Abstract
1. The whole-cell patch-clamp technique was employed with the free intracellular [Ca2+] fixed at 1.4 microM in order to study the isoprenaline (Iso)-induced increase in the Na(+)-K+ pump current (Ip) in acutely isolated guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. 2. The non-specific protein kinase inhibitor, H-7, eliminated the stimulatory effect of Iso, suggesting a phosphorylation step is involved in the beta-agonist stimulation of Ip. 3. H-7 or the phosphatase inhibitor calyculin A individually had no effect on basal Ip; however, when Ip was first increased by Iso, H-7 inhibited and calyculin A further increased Ip. This suggests phosphorylation is not important to the basal regulation of Ip, but does have an effect during beta-stimulation. 4. The Iso-induced increase in Ip could be mimicked by adding the membrane-permanent cAMP analogue chlorophenylthio-cAMP, blocking cAMP degradation with IBMX or stimulating cAMP production with forskolin. Alternatively the protein kinase A inhibitor PKI blocked the stimulatory effect of Iso. This suggests the Iso-induced phosphorylation responsible for increasing Ip is mediated by cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA). 5. We conclude that the beta-agonist-induced increase in Ip in the presence of high intracellular [Ca2+] is mediated by a phosphorylation step via the cAMP-dependent PKA pathway. During beta-stimulation, this increase in active Na(+)-K+ transport can serve to offset the effects of increases in passive membrane conductances.
Full text
PDF
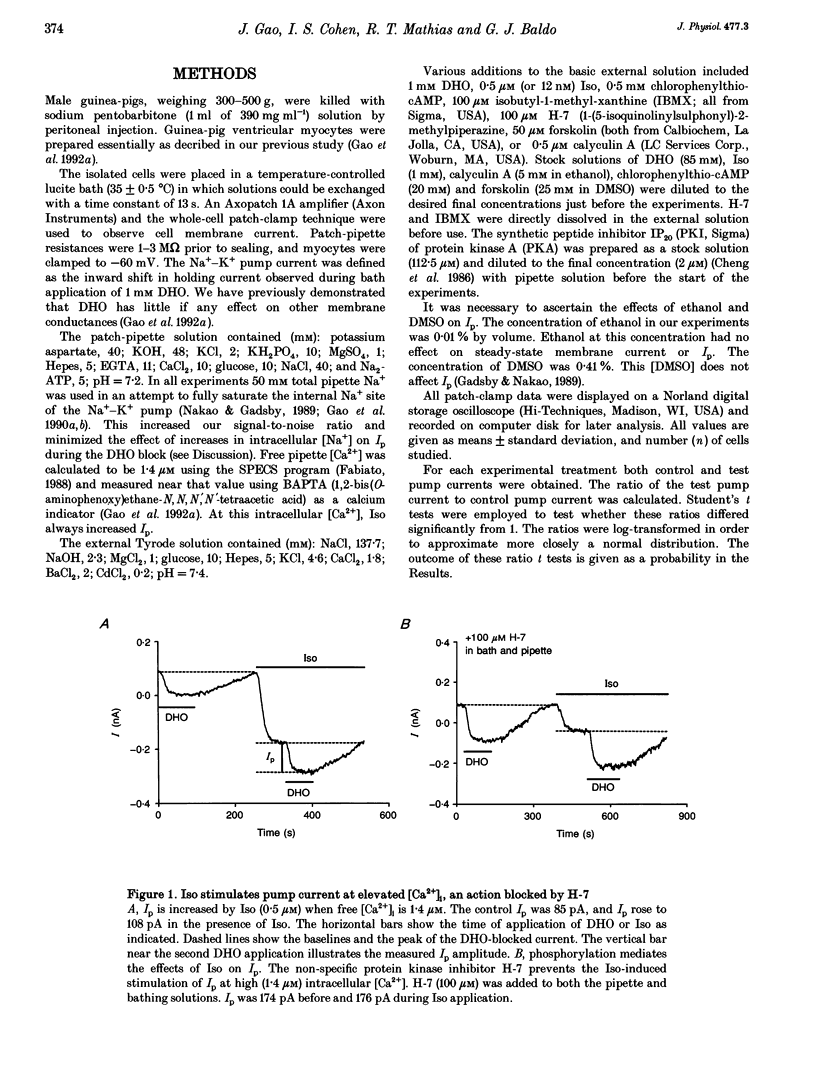
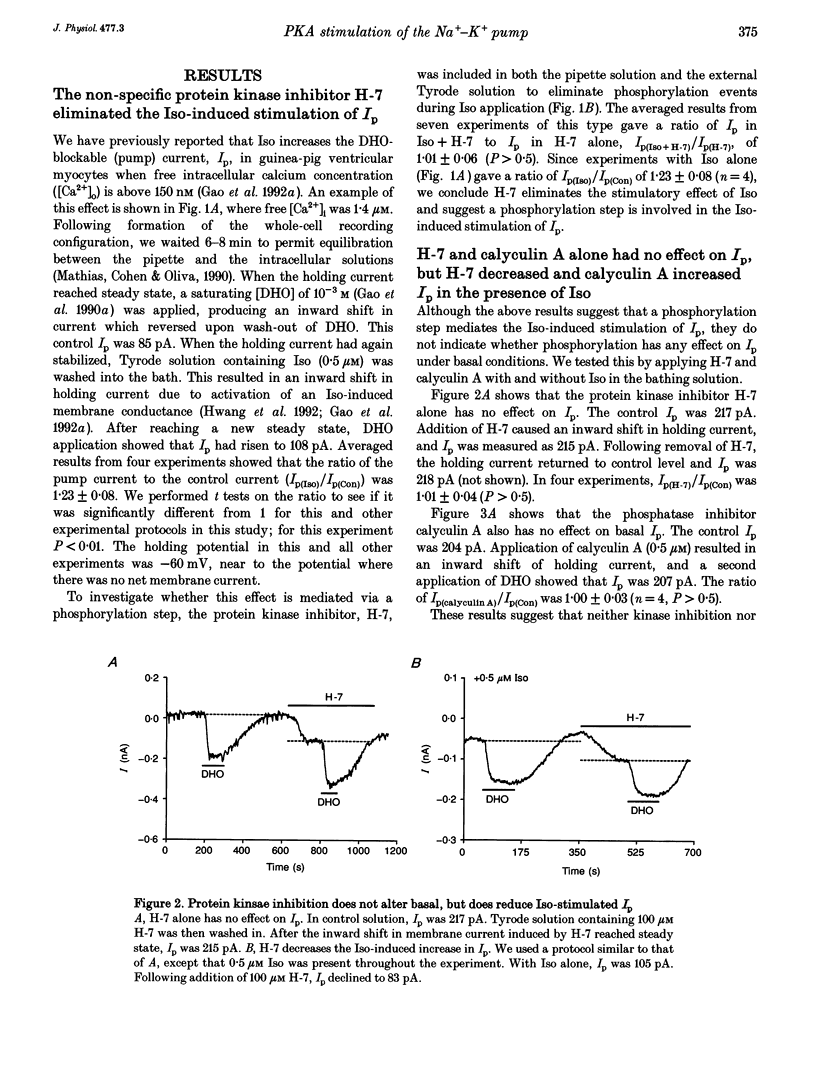
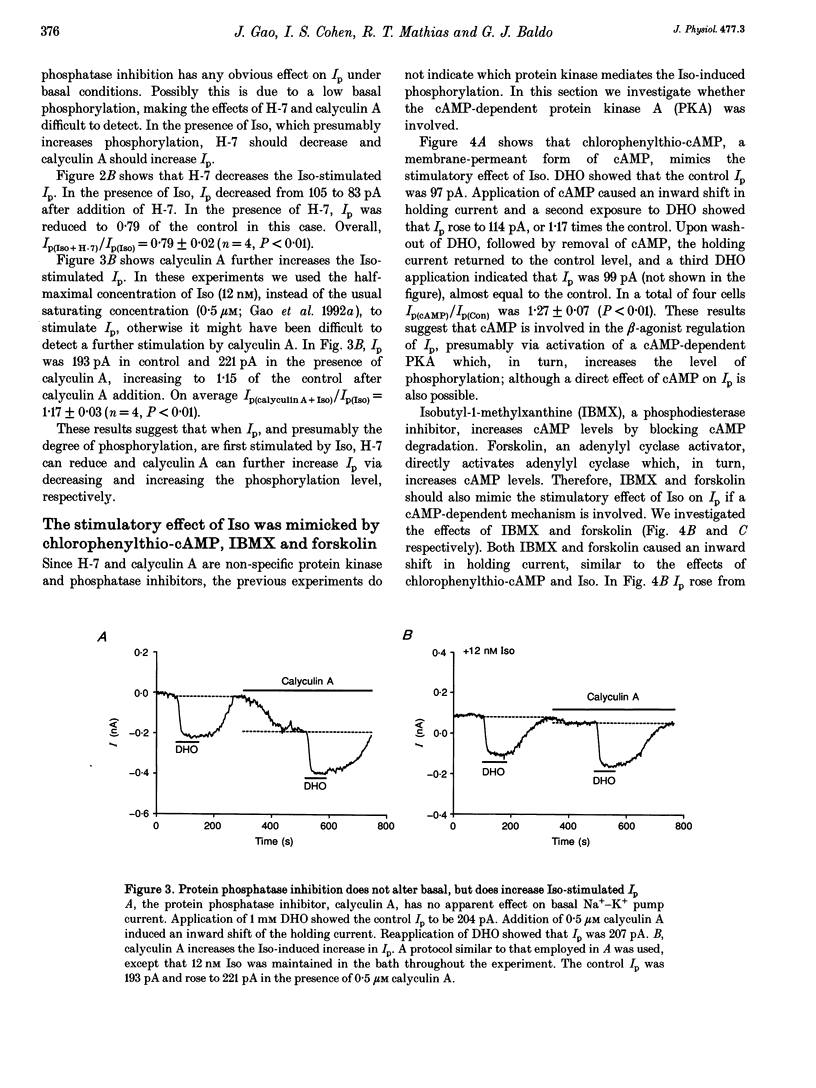
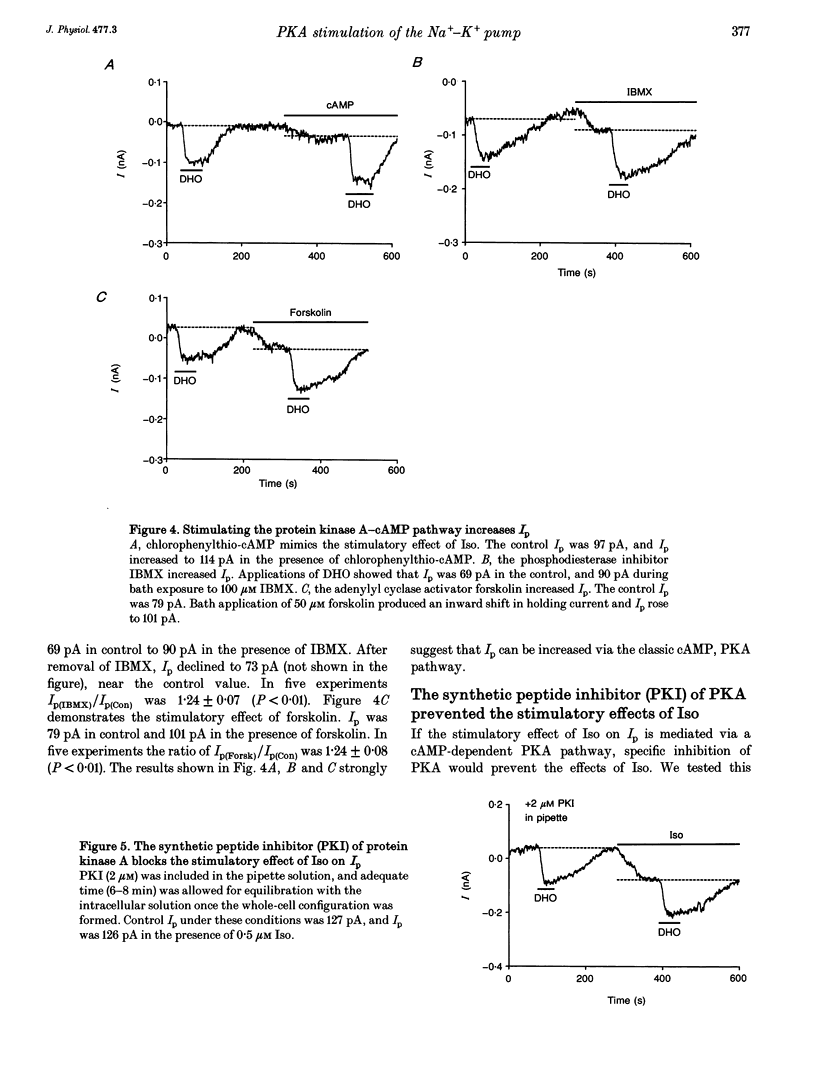



