Abstract
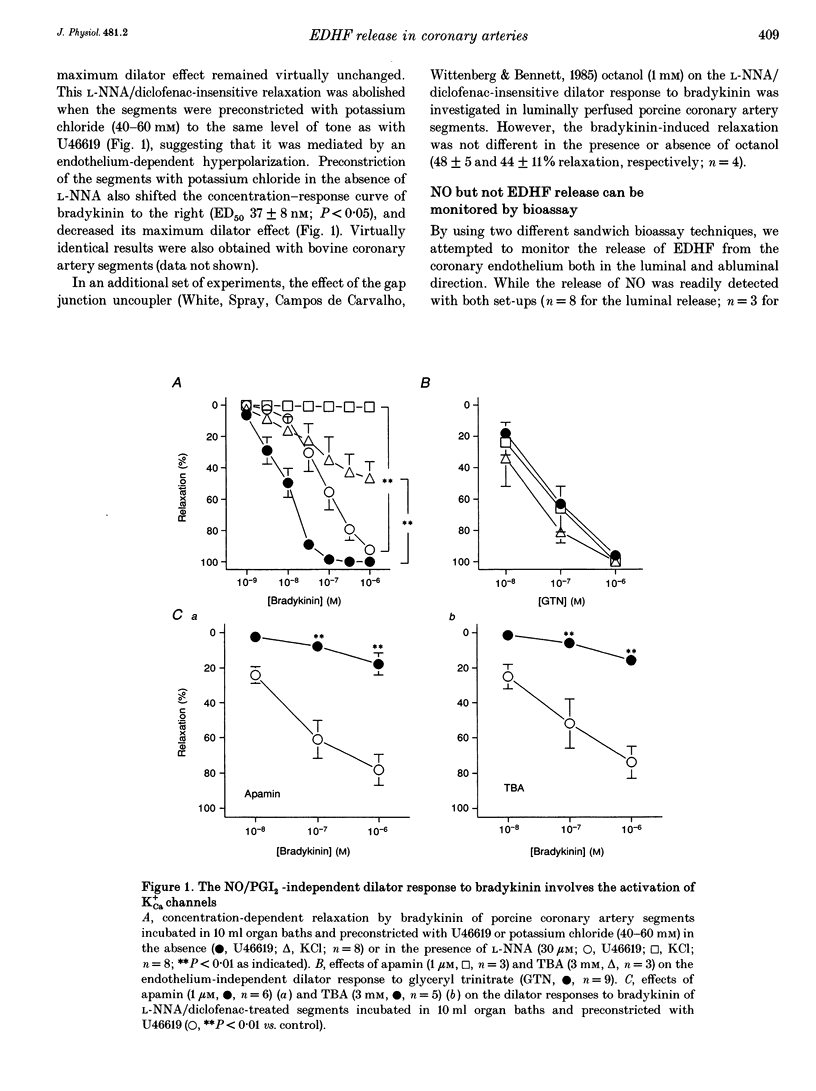
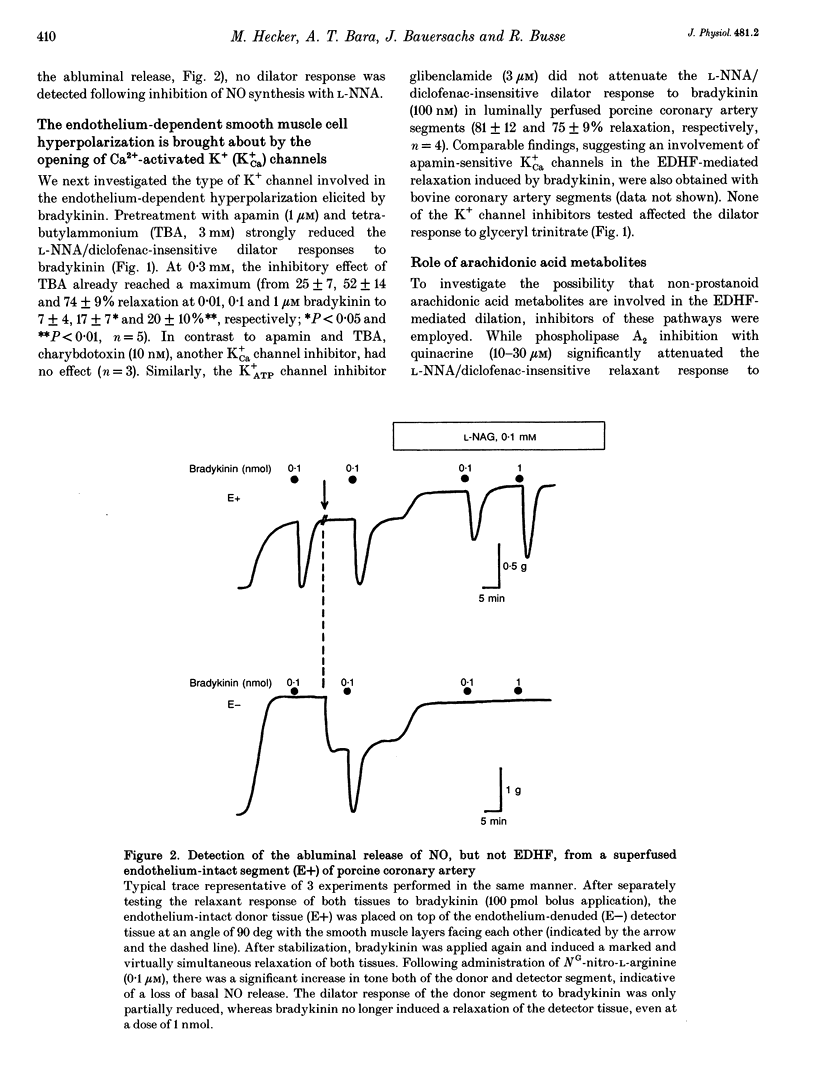
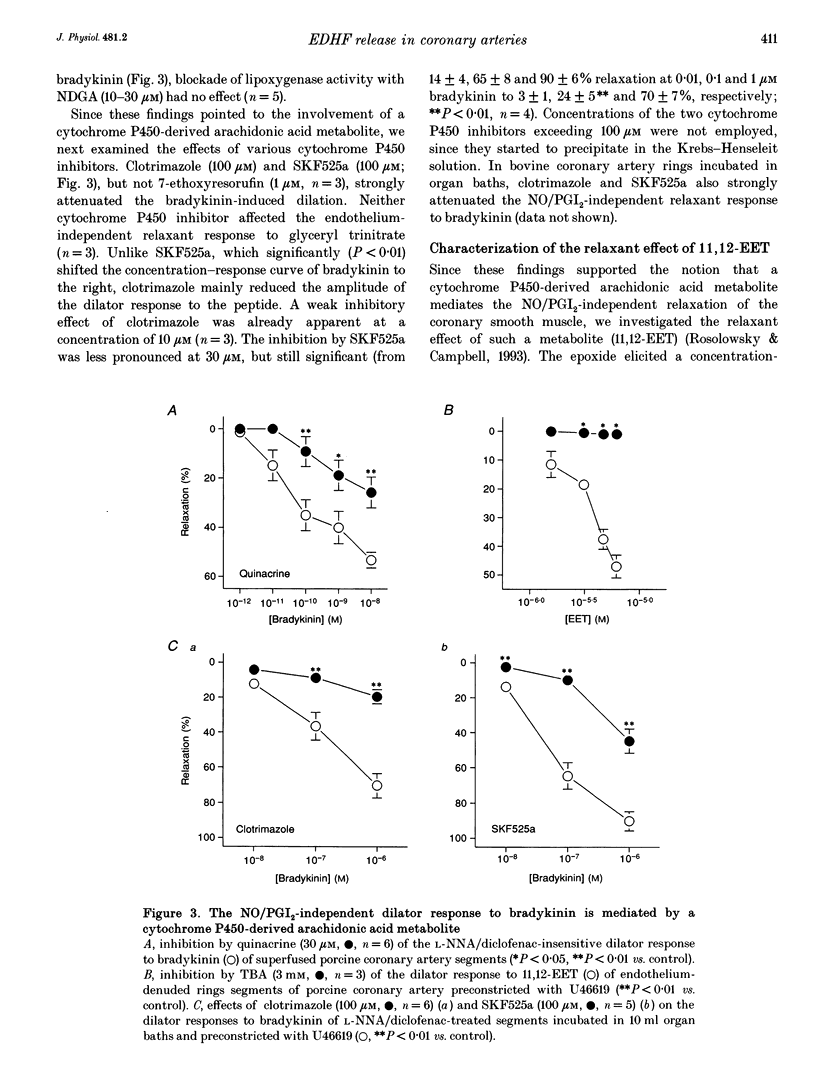
1. In addition to nitric oxide (NO) and prostacyclin (PGI2) an as yet unidentified endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) contributes to the dilator effect of bradykinin in different vascular beds. We have investigated the nature and mechanism of action of this factor in freshly isolated bovine and porcine coronary artery segments which were preconstricted with the thromboxane mimetic U46619 (9,11-dideoxy-11 alpha, 9 alpha-epoxymethano-prostaglandin F2 alpha, 10-30 nM). 2. The concentration-response curve of bradykinin was significantly shifted to the right after inhibition of NO synthesis with NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA, 30 microM), whereas cyclo-oxygenase blockade with diclofenac (1 microM) had no effect. Preconstriction of the segments with potassium chloride (40-60 mM) completely abrogated the NO/PGI2-independent dilator response to bradykinin. In sandwich bioassay experiments, both the luminal and abluminal release of NO, but not that of EDHF, was readily detectable. 3. Inhibitors of Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels (K+Ca), such as apamin (1 microM) and tetrabutylammonium (TBA, 3 mM), strongly attenuated the EDHF-mediated bradykinin-induced relaxation, while glibenclamide (3 microM), an inhibitor of K+ATP channels, had no effect. 4. These relaxations were also significantly inhibited by the phospholipase A2 inhibitor, quinacrine (30 microM), and the cytochrome P450 inhibitors, SKF525a (30-100 microM) and clotrimazole (100 microM). Moreover, incubation of endothelium-denuded coronary artery rings with a cytochrome P450-derived arachidonic acid metabolite, 11,12-epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid, elicited a concentration-dependent (1-10 microM) dilatation which was abolished both in the presence of TBA (3 mM) and following preconstriction of the segments with potassium chloride instead of U46619.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baydoun A. R., Woodward B. Effects of bradykinin in the rat isolated perfused heart: role of kinin receptors and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;103(3):1829–1833. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):718–720. doi: 10.1038/323718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bény J. L., Pacicca C. Bidirectional electrical communication between smooth muscle and endothelial cells in the pig coronary artery. