Abstract
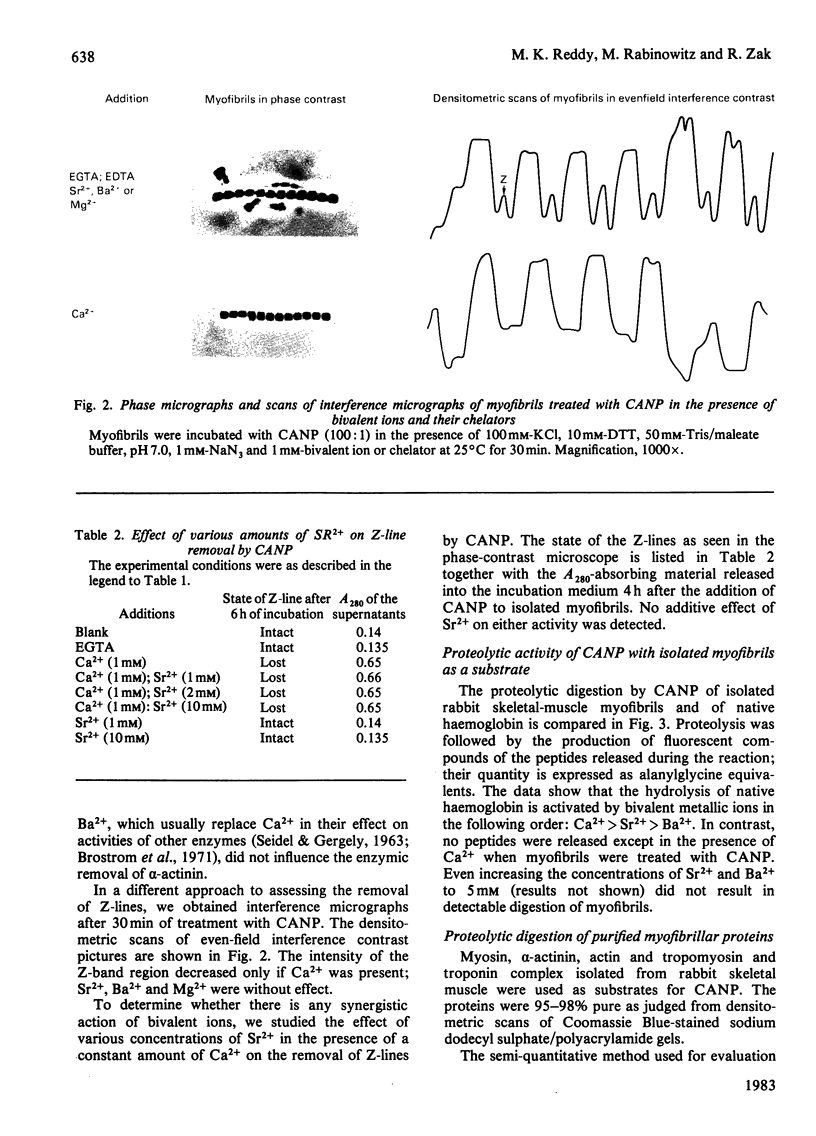
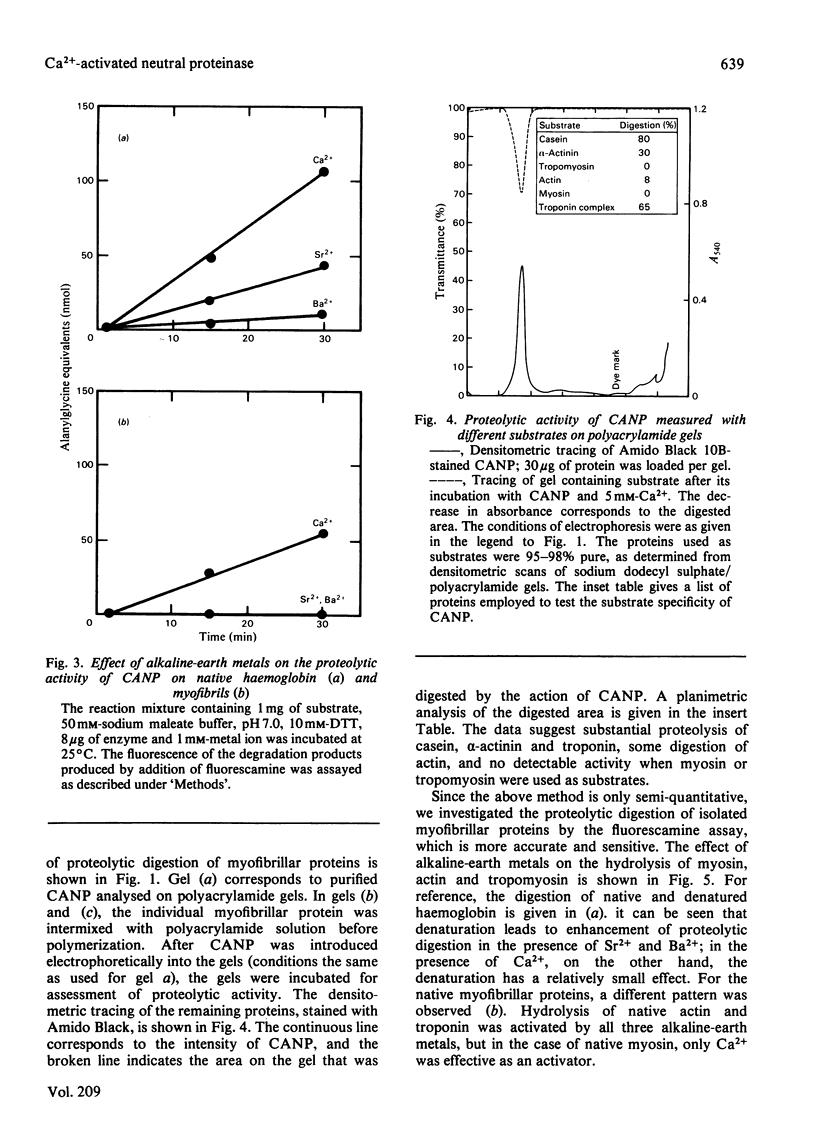
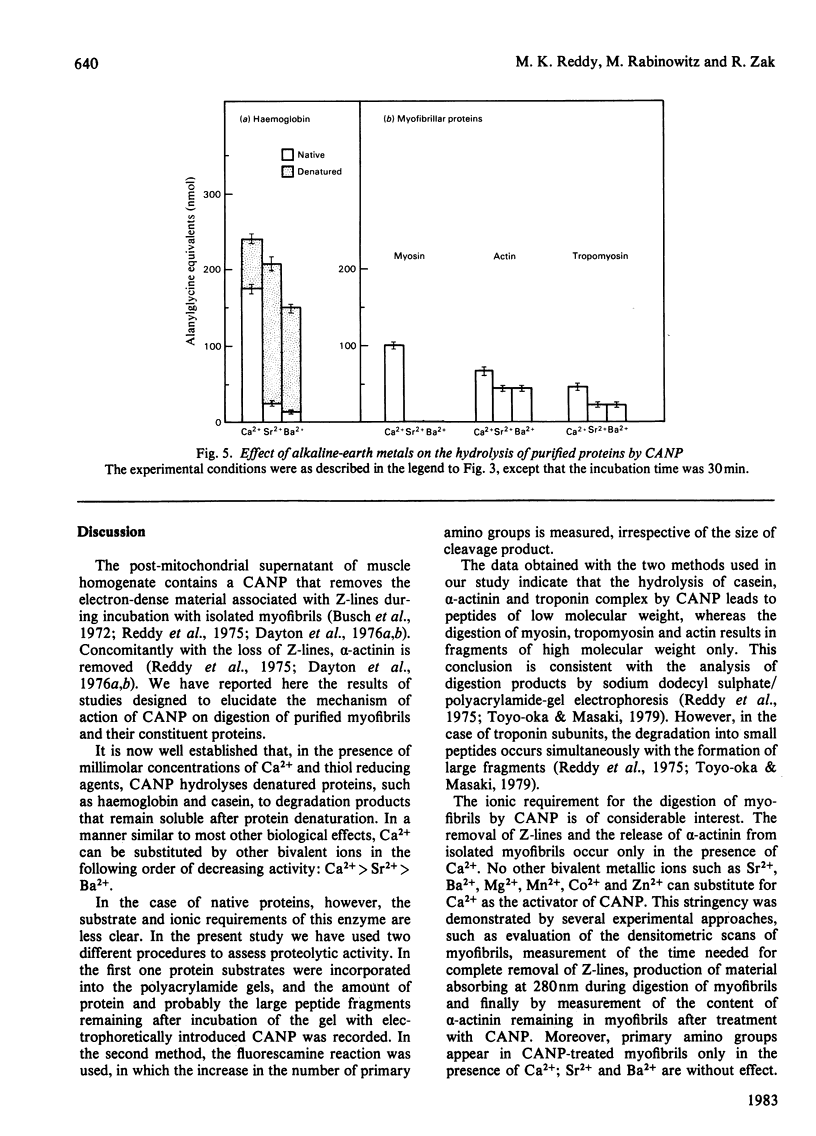
Treatment of isolated myofibrils with Ca2+-activated neutral proteinase (CANP) results in specific removal of Z-line and of alpha-actinin. To investigate the ionic requirement for these processes, we measured Z-line removal by phase-contrast and interference microscopy and alpha-actinin removal by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoretic analysis of myofibrillar proteins. The proteolytic digestion of native purified proteins was measured directly on polyacrylamide gels and by the fluorescamine technique. We found that the removal of Z-line and alpha-actinin as well as the release of proteolytic degradation products from isolated myofibrils by CANP occur only in the presence of Ca2+; Sr2+, Ba2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, Co2+ and Zn2+ are all ineffective. In contrast with this stringent requirement for Ca2+, the proteolytic activity of CANP measured with denatured casein, native and denatured haemoglobin, native actin and tropomyosin also occurs in the presence of other bivalent cations, in the following order: Ca2+ greater than Sr2+ greater than Ba2+. These data suggest that only Ca2+ can produce the conformational change in myofibrils that renders them susceptible to the action of CANP, whereas its proteolytic activity is stimulated by several bivalent ions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa N., Robson R. M., Goll D. E. An improved method for the preparation of alpha-actinin from rabbit striated muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):284–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Hunkeler F. L., Krebs E. G. The regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch W. A., Stromer M. H., Goll D. E., Suzuki A. Ca 2+ -specific removal of