Abstract
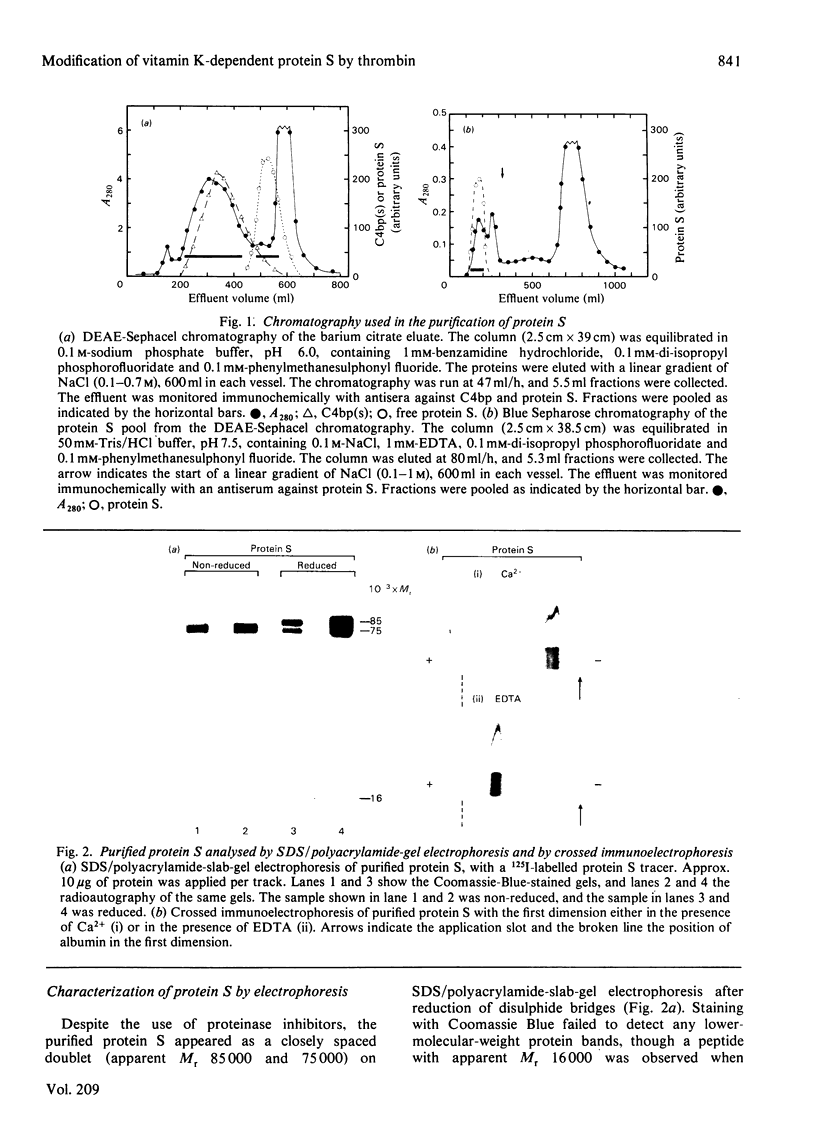
Vitamin K-dependent protein S exists in two forms in human plasma, namely as the free protein and in complex with C4b-binding protein [Dahlbäck & Stenflo (1981) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 2512-2516]. Now reported is a simple purification procedure for human protein S that includes barium citrate adsorption, DEAE-Sephacel chromatography and chromatography on Blue Sepharose. The yield was approx. 30% relative to the concentration of free protein S in plasma, which was found to be approx. 10 mg/l. Purified protein S migrated as a single-chain band on sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis under non-reducing conditions and as a doublet of Mr approx. 85 000 and 75 000 on reduction. A third band of Mr 16 000 was observed after electrophoresis of 125I-labelled protein S and radioautography of reduced samples. This band appears to be disulphide-linked to the 75 000-Mr chain before reduction. Thrombin converted the 85 000-Mr chain of protein S into a 75 000-Mr chain and an 8000-Mr fragment, the latter again being detectable only by radioautography of reduced samples. The 16 000-Mr fragment was not observed, suggesting its degradation by thrombin. Under non-reducing conditions, no change in apparent molecular weight of thrombin-treated protein S was observed, indicating disulphide linkage of the fragments. Thrombin also affected the mobility of protein S on agarose-gel electrophoresis in the presence of Ca2+, suggesting a decreased affinity to Ca2+ of the cleaved form of protein S as compared with the undegraded molecule. After activation of the complement system in human serum, protein S was found to be a constituent part of the complex formed by C4b-binding protein and component C4b.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieth J., Spiess B., Wermuth C. G. The synthesis and analytical use of a highly sensitive and convenient substrate of elastase. Biochem Med. 1974 Dec;11(4):350–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley L. G., Porter R. R. Purification of the human complement control protein C3b inactivator. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):173–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1910173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B. Degradation of human complement component C4b in the presence of the C4b-binding protein-protein S complex. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):857–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2090857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Purification of human C4b-binding protein and formation of its complex with vitamin K-dependent protein S. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):847–856. doi: 10.1042/bj2090847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J. High molecular weight complex in human plasma between vitamin K-dependent protein S and complement component C4b-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2512–2516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiScipio R. G., Davie E. W. Characterization of protein S, a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid containing protein from bovine and human plasma. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 6;18(5):899–904. doi: 10.1021/bi00572a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J. Polyethylene glycol 6,000 enhancement of the clotting of fibrinogen solutions in visual and mechanical assays. Thromb Res. 1974 Jun;4(6):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P., Stenflo J., Roepstorff P., Thomsen J. Vitamin K and the biosynthesis of prothrombin. V. Gamma-carboxyglutamic acids, the vitamin K-dependent structures in prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6125–6133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. II. Role in proteolysis of C4b by C3b-inactivator. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1044–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Porter R. R., Sim R. B. The unactivated form of the first component of human complement, C1. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1570541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppsson J. O., Laurell C. B., Franzén B. Agarose gel electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1979 Apr;25(4):629–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Nemerson Y. The activation of bovine coagulation factor X. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:95–107. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Canfield W. M., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5824–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Hermodson M. A., Davie E. W. Factor X activating enzyme from Russell's viper venom: isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4901–4906. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Uhteg L. C., Vogel C. N., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. Preparation and partial characterization of two forms of bovine thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):482–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Ichihara C., Stroud R. M. Cleavage of C4b by C3b inactivator: production of a nicked form of C4b, C4b', as an intermediate cleavage product of C4b by C3b inactivator. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):578–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Kisiel W., Di Scipio R. G. Interaction of vitamin K dependent proteins with membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2134–2138. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Prendergast F. G., Mann K. G. Interactions of a fluorescent active-site-directed inhibitor of thrombin: dansylarginine N-(3-ethyl-1,5-pentanediyl)amide. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):996–1003. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharfstein J., Ferreira A., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. I. Isolation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):207–222. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Jönsson M. Protein S, a new vitamin K-dependent protein from bovine plasma. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 15;101(2):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11128–11131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]