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 2):H1465–H1472. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.4.H1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Yamamoto Y., Miwa K., Suzuki H. Hyperpolarization of arterial smooth muscle induced by endothelial humoral substances. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):H1888–H1892. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.6.H1888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan C. L., Cohen R. A. Two mechanisms mediate relaxation by bradykinin of pig coronary artery: NO-dependent and -independent responses. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):H830–H835. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.3.H830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton D., McGiff J. C., Quilley J. Contribution of NO and cytochrome P450 to the vasodilator effect of bradykinin in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):722–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Mülsch A., Bassenge E., Busse R. Vasoconstriction and increased flow: two principal mechanisms of shear stress-dependent endothelial autacoid release. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):H828–H833. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.3.H828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffner U., Feletou M., Flavahan N. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Canine arteries release two different endothelium-derived relaxing factors. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 2):H330–H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.1.H330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann S., Kukovetz W. R., Windischhofer W., Paschke E., Graier W. F. Pharmacologic differentiation between endothelium-dependent relaxations sensitive and resistant to nitro-L-arginine in coronary arteries. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1994 May;23(5):747–756. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199405000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S., Kim H. S. Activation of K+ channel in vascular smooth muscles by cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 12;230(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90805-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauser K., Rubanyi G. M. Bradykinin-induced, N omega-nitro-L-arginine-insensitive endothelium-dependent relaxation of porcine coronary arteries is not mediated by bioassayable relaxing substances. