Abstract
Neurotensin is a 13-amino acid peptide (pGlu-Leu-Tyr-Glu-Asn-Lys-Pro-Arg-Arg-Pro-Tyr-Ile-Leu) originally isolated from hypothalami (Carraway and Leeman, 1973) and later from intestines (Kitabgiet al., 1976) of bovine. The peptide is present throughout the animal kingdom, suggesting its participation to important processes basic to animal life (Carrawayet al., 1982). Neurotensin and its analogue neuromedin-N (Lys-Ile-Pro-Tyr-Ile-Leu) (Minaminoet al., 1984) are synthesized by a common precursor in mammalian brain (Kislauskiset al., 1988) and intestine (Dobneret al., 1987). The central and peripheral distribution and effects of neurotensin have been extensively studied. In the brain, neurotensin is exclusively found in nerve cells, fibers, and terminals (Uhlet al., 1979), whereas the majority of peripheral neurotensin is found in the endocrine N-cells located in the intestinal mucosa (Orciet al., 1976; Helmstaedteret al., 1977). Central or peripheral injections of neurotensin produce completely different pharmacological effects (Table I) indicating that the peptide does not cross the blood-brain barrier. Many of the effects of centrally administered neurotensin are similar to those of neuroleptics or can be antagonized by simultaneous administration of TRH (Table I). The recently discovered nonpeptide antagonist SR 48692 (Gullyet al., 1993) can inhibit several of the central and peripheral effects of neurotensin (Table I).
Like many other neuropeptides, neurotensin is a messenger of intracellular communication working as a neurotransmitter or neuromodulator in the brain (Nemeroffet al., 1982) and as a local hormone in the periphery (Hirsch Fernstromet al., 1980). Thus, several pharmacological, morphological, and neurochemical data suggest that one of the functions of neurotensin in the brain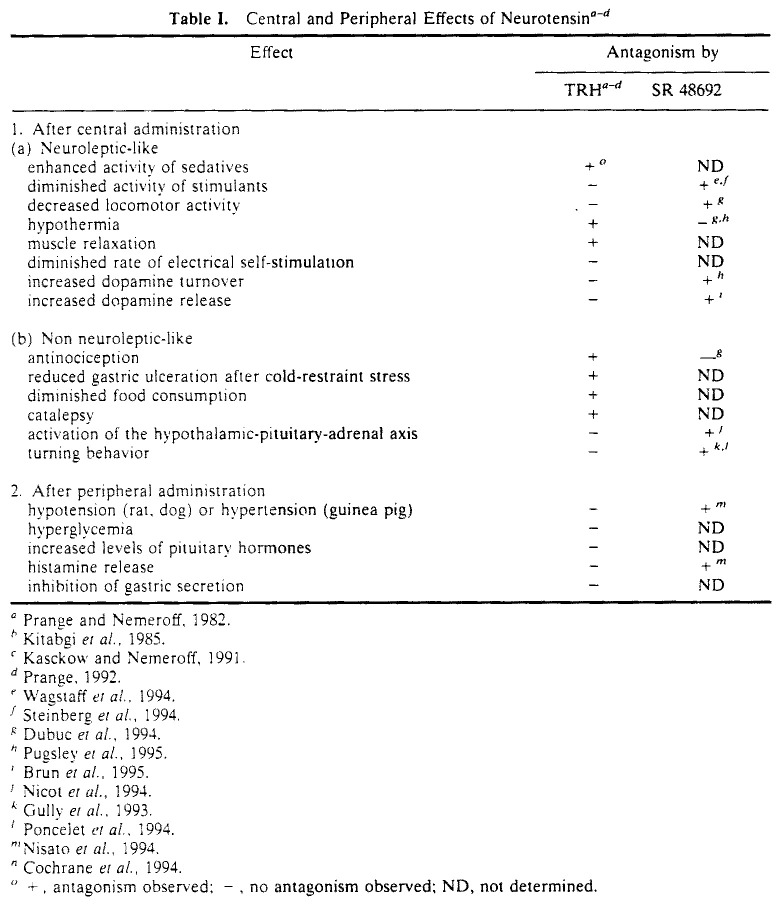 is to regulate dopamine neurotransmission along the nigrostriatal and mesolimbic pathways (Quirion, 1983; Kitabgi, 1989). On the other hand, the likely role of neurotensin as a parahormone in the gastrointestinal tract has been well documented (Rosell and Rökaeus, 1981; Kitabgi, 1982).
is to regulate dopamine neurotransmission along the nigrostriatal and mesolimbic pathways (Quirion, 1983; Kitabgi, 1989). On the other hand, the likely role of neurotensin as a parahormone in the gastrointestinal tract has been well documented (Rosell and Rökaeus, 1981; Kitabgi, 1982).
