Abstract
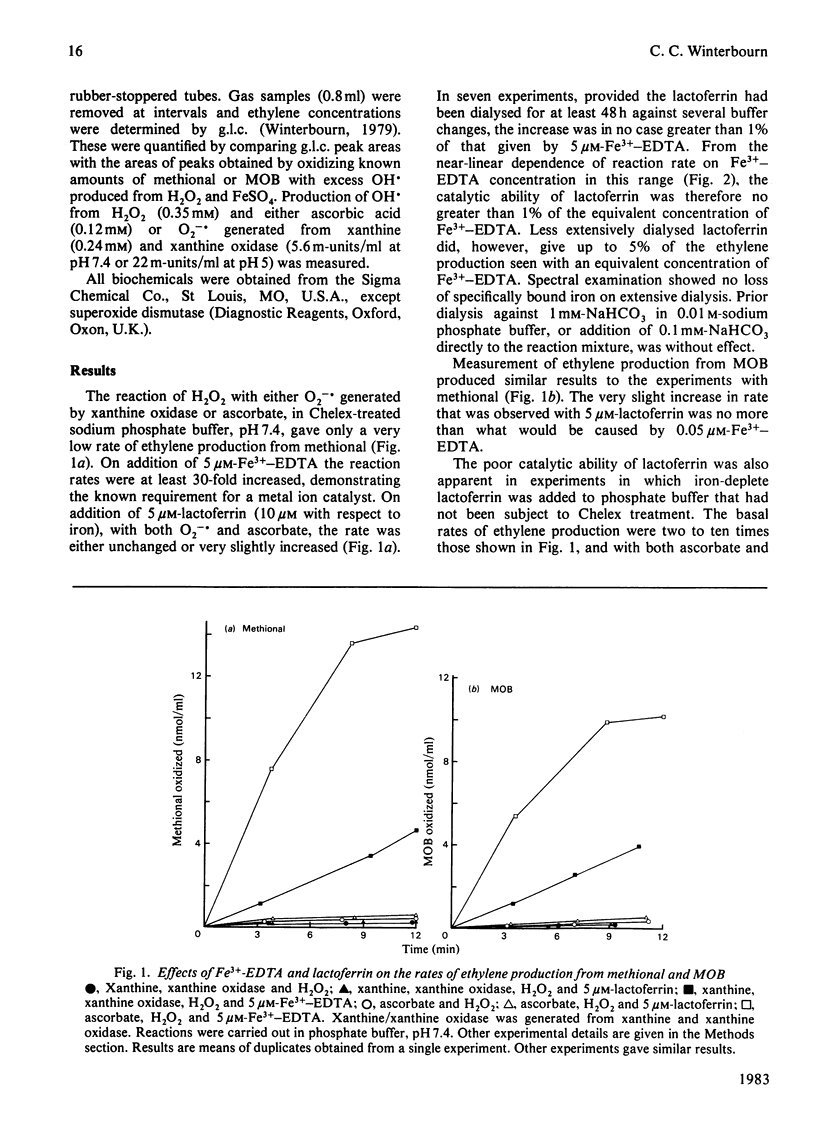
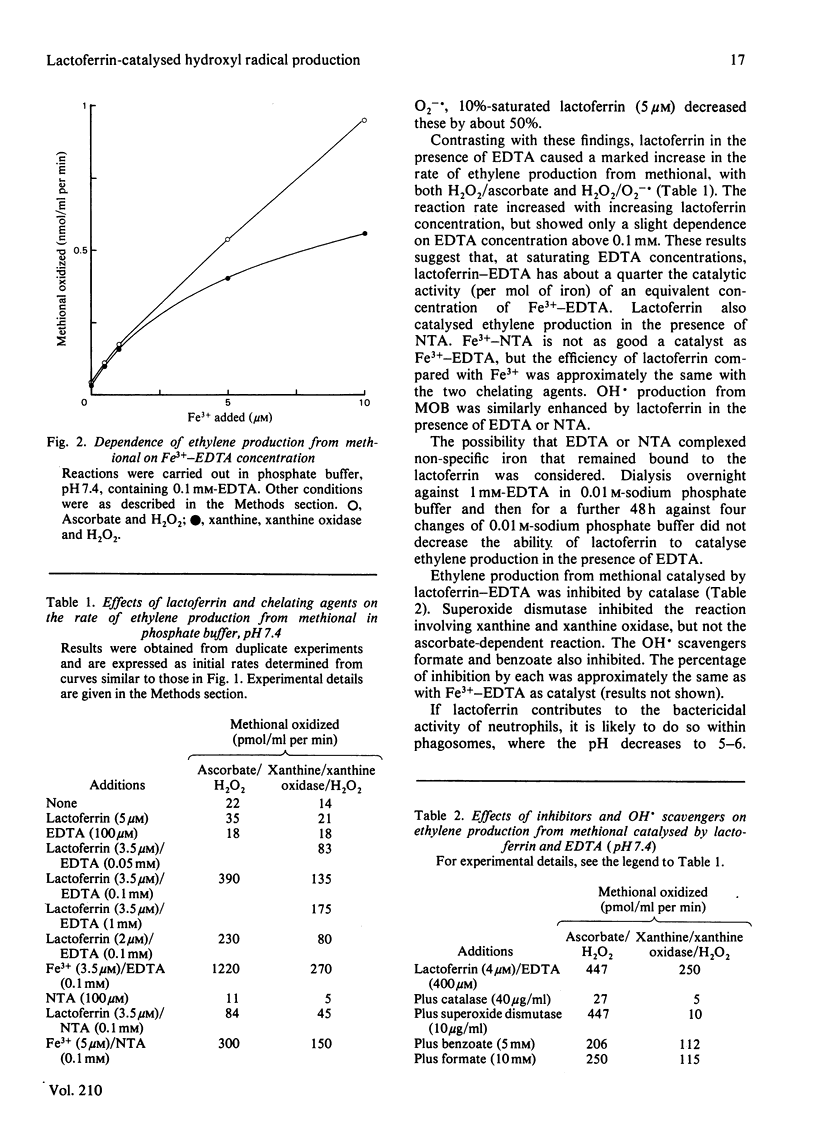
The ability of lactoferrin to catalyse hydroxyl radical production was determined by measuring ethylene production from methional (2-amino-4-methylthiobutyraldehyde) or 4-methylthio-2-oxobutyrate. Lactoferrin, isolated from human milk and saturated by adding the exact equivalents of Fe3+-nitrilotriacetic acid and dialysing, give little if any catalysis of the reaction between H2O2 and either O2-. or ascorbic acid at either pH 7.4 or pH 5.0. However, in the presence of chelating agents such as EDTA or nitrilotriacetic acid that can complex with lactoferrin, hydroxyl radical production by both mechanisms was observed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Listowsky I. Iron transport and storage proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:357–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambruso D. R., Johnston R. B., Jr Lactoferrin enhances hydroxyl radical production by human neutrophils, neutrophil particulate fractions, and an enzymatic generating system. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):352–360. doi: 10.1172/JCI110042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. R., Cole M. F., McGhee J. R. A bactericidal effect for human lactoferrin. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):263–265. doi: 10.1126/science.327545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., De Duve C., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Association of lactoferrin with specific granules in rabbit heterophil leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp C., Fridovich I. A mechanism for the production of ethylene from methional. The generation of the hydroxyl radical by xanthine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4641–4646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Armstrong J. A. The role of lactoferrin in the bactericidal function of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Immunology. 1979 Apr;36(4):781–791. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diguiseppi J., Fridovich I. Ethylene from 2-keto-4-thiomethyl butyric acid: the Haber-Weiss reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Hill H. A., Okolow-Zubkowska M. J., Segal A. W. The production of hydroxyl and superoxide radicals by stimulated human neutrophils- measurements by EPR spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge J. M., Paterson S. K., Segal A. W., Halliwell B. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by the iron-binding protein lactoferrin. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):259–261. doi: 10.1042/bj1990259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Rosen H. Ethylene formation by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Role of myeloperoxidase. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):490–506. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Metal-combining properties of human lactoferrin (red milk protein). 1. The involvement of bicarbonate in the reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Dec 5;6(4):579–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor W. A., Tang R. H. Ethylene formation from methional. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):498–503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91562-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querinjean P., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Molecular weight, single-chain structure and amino acid composition of human lactoferrin. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):420–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Role of iron and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in the bactericidal activity of a superoxide anion-generating system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 May;208(2):512–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlabach M. R., Bates G. W. The synergistic binding of anions and Fe3+ by transferrin. Implications for the interlocking sites hypothesis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2182–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Babior B. M. Evidence for hydroxyl radical production by human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):374–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI108786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Rustagi P. K., LoBuglio A. F. Human granulocyte generation of hydroxyl radical. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):316–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C. Comparison of superoxide with other reducing agents in the biological production of hydroxyl radicals. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):625–628. doi: 10.1042/bj1820625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C. Hydroxyl radical production in body fluids. Roles of metal ions, ascorbate and superoxide. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):125–131. doi: 10.1042/bj1980125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


