Abstract
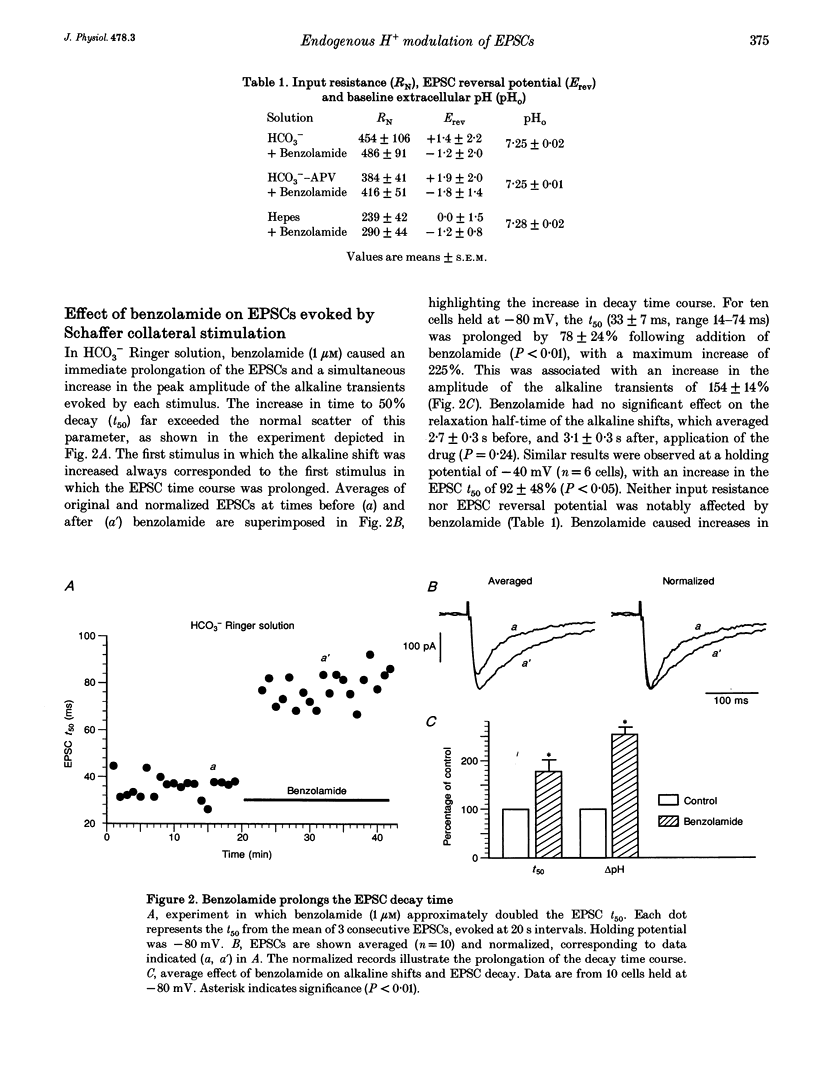
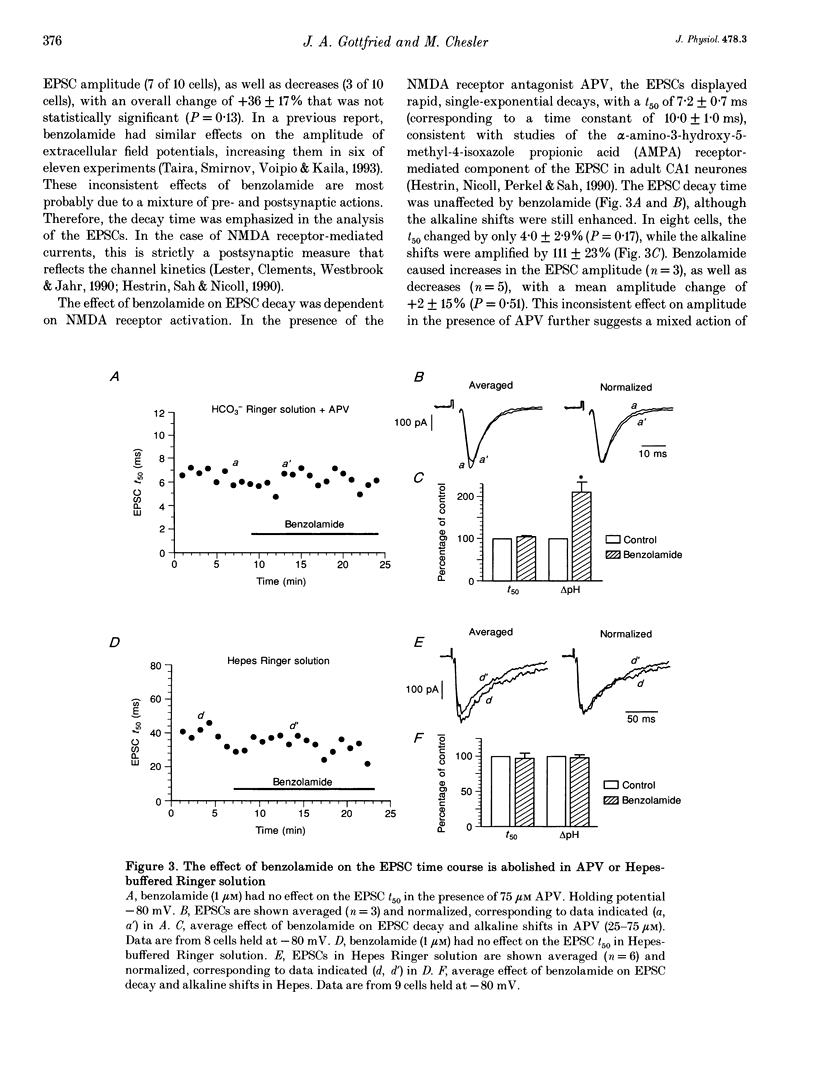
1. The occurrence of extracellular alkaline transients during excitatory synaptic transmission suggests that the NMDA receptor H(+)-modulatory site may have a physiological role. Here we amplify these pH shifts using benzolamide (a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor) and describe concomitant effects on EPSCs in whole-cell clamped CA1 neurones in rat hippocampal slices. 2. In CO2-HCO3(-)-buffered media, benzolamide increased the time to 50% decay (t50) of the EPSCs by 78 +/- 14% (P < 0.01, n = 10). This occurred simultaneously with amplification of the extracellular alkaline shift (154 +/- 14%). 3. In CO2-HCO3(-)-buffered media containing DL-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (APV), the EPSC t50 was unaltered by benzolamide, while the extracellular alkaline shifts were increased (111 +/- 23%, n = 8). 4. In Hepes-buffered media, neither the EPSC t50 nor the extracellular alkaline shift was altered by benzolamide (n = 9). 5. These data demonstrate that NMDA receptor activity is dependent on the buffering kinetics of the brain extracellular space. The results suggest that endogenous pH shifts can modulate NMDA receptor function in a physiologically relevant time frame.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammann D., Lanter F., Steiner R. A., Schulthess P., Shijo Y., Simon W. Neutral carrier based hydrogen ion selective microelectrode for extra- and intracellular studies. Anal Chem. 1981 Dec;53(14):2267–2269. doi: 10.1021/ac00237a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton M. G., Lo Turco J. J., Kriegstein A. R. Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Methods. 1989 Dec;30(3):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. C., Chesler M. Extracellular alkaline shifts in rat hippocampal slice are mediated by NMDA and non-NMDA receptors. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jul;68(1):342–344. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.1.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. C., Chesler M. Modulation of extracellular pH by glutamate and GABA in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jan;67(1):29–36. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. C., Chesler M. pH transients evoked by excitatory synaptic transmission are increased by inhibition of extracellular carbonic anhydrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7786–7790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesler M., Chan C. Y. Stimulus-induced extracellular pH transients in the in vitro turtle cerebellum. Neuroscience. 1988 Dec;27(3):941–948. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesler M., Kaila K. Modulation of pH by neuronal activity. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Oct;15(10):396–402. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90191-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesler M. The regulation and modulation of pH in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;34(5):401–427. