Abstract
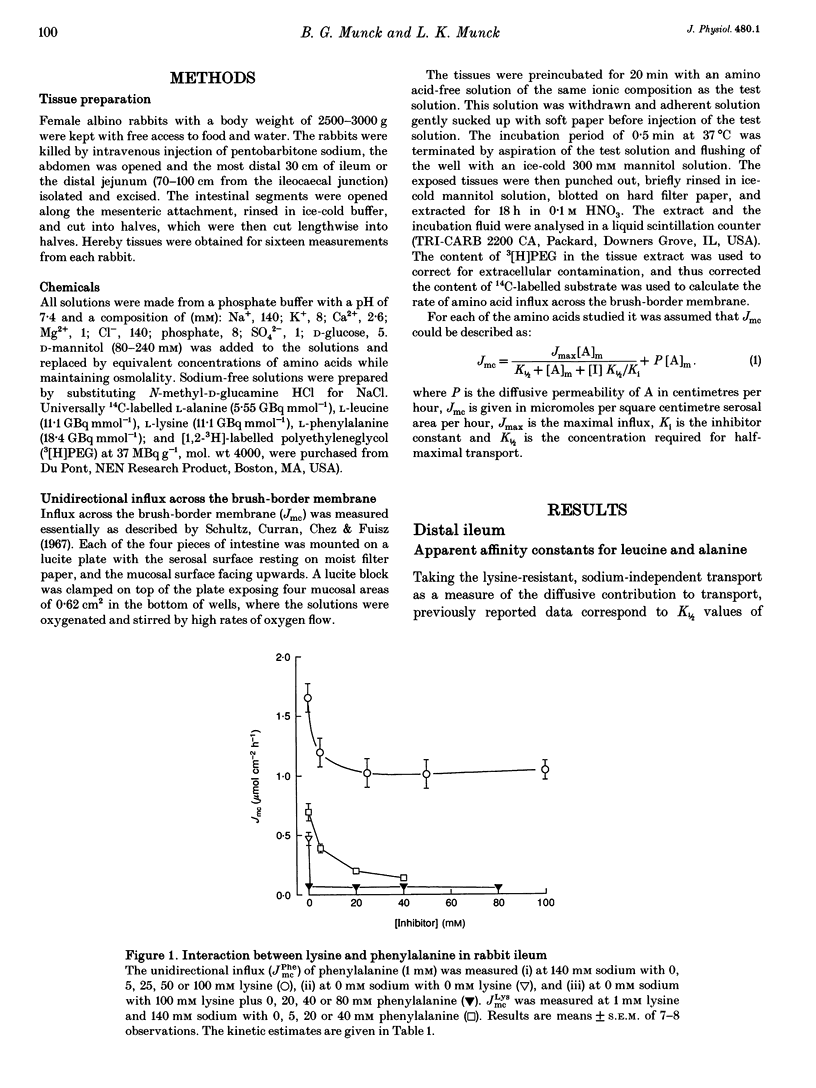
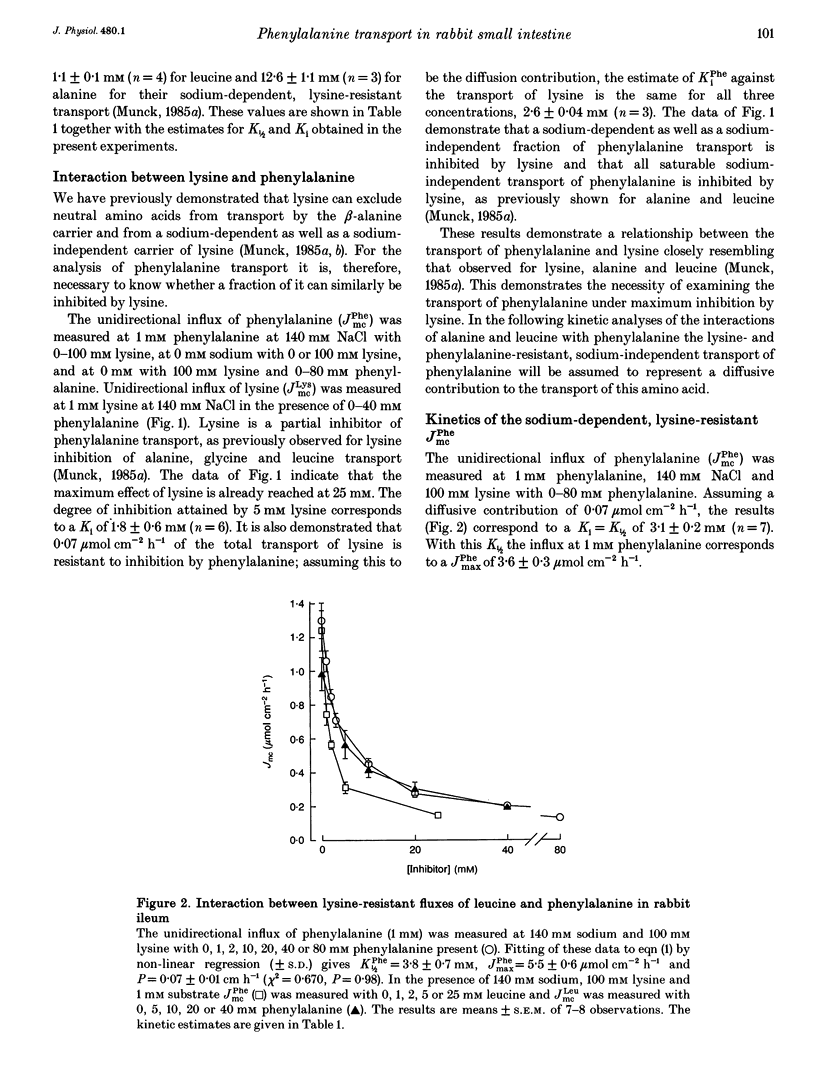
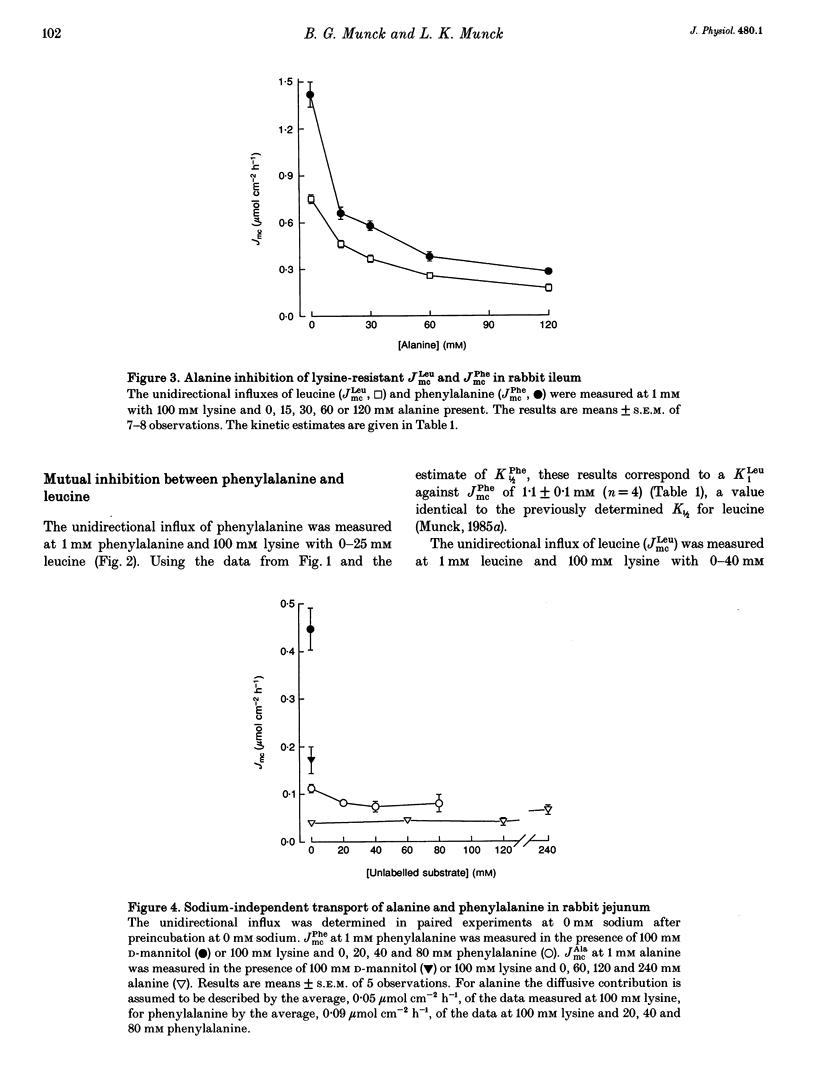
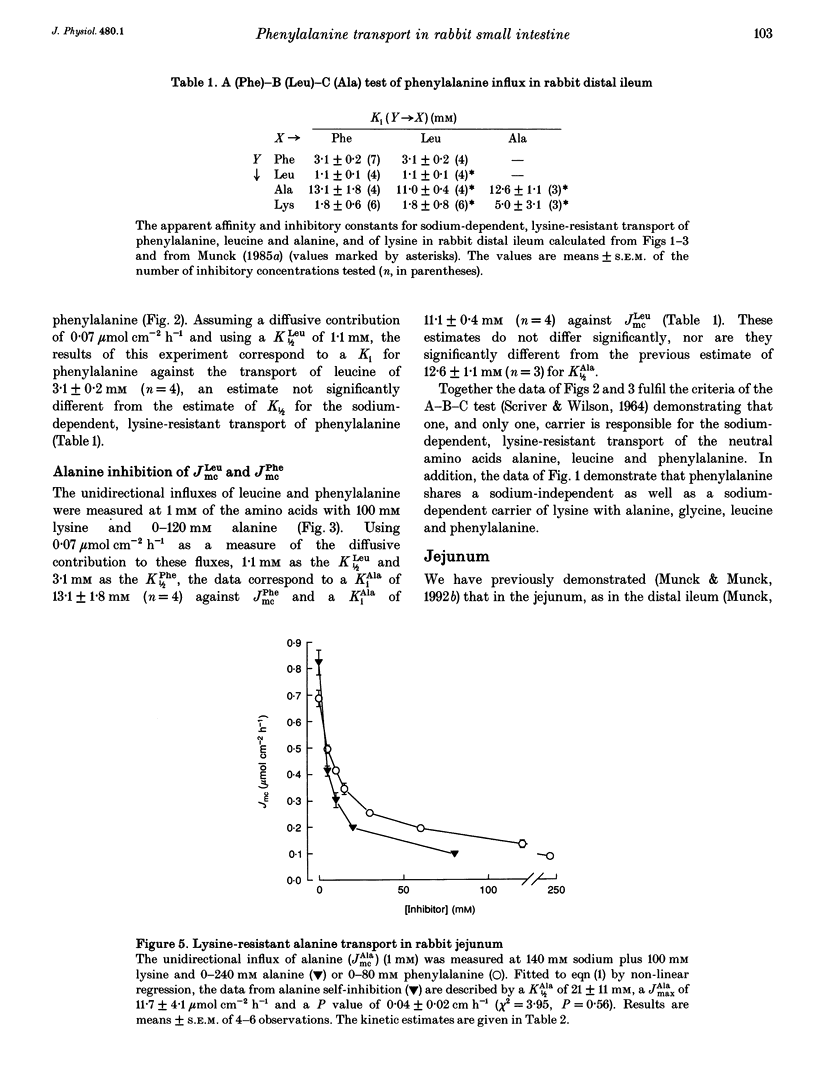
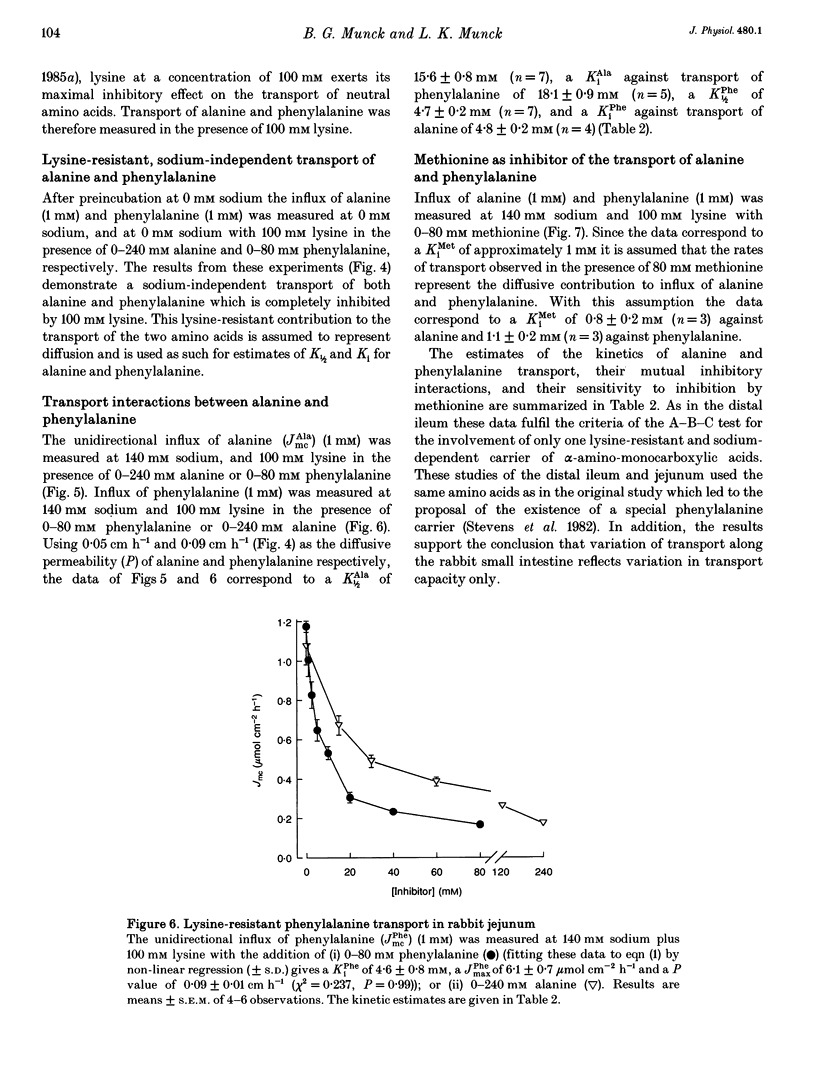
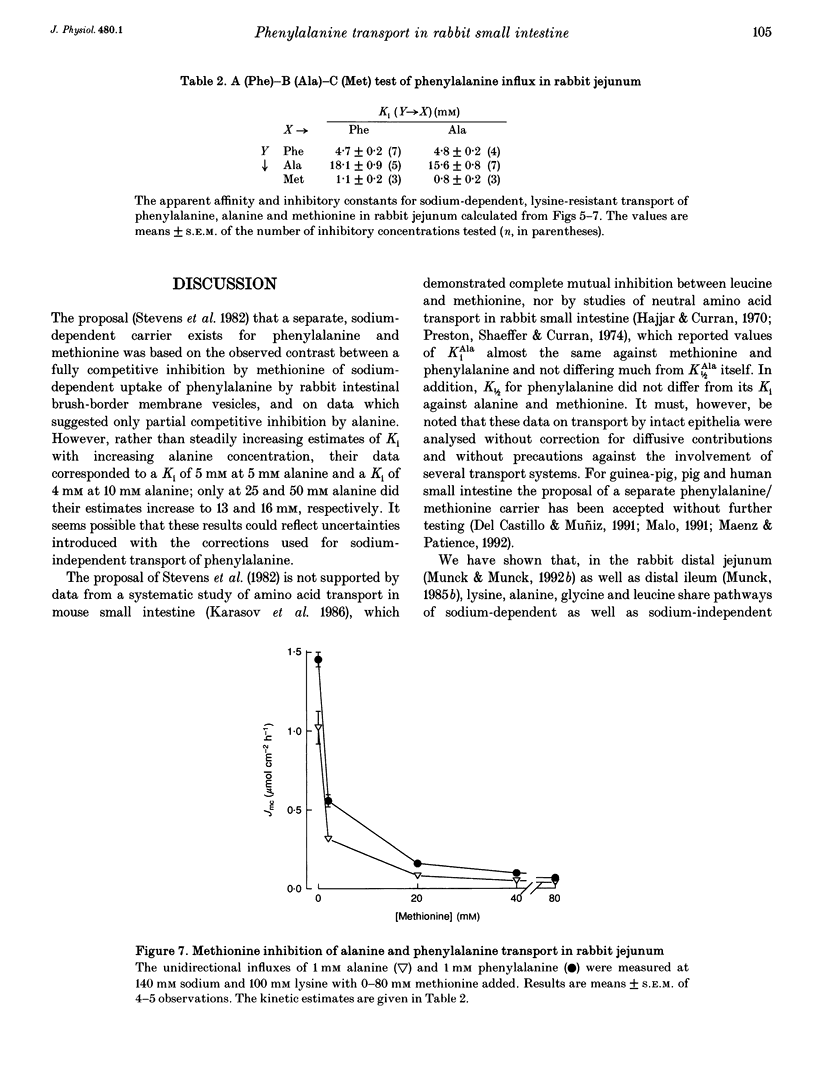
1. The proposal that rabbit small intestine possesses a separate, sodium-dependent carrier of phenylalanine has been examined by measurements of the unidirectional influx of amino acids across the brush-border membrane of the intact epithelium of the rabbit small intestine. 2. We demonstrate that, like alanine, glycine and leucine, phenylalanine shares sodium-dependent as well as sodium-independent transport with lysine. 3. Using the distal ileum we applied the A (phenylalanine)-B (leucine)-C (alanine) test on the sodium-dependent, lysine-resistant transport of phenylalanine. For phenylalanine, K1/2 (concentration required for half-maximal transport) was 3.1 +/- 0.2 mM (n = 7) and Ki (inhibitor constant) against leucine transport was 3.1 +/- 0.2 mM (n = 4). For leucine, K1/2 was 1.1 +/- 0.1 mM (n = 4) and Ki against transport of phenylalanine was 1.1 +/- 0.1 mM (n = 4). For alanine, K1/2 was 12.6 +/- 1.1 mM (n = 3), Ki against phenylalanine was 13.1 +/- 1.8 mM (n = 4) and Ki against leucine was 11.0 +/- 0.4 mM (n = 4). 