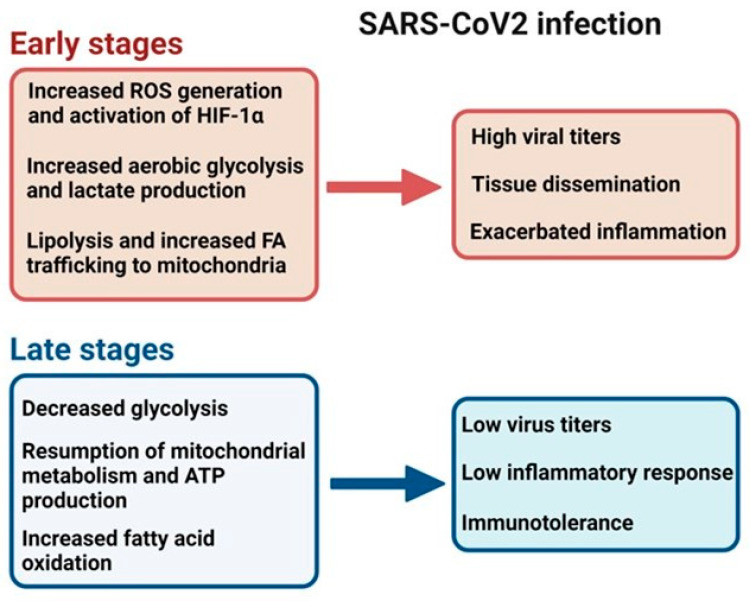
Figure 5.
Metabolic switch in SARS-CoV2 infection. SARS-CoV2 infection follows a bimodal metabolic reprogramming. Initial SARS-CoV2 infection is characterized by mitochondrial ROS production that promotes hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) expression, lipolysis, and an increase in FA synthesis. Together with the induction of the Warburg effect, virus replication is enhanced, accompanied by a severe pro-inflammatory response (cytokine storm). During the second stage, glycolysis and oxygen consumption decrease, FA oxidation increases, and the mitochondria return to regular respiration and ATP production. It is a hypo-inflammatory stage, with decreased virus titers and immunotolerance [92,133].