Both central and peripheral modes of action of neurotensin imply as a first step the recognition of the peptide by a specific receptor located on the plasma membrane of the target cell. Formation of the neurotensin-receptor complex is then translated inside the cell by a change in the activity of an intracellular enzyme. This paper describes the binding and structural properties of neurotensin receptors as well as the signal transduction pathways that are activated by the peptide in various target tissues and cells.
Key words: neurotensin, receptor, binding, transduction, structure
References
- Al-Rodhann, N. R. F., Richelson, E., Gilbert, J. A., McCormick, D. J., Kanba, K. S., Pfenning, M. A., Larson, E. W., and Yaksh, T. L. (1991). Structure-antinociceptive activity of neurotensin and some novel analogues in the periaqueductal gray region of the brainstem.Brain Res.557227–235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar, S., Mazella, J., Checler, F., Kitabgi, P., and Vincent, J. P. (1985). Regulation of cyclic GMP levels by neurotensin in neuroblastoma clone N1E115.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.129117–125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar, S., Kitabgi, P., and Vincent, J. P. (1986). Activation of phosphatidylinositol turnover by neurotensin receptors in the human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line HT29.FEBS Lett.20131–36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar, S., Kitabgi, P., and Vincent, J. P. (1987). Stimulation of inositol phosphate production by neurotensin in neuroblastoma N1E115 cells: Implication of GTP-binding proteins and relationship with the cyclic GMP response.J. Neurochem.49999–1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozou, J. C., Amar, S., Vincent, J. P., and Kitabgi, P. (1986). Neurotensin-mediated inhibition of cyclic AMP formation in neuroblastoma N1E115 cells: Involvement of the inhibitory GTP-binding component of adenylate cyclase.Mol. Pharmacol.29489–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozou, J. C., Rochet, N., Magnaldo, I., Vincent, J. P., and Kitabgi, P. (1989). Neurotensin stimulates inositol trisphosphate-mediated calcium mobilization but not protein kinase C activation in HT29 cells. Involvement of a G protein.Biochem. J.264871–878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun, P., Steinberg, R., Le Fur, G., and Soubrié, P. (1995). Blockade of neurotensin receptors by SR 48692 potentiates the facilitatory effect of haloperidol on the evokedin vivo dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens.J. Neurochem.642073–2079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway, R. E., and Leeman, S. E. (1973). The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami.J. Biol. Chem.2486854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway, R., Ruane, S. E., and Hye-Ryeong, K. (1982). Distribution and immunochemical character of neurotensin-like material in representative vertebrates and invertebrates: Apparent conservation of the COOH-terminal region during evolution.Peptides3115–123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabry, J., Gaudriault, G., Vincent, J. P., and Mazella, J. (1993). Implication of various forms of neurotensin receptors in the mechanism of internalization of neurotensin in cerebral neurons.J. Biol. Chem.26817138–17144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabry, J., Labbé-Jullié, C., Gully, D., Kitabgi, P., Vincent, J. P., and Mazella, J. (1994). Stable expression of the cloned rat brain neurotensin receptor into fibroblasts: Binding properties, photoaffinity labeling, transduction mechanisms and internalization.J. Neurochem.6319–27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler, F., Mazella, J., Kitabgi, P., and Vincent, J. P. (1986). High affinity receptor sites and rapid proteolytic inactivation of neurotensin in primary cultured neurons.J. Neurochem.471742–1748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane, D. E., Feldberg, R. S., Miller, L. A., Carraway, R. E., and Barrocas, A. (1994). Inhibition of neurotensin (NT)-stimulated mast cell histamine secretion by NT-receptor(NT-R) antagonist and by pertussis toxin(PT): Evidence for a NT-R on the rat cell.Faseb J.8:7 (Abs. 1195). [Google Scholar]
