Abstract
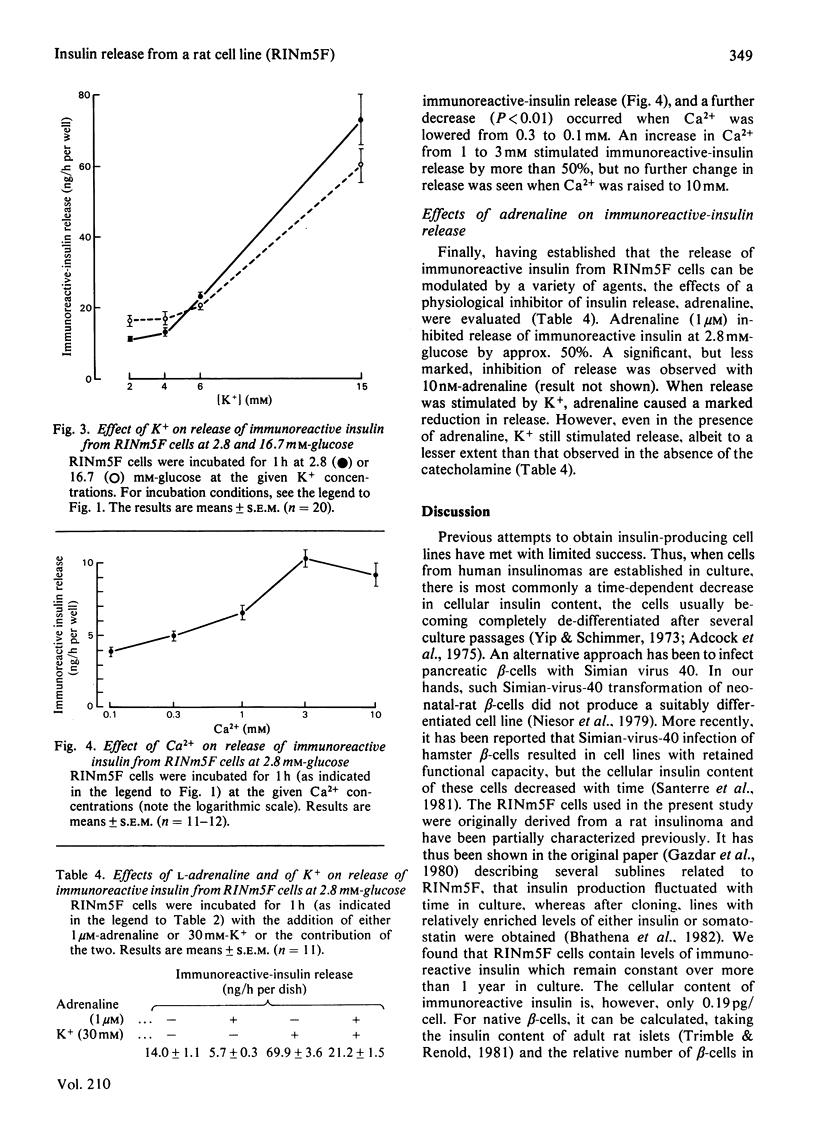
1. An insulin-producing cell line, RINm5F, derived from a rat insulinoma was studied. 2. The cellular content of immunoreactive insulin was 0.19 pg/cell, which represents approx. 1% of the insulin content of native rat beta-cells, whereas that of immunoreactive glucagon and somatostatin was five to six orders of magnitude less than that of native alpha- or delta-cells respectively. 3. RINm5F cells released 7-12% of their cellular immunoreactive-insulin content at 2.8 mM-glucose during 60 min in Krebs-Ringer bicarbonate buffer. 4. Glucose utilization was increased by raising glucose from 2.8 to 16.7 mM. There was, however, no stimulation of immunoreactive-insulin release even when glucose was increased from 2.8 to 33.4 mM. A small stimulation of release was, however, found when glucose was raised from 0 to 2.8 mM. 5. Glyceraldehyde stimulated the release of immunoreactive insulin in a dose-dependent manner. 6. At 20 mM, leucine or arginine stimulated release at 2.8 mM-glucose. 7. Raising intracellular cyclic AMP by glucagon or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine stimulated release at 2.8 mM-glucose with no additional stimulation at 16.7 mM-glucose. 8. Stimulation of immunoreactive-insulin release by K+ was dose-related between 2 and 30 mM. Another depolarizing agent, ouabain, also stimulated release. 9. Adrenaline (epinephrine) inhibited both basal (2.8 mM-glucose) release and that stimulated by 30 mM-K+. 10. Raising Ca2+ from 1 to 3 mM stimulated immunoreactive-insulin release, whereas a decrease from 1 to 0.3 or to 0.1 mM-Ca2+ lowered the release. 11. These findings could reflect a relatively specific impairment in glucose handling by RINm5F cells, contrasting with the preserved response to other modulators of insulin release.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adcock K., Austin M., Duckworth W. C., Solomon S. S., Murrell L. R. Human islet cell adenoma: metabolic analysis of the patient and of tumor cells in monolayer culture. Diabetologia. 1975 Dec;11(6):527–534. doi: 10.1007/BF01222102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agren A., Andersson A., Hellerström C. Effects of D-glyceraldehyde and D-glucose of the insulin release of pancreatic islets isolated from the newborn rat. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80927-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J. Glucoreceptor mechanisms and the control of insulin release and biosynthesis. Diabetologia. 1980 Jan;18(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01228295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Bassett J. M., Randle P. J. The pentose cycle and insulin release in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1260525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Eddlestone G. T., Rojas E. Voltage noise measurements across the pancreatic beta-cell membrane: calcium channel characteristics. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:195–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetens D., Malaisse-Lagae F., Perrelet A., Orci L. Endocrine pancreas: three-dimensional reconstruction shows two types of islets of langerhans. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1323–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.390711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhathena S. J., Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F., Voyles N. R., Wilkins S. D., Recant L. Insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin receptors on cultured cells and clones from rat islet cell tumor. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):521–531. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhathena S. J., Voyles N. R., Oie H. K., Smith S. S., Gazdar A. F., Recant L. Glucagon secreting clones of rat islet cell tumor. Horm Metab Res. 1980 Nov;12(11):632–633. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-999218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch P. T., Trus M. D., Berner D. K., Leontire A., Zawalich K. C., Matschinsky F. M. Adaptation of glycolytic enzymes: glucose use and insulin release in rat pancreatic islets during fasting and refeeding. Diabetes. 1981 Nov;30(11):923–928. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.11.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick W. L., Warren S., Chute R. N., Like A. A., Lauris V., Kitchen K. C. A transplantable insulinoma in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):628–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chick W. L., Oie H. K., Sims H. L., King D. L., Weir G. C., Lauris V. Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Meda P., Niesor E. N., Mintz D. H. The possible importance of contact between pancreatic islet cells for the control of insulin release. Endocrinology. 1982 Jul;111(1):86–94. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-1-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Renold A. E. Long-term exposure of isolated pancreatic islets to mannoheptulose: evidence for insulin degradation in the beta cell. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 1;29(19):2625–2633. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeskov C. J. Mechanism of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):442–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain K., Logothetopoulos J., Zucker P. The effects of D- and L-glyceraldehyde on glucose oxidation, insulin secretion and insulin biosynthesis by pancreatic islets of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 13;399(2):384–394. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakita K., O'Connell K., Permutt M. A. Immunodetection of insulin after transfer from gels to nitrocellulose filters. A method of analysis in tissue extracts. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):648–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan E. L., Rubenstein A. H., Evans R., Lee C. H., Klementschitsch P. Calcium infusion: a new provocative test for insulinomas. Ann Surg. 1979 Oct;190(4):501–507. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197910000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins R. G., Simeonova L., Veroni M. C. Glucose utilization in relation to insulin secretion in NZO and C57Bl mouse islets. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1634–1638. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson L. G., Siegel E., Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Insulin release during fasting: studies on adenylate cyclase, phosphodiesterase, protein kinase, and phosphoprotein phosphatase in isolated islets of langerhans of the rat. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):702–707. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Orci L., Lambert A. E., Stauffacher W., Like A. A., Renold A. E. Insulin and glucagon release from monolayer cell cultures of pancreas from newborn rats. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;3(1):16–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niesor E. J., Wollheim C. B., Mintz D. H., Blondel B., Renold A. E., Weil R. Establishment of rat pancreatic endocrine cell lines by infection with simian virus 40. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):559–568. doi: 10.1042/bj1780559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Blondel B., Murray T., Mintz D. H. Cyclic adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate stimulates islet B cell replication in neonatal rat pancreatic monolayer cultures. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1065–1071. doi: 10.1172/JCI109935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. A., Yip C. C., Schimmer B. P. Isolation of cloned Syrian hamster insulinoma cell lines with limited capacity for insulin production. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;57(8):819–824. doi: 10.1139/y79-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santerre R. F., Cook R. A., Crisel R. M., Sharp J. D., Schmidt R. J., Williams D. C., Wilson C. P. Insulin synthesis in a clonal cell line of simian virus 40-transformed hamster pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4339–4343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E. G., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Evidence for the involvement of Na/Ca exchange in glucose-induced insulin release from rat pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):996–1003. doi: 10.1172/JCI109969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopwith A. M., Hutton J. C., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Hales C. N. Insulin secretion by a transplantable rat islet cell tumour. Diabetologia. 1981 Sep;21(3):224–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00252658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble E. R., Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E. Functional differences between rat islets of ventral and dorsal pancreatic origin. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):405–413. doi: 10.1172/JCI110464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble E. R., Renold A. E. Ventral and dorsal areas of rat pancreas: islet hormone content and secretion. Am J Physiol. 1981 Apr;240(4):E422–E427. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.4.E422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Siegel E. G., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. The role of extracellular Ca++ and islet calcium stores in the regulation of biphasic insulin release. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Schimmer B. P. Human pancreatic islet tumor cells maintained in vitro. Diabetologia. 1973 Aug;9(4):251–254. doi: 10.1007/BF01221850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