4. Using the jejunum we applied the A (phenylalanine)-B (alanine)-C (methionine) test on the lysine-resistant, sodium-dependent transport of phenylalanine. For phenylalanine, K1/2 was 4.7 +/- 0.2 mM (n = 7) and Ki against alanine was 4.8 +/- 0.2 mM (n = 4). For alanine, K1/2 was 15.6 +/- 0.8 mM (n = 7) and Ki against phenylalanine was 18.1 +/- 0.9 mM (n = 5).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker G. A., Ellory J. C. The identification of neutral amino acid transport systems. Exp Physiol. 1990 Jan;75(1):3–26. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1990.sp003382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo J. R., Muñiz R. Neutral amino acid transport by isolated small intestinal cells from guinea pigs. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):G1030–G1036. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.6.G1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar J. J., Curran P. F. Characteristics of the amino acid transport system in the mucosal border of rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Dec;56(6):673–691. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.6.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasov W., Solberg D., Carter S., Hughes M., Phan D., Zollman F., Diamond J. Uptake pathways for amino acids in mouse intestine. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):G501–G508. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.4.G501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maenz D. D., Patience J. F. L-threonine transport in pig jejunal brush border membrane vesicles. Functional characterization of the unique system B in the intestinal epithelium. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22079–22086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo C. Multiple pathways for amino acid transport in brush border membrane vesicles isolated from the human fetal small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jun;100(6):1644–1652. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G. Lysine transport in the guinea-pig small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 29;770(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G. Transport of imino acids and non-alpha-amino acids across the brush-border membrane of the rabbit ileum. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(1-2):15–24. doi: 10.1007/BF01868734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G. Transport of neutral and cationic amino acids across the brush-border membrane of the rabbit ileum. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(1-2):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF01868733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck L. K., Munck B. G. Chloride-dependence of amino acid transport in rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 10;1027(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90041-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck L. K., Munck B. G. Distinction between chloride-dependent transport systems for taurine and beta-alanine in rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):G609–G615. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.4.G609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck L. K., Munck B. G. Variation in amino acid transport along the rabbit small intestine. Mutual jejunal carriers of leucine and lysine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 22;1116(2):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(92)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston R. L., Schaeffer J. F., Curran P. F. Structure-affinity relationships of substrates for the neutral amino acid transport system in rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Oct;64(4):443–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.4.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCRIVER C. R., WILSON O. H. POSSIBLE LOCATIONS FOR A COMMON GENE PRODUCT IN MEMBRANE TRANSPORT OF IMINO-ACIDS AND GLYCINE. Nature. 1964 Apr 4;202:92–93. doi: 10.1038/202092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F., Chez R. A., Fuisz R. E. Alanine and sodium fluxes across mucosal border of rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1241–1260. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. R., Ross H. J., Wright E. M. Multiple transport pathways for neutral amino acids in rabbit jejunal brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1982;66(3):213–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01868496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle L. J. Amino acid transport in developing animal oocytes and early conceptuses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):173–208. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle L. J., Campione A. L., Gorman J. M. Na+-independent transport of basic and zwitterionic amino acids in mouse blastocysts by a shared system and by processes which distinguish between these substrates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3150–3163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle L. J., Christensen H. N., Campione A. L. Na+-dependent transport of basic, zwitterionic, and bicyclic amino acids by a broad-scope system in mouse blastocysts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12118–12123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


