Abstract
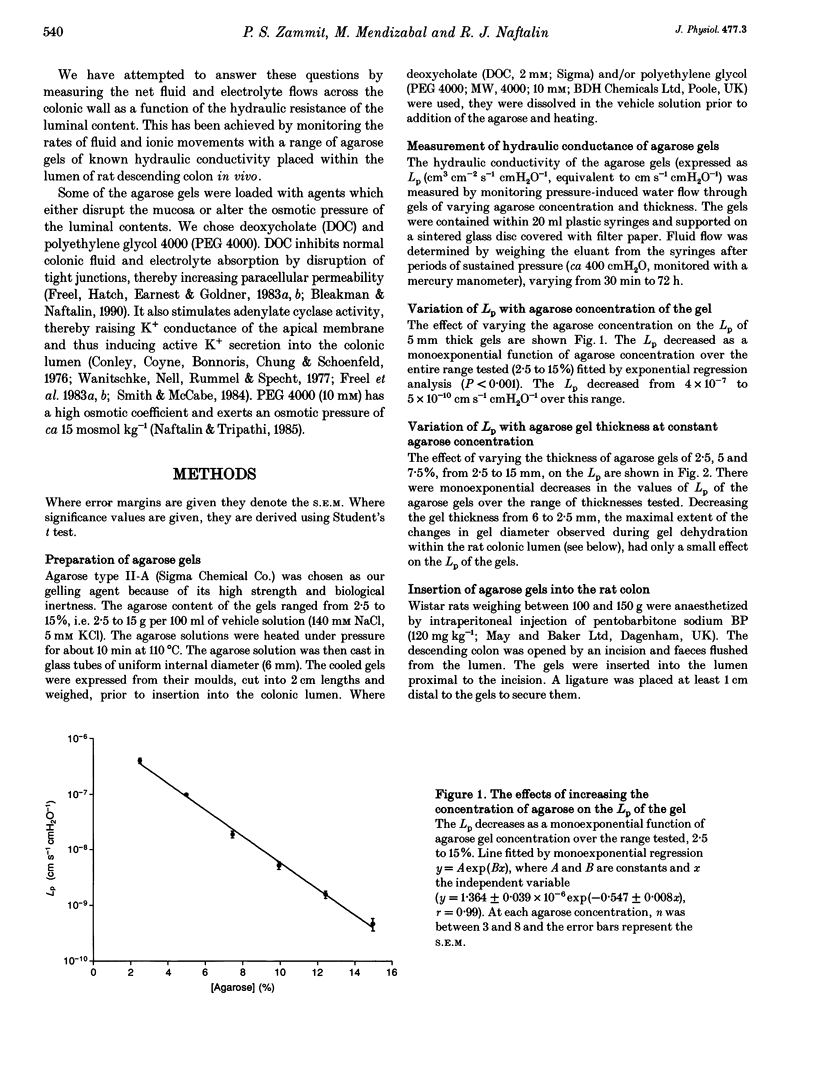
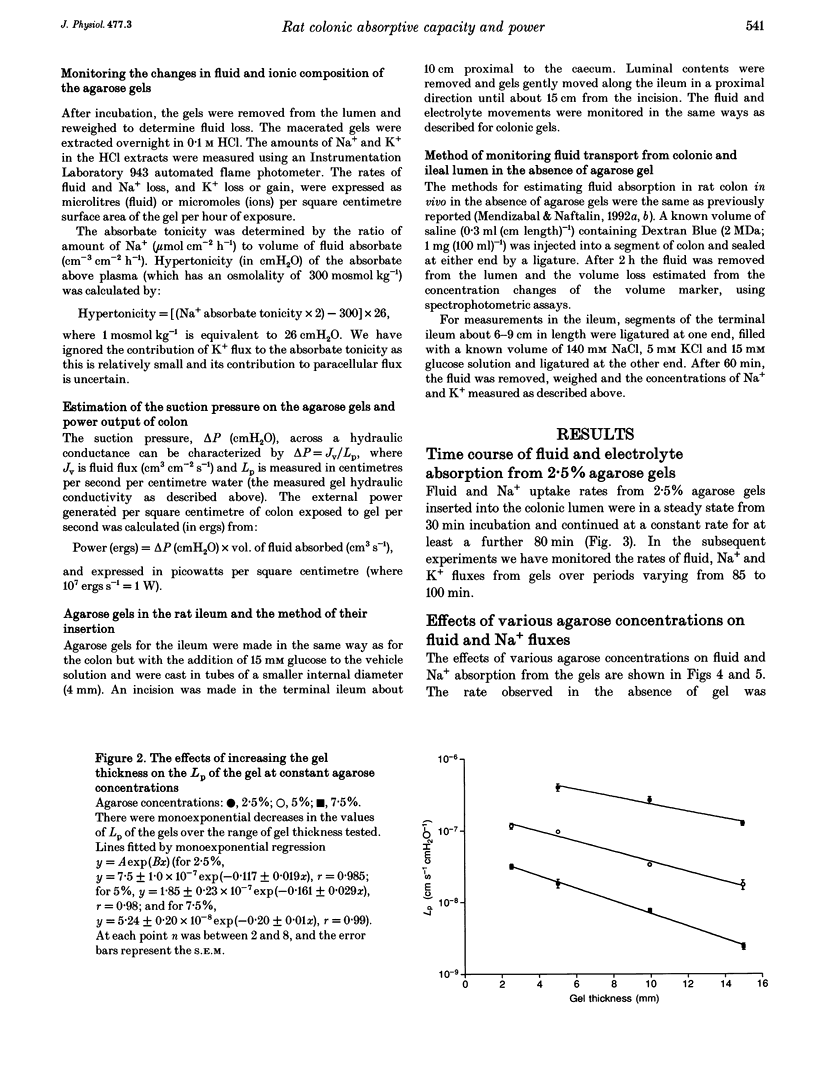
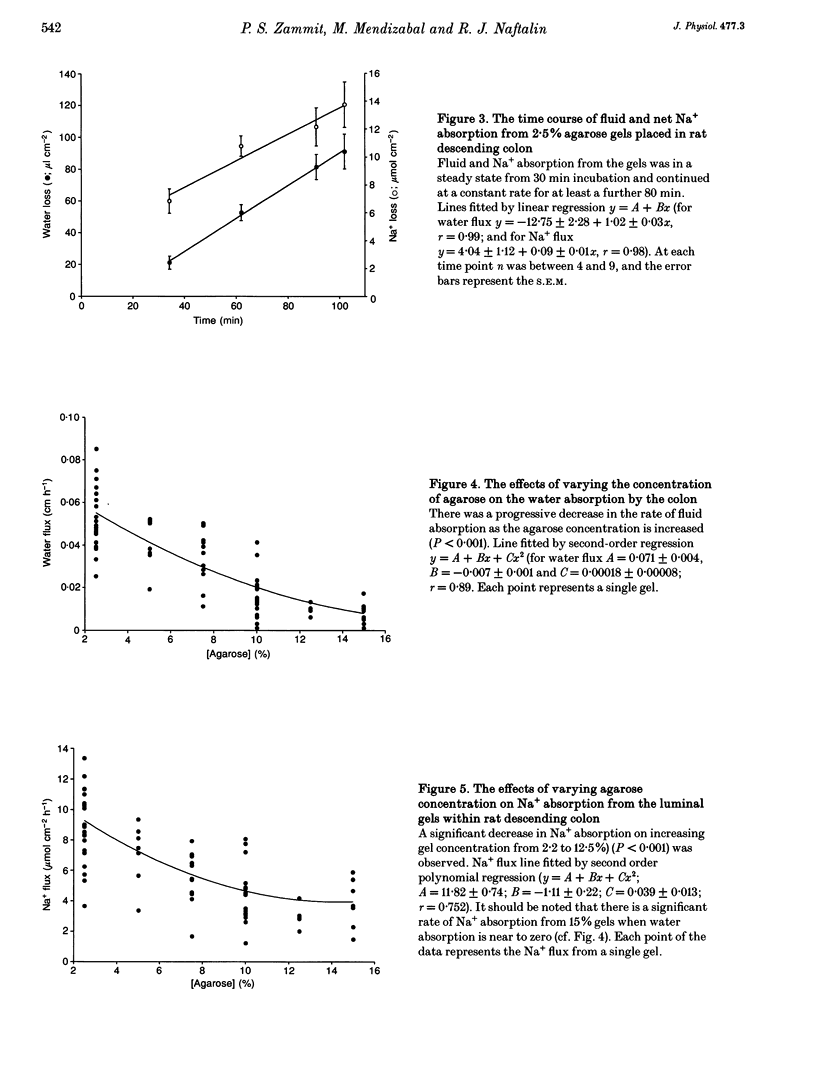
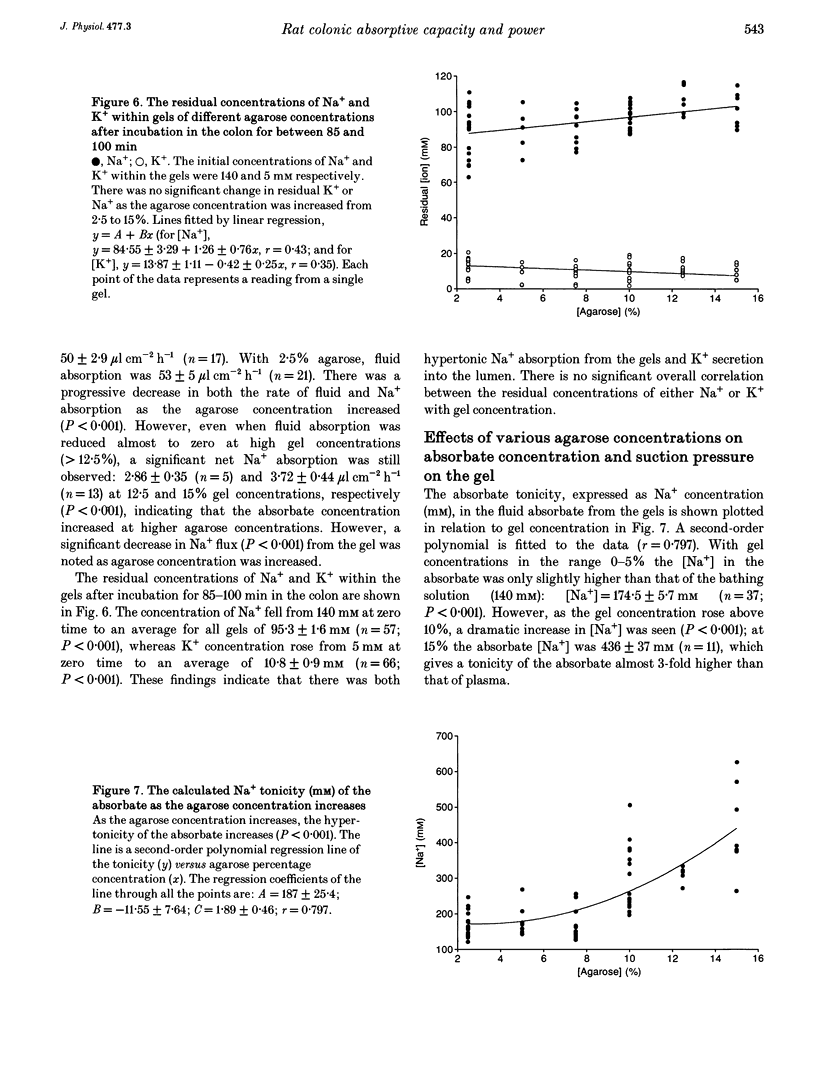
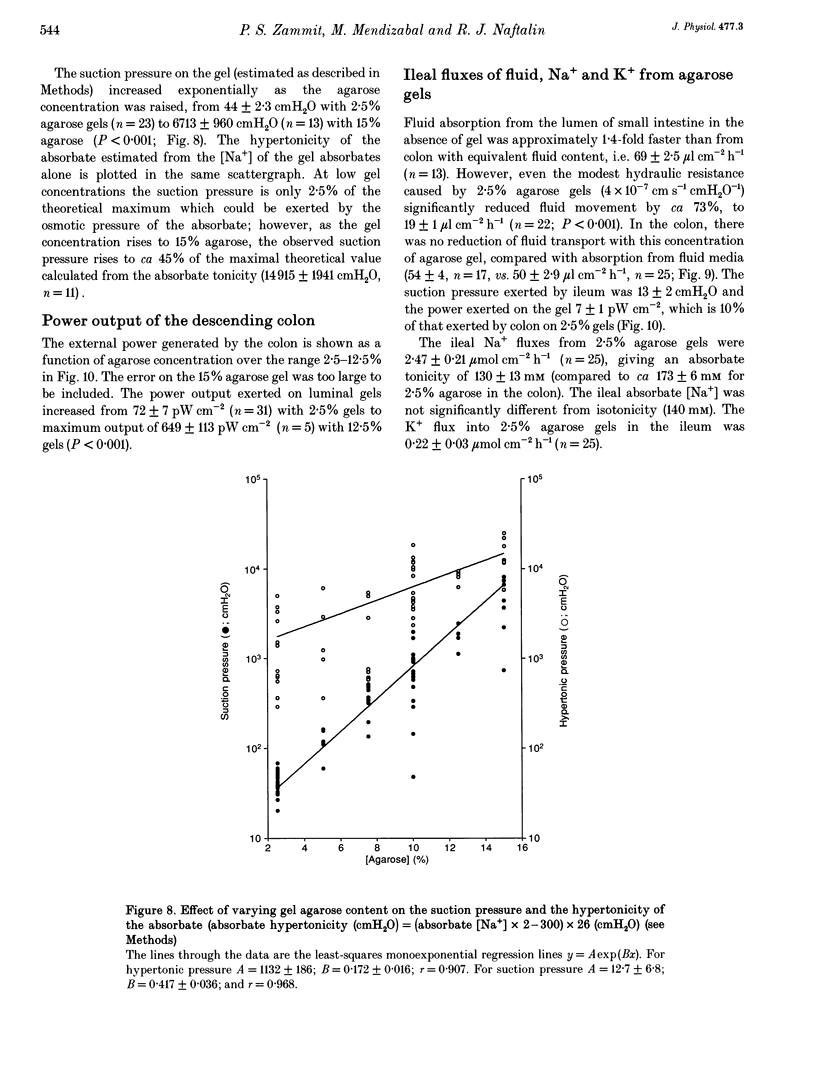
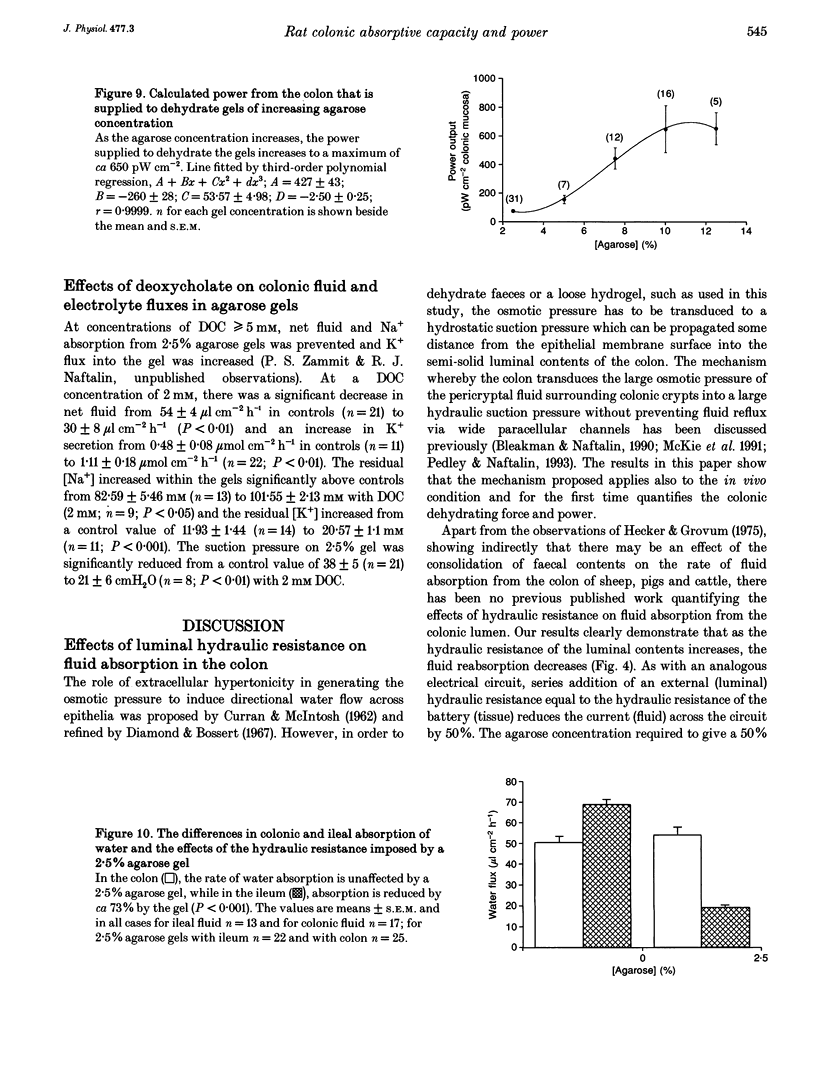
1. A new method of measuring fluid and ionic movements and the dehydrating power of the colon in vivo is described. A range of agarose gel cylinders, with calibrated hydraulic conductivities (Lp), were inserted into the lumen of the descending colon of anaesthetized rats. Fluxes of fluid, Na+ and K+ out of the gels were measured over a period of 60-110 min. 2. Fluid absorption by the colon from 2.5% agarose gels was not slower than from solution without gel. Fluid absorption was inhibited by 66% when the agarose concentration was raised to 10%. In contrast 2.5% agarose gels caused a 73% (P < 0.001) reduction in water flow from rat ileum. 3. Increasing gel concentration to 10% or above caused the absorbate from the gels to become hypertonic (P < 0.001). 4. The measured suction pressure applied by the colonic hypertonic absorbate to the gels increased from 44 +/- 2.3 cmH2O (n = 23) with 2.5% agarose gels to 6713 +/- 960 cmH2O (n = 13) with 15% (P < 0.001). 5. Deoxycholate (2 mM) produced a decrease in fluid and Na+ absorption and reduced the suction pressure and power exerted by the colon.