Z lines from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):367–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton W. R., Goll D. E., Zeece M. G., Robson R. M., Reville W. J. A Ca2+-activated protease possibly involved in myofibrillar protein turnover. Purification from porcine muscle. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2150–2158. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton W. R., Reville W. J., Goll D. E., Stromer M. H. A Ca2+-activated protease possibly involved in myofibrillar protein turnover. Partial characterization of the purified enzyme. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2159–2167. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Mueller H. The preparation of tropomyosin and troponin from natural actomyosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar;175(2):301–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston R. B., Krebs E. G. Activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. II. Identification of the kinase activating factor as a proteolytic enzyme. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2116–2122. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Studies on a cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase and its proenzyme in mammalian tissues. II. Proenzyme and its activation by calcium-dependent protease from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7610–7616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura S., Murofushi H., Suzuki K., Imahori K. Studies of a calcium-activated neutral protease from chicken skeletal muscle. I. Purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1978 Jul;84(1):225–230. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jakábová M. Ca2+-dependent protease in human platelets. Specific cleavage of platelet polypeptides in the presence of added Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5602–5605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puca G. A., Nola E., Sica V., Bresciani F. Estrogen binding proteins of calf uterus. Molecular and functional characterization of the receptor transforming factor: A Ca2+-activated protease. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1358–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. K., Etlinger J. D., Rabinowitz M., Fischman D. A., Zak R. Removal of Z-lines and alpha-actinin from isolated myofibrils by a calcium-activated neutral protease. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4278–4284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEIDEL J. C., GERGELY J. STUDIES ON MYOFIBRILLAR ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE WITH CALCIUM-FREE ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE. I. THE EFFECT OF ETHYLENEDIAMINETETRAACETATE, CALCIUM, MAGNESIUM, AND ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3648–3653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe C. A fluorescent assay for proteolytic enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):484–490. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiverick K. T., Thomas L. L., Alpert N. R. Purification of cardiac myosin. Application to hypertrophied myocardium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 30;393(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyo-Oka T., Masaki T. Calcium-activated neutral protease from bovine ventricular muscle: isolation and some of its properties. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1979 Aug;11(8):769–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(79)90402-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Krebs E. G. Identification of two protease inhibitors from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5888–5891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]