Abstract
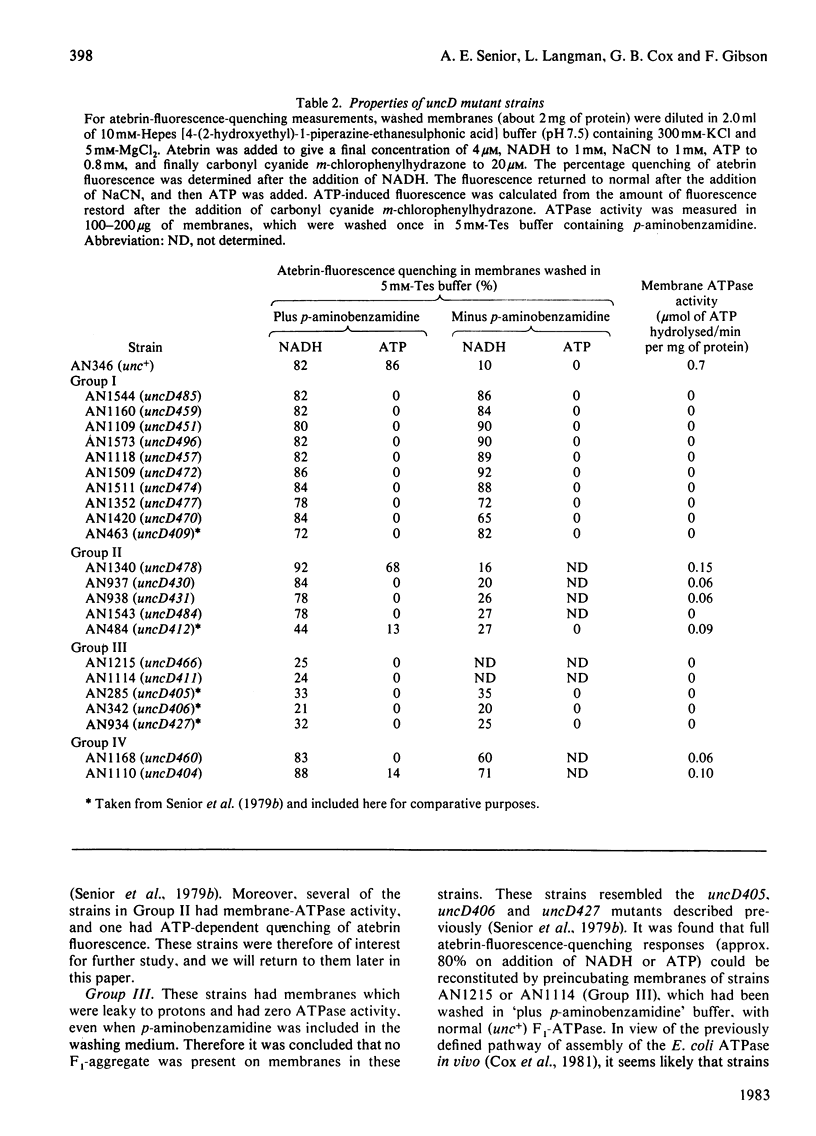
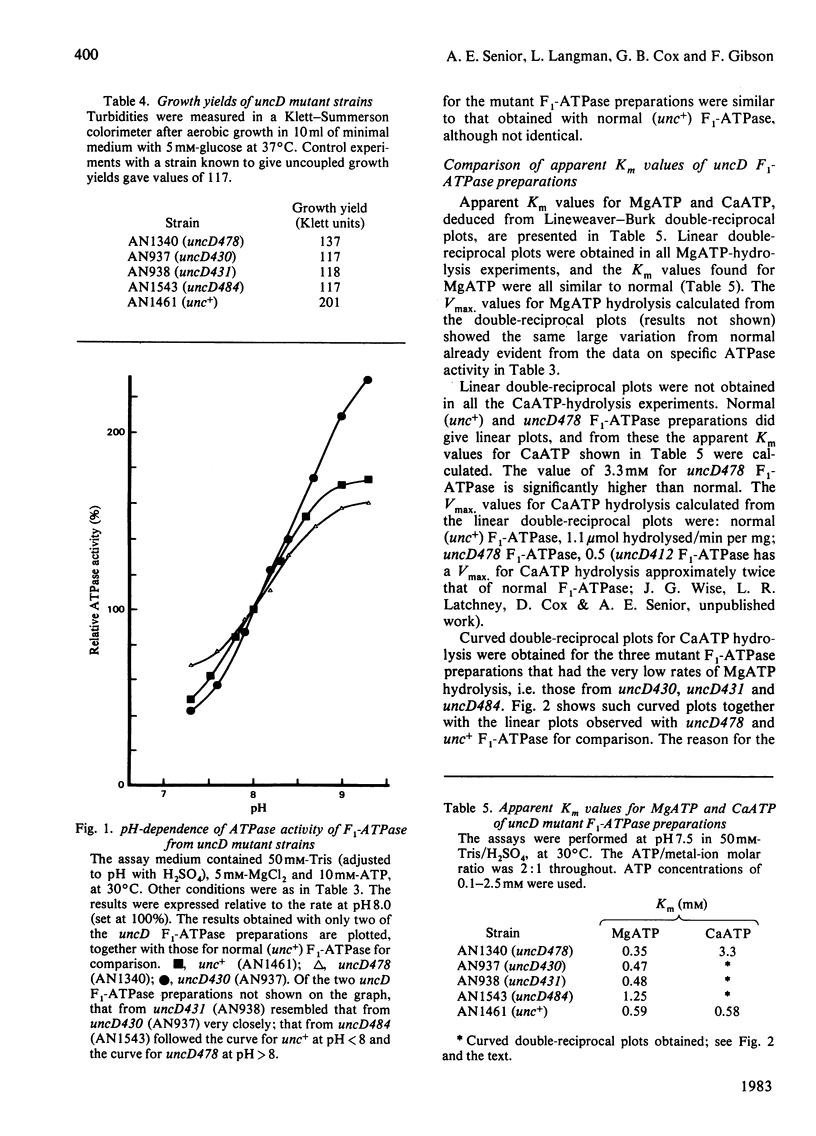
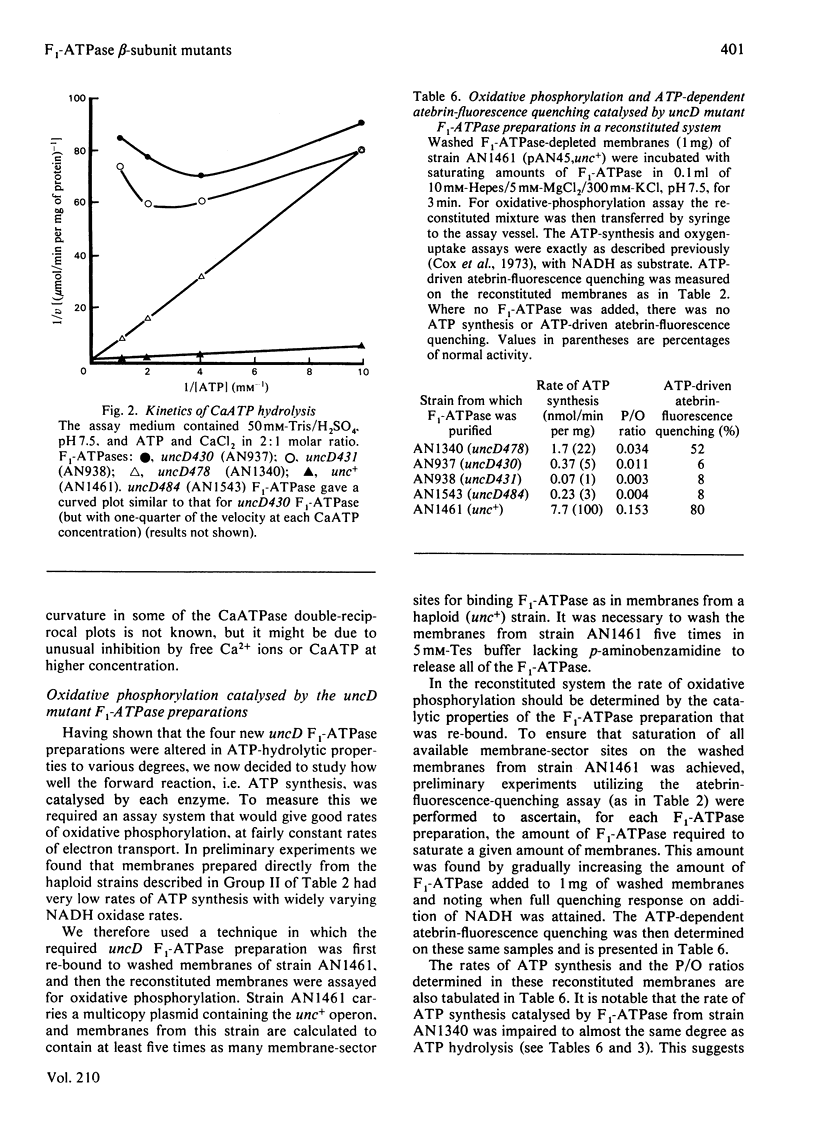
To facilitate study of the role of the beta-subunit in the membrane-bound proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli, we identified mutant strains from which an F1-ATPase containing abnormal beta-subunits can be purified. Seventeen strains of E. coli, characterized by genetic complementation tests as carrying mutations in the uncD gene (which codes for the beta-subunit), were studied. The majority of these strains (11) were judged to be not useful, as their membranes lacked ATPase activity, and were either proton-permeable as prepared or remained proton-impermeable after washing with buffer of low ionic strength. A further two strains were of a type not hitherto reported, in that their membranes had ATPase activity, were proton-impermeable as prepared, and were not rendered proton-permeable by washing in buffer of low ionic strength. Presumably in these two strains F1-ATPase is not released in soluble form by this procedure. F1-ATPase of normal molecular size were purified from strains AN1340 (uncD478), AN937 (uncD430), AN938 (uncD431) and AN1543 (uncD484). F1-ATPase from strain AN1340 (uncD478) had 15% of normal specific Mg-dependent ATPase activity and 22% of normal ATP-synthesis activity. The F1-ATPase preparations from strains AN937, AN938 and AN1543 had respectively 1.7%, 1.8% and 0.2% of normal specific Mg-dependent ATPase activity, and each of these preparations had very low ATP-synthesis activity. The yield of F1-ATPase from the four strains described was almost twice that obtained from a normal haploid strain. The kinetics of Ca-dependent ATPase activity were unusual in each of the four F1-ATPase preparations. It is likely that these four mutant uncD F1-ATPase preparations will prove valuable for further experimental study of the F1-ATPase catalytic mechanism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox G. B., Downie J. A., Gibson F., Radik J. Genetic complementation between two mutant unc alleles (unc A401 and unc D409) affecting the Fl portion of the magnesium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):593–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1700593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Downie J. A. Isolation and characterization of mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 affected in oxidative phosphorylation of quinone biosynthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:106–117. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Downie J. A., Langman L., Senior A. E., Ash G., Fayle D. R., Gibson F. Assembly of the adenosine triphosphatase complex in Escherichia coli: assembly of F0 is dependent on the formation of specific F1 subunits. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):30–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.30-42.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Gibson F., McCann L. Reconstitution of oxidative phosphorylation and the adenosine triphosphate-dependent transhydrogenase activity by a combination of membrane fractions from unCA- and uncB- mutant strains of Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1015–1021. doi: 10.1042/bj1341015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L. The mechanism and regulation of ATP synthesis by F1-ATPases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:681–714. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A., Gibson F., Cox G. B. Membrane adenosine triphosphatases of prokaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:103–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A., Langman L., Cox G. B., Yanofsky C., Gibson F. Subunits of the adenosine triphosphatase complex translated in vitro from the Escherichia coli unc operon. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):8–17. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.8-17.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Allison W. S. Identification of a tyrosine residue at a nucleotide binding site in the beta subunit of the mitochondrial ATPase with p-fluorosulfonyl[14C]-benzoyl-5'-adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6100–6106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Böhlen P., Otsuka A. S., Yoshida M., Allison W. S. Inactivation of the bovine mitochondrial F1-ATPase with dicyclohexyl[14C]carbodiimide leads to the modification of a specific glutamic acid residue in the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9084–9089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayle D. R., Downie J. A., Cox G. B., Gibson F., Radik J. Characterization of the mutant-unc D-gene product in a strain of Escherichia coli K12. An altered beta-subunit of the magnesium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 15;172(3):523–531. doi: 10.1042/bj1720523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson F., Cox G. B., Downie J. A., Radik J. A mutation affecting a second component of the F0 portion of the magnesium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli K12. The uncC424 allele. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):193–198. doi: 10.1042/bj1640193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson F., Downie J. A., Cox G. B., Radik J. Mu-induced polarity in the unc operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):728–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.728-736.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubmeyer C., Penefsky H. S. The presence of two hydrolytic sites on beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3718–3727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Brusilow W. S., Simoni R. D. Gene order and gene-polypeptide relationships of the proton-translocating ATPase operon (unc) of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):320–324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa H., Horiuchi Y., Takagi M., Ishino Y., Futai M. Coupling factor F1 ATPase with defective beta subunit from a mutant of Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1980 Sep;88(3):695–703. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Downie J. A., Cox G. B., Gibson F., Langman L., Fayle D. R. The uncA gene codes for the alpha-subunit of the adenosine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli. Electrophoretic analysis of uncA mutant strains. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):103–109. doi: 10.1042/bj1800103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Fayle D. R., Downie J. A., Gibson F., Cox G. B. Properties of membranes from mutant strains of Escherichia coli in which the beta-subunit of the adenosine triphosphatase is abnormal. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):111–118. doi: 10.1042/bj1800111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E. Tightly bound magnesium in mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase from beef heart. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11319–11322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. G., Latchney L. R., Senior A. E. The defective proton-ATPase of uncA mutants of Escherichia coli. Studies of nucleotide binding sites, bound aurovertin fluorescence, and labeling of essential residues of the purified F1-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10383–10389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