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992;20 (Suppl 12):S101–S104. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199204002-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombouli J. V., Illiano S., Nagao T., Scott-Burden T., Vanhoutte P. M. Potentiation of endothelium-dependent relaxations to bradykinin by angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors in canine coronary artery involves both endothelium-derived relaxing and hyperpolarizing factors. Circ Res. 1992 Jul;71(1):137–144. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima M., Mombouli J. V., Taylor A. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization caused by bradykinin in human coronary arteries. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2867–2871. doi: 10.1172/JCI116907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shaughnessy K. M., Newman C. M., Warren J. B. Inhibition in the rat of nitric oxide synthesis in vivo does not attenuate the hypotensive action of acetylcholine, ATP or bradykinin. Exp Physiol. 1992 Mar;77(2):285–292. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacicca C., von der Weid P. Y., Beny J. L. Effect of nitro-L-arginine on endothelium-dependent hyperpolarizations and relaxations of pig coronary arteries. J Physiol. 1992 Nov;457:247–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A., Abraham N. G., Mullane K. M. Arachidonic acid-induced endothelial-dependent relaxations of canine coronary arteries: contribution of a cytochrome P-450-dependent pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):856–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosolowsky M., Campbell W. B. Role of PGI2 and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in relaxation of bovine coronary arteries to arachidonic acid. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 2):H327–H335. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.2.H327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Chen G., Yamamoto Y. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF). Jpn Circ J. 1992 Feb;56(2):170–174. doi: 10.1253/jcj.56.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. L., Spray D. C., Campos de Carvalho A. C., Wittenberg B. A., Bennett M. V. Some electrical and pharmacological properties of gap junctions between adult ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 1):C447–C455. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.5.C447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