- Dobner, P. R., Barber, D. L., Villa-Komaroff, L., and McKierman, C. (1987). Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for the canine neurotensin/neuromedin N precursor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA843516–3520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubuc, I., Costentin, J., Terranova, J. P., Barnouin, M. C., Soubrié, P., Le Fur, G., Rostène, W., and Kitabgi, P. (1994). The nonpeptide neurotensin antagonist SR 48692 as a tool to reveal putative neurotensin receptor subtypes.Br. J. Pharmacol.112352–354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fostermann, U., Gorsky, L. D., Pollock, J. S., Ishii, K., Schmidt, H. H. H. W., Heller, M., and Murad, F. (1990). Hormone-induced biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide-like material in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells requires calcium and calmodulin.Mol. Pharmacol.387–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudriault, G., and Vincent, J. P. (1992). Selective labeling of α-or ε-amino groups in peptides by the Bolton-Hunter reagent.Peptides131187–1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J. A., and Richelson, E. (1984). Neurotensin stimulates formation of cyclic GMP in murine neuroblastoma clone N1E115.Eur. J. Pharmacol.99245–246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J. A., Moses, C. J., Pfenning, M. A., and Richelson, E. (1986). Neurotensin and its analogs-Correlation of specific binding with stimulation of cylic GMP formation in neuroblastoma clone N1E115.Biochem. Pharmacol.35391–397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert, M., Pinnock, R. D., Downes, C. P., Mantyh, P. W., and Emson, P. C. (1984). Neurotensin stimulates inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat brain slices.Brain Res.323193–197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gully, D., Canton, M., Boigegrain, R., Jeanjean, F., Molimard, J. C., Poncelet, M., Gueudet, C., Heaulme, M., Leyris, R., Brouard, A., Pelaprat, D., Labbé-Jullié, C., Mazella, J., Soubrié, P., Maffrand, J. P., Rostène, W., Kitabgi, P., and Le Fur, G. (1993). Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a potent and selective non-peptide antagonist of neurotensin receptor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA9065–69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstaedter, V., Feurle, G. E., and Forsmann, W. G. (1977). Ultrastructural identification of a new cell type—the N-cell as the source of neurotensin in the gut mucosa.Cell Tissue Res.184445–452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, E., Maloteaux, J. M., and Octave, J. N. (1992). Phospholipase C activation by neurotensin and neuromedin N in chinese hamster ovary cells expressing the rat neurotensin receptor.Mol. Brain Res.15332–338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch Fernstron, M., Carraway, R. E., and Leeman, S. E. (1980). Neurotensin. In Martini, L., and Ganong, W. F. (eds.),Front Neuroendocrinol., Raven Press, New York, pp. 103–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kasckow, J., and Nemeroff, C. B. (1991). The neurobiology of neurotensin: Focus on neurotensin-dopamine interactions.Regul. Pepti.36153–164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislauskis, E., Bullock, B., McNeil, S., and Dobner, P. R. (1988). The rat gene encoding neurotensin and neuromedin N. Structure, tissue-specific expression, and evolution of exon sequences.J. Biol. Chem.2634963–4968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi, P. (1982). Effects of neurotensin on intestinal smooth muscle: Application to the study of structure-activity relationships.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.40037–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi, P. (1989). Neurotensin modulates dopamine neurotransmission at several levels along brain dopaminergic pathways.Neurochem. Int.14111–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi, P., Carraway, R. E., and Leeman, S. E. (1976). Isolation of a tridecapeptide from bovine intestinal tissue and its partial characterization as neurotensin.J. Biol. Chem.2517053–7058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi, P., Carraway, R. E., Van Rietschoten, J., Granier, C., Morgat, J. L., Menez, A., Leeman, S., and Freychet, P. (1977). Neurotensin: Specific binding to synaptic membranes from rat brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA741846–1850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi, P., Checler, F., Mazella, J., and Vincent, J. P. (1985). Pharmacology and biochemistry of neurotensin receptors.Rev. Basic Clin. Pharmacol.5397–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi, P., Rostène, W., Dussaillant, M., Schotte, A., Laduron, P. M., and Vincent, J. P. (1987). Two populations of neurotensin binding sites in murine brain; discrimination by the antihistamine levocabastine reveals markedly different radioautographic distribution.Eur. J. Pharmacol.140285–293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé-Jullié, C., Dubuc, I., Brouard, A., Doulut, S., Bourdel, E., Pelaprat, D., Mazella, J., Martinez, J., Rostene, W., Costentin, J., and Kitabgi, P. (1994).In vivo andin vitro structure-activity studies with peptide and pseudopeptide neurotensin analogs suggest the existence of distinct central neurotensin receptor subtypes.