Abstract
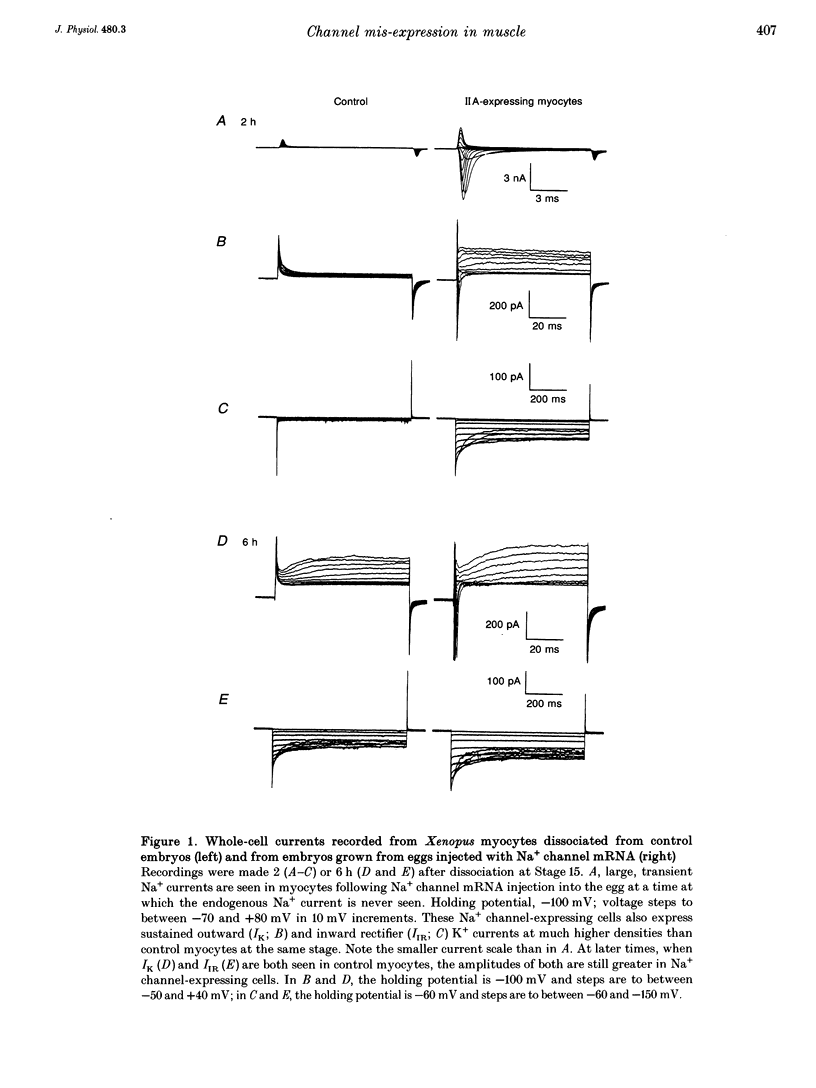
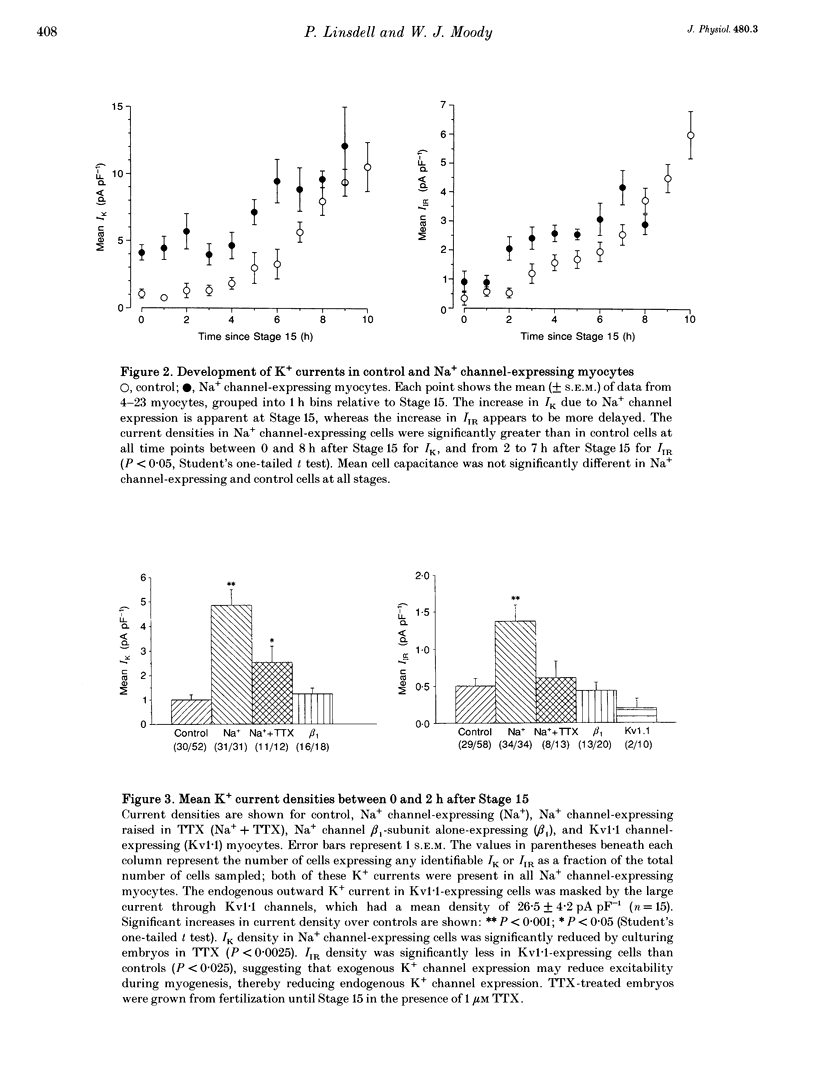
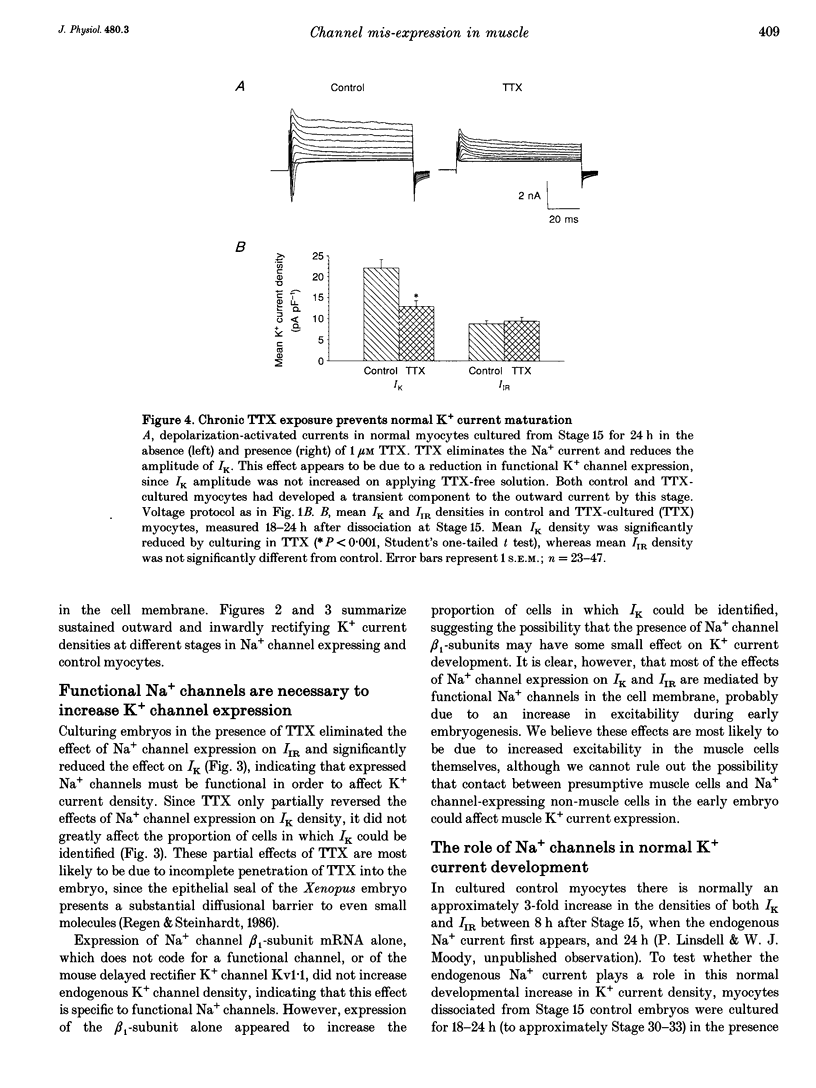
1. The normal developmental pattern of voltage-gated ion channel expression in embryonic skeletal muscle cells of the frog Xenopus laevis was disrupted by introduction of cloned rat brain Na+ channels. 2. Following injection of channel mRNA into fertilized eggs, large Na+ currents were observed in muscle cells at the earliest developmental stage at which they could be uniquely identified. Muscle cells normally have no voltage-gated currents at this stage. 3. Muscle cells expressing exogenous Na+ channels showed increased expression of at least two classes of endogenous K+ currents. 4. This increase in K+ current expression was inhibited by the Na+ channel blocker tetrodotoxin, suggesting that increased electrical activity caused by Na+ channel mis-expression triggers a compensatory increase in K+ channel expression. 5. Block of endogenous Na+ channels in later control myocytes retards K+ current development, indicating that a similar compensatory mechanism to that triggered by Na+ channel mis-expression operates to balance Na+ and K+ current densities during normal muscle development.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Marshall J., Dunn J. M., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunit with novel gating properties. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):449–461. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadie K. S., Bate M. Development of larval muscle properties in the embryonic myotubes of Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurosci. 1993 Jan;13(1):167–180. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-01-00167.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama M., Kakei M., Sato R., Shibasaki T., Matsuda H., Irisawa H. Intracellular Na+ activates a K+ channel in mammalian cardiac cells. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):354–356. doi: 10.1038/309354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody W. J., Bosma M. M. Hormone-induced loss of surface membrane during maturation of starfish oocytes: differential effects on potassium and calcium channels. Dev Biol. 1985 Dec;112(2):396–404. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90412-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd D. K., Ribera A. B., Spitzer N. C. Development of voltage-dependent calcium, sodium, and potassium currents in Xenopus spinal neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Mar;8(3):792–805. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-03-00792.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. J., Catterall W. A. Electrical activity and cytosolic calcium regulate levels of tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in cultured rat muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Moody W. J. Developmental sequence of expression of voltage-dependent currents in embryonic Xenopus laevis myocytes. Dev Biol. 1992 Nov;154(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90043-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of a probable potassium channel gene from mouse brain. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):837–839. doi: 10.1038/332837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Scheuer T., Maechler L., Catterall W. A. Efficient expression of rat brain type IIA Na+ channel alpha subunits in a somatic cell line. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90108-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


