Abstract
1. Single-channel calcium-activated non-selective cation currents from isolated rat brown fat cells were measured using the inside-out patch configuration of the patch-clamp technique. The existence of a possible modulatory effect of nitric oxide on the putative redox-modulatory site located on the intracellular side of the non-selective cation channel was investigated. 2. The nitric oxide-releasing substances nitroglycerin, sodium nitroprusside, S-nitrosocysteine and S-nitroso-N-acetyl-D,L-penicillamine (all at 100 microM) were able to block channel activity almost completely. 3. In each case the blockade was persistent and could not be washed away. Dithiothreitol (DTT, 2 mM) was able to reverse the blockade to a large extent, whereas oxidized DTT (2 mM) was without effect. 4. It was concluded that nitric oxide can modulate non-selective cation channel activity by oxidizing sulfhydryl groups and that this effect can be reversed by reduction.
Full text
PDF
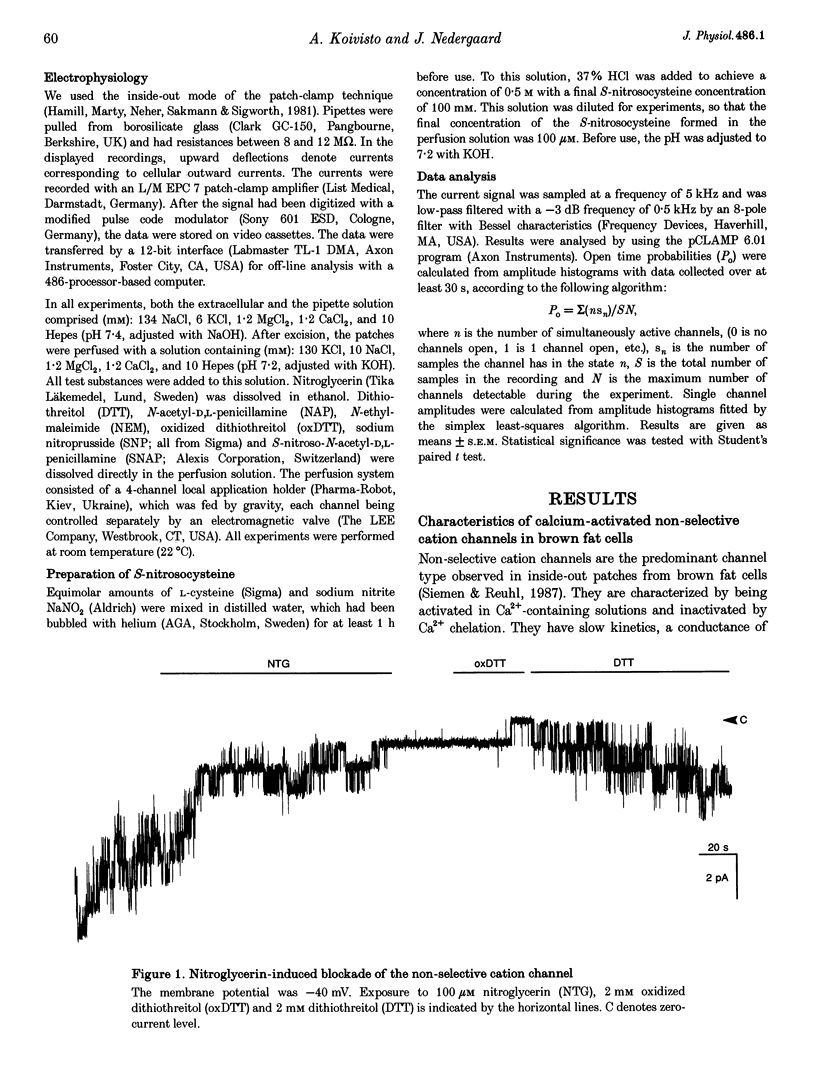

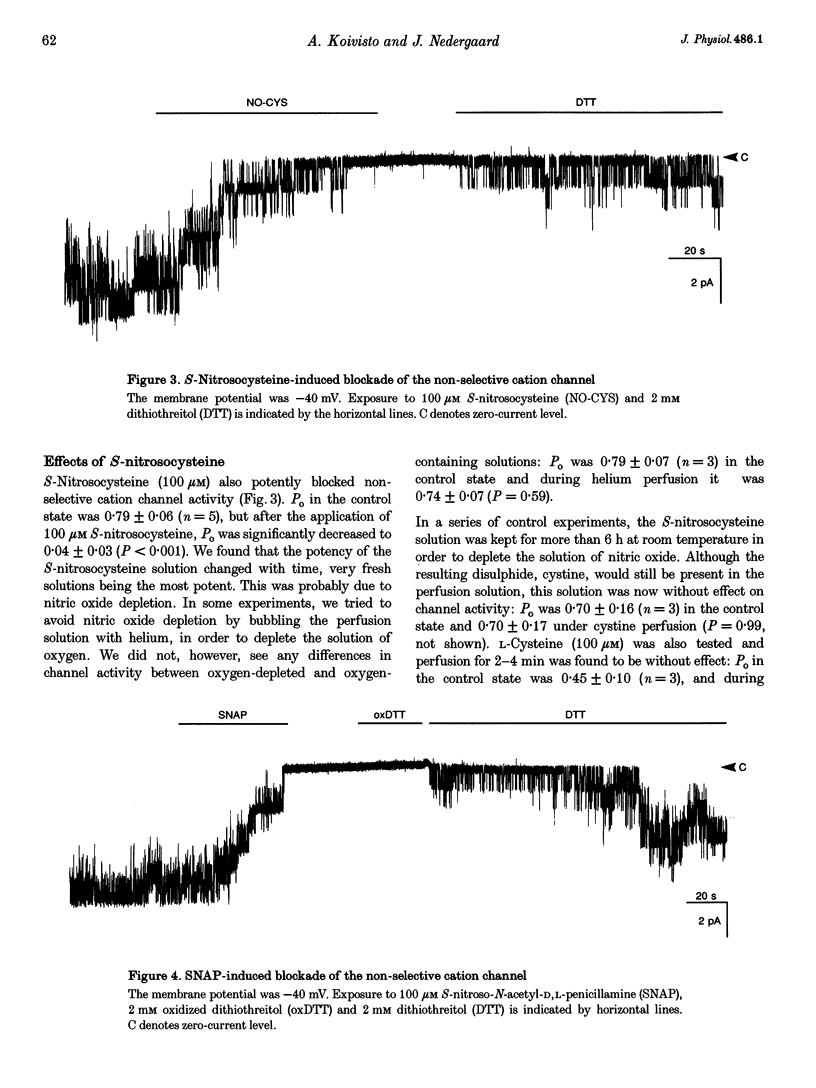
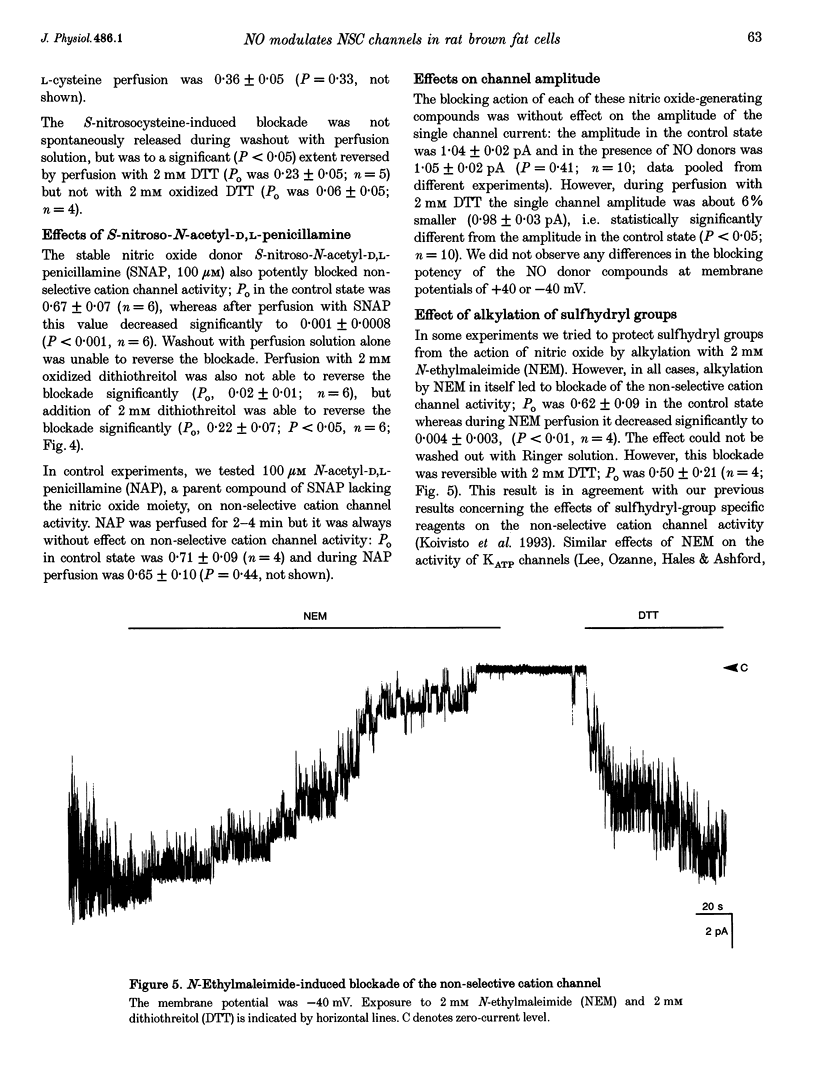


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizenman E., Lipton S. A., Loring R. H. Selective modulation of NMDA responses by reduction and oxidation. Neuron. 1989 Mar;2(3):1257–1263. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolotina V. M., Najibi S., Palacino J. J., Pagano P. J., Cohen R. A. Nitric oxide directly activates calcium-dependent potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):850–853. doi: 10.1038/368850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly E., Nånberg E., Nedergaard J. Norepinephrine-induced Na+ influx in brown adipocytes is cyclic AMP-mediated. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14377–14385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard P., Potier P. NO, thiols and disulfides. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 29;320(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81645-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardier L., Seydoux J., Clausen T. Membrane potential of brown adipose tissue. A suggested mechanism for the regulation of thermogenesis. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Dec;52(6):925–940. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. G., Bates J. N. The nitrovasodilators. New ideas about old drugs. Circulation. 1993 May;87(5):1461–1467. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.5.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 1;298(Pt 2):249–258. doi: 10.1042/bj2980249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto A., Siemen D., Nedergaard J. Reversible blockade of the calcium-activated nonselective cation channel in brown fat cells by the sulfhydryl reagents mercury and thimerosal. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Dec;425(5-6):549–551. doi: 10.1007/BF00374884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K., Ozanne S. E., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Effects of chemical modification of amino and sulfhydryl groups on KATP channel function and sulfonylurea binding in CRI-G1 insulin-secreting cells. J Membr Biol. 1994 May;139(3):167–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00232621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Nuccitelli R., Pappone P. A. Adrenergically activated Ca2+ increases in brown fat cells: effects of Ca2+, K+, and K channel block. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 1):C217–C228. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.1.C217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei S. Z., Pan Z. H., Aggarwal S. K., Chen H. S., Hartman J., Sucher N. J., Lipton S. A. Effect of nitric oxide production on the redox modulatory site of the NMDA receptor-channel complex. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1087–1099. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Choi Y. B., Pan Z. H., Lei S. Z., Chen H. S., Sucher N. J., Loscalzo J., Singel D. J., Stamler J. S. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):626–632. doi: 10.1038/364626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucero M. T., Pappone P. A. Membrane responses to norepinephrine in cultured brown fat cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Mar;95(3):523–544. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinski T., Taha Z. Nitric oxide release from a single cell measured in situ by a porphyrinic-based microsensor. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):676–678. doi: 10.1038/358676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima T., Ohinata H., Kuroshima A. Involvement of nitric oxide in noradrenaline-induced increase in blood flow through brown adipose tissue. Life Sci. 1994;54(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00573-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge L. D., Swandulla D. Calcium-activated non-specific cation channels. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Feb;11(2):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemen D., Reuhl T. Non-selective cationic channel in primary cultured cells of brown adipose tissue. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):534–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00585082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Hogg R. C., Large W. A. A monovalent ion-selective cation current activated by noradrenaline in smooth muscle cells of rabbit ear artery. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Apr;423(1-2):28–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00374957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