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.268328–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, L. H., Perrin, M. H., and Brown, M. R. (1977). Mast cell binding of neurotensin. I. lodination of neurotensin and characterization of the interaction of neurotensin with mast cell receptor sites.J. Biol. Chem.2527174–7179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsault, R., and Frelin, C. (1992). The activation by nitric oxide of guanylate cyclase in endothelial cells from brain capillaries.J. Neurochem.59942–945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazella, J., Poustis, C., Labbé, C., Checler, F., Kitabgi, P., Granier, C., Van Rietschoeten, J., and Vincent, J. P. (1983). Monoiodo-Trp11 neurotensin, a highly radioactive ligand of neurotensin receptors. Preparation, biological activity and binding properties to rat brain synaptic membranes.J. Biol. Chem.2583476–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazella, J., Chabry, J., Zsürger, N., and Vincent, J. P. (1989). Purification of the neurotensin receptor from mouse brain by affinity chromatography.J. Biol. Chem.2645559–5563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazella, J., Chabry, J., Checler, F., Beaudet, A., and Vincent, J. P. (1993). Neurotensin receptors in primary culture of neurons. In Conn, M. P. (ed.),Methods in Neurosciences, Academic Press, pp. 334–351.
- McKinney, M., Bolden, C., Smith, C., Johnson, A., and Richelson, E. (1990). Selective blockade of receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells by an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis.Eur. J. Pharmacol.178139–140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino, N., Kangawa, K., and Matsuo, H. (1984). Neuromedin N: a novel neurotensin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.122542–549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff, C. B., Luttinger, D., and Prange, A. J. (1982). Neurotensin and bombesin.Handbook Psychopharmacol.16363–467. [Google Scholar]
- Nicot, A., Berod, A., Gully, D., Rowe, W., Quirion, R., De Kloet, E. R., and Rostène, W. (1994). Blockade of neurotensin binding in the rat hypothalamus and of the central action of neurotensin on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis with non-peptide receptor antagonists.Neuroendocrinology59572–578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisato, D., Guiraudou, P., Barthelemy, G., Gully, D., and Le Fur, G. (1994). SR 48692, a non peptide neurotensin receptor antagonist, blocks the cardiovascular effects elicited by neurotensin in guinea pigs.Life Sci.5495–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci, L., Baetens, O., Rufener, C., Brown, M., Vale, W., and Guillemin, R. (1976). Evidence for immunoreactive neurotensin in dog intestinal mucosa.Life Sci.19559–562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncelet, M., Gueudet, C., Gully, D., Soubrié, P., and Le Fur, G. (1994). Turning behavior induced by intrastriatal injection of neurotensin in mice: Sensitivity to non-peptide neurotensin antagonists.Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.60347–349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustis, C., Mazella, J., Kitabgi, P., and Vincent, J. P. (1984). High-affinity neurotensin binding sites in differentiated neuroblastoma N1E115 cells.J. Neurochem.421094–1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prange, A. J. Jr. (1992). The manifold actions of neurotensin, a trophotropic agent.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.668298–306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prange, A. J., Jr., and Nemeroff, C. B. (1982). The manifold actions of neurotensin: A first synthesis.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.400368–375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley, T. A., Akunne, H. C., Whetzel, S. Z., Demattos, S., Corbin, A. E., Wiley, J. N., Wustrow, D. J., Wisc, L. D., and Heffner, T. G. (1995). Differential effects of the nonpeptide neurotensin antagonist, SR 48692, on the pharmacological effects of neurotensin agonists.Peptides1637–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion, R. (1983). Interactions between neurotensin and dopamine in the brain: An overview.Peptides4609–614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosell, S., and Rökaeus, A. (1981). Actions and possible hormonal functions of circulating neurotensin.Clin. Physiol.13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sadoul, J. L., Mazella, J., Amar, S., Kitabgi, P., and Vincent, J. P. (1984). Preparation of neurotensin selectively iodinated on the tyrosine 3 residue. Biological activity and binding properties on mammalian neurotensin receptors.