Abstract
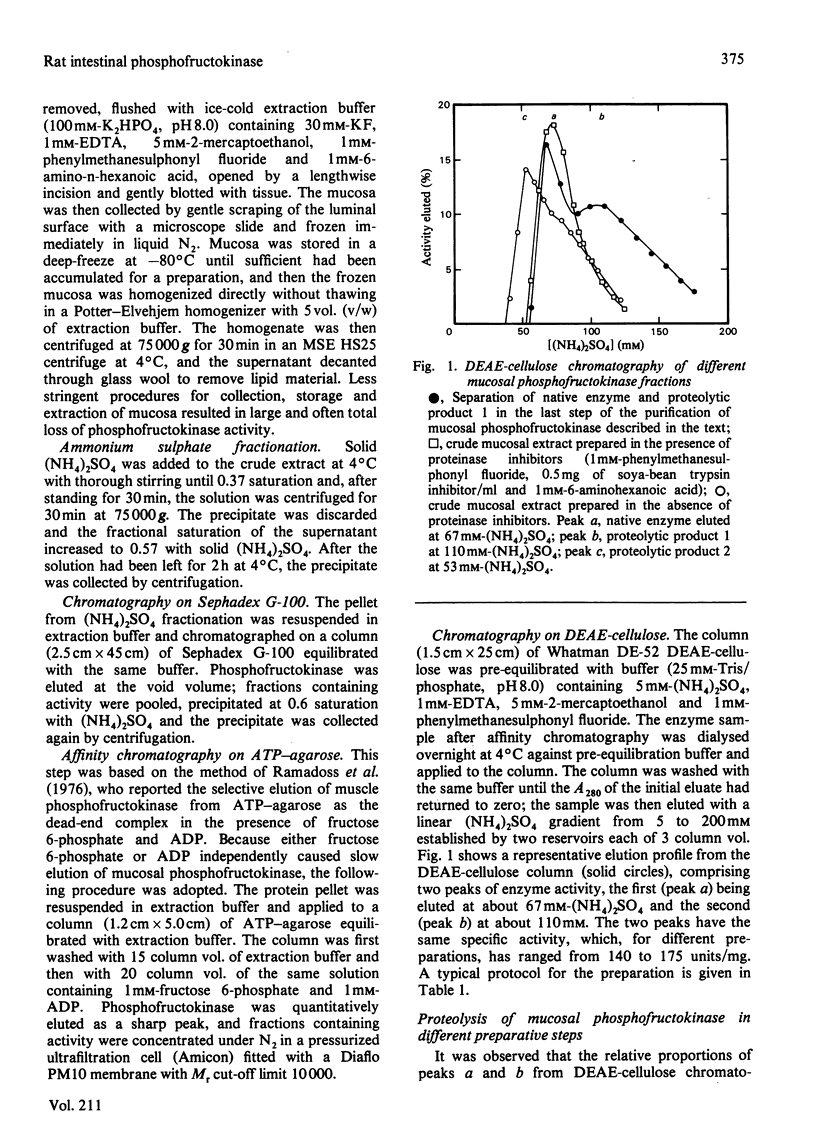
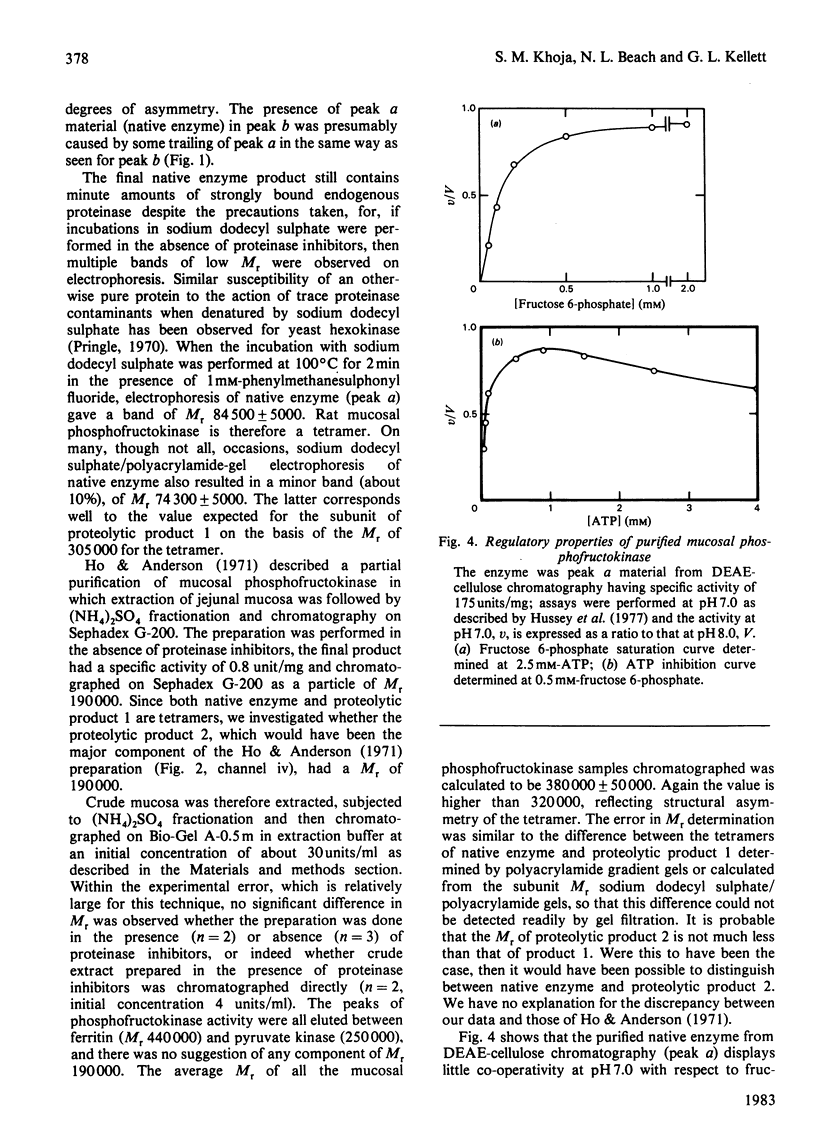
1. Only a single phosphofructokinase isoenzyme is present in the mucosa of rat small intestine. 2. Mucosal phosphofructokinase was purified to yield a homogeneous preparation of specific activity 175 units/mg of protein. 3. The native enzyme is a tetramer, with monomer Mr 84 500 +/- 5000. 4. The native enzyme may be degraded by the action of endogenous proteinases to give two products with the same specific activity as the native enzyme: degradation occurs in the order native enzyme leads to proteolytic product 1 leads to proteolytic product 2. 5. Proteolytic product 1 has a greater mobility in cellulose acetate electrophoresis at pH8 and binds more strongly to DEAE-cellulose than does native enzyme; the converse is true for proteolytic product 2. 6. Proteolytic product 1 is a tetramer with a monomer Mr about 74 300; proteolytic product 2 is also a tetramer. 7. Native enzyme can only be prepared in the presence of proteinase inhibitors; partial purifications based on simple fractionation of crude mucosal extracts in the absence of proteinases inhibitors contain proteolytic product 2 as the main component and proteolytic product 1 together with little native enzyme. 8. Purified native mucosal phosphofructokinase displayed little co-operativity with respect to fructose 6-phosphate at pH 7.0 and was only weakly inhibited by ATP.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Budohoski L., Challis R. A., Newsholme E. A. Effects of starvation on the maximal activities of some glycolytic and citric acid-cycle enzymes and glutaminase in mucosa of the small intestine of the rat. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):169–172. doi: 10.1042/bj2060169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldhammer A. R., Paradies H. H. Phosphofructokinase: structure and function. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1979;15:109–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González F., Tsai M. Y., Kemp R. G. Distribution of phosphofructokinase isozymes in rabbit, mouse, guinea pig and rat. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1975 Oct 15;52(2):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(75)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. J., Parsons D. S. The utilization of glucose and production of lactate by in vitro preparations of rat small intestine: effects of vascular perfusion. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):775–795. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho W., Anderson J. W. Phosphofructokinase in rat jejunal mucosa. Subcellular distribution, isolation, and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 10;227(2):354–363. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey C. R., Liddle P. F., Ardron D., Kellett G. L. The isolation and characterization of differentially phosphorylated fractions of phosphofructokinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):497–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamal A., Kellett G. L. The effect of starvation on the control of phosphofructokinase activity in the epithelial cells of the rat small intestine. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 15;210(1):129–135. doi: 10.1042/bj2100129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A., Cottreau D., Meienhofer M. C. Purification of F4 phosphofructokinase from human platelets and comparison with the other phosphofructokinase forms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 11;611(1):114–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp R. G. Rabbit liver phosphofructokinase. Comparison of some properties with those of muscle phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING K. H., MARCUS F., LARDY H. A. PURIFICATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1893–1899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers J. M., Hülsmann W. C. Pasteur effect in the in vitro vascularly perfused rat small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 20;275(3):491–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteous J. W. Glucose as a fuel for small intestine. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(3):534–539. doi: 10.1042/bst0060534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R. The molecular weight of the undegraded polypeptide chain of yeast hexokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 8;39(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90755-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadoss C. S., Luby L. J., Uyeda K. Affinity chromatography of phosphofructokinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Aug;175(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaiah A. Pasteur effect and phosphofructokinase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):297–345. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152808-9.50014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava L. M., Hübscher G. Glucose metabolism in the mucosa of the small intestine. Glycolysis in subcellular preparations from the cat and rat. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):458–466. doi: 10.1042/bj1000458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejwani G. A., Kaur J., Ananthanarayanan M., Ramaiah A. Concentrations of various effectors and substrates of phosphofructokinase in the jejunum of rat and their relation to the lack of Pasteur effect in this tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 25;370(1):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejwani G. A., Ramaiah A. Properties of phosphofructokinase from the mucosa of rat jejunum and their relation to the lack of Pasteur effect. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):507–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1250507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. Y., Kemp R. G. Rabbit brain phosphofructokinase. Comparison of regulatory properties with those of other phosphofructokinase isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6590–6596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K. Phosphofructokinase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;48:193–244. doi: 10.1002/9780470122938.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker I. D., Harris J. I., Runswick M. J., Hudson P. The subunits of rabbit-muscle phosphofructokinase. A search for sequence repetition. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):255–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]