Abstract
A new affinity column for renin was prepared by coupling the isosteric peptide inhibitor of renin, H.77 (D-His-Pro-Phe-His-LeuR-Leu-Val-Tyr, where R is a reduced isosteric bond, -CH2-NH-), to activated 6-aminohexanoic acid-Sepharose 4B. Chromatography of a crude extract of human kidney cortex on this material resulted in a 5500-fold purification of renin in 76% yield. The purified enzyme (specific activity 871 units/mg) was free of non-specific acid-proteinase activity and was stable at pH 6.8 and -20 degrees C over a period of several weeks.
Full text
PDF

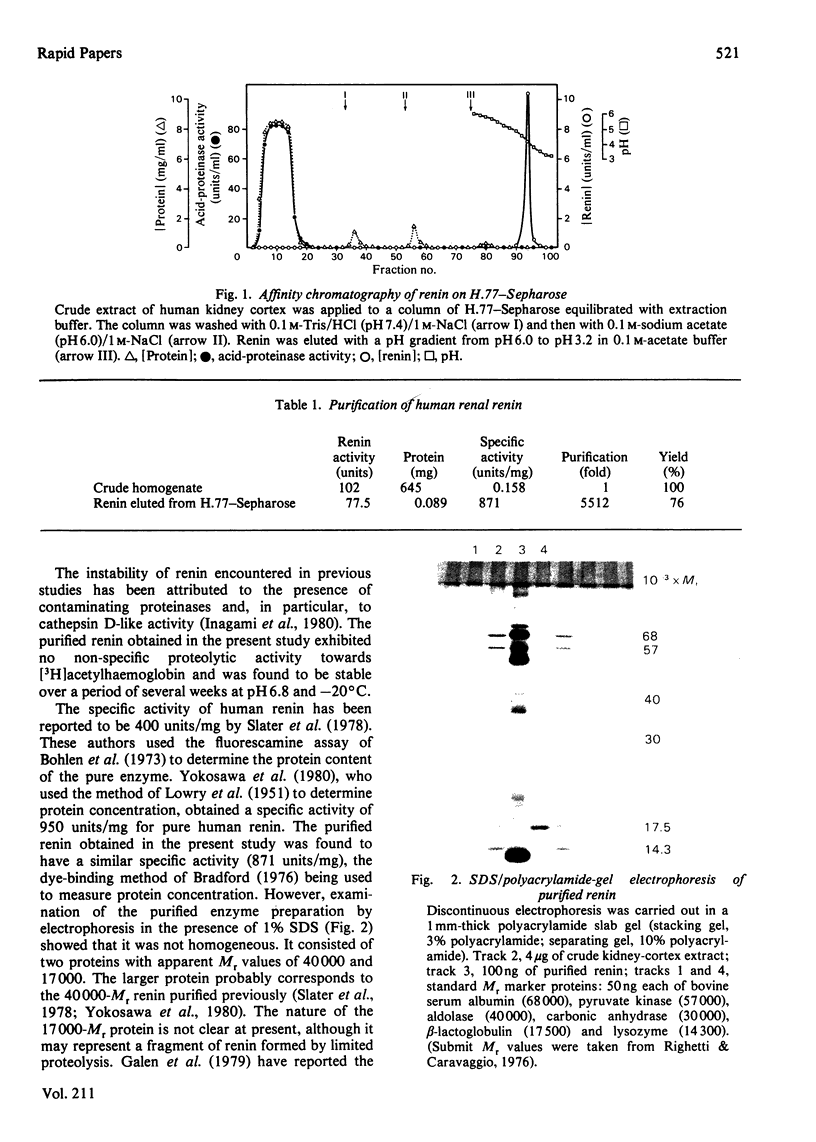

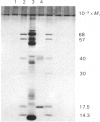
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Suen E. T., Delaney R., Chiu A., Johnson B. C. Regulation of vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen F. X., Devaux C., Guyenne T., Menard J., Corvol P. Multiple forms of human renin. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4848–4855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAAS E., LAMFROM H., GOLDBLATT H. A simple method for the extraction and partial purification of renin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Feb;48(2):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille M. B., Barrett A. J., Dingle J. T., Fell H. B. Microassay for cathepsin D shows an unexpected effedt of cycloheximide on limb-bone rudiments in organ culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Aug;61(2):470–472. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macart M., Gerbaut L. An improvement of the Coomassie Blue dye binding method allowing an equal sensitivity to various proteins: application to cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Jun 16;122(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. A., Leckie B. J., Morton J. J., Jordan J., Tree M. A microassay for active and total renin concentration in human plasma based on antibody trapping. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Feb 14;101(1):5–15. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peart W. S., Lloyd A. M., Thatcher G. N., Lever A. F., Payne N., Stone N. Purification of pig renin. Biochem J. 1966 Jun;99(3):708–716. doi: 10.1042/bj0990708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P. G., Caravaggio T. Isoelectric points and molecular weights of proteins. J Chromatogr. 1976 Apr 21;127(11):1–28. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)98537-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. E. Renin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):427–442. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szelke M., Leckie B. J., Tree M., Brown A., Grant J., Hallett A., Hughes M., Jones D. M., Lever A. F. H-77: a potent new renin inhibitor. In vitro and in vivo studies. Hypertension. 1982 May-Jun;4(3 Pt 2):59–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szelke M., Leckie B., Hallett A., Jones D. M., Sueiras J., Atrash B., Lever A. F. Potent new inhibitors of human renin. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):555–557. doi: 10.1038/299555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]