Abstract
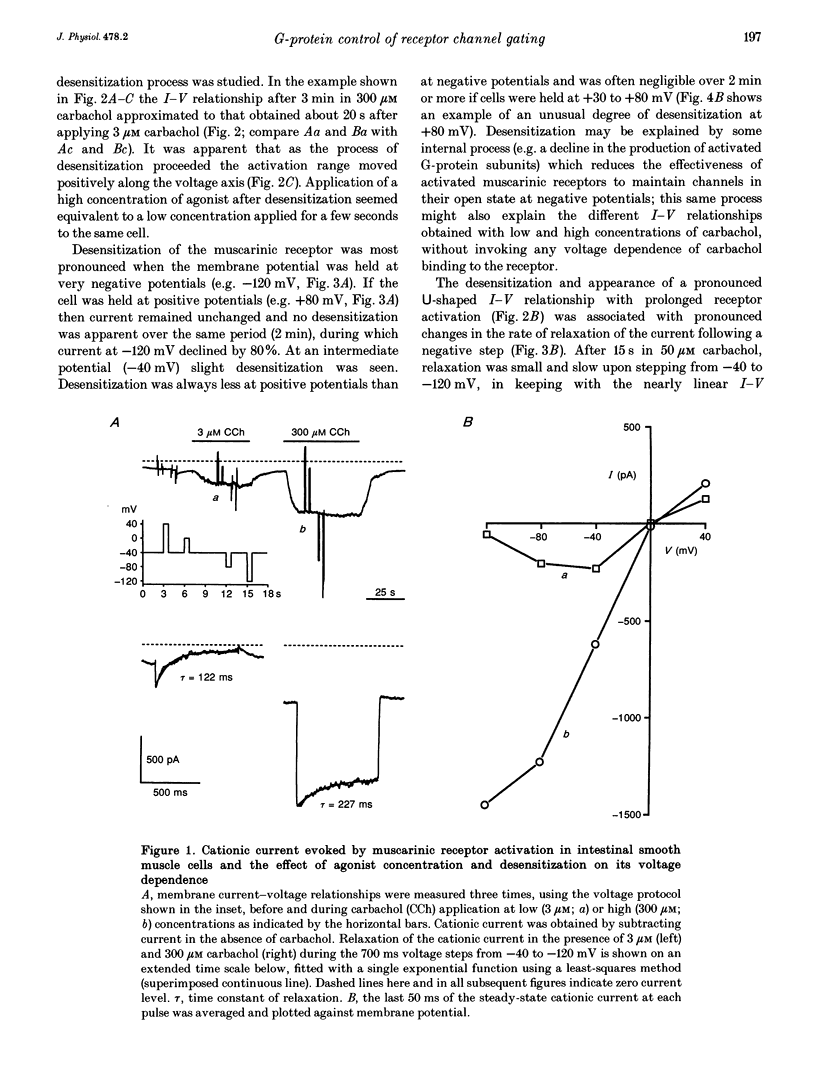
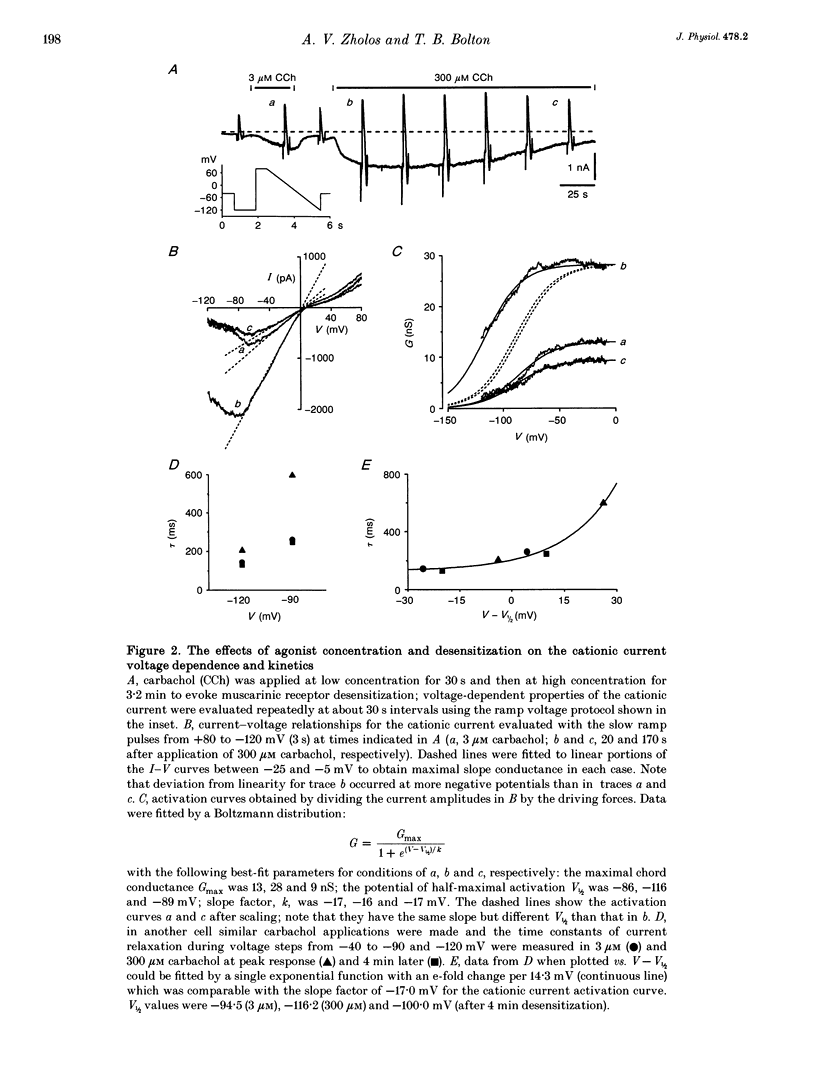
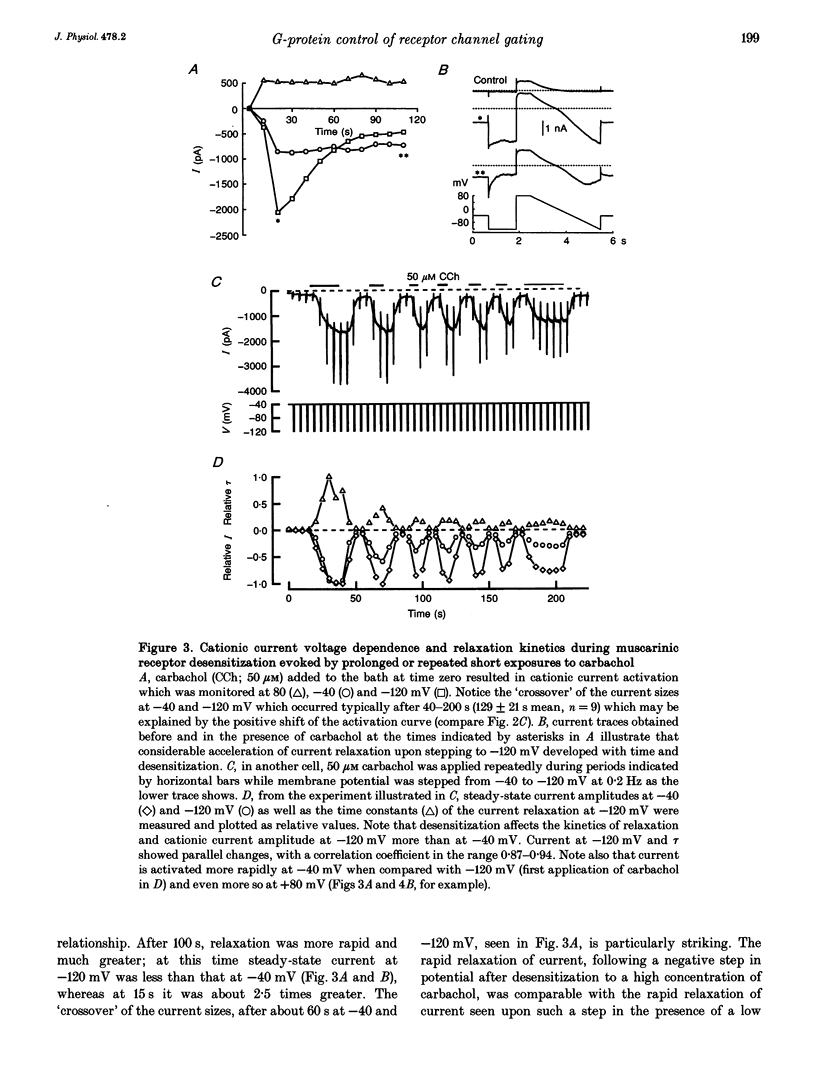
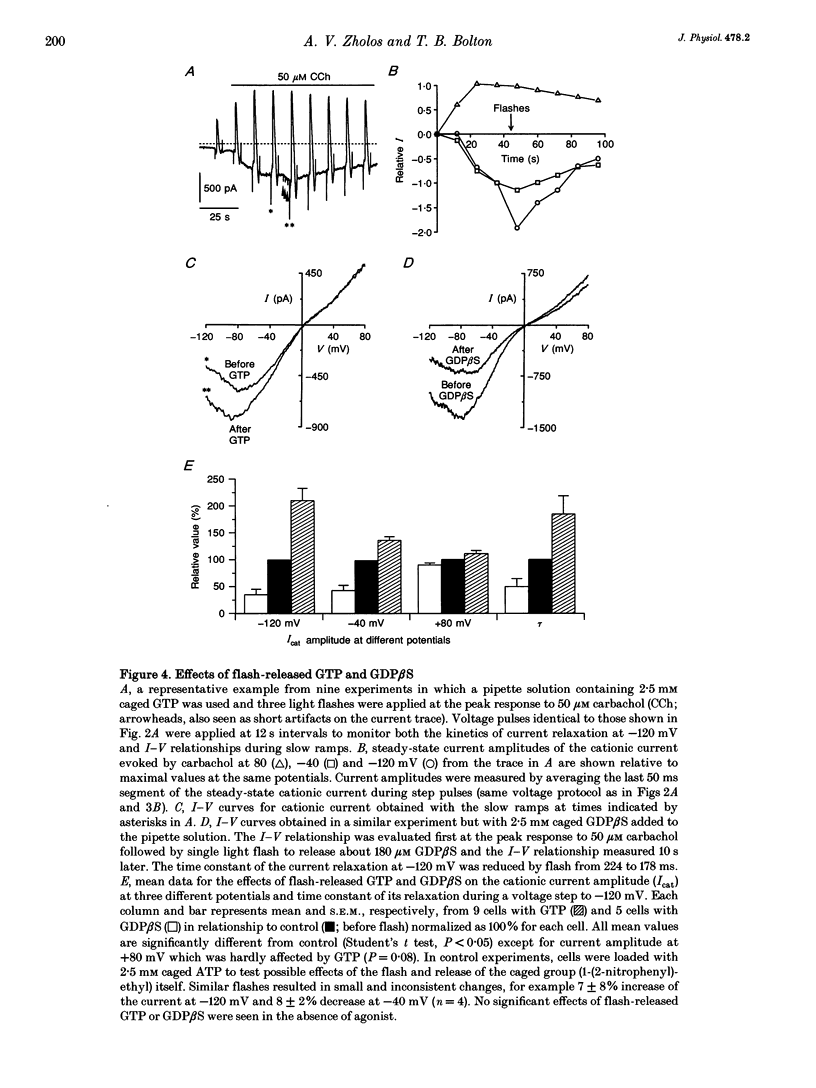
1. Voltage-dependent properties of muscarinic receptor cationic current activated by carbachol in single smooth muscle cells have been studied using patch-clamp recording techniques. Cells were obtained by enzymic digestion from the longitudinal muscle layer of guinea-pig small intestine. 2. The inward cationic current showed a pronounced U-shaped current-voltage relationship (inward current negative). The relationship of cationic conductance to voltage could be described by a Boltzman distribution which was shifted 36 mV in the negative direction on the voltage axis by increasing fractional receptor occupancy (by increasing agonist concentration from 3 to 300 microM), and in the positive direction by desensitization during prolonged application of agonist. Cationic channels opened by low and high concentrations of carbachol at the same potential do not have identical properties. 3. Release of GTP within the cell, by flash photolysis of an inert caged precursor, had the same effect on the current-voltage relationship as increasing receptor occupancy by the agonist. Release of GDP beta S by flash photolysis had the opposite effect. 4. These various results could be explained if cationic channel opening upon receptor activation required binding of at least one alpha-GTP subunit, but the position of the activation curve on the voltage axis depended critically on the concentration of activated G-protein alpha-subunits in the cell.