Abstract
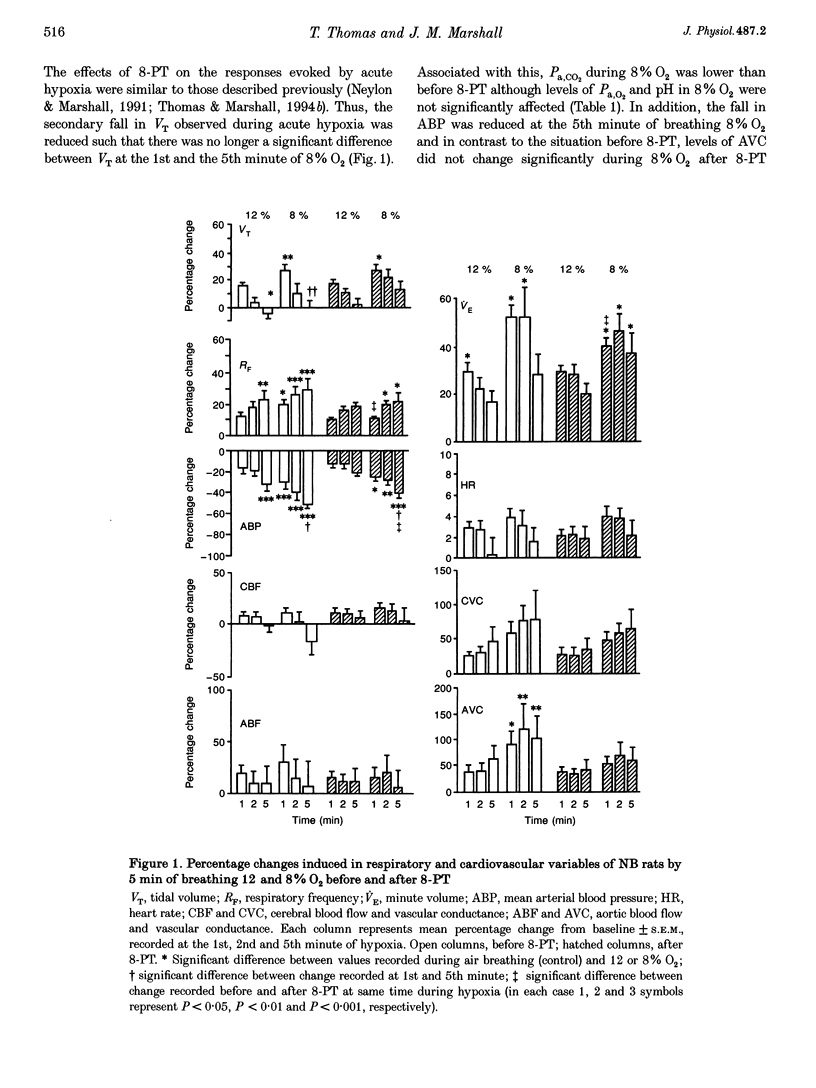
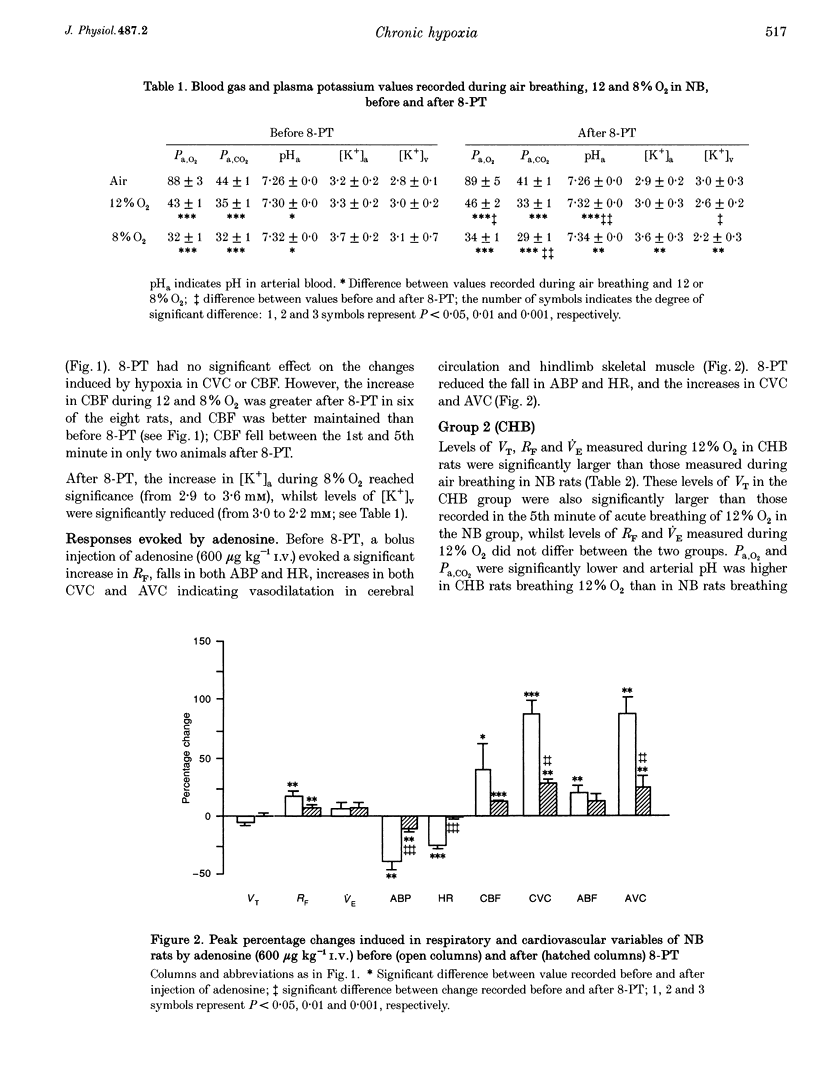
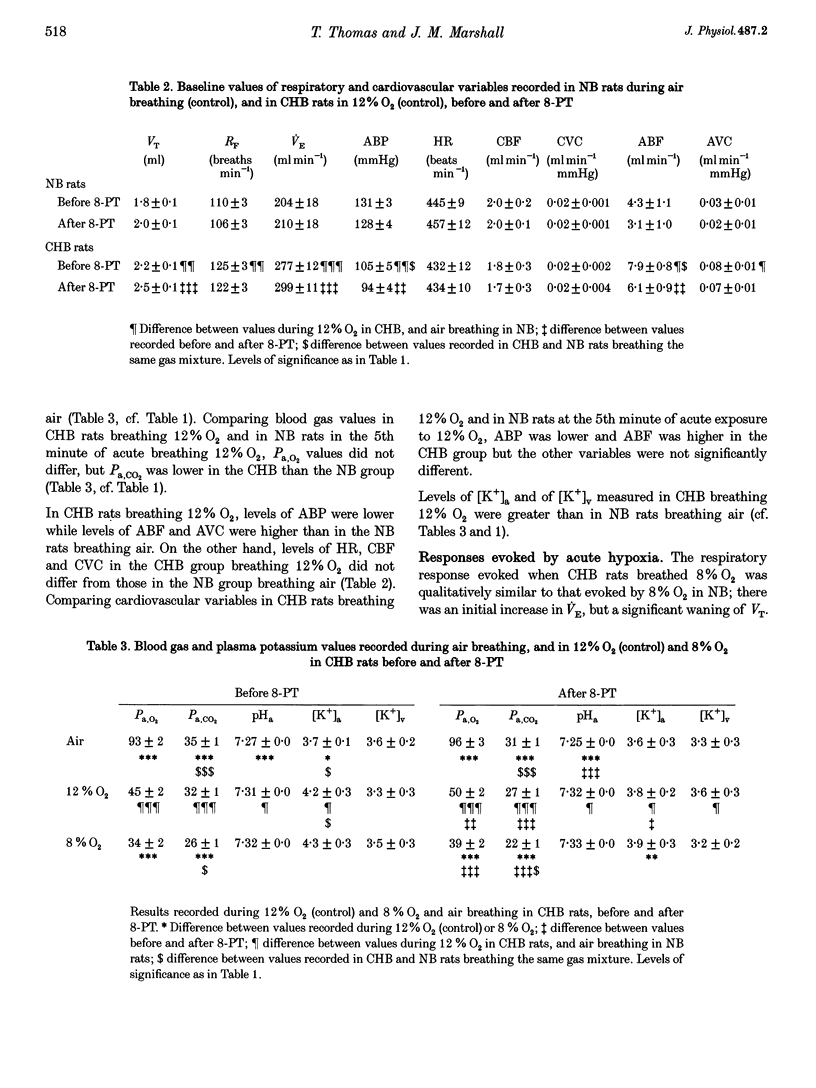
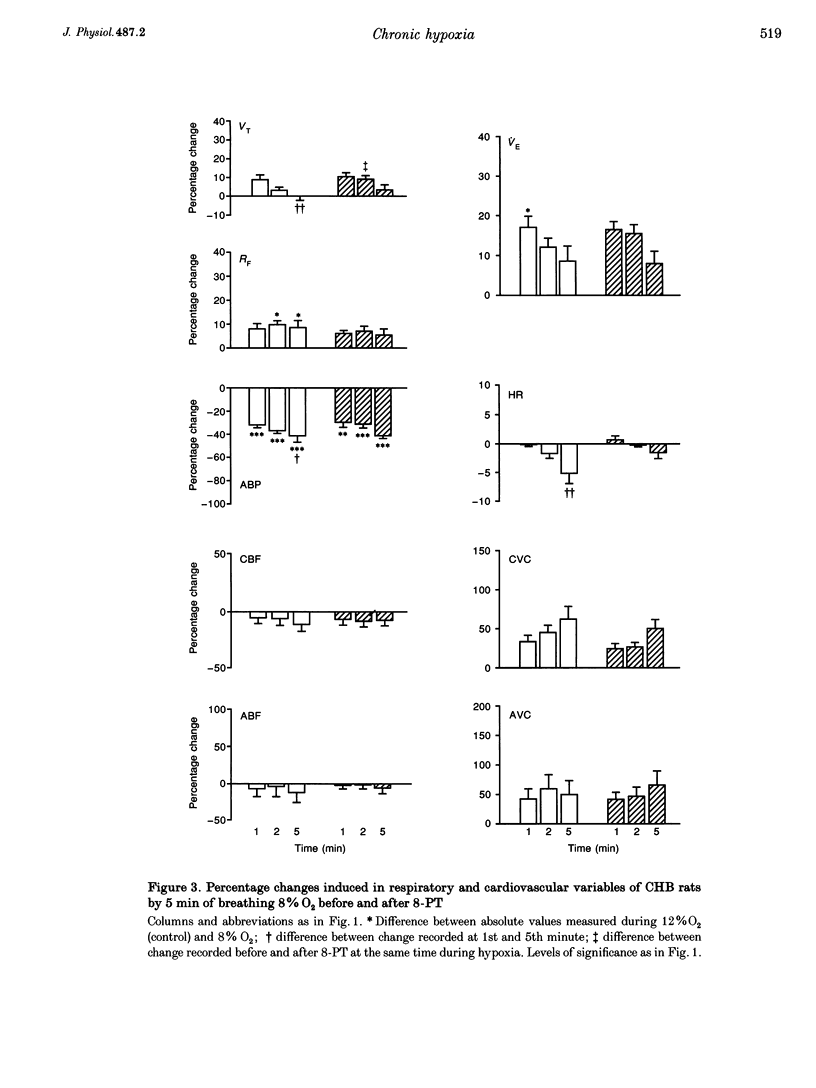
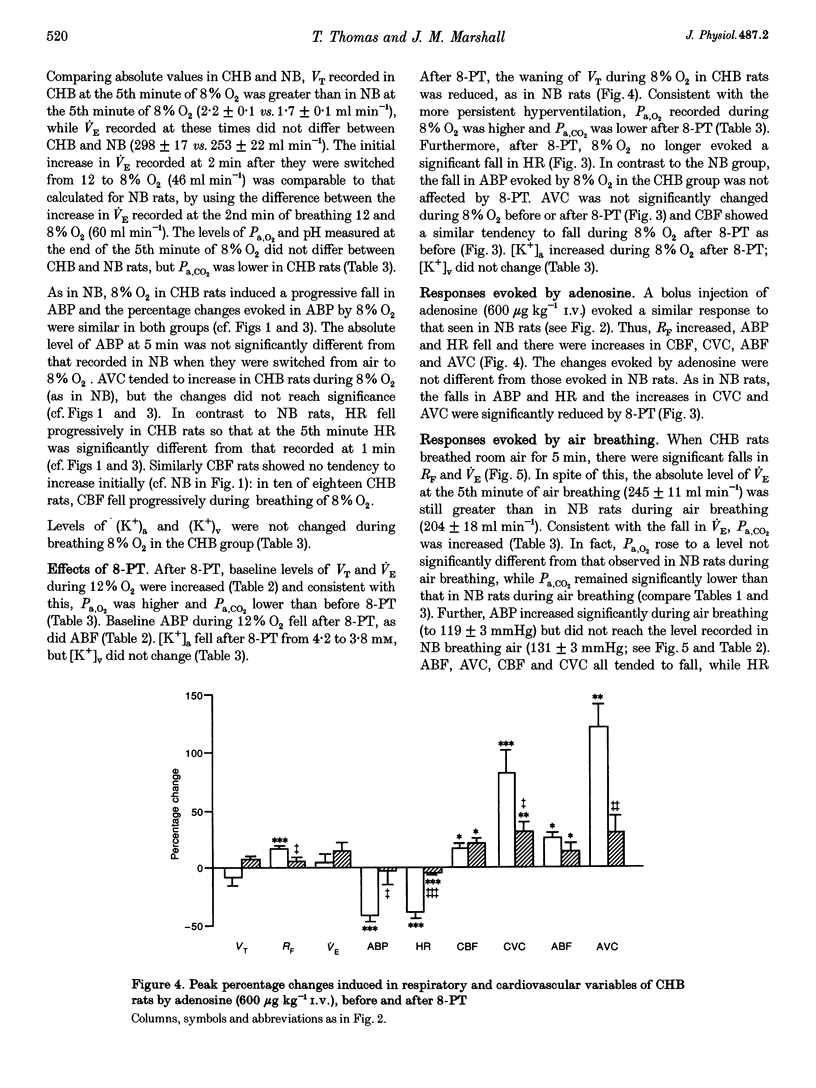
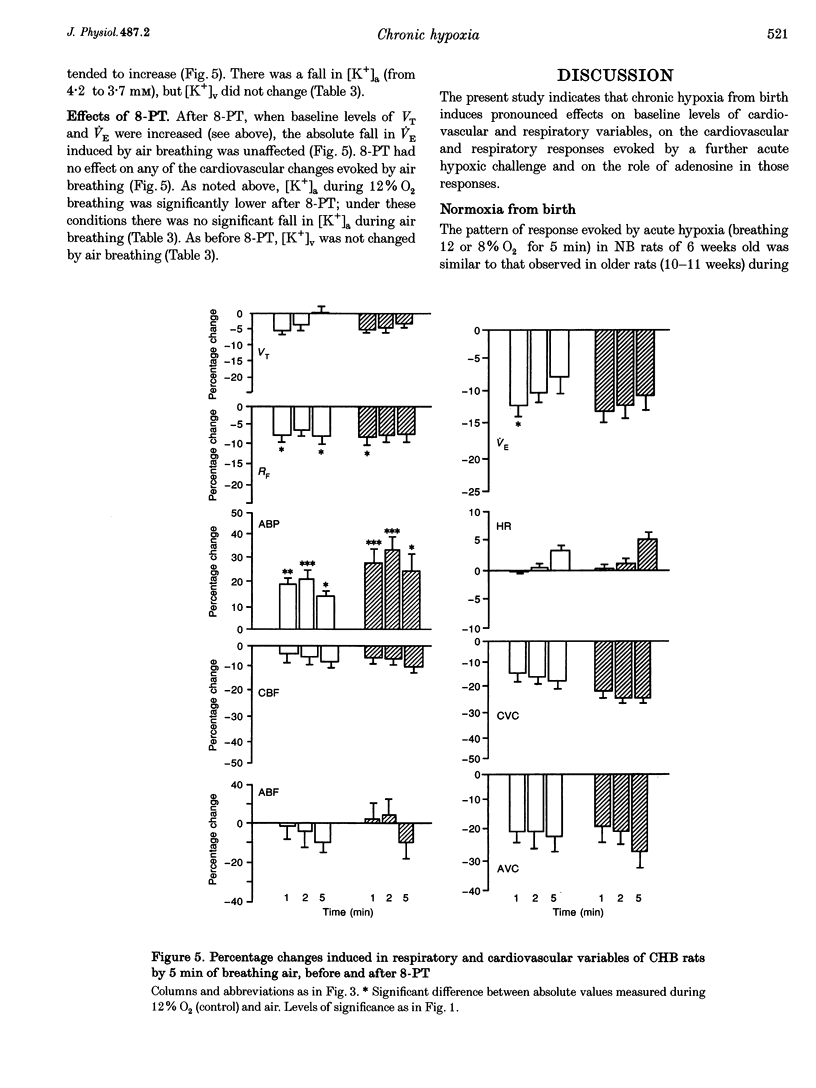
1. Comparative studies were performed on eighteen rats 54 days old made chronically hypoxic from birth in an hypoxic chamber at 12% O2 (CHB), and in eight weight-matched control rats (NB, 42 days old); both CHB and NB rats were anaesthetized with Saffan. 2. In NB rats, breathing 12 or 8% O2 for 5 min induced a pattern of response comparable to that described in older rats (10-11 weeks old): an initial increase and secondary fall in minute volume (VE), a fall in arterial pressure (ABP), an increase in muscle vascular conductance, while cerebral blood flow (CBF) increased at the 1st minute in six animals and fell by the 5th minute in all animals. The adenosine receptor antagonist 8-phenyl-theophylline (8-PT, 10 mg kg-1) reduced the secondary fall in VE, the fall in ABP and muscle vasodilatation, indicating they were partly mediated by adenosine. 