Abstract
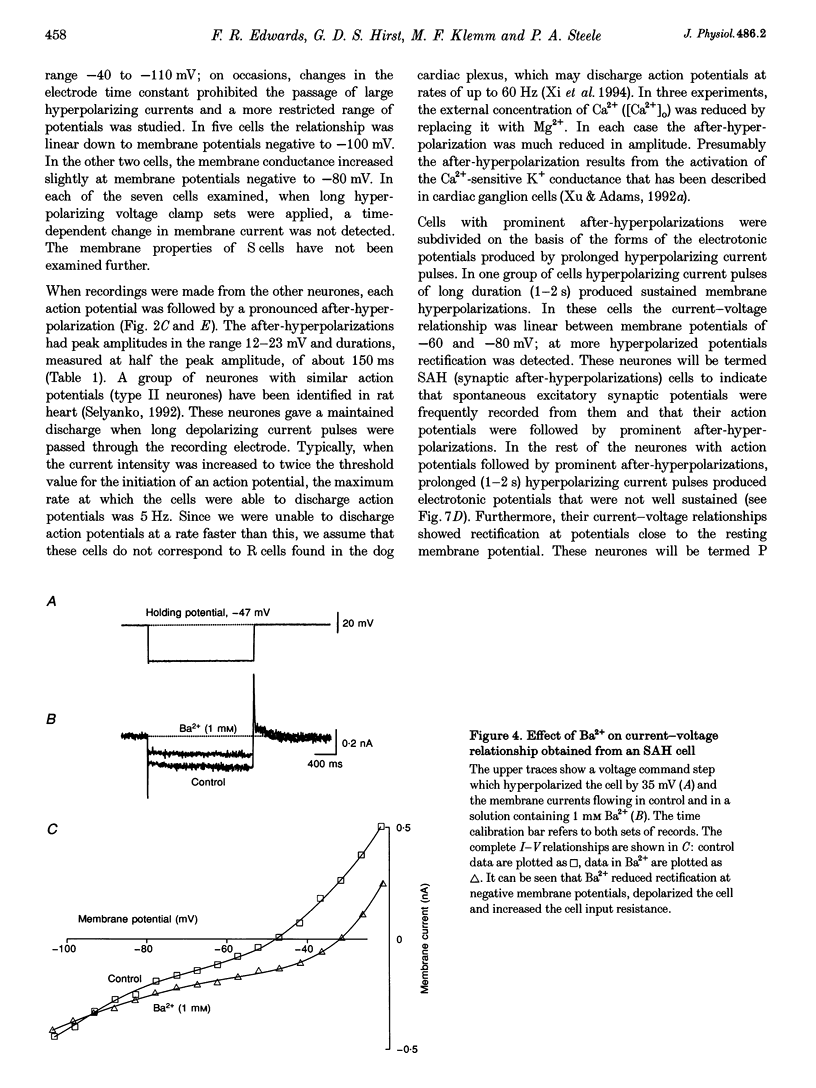
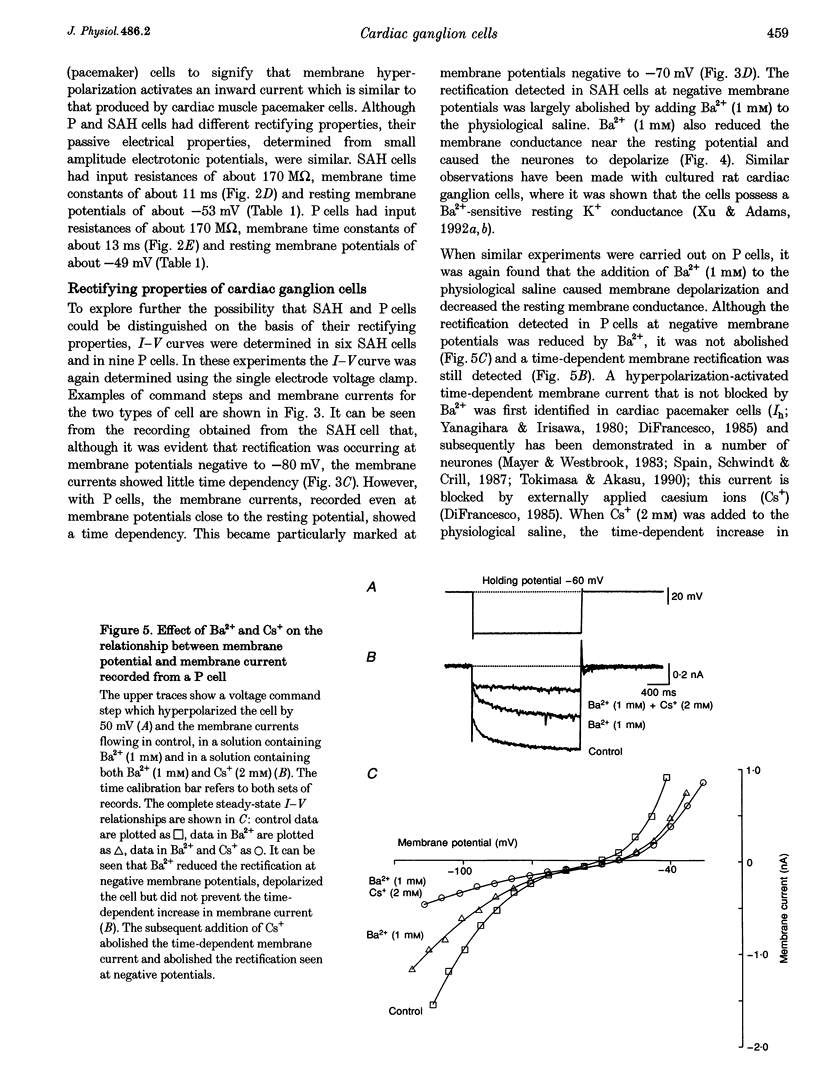
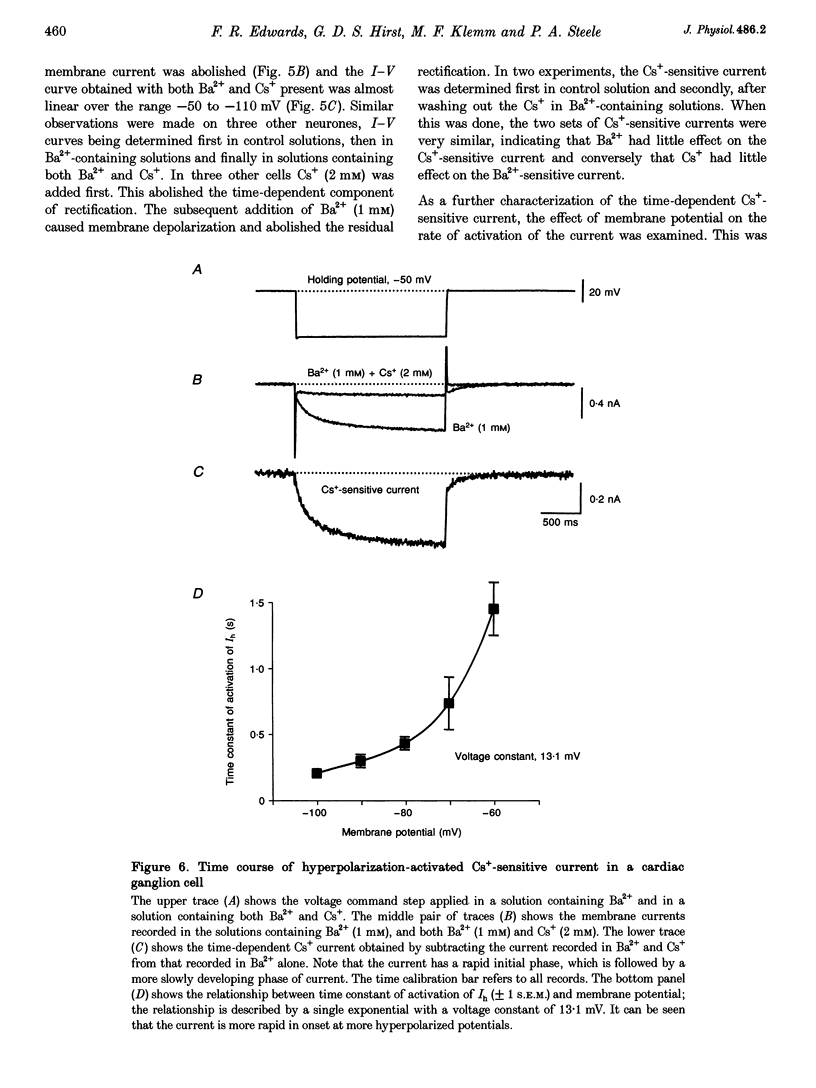
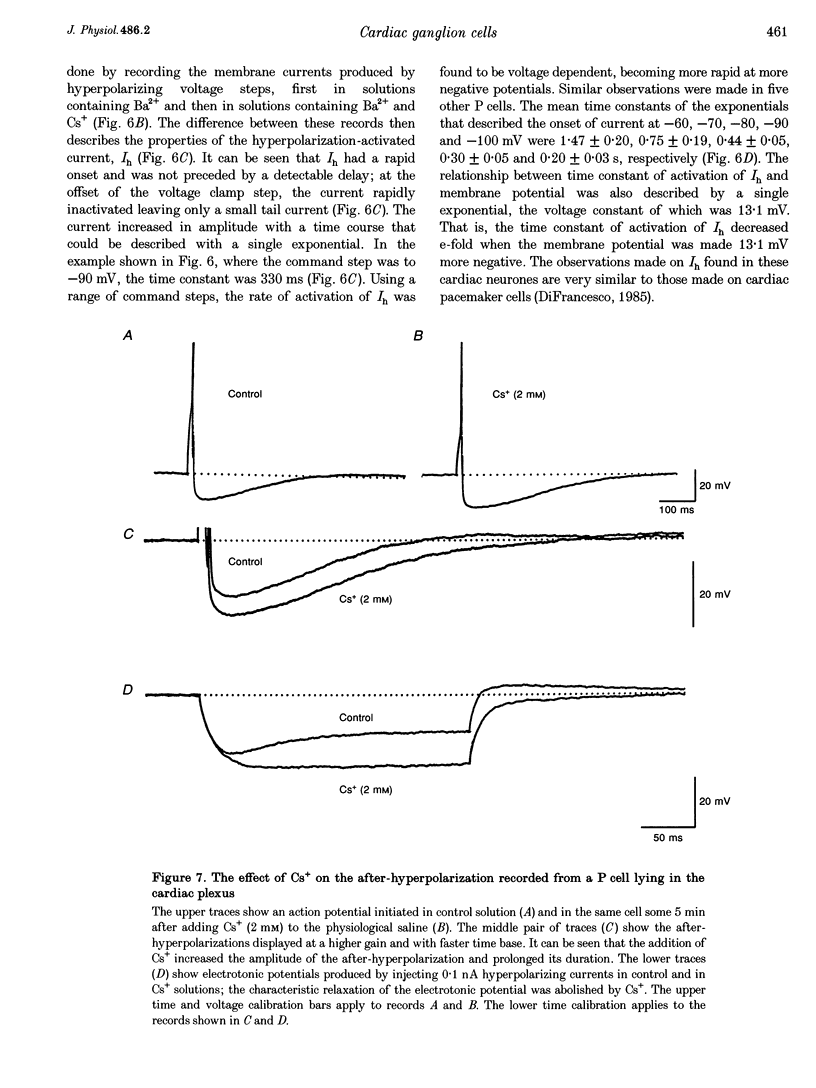
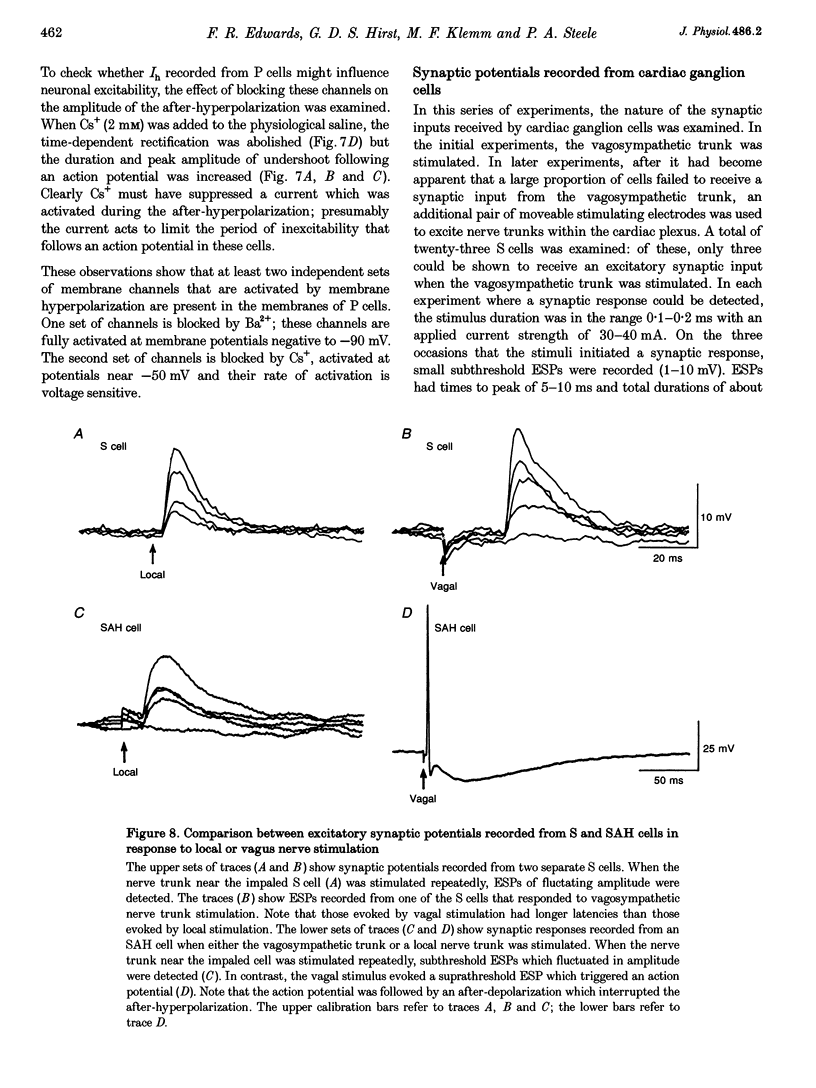
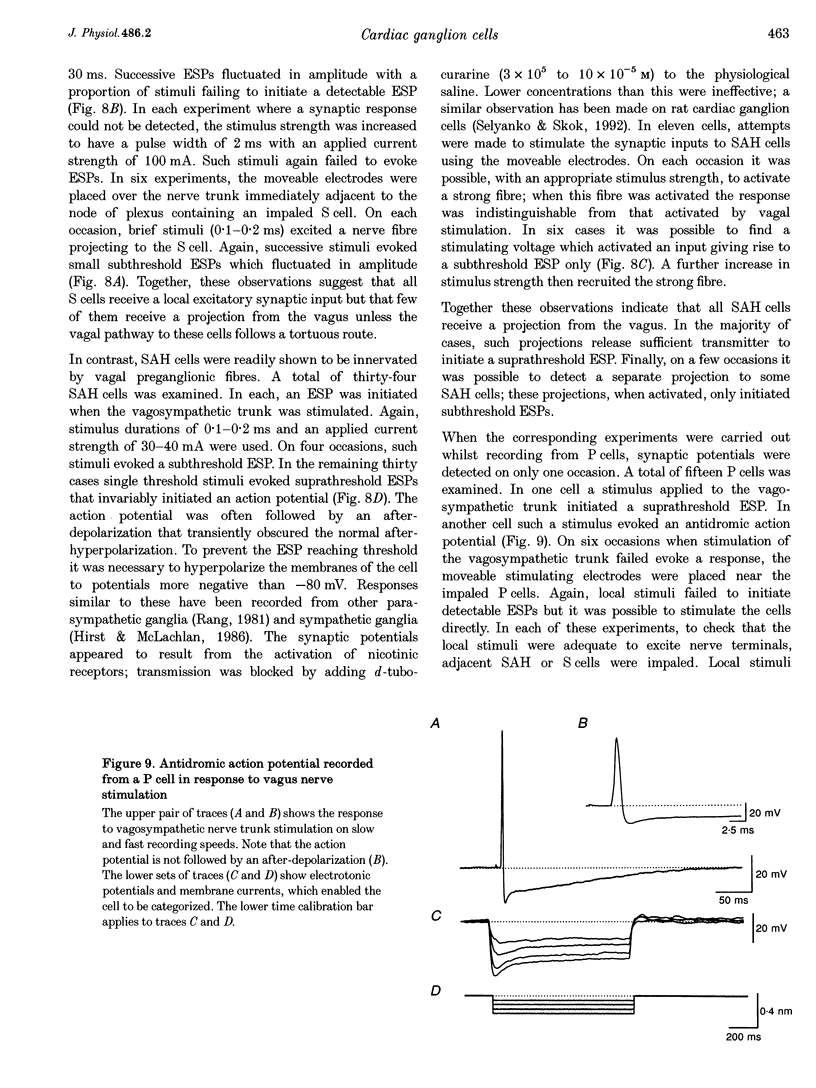
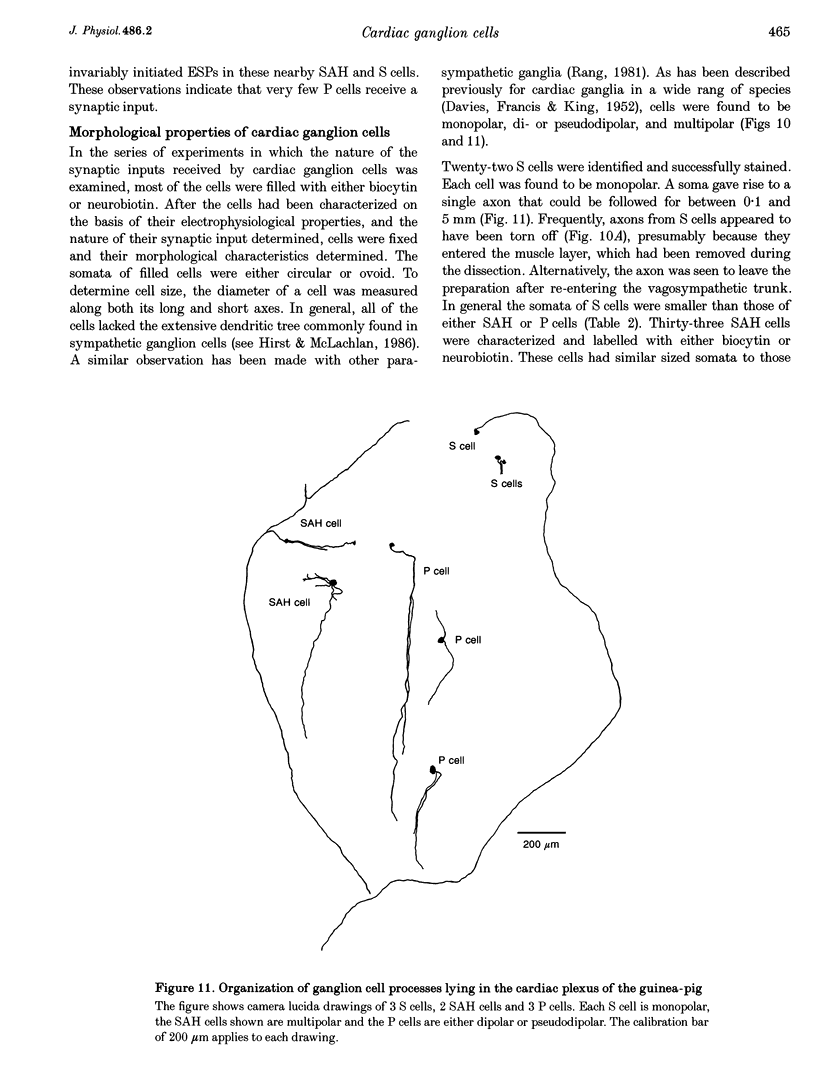
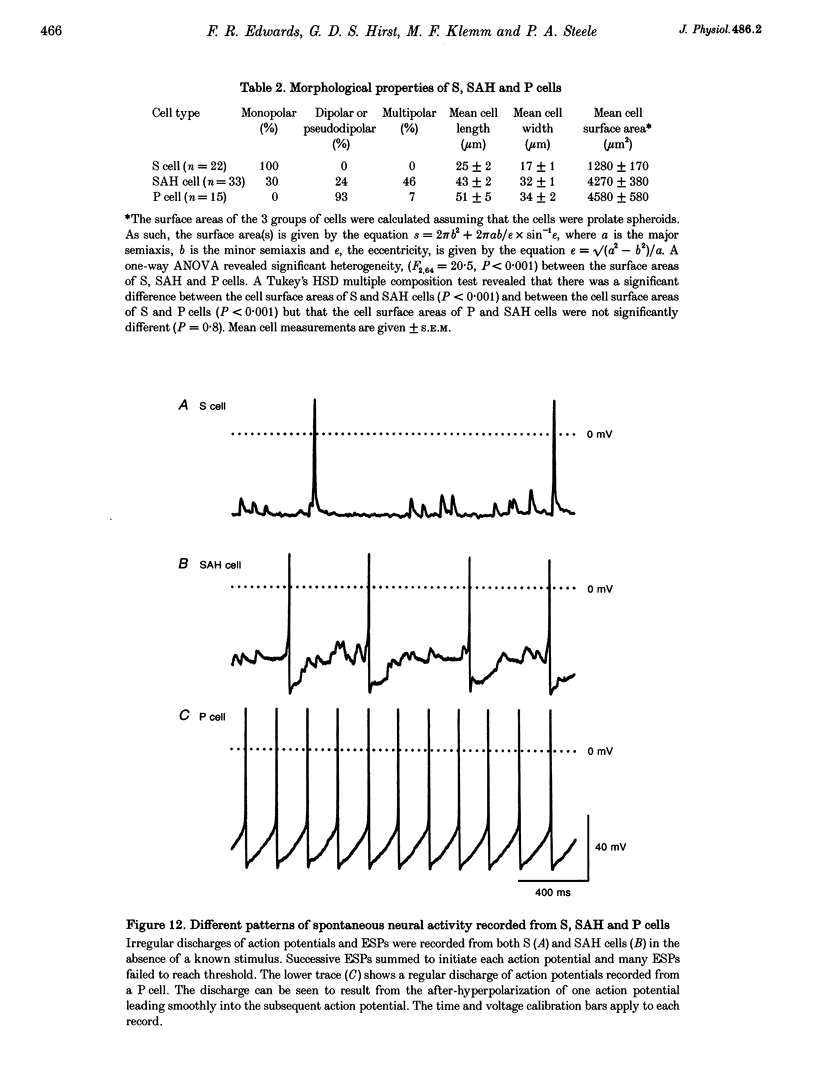
1. Intracellular recordings were made from the parasympathetic ganglion cells that lie in the epicardium of the left atrium of guinea-pig heart near the interatrial septum. 2. Three distinct types of neurone were identified on the basis of their electrophysiological properties. In one group of neurones, S cells, somatic action potentials were followed by brief after-hyperpolarizations. In the other two sets of neurones, somatic action potentials were followed by prolonged after-hyperpolarizations. The neurones with prominent after-hyperpolarization were further subdivided: one group of neurones, P cells, showed inward rectification at membrane potentials near the resting membrane potential whilst neurones in the other group, SAH cells, did so only at more negative potentials. 3. In the group of neurones that displayed inward rectification at potentials near rest, rectification resulted from the activation of an inward current, which resembled the hyperpolarization-activated inward current present in cardiac muscle pacemaker cells. 