Abstract
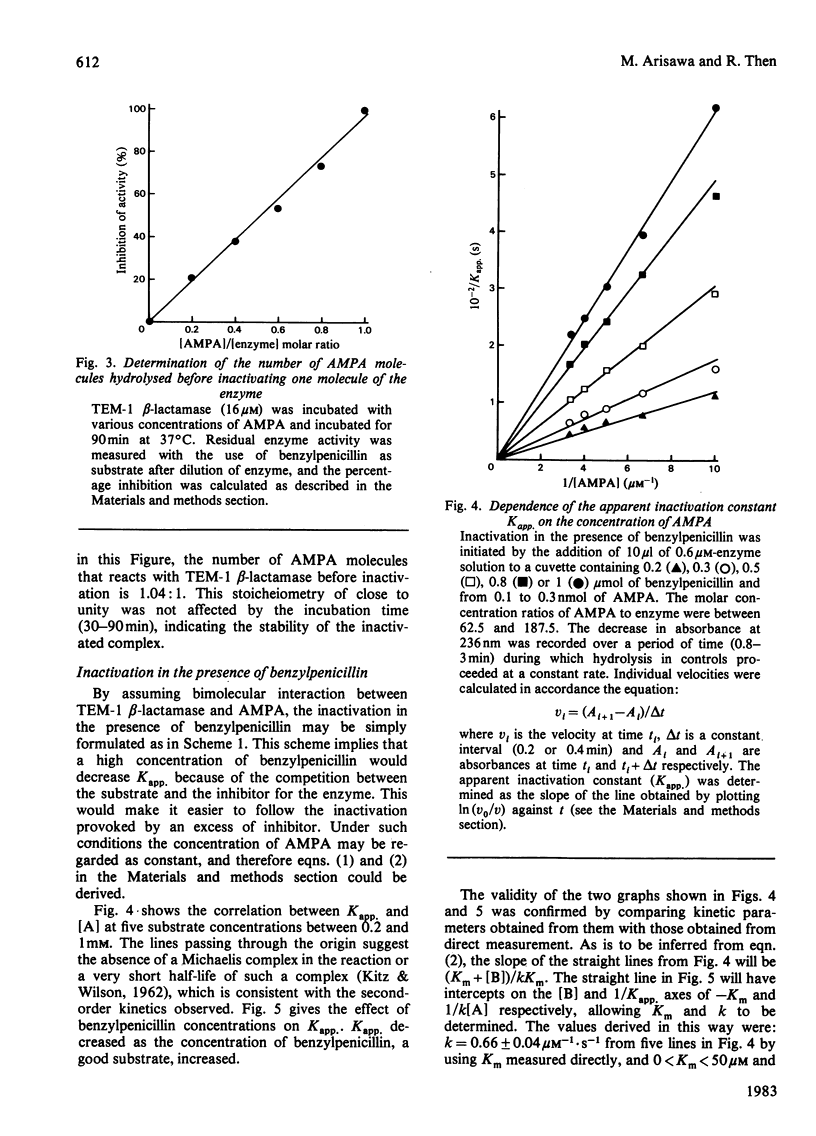
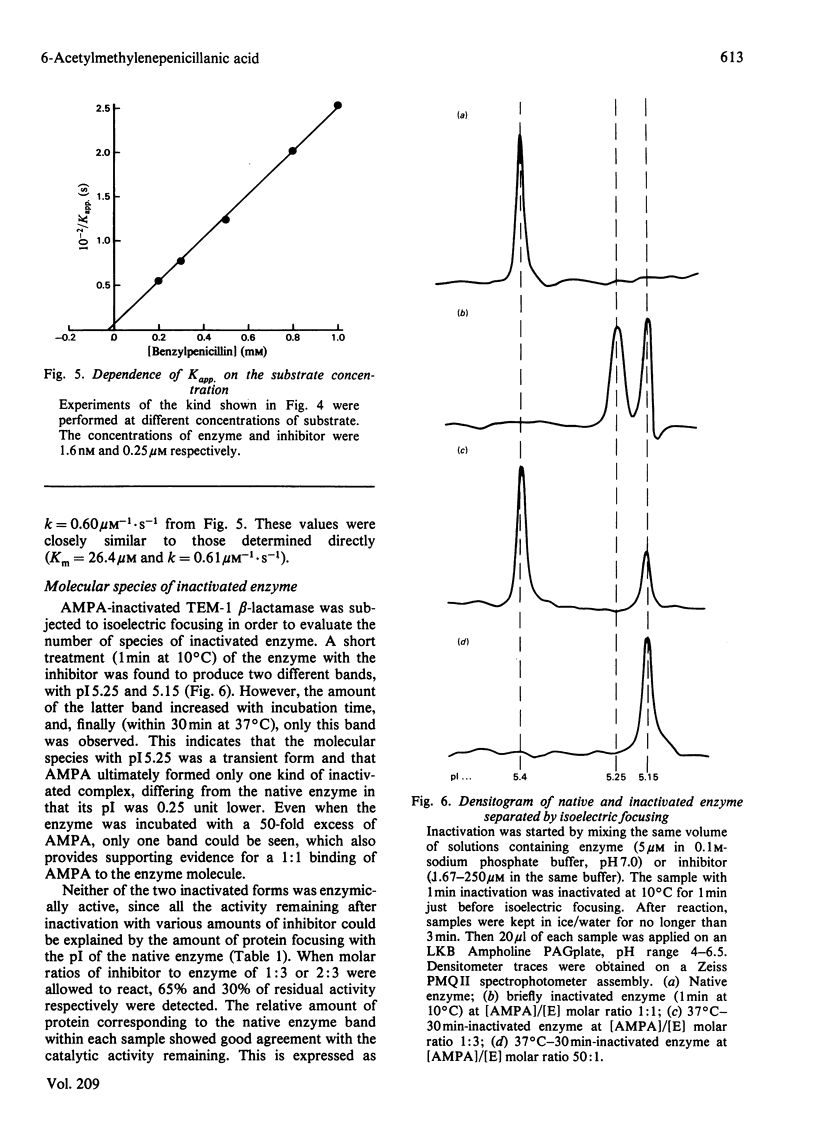
6-Acetylmethylenepenicillanic acid is a new kinetically irreversible inhibitor of various beta-lactamases. Interaction between 6-acetylmethylenepenicillanate and purified TEM-1 beta-lactamase during the inactivation process was investigated. 6-Acetylmethylenepenicillanate inhibited the enzyme in a second-order fashion with a rate constant of 0.61 microM-1 . S-1. The apparent inactivation constant decreased in the presence of increasing concentrations of the substrate benzylpenicillin. Native enzyme (pI 5.4) was converted into two inactive forms with pI 5.25 and 5.15, the latter form being transient and readily converted into the more stable form with pI 5.15. Even a 50-fold excess of inhibitor over enzyme did not produce any other inactivated species of the enzyme. All the results obtained suggest that 6-acetylmethylenepenicillanate is a potent irreversible and active-site-directed inhibitor of TEM-1 beta-lactamase.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Scott G. K. Partial amino acid sequence of penicillinase coded by Escherichia coli plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3732–3736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. G., Knowles J. R. Penicillanic acid sulfone: an unexpected isotope effect in the interaction of 6 alpha- and 6 beta-monodeuterio and of 6,6-dideuterio derivatives with RTEM beta-lactamase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3680–3687. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnas R. L., Fisher J., Knowles J. R. Chemical studies on the inactivation of Escherichia coli RTEM beta-lactamase by clavulanic acid. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2185–2189. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnas R. L., Knowles J. R. Inactivation of RTEM beta-lactamase from Escherichia coli by clavulanic acid and 9-deoxyclavulanic acid. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3214–3219. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnas R. L., Knowles J. R. Inhibition of the RTEM beta-lactamase from Escherichia coli. Interaction of enzyme with derivatives of olivanic acid. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2732–2737. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Belasco J. G., Khosla S., Knowles J. R. beta-Lactamase proceeds via an acyl-enzyme intermediate. Interaction of the Escherichia coli RTEM enzyme with cefoxitin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2895–2901. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITZ R., WILSON I. B. Esters of methanesulfonic acid as irreversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3245–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott-Hunziker V., Orlek B. S., Sammes P. G., Waley S. G. Kinetics of inactivation of beta-lactamase I by 6 beta-bromopenicillanic acid. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):797–802. doi: 10.1042/bj1870797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Lelievre V., Peduzzi J. Inhibition kinetics of three R-factor-mediated beta-lactamases by a new beta-lactam sulfone (CP 45899). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 14;611(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Hedges R. W., Smith J. T. Types of beta-lactamase determined by plasmids in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):657–662. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.657-662.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Hepburn P. The inhibition of staphylococcal beta-lactamase by clavulanic acid. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):67–76. doi: 10.1042/bj1790067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. W., O'Callaghan C. H. Beta-lactamase assays. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:69–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