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billich C. O., Levitan R. Effects of sodium concentration and osmolality on water and electrolyte absorption form the intact human colon. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1336–1347. doi: 10.1172/JCI106100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindslev N., Tormey J. M., Wright E. M. The effects of electrical and osmotic gradients on lateral intercellular spaces and membrane conductance in a low resistance epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(4):357–380. doi: 10.1007/BF01869986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleakman D., Naftalin R. J. Hypertonic fluid absorption from rabbit descending colon in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 1):G377–G390. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.3.G377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., MACINTOSH J. R. A model system for biological water transport. Nature. 1962 Jan 27;193:347–348. doi: 10.1038/193347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., SCHWARTZ G. F. Na, Cl, and water transport by rat colon. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:555–571. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley D. R., Coyne M. J., Bonorris G. G., Chung A., Schoenfield L. J. Bile acid stimulation of colonic adenylate cyclase and secretion in the rabbit. Am J Dig Dis. 1976 Jun;21(6):453–458. doi: 10.1007/BF01072128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE H. L., WATTS J. M., DEDOMBAL F. T., GOLIGHER J. C. SERUM ELECTROLYTES AND COLONIC TRANSFER OF WATER AND ELECTROLYTES IN CHRONIC ULCERATIVE COLITIS. Gastroenterology. 1964 Nov;47:525–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Bossert W. H. Standing-gradient osmotic flow. A mechanism for coupling of water and solute transport in epithelia. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Sep;50(8):2061–2083. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.8.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freel R. W., Hatch M., Earnest D. L., Goldner A. M. Dihydroxy bile salt-induced alterations in NaCl transport across the rabbit colon. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):G808–G815. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.6.G808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freel R. W., Hatch M., Earnest D. L., Goldner A. M. Role of tight-junctional pathways in bile salt-induced increases in colonic permeability. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):G816–G823. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.6.G816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J., Shields R. Absorption and secretion of water and electrolytes by the intact human colon in diffuse untreated proctocolitis. Gut. 1970 Jan;11(1):27–33. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker P. C., McKay J. S., Turnberg L. A. Electrolyte transport across colonic mucosa from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1980 Sep;79(3):508–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker J. F., Grovum W. L. Rates of passage of digesta and water absorption along the larg intestines of sheep, cows and pigs. Aust J Biol Sci. 1975 Apr;28(2):161–167. doi: 10.1071/bi9750161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugliak P., Hollander D., Ma T. Y., Tran D., Dadufalza V. D., Katz K. D., Le K. Mechanisms of polyethylene glycol 400 permeability of perfused rat intestine. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1164–1170. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91686-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeschke K., Bentzel C. J., Csáky T. Z. Asymmetry of osmotic flow in frog intestine: functional and structural correlation. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jun;218(6):1723–1731. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.6.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKie A. T., Goecke I. A., Naftalin R. J. Comparison of fluid absorption by bovine and ovine descending colon in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 1):G433–G442. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.3.G433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKie A. T., Powrie W., Naftalin R. J. Mechanical aspects of rabbit fecal dehydration. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 1):G391–G394. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.3.G391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendizabal M. V., Naftalin R. J. Effects of spermine on water absorption, polyethylene glycol 4000 permeability and collagenase activity in rat descending colon in vivo. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992 Oct;83(4):417–423. doi: 10.1042/cs0830417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendizabal M. V., Naftalin R. J. Exposure of rat colonic mucosa to human semen in vivo induces mucosal cytolysis, abolishes fluid absorption and raises paracellular permeability. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992 Mar;82(3):277–282. doi: 10.1042/cs0820277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftalin R. J., Pedley K. C. Video enhanced imaging of the fluorescent Na+ probe SBFI indicates that colonic crypts absorb fluid by generating a hypertonic interstitial fluid. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 29;260(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80100-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftalin R. J., Tripathi S. Passive water flows driven across the isolated rabbit ileum by osmotic, hydrostatic and electrical gradients. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:27–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley K. C., Naftalin R. J. Evidence from fluorescence microscopy and comparative studies that rat, ovine and bovine colonic crypts are absorptive. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:525–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Malawer S. J. Relationship between water and solute transport from isosmotic solutions by rat intestine in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):49–55. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond J. E., Funte L. R., Smith W. L., Price D. A., Haydon P. G. Activation of a peptidergic synapse locally modulates postsynaptic calcium influx. J Exp Biol. 1991 Nov;161:257–271. doi: 10.1242/jeb.161.1.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., McCabe R. D. Mechanism and regulation of transcellular potassium transport by the colon. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 1):G445–G456. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.5.G445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanitschke R., Nell G., Rummel W. Influence of hydrostatic pressure gradients on net transfer of sodium and water across isolated rat colonic mucosa. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;297(2):191–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00499930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