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90034-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S., Nicoll R. A., Perkel D. J., Sah P. Analysis of excitatory synaptic action in pyramidal cells using whole-cell recording from rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:203–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S., Sah P., Nicoll R. A. Mechanisms generating the time course of dual component excitatory synaptic currents recorded in hippocampal slices. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaila K., Paalasmaa P., Taira T., Voipio J. pH transients due to monosynaptic activation of GABAA receptors in rat hippocampal slices. Neuroreport. 1992 Jan;3(1):105–108. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199201000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. A., Clements J. D., Westbrook G. L., Jahr C. E. Channel kinetics determine the time course of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):565–567. doi: 10.1038/346565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAVIS D. M., WILEY C., NECHAY B. R., MAREN T. H. SELECTIVE RENAL CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITION WITHOUT RESPIRATORY EFFECT: PHARMACOLOGY OF 2-BENZENESULFONAMIDO-1,3, 4-THIADIAZOLE-5-SULFONAMIDE (CL 11,366). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Mar;143:383–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira T., Smirnov S., Voipio J., Kaila K. Intrinsic proton modulation of excitatory transmission in rat hippocampal slices. Neuroreport. 1993 Jan;4(1):93–96. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199301000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Dichter M., Morad M. Modulation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate channel by extracellular H+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6445–6449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynelis S. F., Cull-Candy S. G. Pharmacological properties and H+ sensitivity of excitatory amino acid receptor channels in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:727–763. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynelis S. F., Cull-Candy S. G. Proton inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):347–350. doi: 10.1038/345347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voipio J., Kaila K. Interstitial PCO2 and pH in rat hippocampal slices measured by means of a novel fast CO2/H(+)-sensitive microelectrode based on a PVC-gelled membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1993 May;423(3-4):193–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00374394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklický L., Jr, Vlachová V., Krůsek J. The effect of external pH changes on responses to excitatory amino acids in mouse hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:497–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