4. The three different types of neurone received different patterns of synaptic input. Each SAH cell received a synaptic excitatory connection from the vagus which in most cells released sufficient transmitter to initiate an action potential in that cell; several SAH cells also received a separate connection, which could be activated by local stimulation. Although most S cells failed to receive a synaptic input from the vagus, all of those tested received an excitatory synaptic input which could be activated by local stimulation. Virtually all P cells failed to receive a synaptic input from the vagus; in addition, local stimulation failed to initiate synaptic potentials in P cells. 5. When the structure of cardiac ganglion cells was determined, by loading the cells with either biocytin or neurobiotin, it was found that most cells lacked extensive dendritic processes. S cells were invariably monopolar, most P cells were dipolar or pseudodipolar, whereas many SAH cells were multipolar. 6. In many neurones an on-going discharge of action potentials was detected in the absence of obvious stimulation. In S and SAH cells, the action potentials resulted from an on-going discharge of excitatory synaptic potentials. However, when a spontaneous discharge of action potentials was detected in P cells a discharge of excitatory synaptic potentials was not detected. 7. The results are discussed in relation to the idea that the three different types of cell may have different functions and that some of the cells may be organized in such a way as to permit the local handling of neuronal information within the heart.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. G., Burnstock G. A voltage-clamp study of the electrophysiological characteristics of the intramural neurones of the rat trachea. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:593–614. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen T. G., Burnstock G. Intracellular studies of the electrophysiological properties of cultured intracardiac neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:349–366. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman J. G., Purves R. D. Intracellular recordings from ganglia of the thoracic sympathetic chain of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):173–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell J. F., Clark A. L., McLachlan E. M. Characteristics of phasic and tonic sympathetic ganglion cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:457–483. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell J. F., McLachlan E. M. The effect of a transient outward current (IA) on synaptic potentials in sympathetic ganglion cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:273–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Tse A., Giles W. R. Electrophysiology of parasympathetic neurones isolated from the interatrial septum of bull-frog heart. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:89–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowcroft P. J., Holman M. E., Szurszewski J. H. Excitatory input from the distal colon to the inferior mesenteric ganglion in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):443–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES F., FRANCIS E. T. B., KING T. S. Neurological studies of the cardiac ventricles of mammals. J Anat. 1952 Apr;86(2):130–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Gerschenfeld H. M. Some physiological properties of identified mammalian neuroglial cells. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):211–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Harris A. J., Kuffler S. W. Synaptic transmission and its duplication by focally applied acetylcholine in parasympathetic neurons in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):509–539. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. The cardiac hyperpolarizing-activated current, if. Origins and developments. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;46(3):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardi M., Randall W. C., Bieger D., Wurster R. D., Hopkins D. A., Armour J. A. Activity of in vivo canine cardiac plexus neurons. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H789–H800. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Bramich N. J., Edwards F. R., Klemm M. Transmission at autonomic neuroeffector junctions. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Feb;15(2):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The slow calcium-dependent potassium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:315–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. A nervous mechanism for descending inhibition in guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):129–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McLachlan E. M. Development of dendritic calcium currents in ganglion cells of the rat lower lumbar sympathetic chain. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:349–368. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McLachlan E. M. Post-natal development of ganglia in the lower lumbar sympathetic chain of the rat. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:119–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julé Y., Szurszewski J. H. Electrophysiology of neurones of the inferior mesenteric ganglion of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:277–292. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keast J. R., McLachlan E. M., Meckler R. L. Relation between electrophysiological class and neuropeptide content of guinea pig sympathetic prevertebral neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Feb;69(2):384–394. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.2.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King B. F., Love J. A., Szurszewski J. H. Intracellular recordings from pancreatic ganglia of the cat. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:379–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. A voltage-clamp analysis of inward (anomalous) rectification in mouse spinal sensory ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:19–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Depression of calcium-dependent potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones by muscarinic agonists. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The characteristics of synaptic currents and responses to acetylcholine of rat submandibular ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:23–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selyanko A. A., Skok V. I. Synaptic transmission in rat cardiac neurones. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1992 Jul;39(3):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(92)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain W. J., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E. Anomalous rectification in neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1987 May;57(5):1555–1576. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.5.1555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele P. A., Gibbins I. L., Morris J. L., Mayer B. Multiple populations of neuropeptide-containing intrinsic neurons in the guinea-pig heart. Neuroscience. 1994 Sep;62(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T., Akasu T. Cyclic AMP regulates an inward rectifying sodium-potassium current in dissociated bull-frog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Jan;420:409–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi X. H., Thomas J. X., Jr, Randall W. C., Wurster R. D. Intracellular recordings from canine intracardiac ganglion cells. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1991 Feb;32(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(91)90068-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi X., Randall W. C., Wurster R. D. Electrophysiological properties of canine cardiac ganglion cell types. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1994 Apr;47(1-2):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z. J., Adams D. J. Resting membrane potential and potassium currents in cultured parasympathetic neurones from rat intracardiac ganglia. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:405–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z. J., Adams D. J. Voltage-dependent sodium and calcium currents in cultured parasympathetic neurones from rat intracardiac ganglia. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:425–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara K., Irisawa H. Inward current activated during hyperpolarization in the rabbit sinoatrial node cell. Pflugers Arch. 1980 May;385(1):11–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00583909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Lipsius S. L. Properties of the pacemaker current (If) in latent pacemaker cells isolated from cat right atrium. J Physiol. 1992;453:503–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]