Abstract
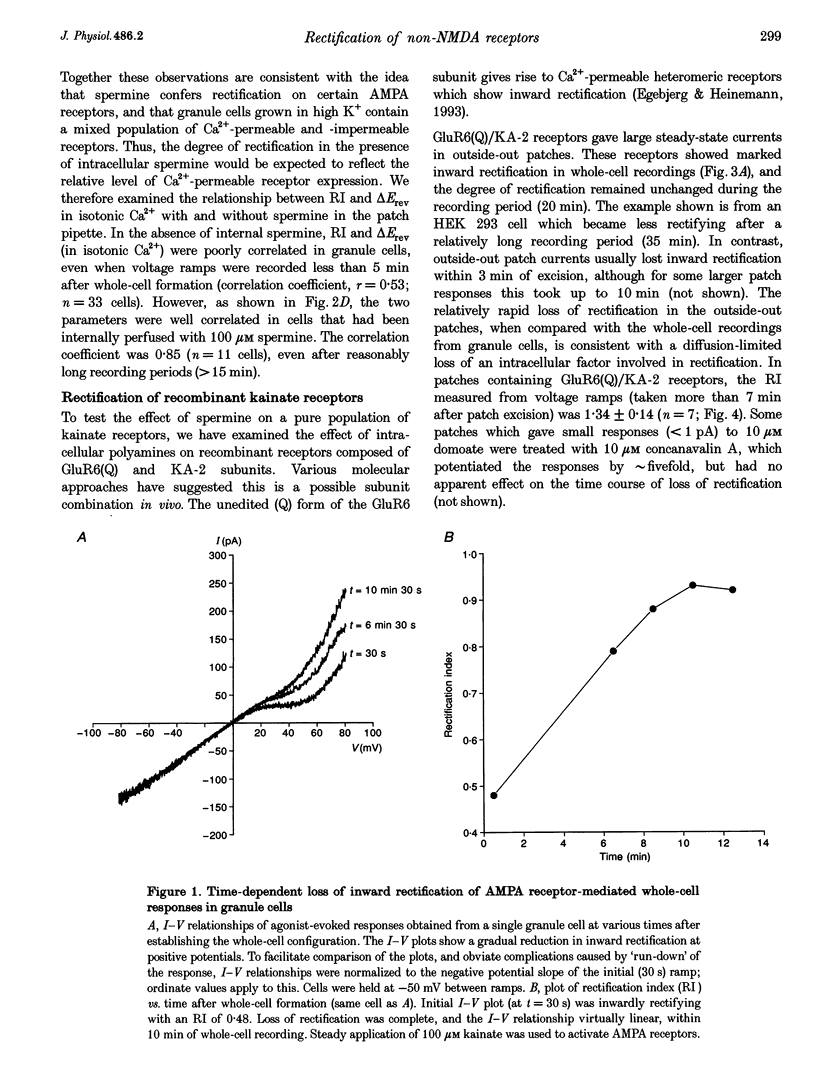
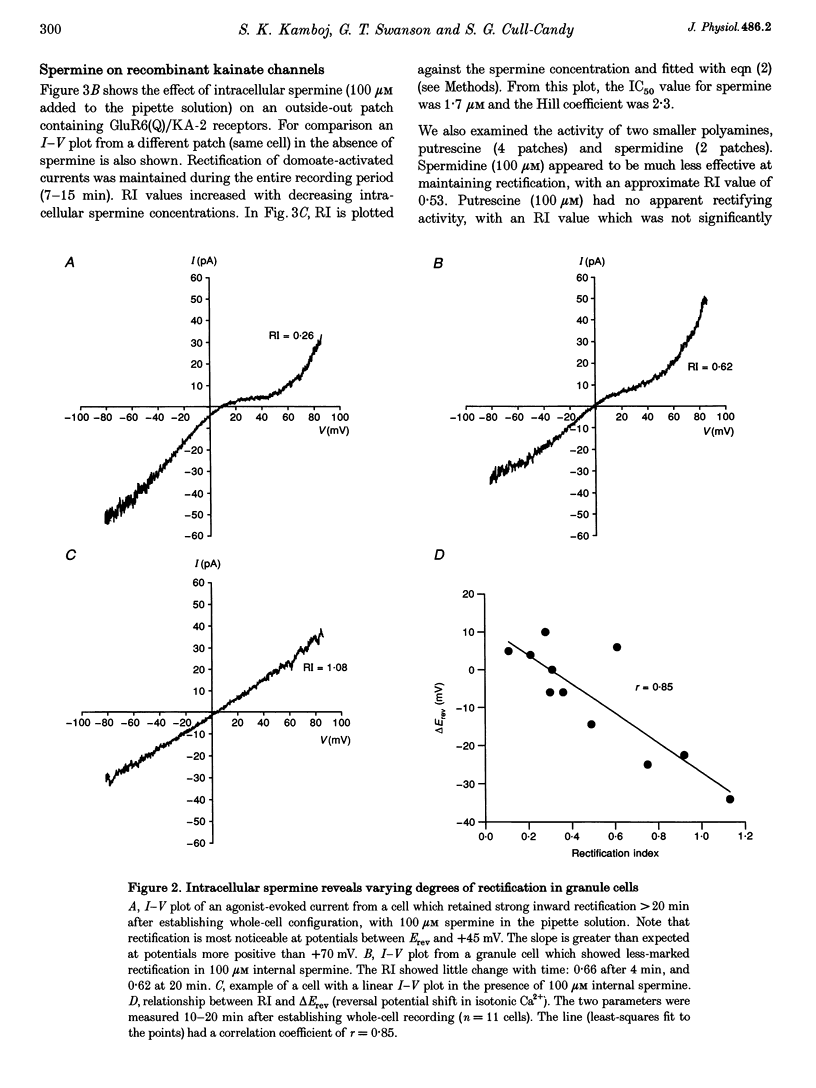
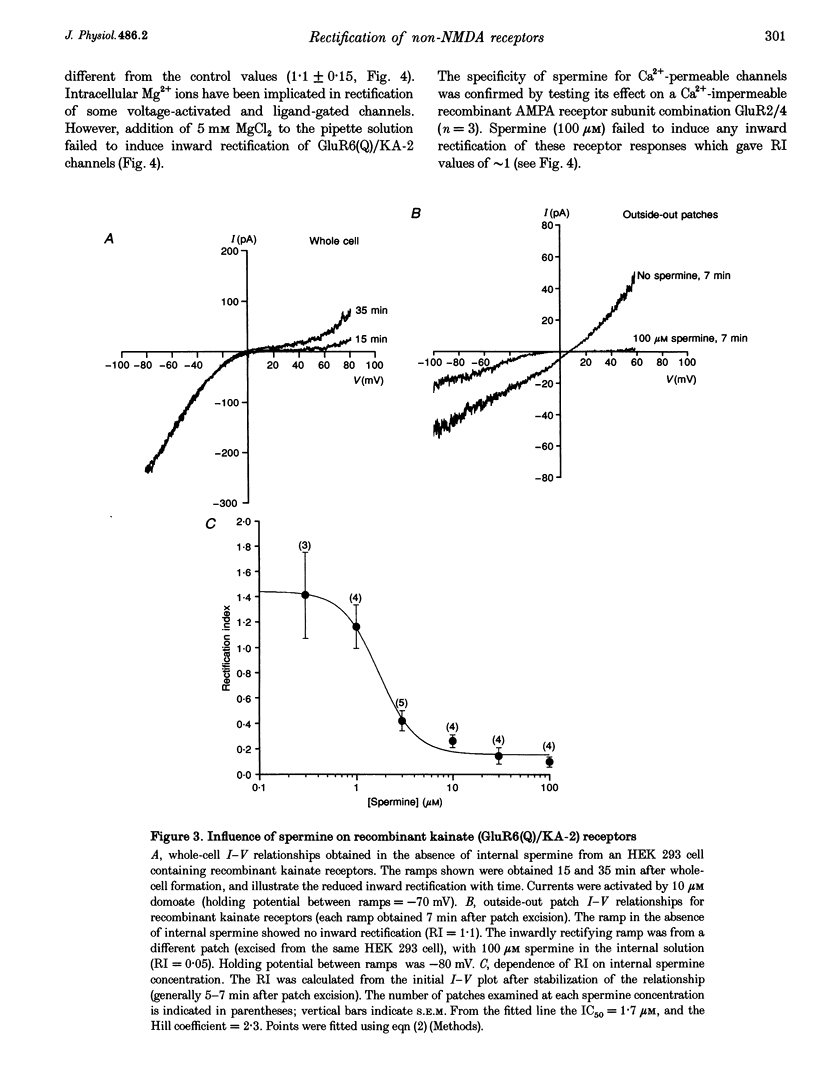
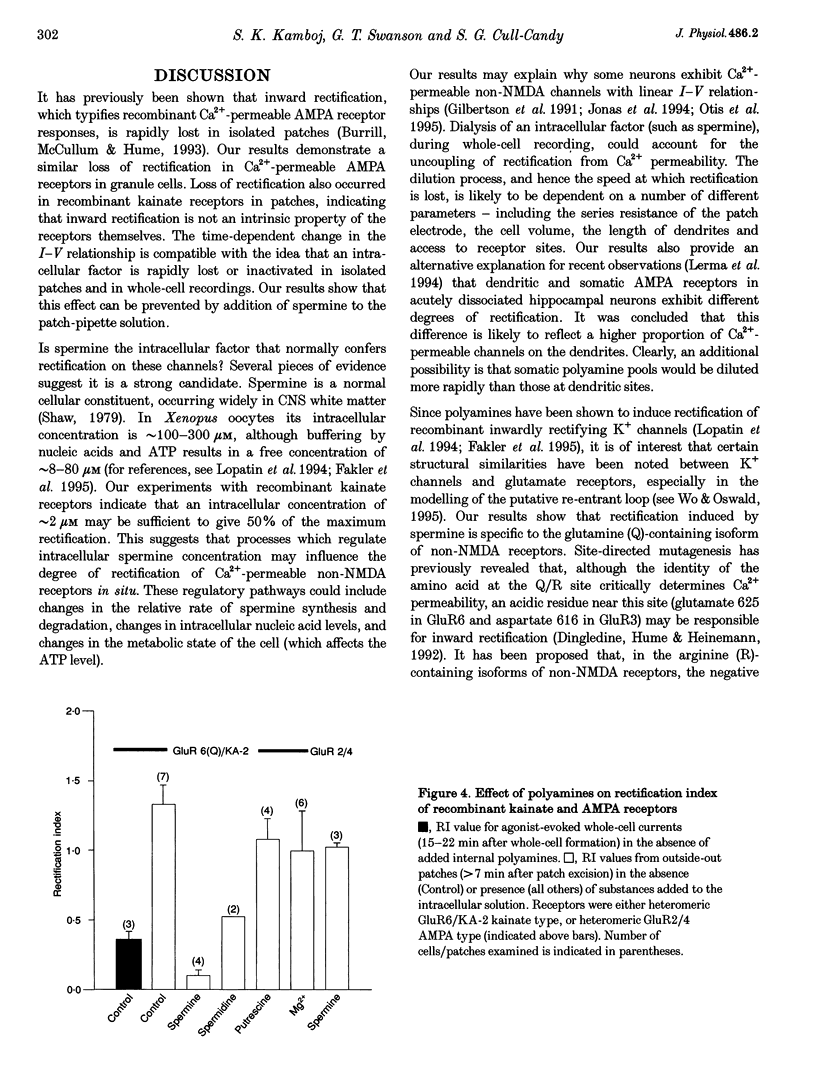
1. Whole-cell recordings were made from cerebellar granule cells cultured in high-K+ medium to induce expression of Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptors. Current-voltage (I-V) plots of agonist-evoked responses showed varying degrees of inward rectification, but became linear within 5-10 min. 2. Recombinant Ca(2+)-permeable kainate receptors, composed of GluR6(Q)/KA-2 subunits, exhibited rectifying whole-cell I-V plots that became linear in outside-out patches. 3. Loss of rectification in granule cells was prevented by including 100 microM spermine in the pipette; the degree of rectification was then correlated with Ca2+ permeability. 4. Spermine also prevented loss of rectification in patches containing GluR6(Q)/KA-2 receptors (IC50, 1.7 microM). 5. We suggest that spermine, or a similar cellular constituent, may act as a cytoplasmic factor conferring inward rectification on Ca(2+)-permeable non-NMDA receptors, and that 'washout' of this factor underlies the observed loss of rectification.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bochet P., Audinat E., Lambolez B., Crépel F., Rossier J., Iino M., Tsuzuki K., Ozawa S. Subunit composition at the single-cell level explains functional properties of a glutamate-gated channel. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Zhou Z., Neher E., Sakmann B. Fractional calcium currents through recombinant GluR channels of the NMDA, AMPA and kainate receptor subtypes. J Physiol. 1995 Jun 1;485(Pt 2):403–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condorelli D. F., Dell'Albani P., Aronica E., Genazzani A. A., Casabona G., Corsaro M., Balázs R., Nicoletti F. Growth conditions differentially regulate the expression of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate (AMPA) receptor subunits in cultured neurons. J Neurochem. 1993 Dec;61(6):2133–2139. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb07451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Hume R. I., Heinemann S. F. Structural determinants of barium permeation and rectification in non-NMDA glutamate receptor channels. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4080–4087. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04080.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Heinemann S. F. Ca2+ permeability of unedited and edited versions of the kainate selective glutamate receptor GluR6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakler B., Brändle U., Glowatzki E., Weidemann S., Zenner H. P., Ruppersberg J. P. Strong voltage-dependent inward rectification of inward rectifier K+ channels is caused by intracellular spermine. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90459-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbertson T. A., Scobey R., Wilson M. Permeation of calcium ions through non-NMDA glutamate channels in retinal bipolar cells. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1613–1615. doi: 10.1126/science.1849316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Hartley M., Heinemann S. Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA--gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1709304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Racca C., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H., Monyer H. Differences in Ca2+ permeability of AMPA-type glutamate receptor channels in neocortical neurons caused by differential GluR-B subunit expression. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90444-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerma J., Morales M., Ibarz J. M., Somohano F. Rectification properties and Ca2+ permeability of glutamate receptor channels in hippocampal cells. Eur J Neurosci. 1994 Jul 1;6(7):1080–1088. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb00605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin A. N., Makhina E. N., Nichols C. G. Potassium channel block by cytoplasmic polyamines as the mechanism of intrinsic rectification. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):366–369. doi: 10.1038/372366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain C. J., Dingledine R. Heterogeneity of synaptic glutamate receptors on CA3 stratum radiatum interneurones of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:373–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otis T. S., Raman I. M., Trussell L. O. AMPA receptors with high Ca2+ permeability mediate synaptic transmission in the avian auditory pathway. J Physiol. 1995 Jan 15;482(Pt 2):309–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S., Iino M., Tsuzuki K. Two types of kainate response in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Jul;66(1):2–11. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. G. The polyamines in the central nervous system. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Köhler M., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H. RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90568-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wo Z. G., Oswald R. E. Unraveling the modular design of glutamate-gated ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Apr;18(4):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93895-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie D. J., Cull-Candy S. G. A comparison of non-NMDA receptor channels in type-2 astrocytes and granule cells from rat cerebellum. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 15;475(1):95–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


