Abstract
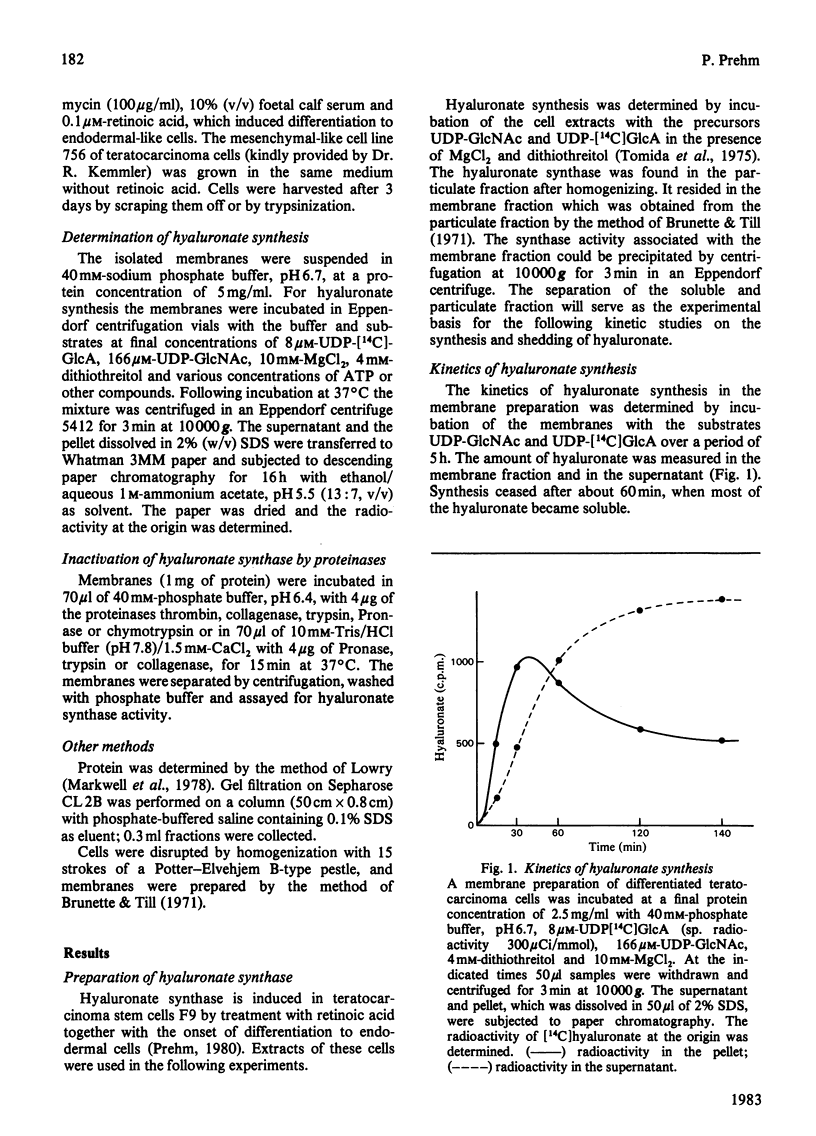
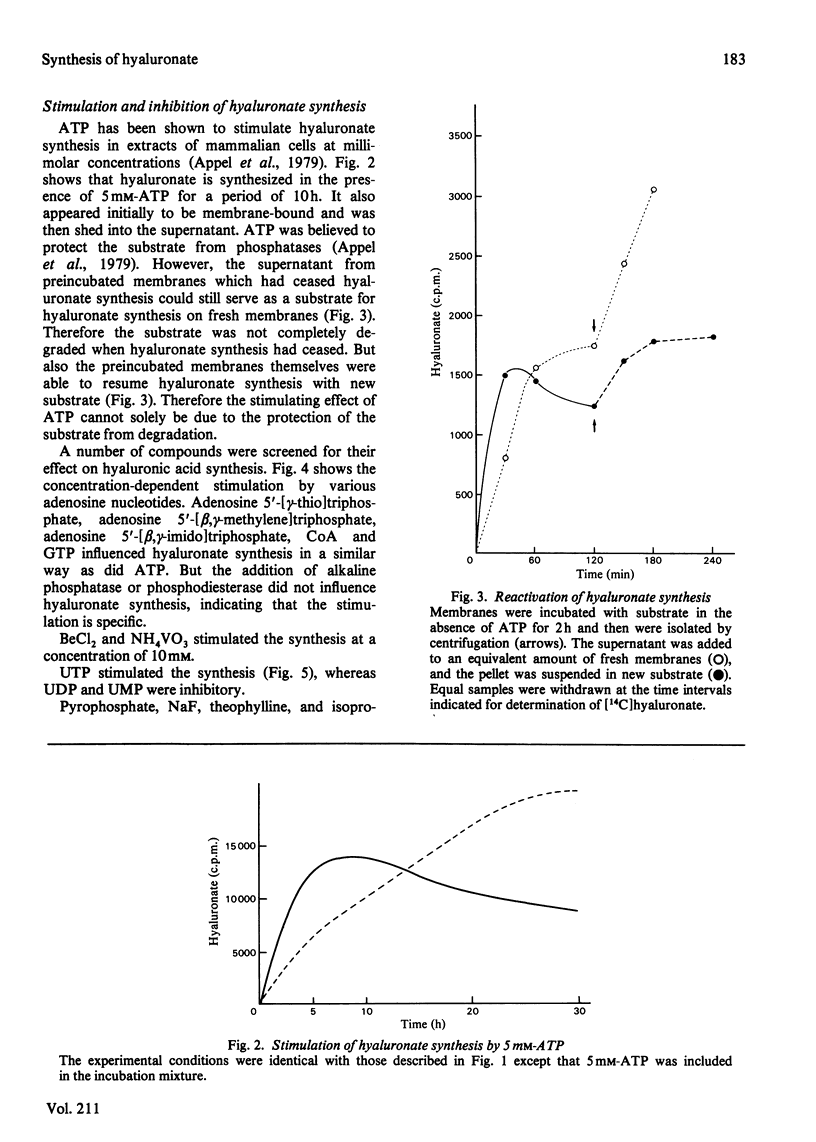
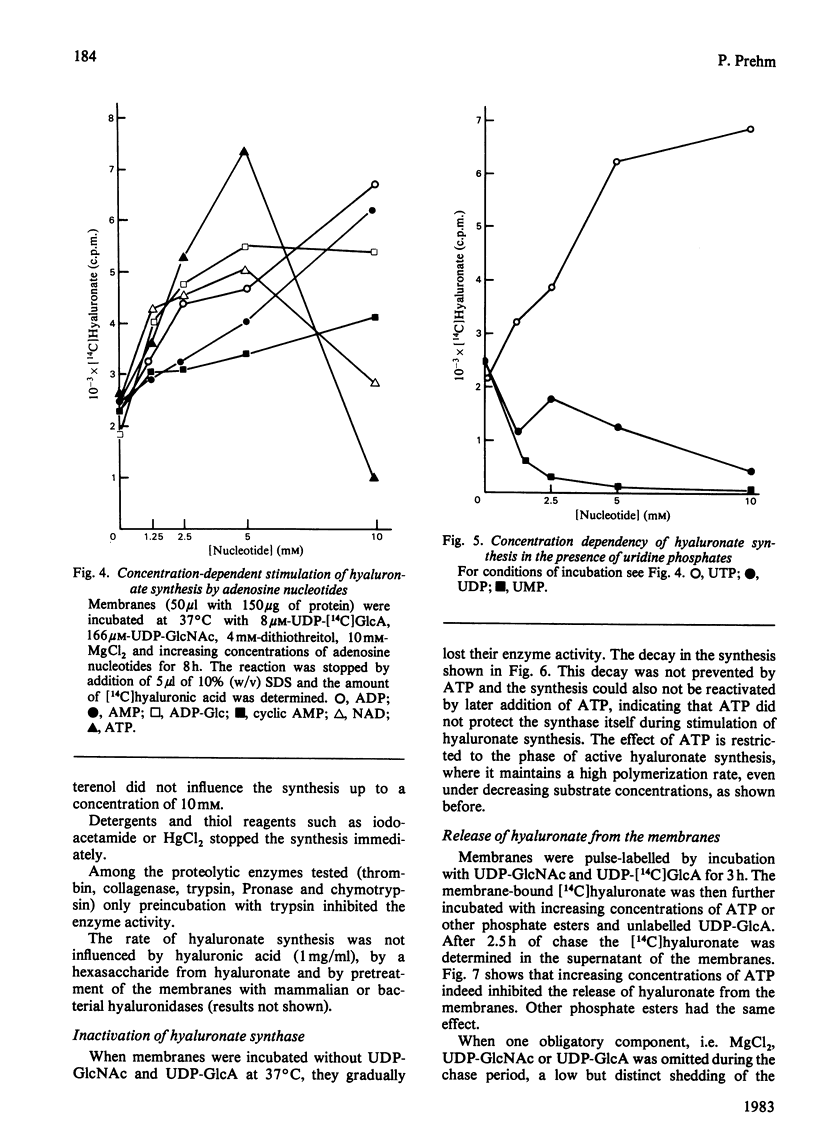
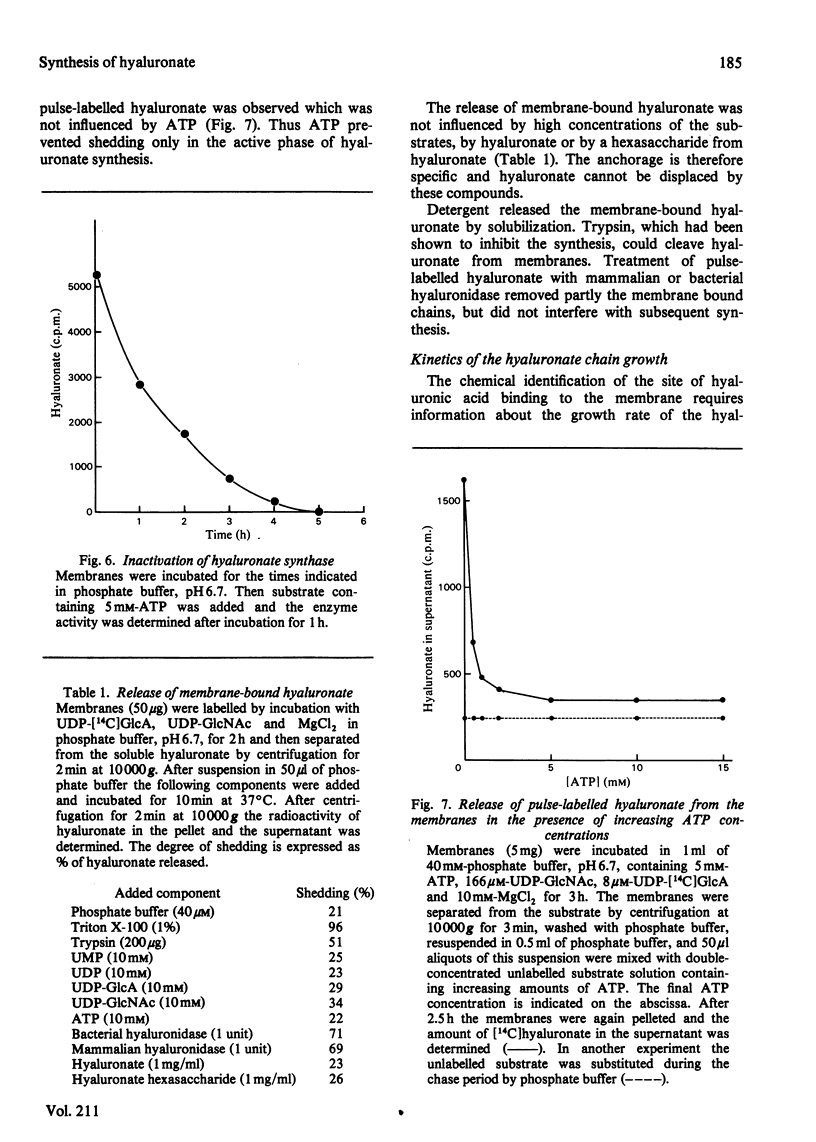
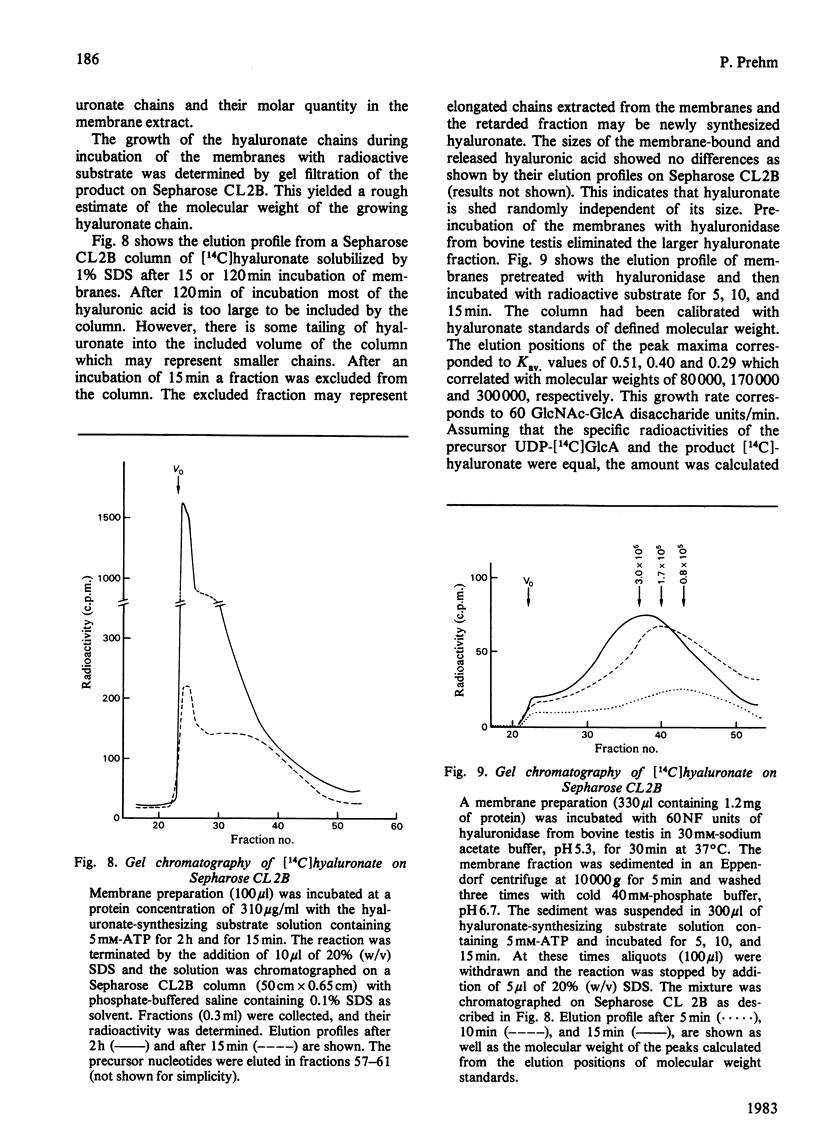
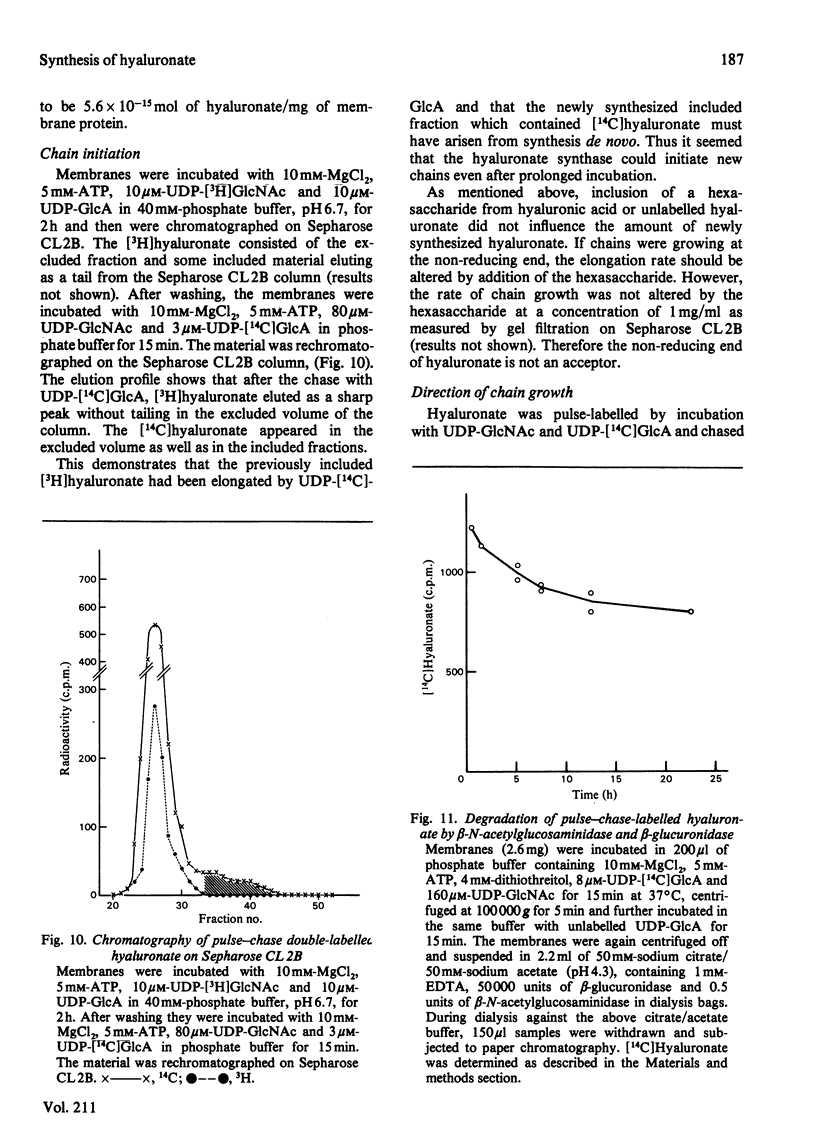
Differentiation of teratocarcinoma cells led to induction of hyaluronate synthesis. The synthase was recovered in the membrane fraction of cell lysates. Hyaluronate was synthesized at the membranes and was then released as a soluble product. The synthase could be stimulated by a variety of phosphate esters which prevented the degradation of the substrates UDP-GlcNAc and UDP-GlcA and the release of the growing hyaluronic acid chain from the membrane. Hyaluronidases or oligosaccharides derived from hyaluronate did not affect the synthesis. The chains grew at a rate of 60 repeating