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J. Acetylcholine activates an inward current in single mammalian smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):345–347. doi: 10.1038/316345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. On the latency and form of the membrane responses of smooth muscle to the iontophoretic application of acetylcholine or carbachol. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Aug 27;194(1114):99–119. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M. Membrane-delimited cell signaling complexes: direct ion channel regulation by G proteins. J Membr Biol. 1993 Jan;131(2):93–104. doi: 10.1007/BF02791318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Mangoni M. Modulation of single hyperpolarization-activated channels (i(f)) by cAMP in the rabbit sino-atrial node. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 1;474(3):473–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tortora P. Direct activation of cardiac pacemaker channels by intracellular cyclic AMP. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):145–147. doi: 10.1038/351145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Zhou W., Jones S. W. LHRH and GTP-gamma-S modify calcium current activation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90035-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi F., Lux H. D. Voltage-dependent GABA-induced modulation of calcium currents in chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 23;105(1-2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Acetylcholine activates nonselective cation channels in guinea pig ileum through a G protein. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1173–C1178. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Effect of membrane potential on acetylcholine-induced inward current in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:57–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Aosaki T. Modulation of Ca-channel current by an adenosine analog mediated by a GTP-binding protein in chick sensory neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00580956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Kawai M., Takewaki T., Ohashi H. GTP-binding protein involvement in membrane currents evoked by carbachol and histamine in guinea-pig ileal muscle. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:105–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez H. S., Brown A. M. Correlation between G protein activation and reblocking kinetics of Ca2+ channel currents in rat sensory neurons. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):1061–1068. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Tan Y. P. The initiation of calcium release following muscarinic stimulation in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:665–687. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Magleby K. L. Accounting for the Ca(2+)-dependent kinetics of single large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:739–777. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollo A., Taglialatela M., Carbone E. Voltage-dependent inhibition and facilitation of Ca channel activation by GTP-gamma-S and Ca-agonists in adult rat sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Feb 25;123(2):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90931-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zang W. J., Yu X. J., Honjo H., Kirby M. S., Boyett M. R. On the role of G protein activation and phosphorylation in desensitization to acetylcholine in guinea-pig atrial cells. J Physiol. 1993 May;464:649–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