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.120812–819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M., Shiosaka, S., and Tohyama, M. (1991). Neurotensin and neuromedin N elevate the cytosolic calcium concentration via transiently appearing neurotensin binding sites in cultured rat cortex cells.Development. Brain Res.5897–103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, P., Laplace, M. C., Savi, P., Pflieger, A. M., Gully, D., and Herbert, J. M. (1995). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells express high affinity neurotensin receptors coupled to intracellular calcium release.J. Biol. Chem.2703409–3413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotte, A., and Laduron, P. M. (1987). Different postnatal ontogeny of two 3H neurotensin binding sites in rat brain.Brain Res.408326–328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotte, A., Leysen, J. E., and Laduron, P. M. (1986). Evidence for a displaceable non-specific 3H neurotensin binding site in rat brain.Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.333400–405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotte, A., Rostène, W., and Laduron, P. M. (1988). Different subcellular localization of neurotensin-receptor and neurotensin-acceptor sites in the rat brain dopaminergic system.J. Neurochem.501026–1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W. X., and Bunney, B. S. (1992). Role of intracellular cAMP and protein kinase A in the actions of dopamine and neurotensin on midbrain dopamine neurons.J. Neurosci.122433–2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider, R. M., Forray, C., Pfenning, M., and Richelson, E. (1986). Neurotensin stimulates inositol phospholipid metabolism and calcium mobilization in murine neuroblastoma clone N1E115.J. Neurochem.471214–1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, R., Brun, P., Fournier, M., Souilhac, J., Rodier, D., Mons, G., Terranova, J. P., Le Fur, G., and Soubrié, P. (1994). SR 48692, a non-peptide neurotensin receptor antagonist differentially affects neurotensin-induced behaviour and changes in dopaminergic transmission.Neuroscience59921–929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K., Masu, M., and Nakanishi, S. (1990). Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor.Neuron4847–854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner, J. T., James-Kracke, M. R., and Camden, J. M. (1990). Regulation of the neurotensin receptor and intracellular calcium mobilization in HT29 cells.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.2531049–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl, G. R., Bennett, J. P., and Snyder, S. H. (1977). Neurotensin, a central nervous system peptide: Apparent receptor binding in brain membranes.Brain Res.130299–313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl, G. R., Goodman, R. R., and Snyder, S. H. (1979). Neurotensin-containing cell bodies, fibers and nerve terminals in the brainstern of the rat: immunohistochemical mapping.Brain Res.16777–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, J. P., Mazella, J., Chabry, J., and Zsürger, N. (1990). The neurotensin receptor from mammalian brain: Solubilization and purification by affinity chromatography. In Litwack, G. (eds.),Receptor Purification, Humana Press, pp. 131–145.
- Vita, N., Laurent, P., Lefort, S., Chalon, P., Dumont, X., Kaghad, M., Gully, D., Le Fur, G., Ferrara, P., and Caput, D. (1993). Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a high affinity human neurotensin receptor.FEBS Lett.317139–142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff, J. D., Bush, L. G., Gibb, J. W., and Hanson, G. R. (1994). Endogenous neurotensin antagonizes methamphetamine-enhanced dopaminergic activity.Brain Res.665237–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson, M. A., Yamada, M., Yamada, M., Cusack, B., Veverka, K., Bolden-Watson, C., and Richelson, E. (1992). The rat neurotensin receptor expressed in chinese hamster ovary cells mediates the release of inositol phosphates.J. Neurochem.591967–1970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, M., Yamada, M., Watson, M. A., and Richelson, E. (1993). Neurotensin stimulates cyclic AMP formation in CHO-rNTR-10 cells expressing the cloned rat neurotensin receptor.Eur. J. Pharmacol.24499–101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsürger, N., Chabry, J., Coquerel, A., and Vincent, J. P. (1992). Ontogenesis and binding properties of high affinity neurotensin receptors in human brain.Brain Res.586303–310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsürger, N., Mazella, J., and Vincent, J. P. (1994). Solubilization and purification of a high affinity neurotensin receptors from new born human brain.Brain Res.639245–252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