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertorello A. M., Aperia A., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase inhibits the activity of the enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11359–11362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielen F. V., Glitsch H. G., Verdonck F. Changes of the subsarcolemmal Na+ concentration in internally perfused cardiac cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 18;1065(2):269–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Cohen I. S., DiFrancesco D., Rosen M. R., Tromba C. Effects of protein kinase inhibitors on canine Purkinje fibre pacemaker depolarization and the pacemaker current i(f). J Physiol. 1991;440:367–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Smith A. J., Misconi L., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):989–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chibalin A. V., Vasilets L. A., Hennekes H., Pralong D., Geering K. Phosphorylation of Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunits in microsomes and in homogenates of Xenopus oocytes resulting from the stimulation of protein kinase A and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22378–22384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tortora P. Direct activation of cardiac pacemaker channels by intracellular cyclic AMP. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):145–147. doi: 10.1038/351145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Désilets M., Baumgarten C. M. Isoproterenol directly stimulates the Na+-K+ pump in isolated cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 2):H218–H225. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.251.1.H218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Nakao M. Steady-state current-voltage relationship of the Na/K pump in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Sep;94(3):511–537. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J., Mathias R. T., Cohen I. S., Baldo G. J. Isoprenaline, Ca2+ and the Na(+)-K+ pump in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:689–704. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C. Regulation of cardiac ion channels by catecholamines, acetylcholine and second messenger systems. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1988;52(3):165–247. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(88)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang T. C., Horie M., Nairn A. C., Gadsby D. C. Role of GTP-binding proteins in the regulation of mammalian cardiac chloride conductance. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Apr;99(4):465–489. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.4.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingham R. B., Sen A. K. Regulation of rat brain (Na+ +K+)-ATPase activity by cyclic AMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 14;688(2):475–485. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Cohen I. S., Oliva C. Limitations of the whole cell patch clamp technique in the control of intracellular concentrations. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):759–770. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82418-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Gadsby D. C. [Na] and [K] dependence of the Na/K pump current-voltage relationship in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Sep;94(3):539–565. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T., Palfrey C., Fozzard H. A. Modulation of the cardiac transient outward current by catecholamines. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1989 Feb;21 (Suppl 1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(89)90845-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Cohen H. T., Katz A. I. Intracellular signaling in the regulation of renal Na-K-ATPase. I. Role of cyclic AMP and phospholipase A2. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1496–1500. doi: 10.1172/JCI115740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert B., VanDongen A. M., Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M. Beta-adrenergic inhibition of cardiac sodium channels by dual G-protein pathways. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):516–519. doi: 10.1126/science.2547248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tromba C., Cohen I. S. A novel action of isoproterenol to inactivate a cardiac K+ current is not blocked by beta and alpha adrenergic blockers. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):791–795. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82422-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung P., Pai G., Johnson D. G., Punzalan R., Levin S. R. Relationships between adenylate cyclase and Na+, K(+)-ATPase in rat pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3936–3939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilets L. A., Schwarz W. Regulation of endogenous and expressed Na+/K+ pumps in Xenopus oocytes by membrane potential and stimulation of protein kinases. J Membr Biol. 1992 Jan;125(2):119–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00233352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Okabe K., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Heart rate regulation by G proteins acting on the cardiac pacemaker channel. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1163–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.1697697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yingst D. R. Modulation of the Na,K-ATPase by Ca and intracellular proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:291–303. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.001451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


