Abstract
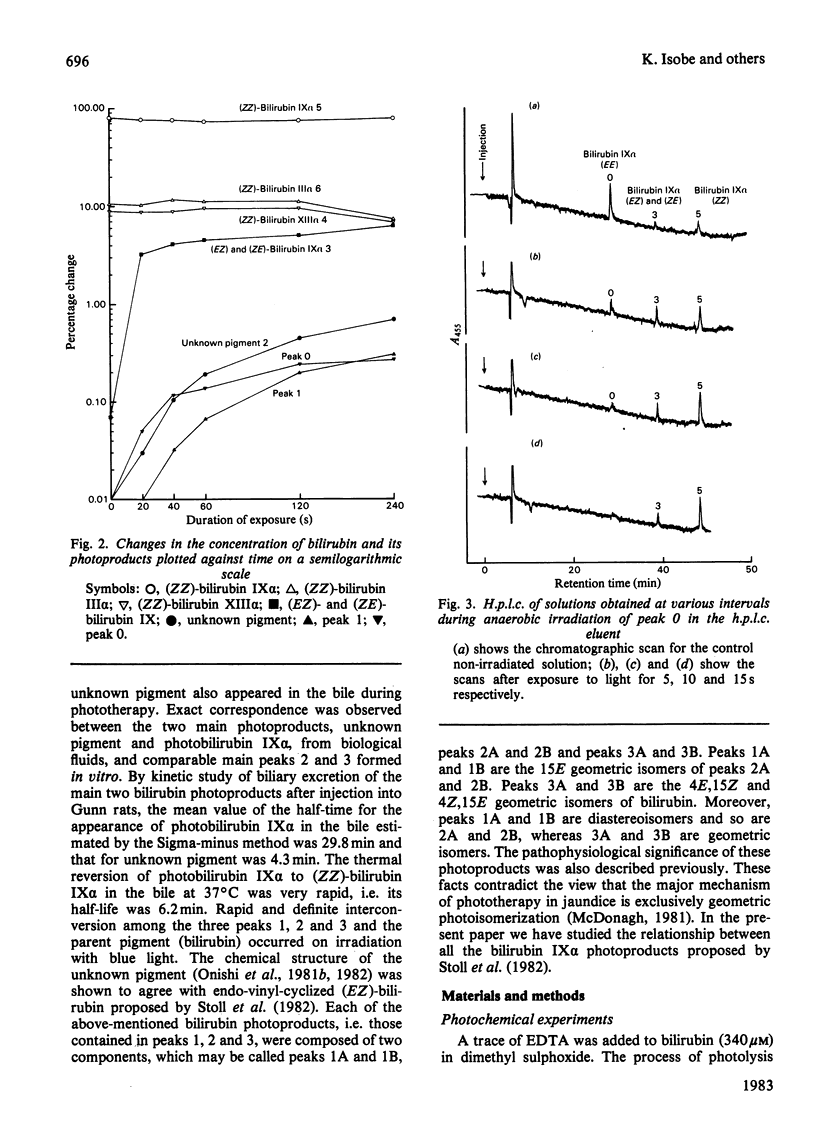
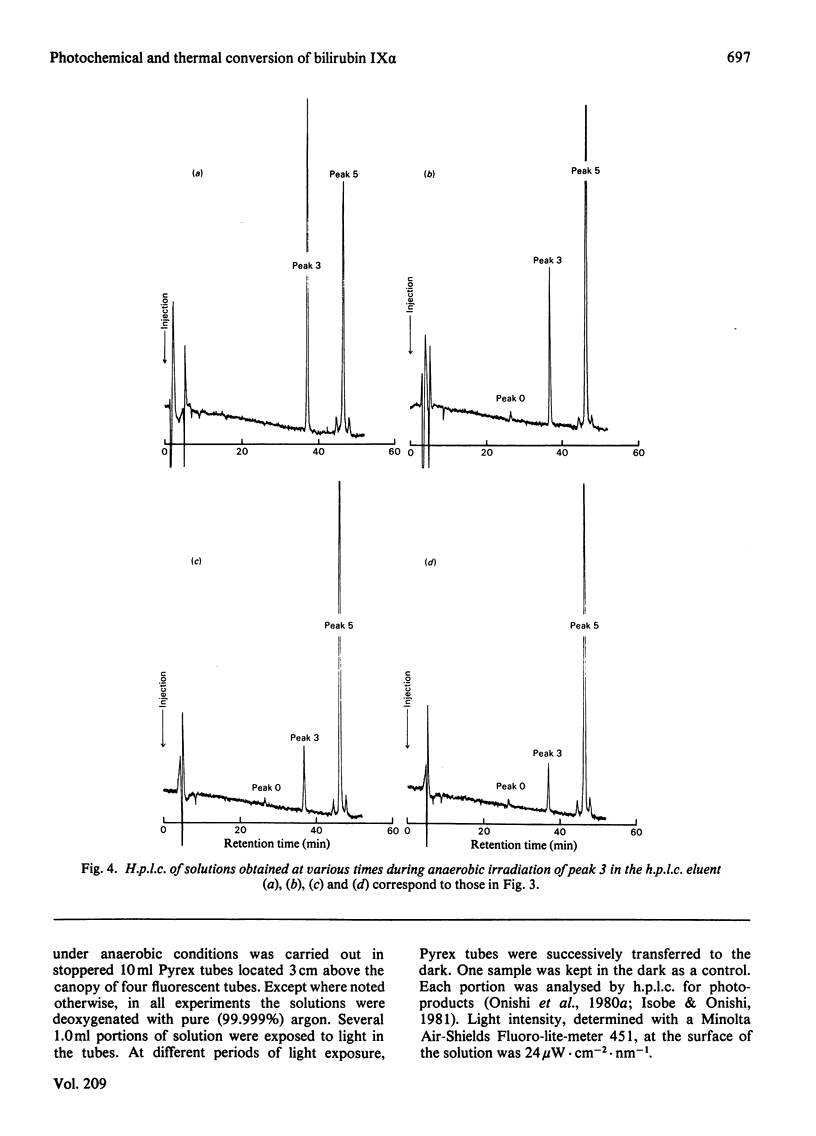
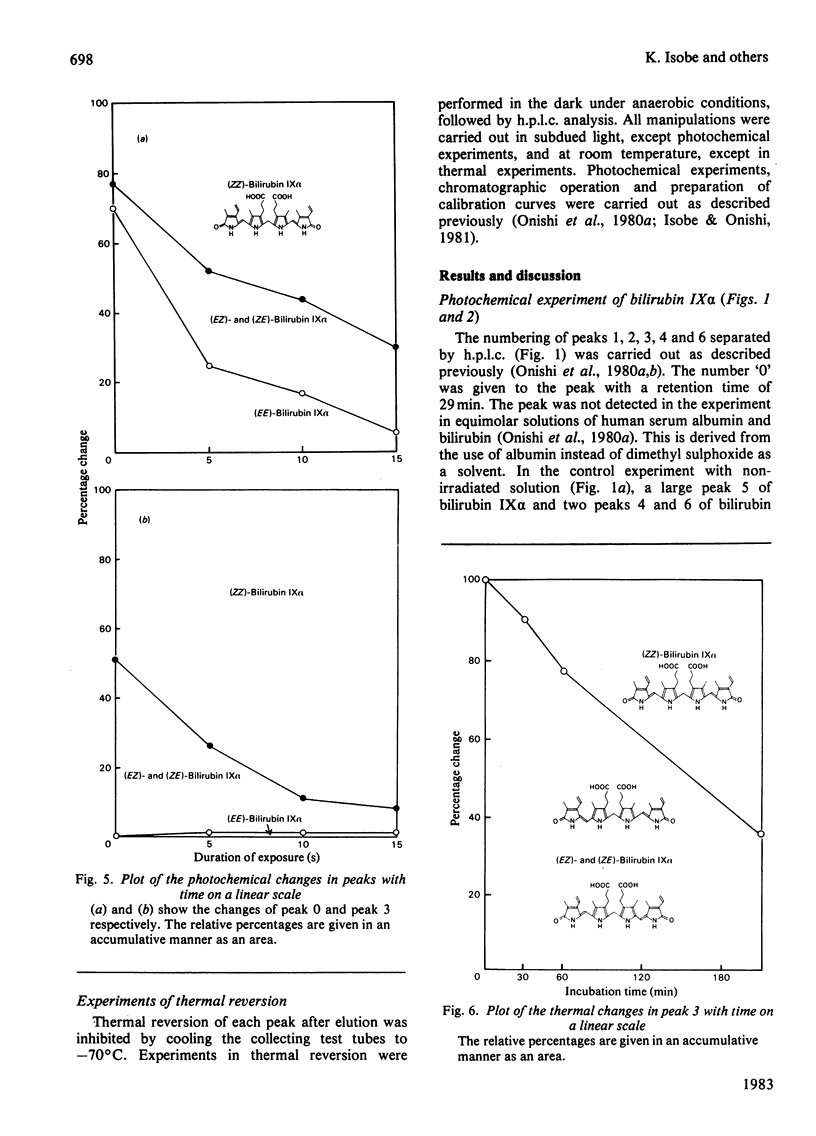
A kinetic study of the photochemical and thermal conversion of photoisomers, especialy peaks 0 and 3 [(EE)-bilirubin IX alpha and (EZ)- and (ZE)-bilirubin IX alpha], under anaerobic conditions, was performed by using reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. Peaks 0 and 3 are spontaneously, photochemically and thermally converted. Short-term photoirradiation of bilirubin gives a mixture containing not only the geometric isomers (EE)-, (EZ)- and (ZE)-bilirubin IX alpha, but also peak 2, (EZ)-cyclobilirubin IX alpha. On prolonged irradiation, cyclization and 15Z leads to 15E isomerization lead to gradual accumulation of two pairs of photoproducts: (EZ)-cyclobilirubin IX alpha A and B and (EE)-cyclobilirubin IX alpha A and B.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen A. N., Ostrow J. D. New concepts in phototherapy: photoisomerization of bilirubin IX alpha and potential toxic effects of light. Pediatrics. 1980 Apr;65(4):740–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe K., Onishi S. Kinetics of the photochemical interconversion among geometric photoisomers of bilirubin. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):1029–1031. doi: 10.1042/bj1931029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightner D. A., Wooldridge T. A., McDonagh A. F. Configurational isomerization of bilirubin and the mechanism of jaundice phototherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 30;86(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90857-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightner D. A., Wooldridge T. A., McDonagh A. F. Photobilirubin: an early bilirubin photoproduct detected by absorbance difference spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):29–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Isobe K., Itoh S., Kawade N., Sugiyama S. Demonstration of a geometric isomer of bilirubin-IX alpha in the serum of a hyperbilirubinaemic newborn infant and the mechanism of jaundice phototherapy. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):533–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1900533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Itoh S., Isobe K., Togari H., Kitoh H., Nishimura Y. Mechanism of development of bronze baby syndrome in neonates treated with phototherapy. Pediatrics. 1982 Mar;69(3):273–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Itoh S., Kawade N., Isobe K., Sugiyama S. The separation of configurational isomers of bilirubin by high pressure liquid chromatography and the mechanism of jaundice phototherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):890–896. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91911-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Kawade N., Itoh S., Isobe K., Sugiyama S. High-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of anaerobic photoproducts of bilirubin-IX alpha in vitro and its comparison with photoproducts in vivo. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):527–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1900527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Vicker N., Gray C. H., Bonnett R. Concerning the structure of photobilirubin II. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):179–188. doi: 10.1042/bj2010179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Zenone E. A., Ostrow J. D. Excretion of administered and endogenous photobilirubins in the bile of the jaundice gunn rat. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):134–141. doi: 10.1172/JCI110229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