3. In CHB rats breathing 12% O2, VE was higher (277 +/- 12 vs. 204 +/- 18 ml min-1), arterial partial pressures of O2 (45 +/- 2 vs. 88 +/- 3 mmHg), CO2 (32 +/- 1 vs. 44 +/- 1 mmHg) and ABP (105 +/- 5 vs. 131 +/- 5 mmHg) were lower, while muscle vascular conductance was higher (0.08 +/- 0.01 vs. 0.03 +/- 0.01 ml min-1 mmHg-1) than in NB rats breathing air; these differences were reduced, but not abolished, when CHB rats acutely breathed air for 5 min. 4. In CHB rats, the smaller change from 12 to 8% O2 for 5 min evoked a similar pattern of response to that evoked by 8% O2 in NB rats, except that heart rate (HR) and CBF decreased progressively. However, 8-PT increased baseline VE and reduced ABP in 12% O2 and reduced the secondary decrease in VE and HR evoked by 8% O2, but had no effect on the fall in ABP, or change in muscle vascular conductance. 5. We propose that in CHB rats (i) there is accentuation of the components of the response to acute hypoxia (the fall in ABP, HR and CBF) that form a positive feedback loop which promotes central ventilatory depression and (ii) that adenosine exerts a tonic inhibitory influence on VE and vasodilator influence in muscle and mediates the secondary fall in VE, but not the muscle vasodilation induced by acute hypoxia.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alippi R. M., Barceló A. C., Río M. E., Bozzini C. E. Growth retardation in the early developing rat exposed to continuous hypobaric hypoxia. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1983;33(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., Dawes G. S., Fisher R., Pinter S., Robinson J. S. Foetal respiratory movements, electrocortical and cardiovascular responses to hypoxaemia and hypercapnia in sheep. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):599–618. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonora M., Marlot D., Gautier H., Duron B. Effects of hypoxia on ventilation during postnatal development in conscious kittens. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Jun;56(6):1464–1471. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.6.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. E., Estavillo J. A., Kumar P., Nye P. C., Paterson D. J. Effects of potassium, oxygen and carbon dioxide on the steady-state discharge of cat carotid body chemoreceptors. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:519–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Förstermann U., Matsuda H., Pohl U. The role of prostaglandins in the endothelium-mediated vasodilatory response to hypoxia. Pflugers Arch. 1984 May;401(1):77–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00581536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T. Regulation of active Na+-K+ transport in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1986 Jul;66(3):542–580. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton P. A., Slykerman L. J., Anthonisen N. R. Ventilatory response to sustained hypoxia in normal adults. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Sep;61(3):906–911. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.3.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden G. J., Hanson M. A. Effects of chronic hypoxia from birth on the ventilatory response to acute hypoxia in the newborn rat. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:11–19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden G. J., Hanson M. A. Maturation of the respiratory response to acute hypoxia in the newborn rat. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:1–9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froldi G., Belardinelli L. Species-dependent effects of adenosine on heart rate and atrioventricular nodal conduction. Mechanism and physiological implications. Circ Res. 1990 Oct;67(4):960–978. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.4.