units/min. Continuous new chain initiation occurred during prolonged synthesis. Digestion of pulse-chase-labelled hyaluronate with beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase and beta-glucuronidase showed that the chains grew at the reducing end.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel A., Horwitz A. L., Dorfman A. Cell-free synthesis of hyaluronic acid in Marfan syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12199–12203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. I. The role of hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4232–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Dorfman A. Glycosaminoglycan synthesis by cultured human skin fibroblasts after transformation with simian virus 40. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4777–4785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hronowski L., Anastassiades T. P. The effect of cell density on net rates of glycosaminoglycan synthesis and secretion by cultured rat fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10091–10099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleine T. O. Biosynthesis of proteoglycans: an approach to locate it in different membrane systems. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1981;9:27–98. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363709-3.50008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Jansson L., Hallén A. Biosynthesis of heparin. II. Formation of sulfamino groups. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7234–7241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longas M. O., Meyer K. Sequential hydrolysis of hyaluronate by beta-glucuronidase and beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):275–282. doi: 10.1042/bj1970275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikuni-Takagaki Y., Toole B. P. Shedding of hyaluronate from the cell surface of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8409–8415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P. Induction of hyaluronic acid synthesis in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 10;111(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80813-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolmiller A. C., Dorfman A. The biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):236–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara K., Schwartz N. B., Dorfman A. Biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6252–6261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomida M., Koyama H., Ono T. Induction of hyaluronic acid synthetase activity in rat fibroblasts by medium change of confluent cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Aug;86(1):121–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Biswas C., Gross J. Hyaluronate and invasiveness of the rabbit V2 carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6299–6303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P. Hyaluronate turnover during chondrogenesis in the developing chick limb and axial skeleton. Dev Biol. 1972 Nov;29(3):321–329. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Okayama M., Orkin R. W., Yoshimura M., Muto M., Kaji A. Developmental roles of hyaluronate and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1977;32:139–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


