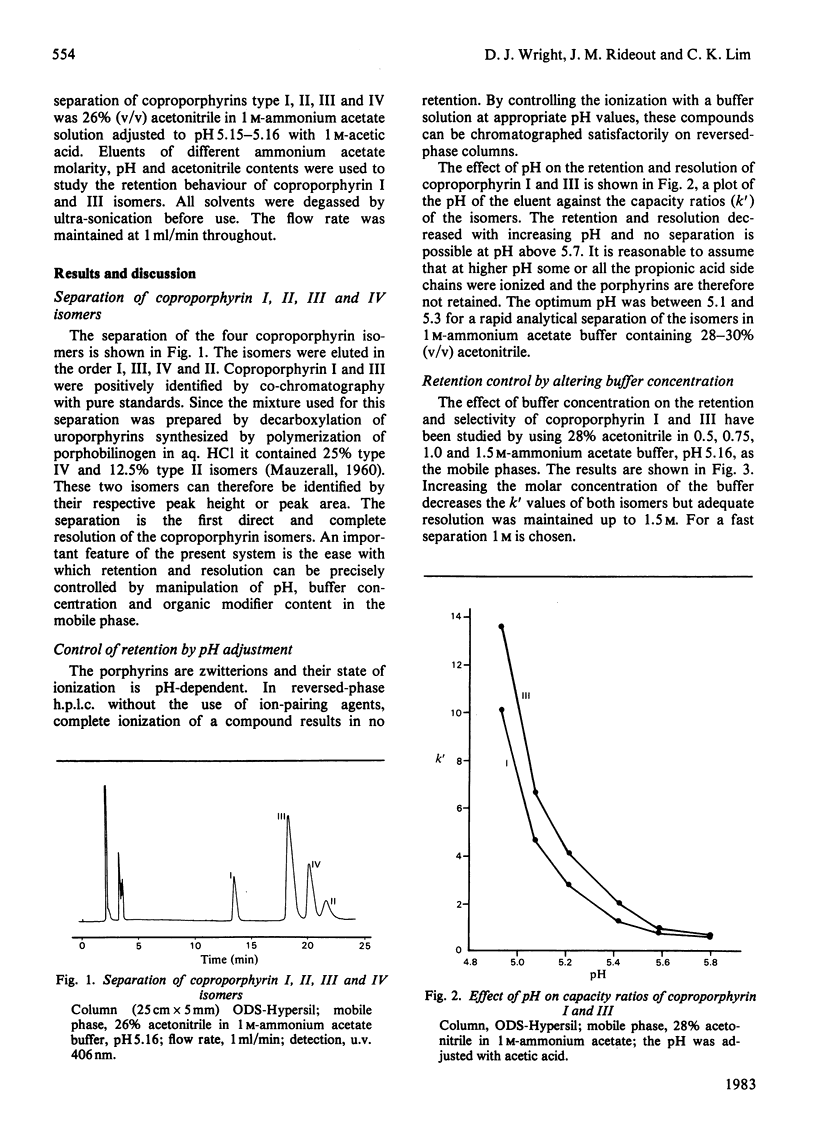
A reversed-phase system is described for the simultaneous isocratic separation of coproporphyrin I, II, III and IV isomers. The retention behaviour of coproporphyrin I and III is studied in detail. The method is suitable for both analytical and semi-preparative separation.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ezzer J., Rimington C., Shani M., Seligsohn U., Sheba C., Szeinberg A. Abnormal excretion of the isomers of urinary coproporphyrin by patients with Dubin-Johnson syndrome in Israel. Clin Sci. 1971 Jan;40(1):17–30. doi: 10.1042/cs0400017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSEN L. Paper chromatographic separation of the coproporphyrin isomers I and III. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1958;10(3):319–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK J. E., DRESEL E. I., BENSON A., KNIGHT B. C. Studies on the biosynthesis of blood pigments. 4. The nature of the porphyrins formed on incubation of chicken erythrocyte preparations with glycine, delta-aminolaevulic acid or porphobilinogen. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):87–94. doi: 10.1042/bj0630087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman R. B., Tomaro M. L., Wanschelbaum A., Frydman B. The enzymatic oxidation of porphobilinogen. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim C. K., Chan J. Y. Normal-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of porphyrin free acids on silica modified with tetraethylenepentamine. J Chromatogr. 1982 Mar 12;228:305–310. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. Porphyrin biosynthesis in erythrocytes. III. Uroporphyrinogen and its decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):1141–1162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. D., Jacob K., Vogt W., Knedel M. Diagnosis of porphyrias by ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980 Oct 31;199:339–343. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schermuly E., Doss M. Separation of the coprophorphyrin isomers I and III by thin-layer chromatography. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1975 Jul;13(7):299–304. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1975.13.7.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- With T. K. Decarboxylation of uroporphyrin by heating at atmospheric pressure. Biochem J. 1975 May;147(2):249–251. doi: 10.1042/bj1470249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- With T. K. Simplified decarboxylation of uroporphyrins. Enzyme. 1974;17(1):76–80. doi: 10.1159/000459310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff A. W., Wolpert E., Pascasio F. N., Arias I. M. Rotor's syndrome. A distinct inheritable pathophysiologic entity. Am J Med. 1976 Feb;60(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