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. A., Kumar P., Williams B. A. The effect of chronic hypoxia upon the development of respiratory chemoreflexes in the newborn kitten. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:563–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Coupling of ATP-sensitive K+ channels to A1 receptors by G proteins in rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):H820–H826. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.3.H820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahira I., Heisler N., Piiper J., Gonzalez N. C. Effect of chronic hypoxia on hemodynamics, organ blood flow and O2 supply in rats. Respir Physiol. 1993 May;92(2):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(93)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaManna J. C., Vendel L. M., Farrell R. M. Brain adaptation to chronic hypobaric hypoxia in rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jun;72(6):2238–2243. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.6.2238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M., Metcalfe J. D. Analysis of the cardiovascular changes induced in the rat by graded levels of systemic hypoxia. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:385–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M., Metcalfe J. D. Effects of systemic hypoxia on the distribution of cardiac output in the rat. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:335–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M., Thomas T., Turner L. A link between adenosine, ATP-sensitive K+ channels, potassium and muscle vasodilatation in the rat in systemic hypoxia. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:1–9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian R., Marshall J. M., Kumar P. Interactions between K+ and beta 2-adrenoreceptors in determining muscle vasodilatation induced in the rat by systemic hypoxia. Exp Physiol. 1990 May;75(3):407–410. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1990.sp003416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian R., Marshall J. M. The roles of catecholamines in responses evoked in arterioles and venules of rat skeletal muscle by systemic hypoxia. J Physiol. 1991 May;436:499–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortola J. P., Morgan C. A., Virgona V. Respiratory adaptation to chronic hypoxia in newborn rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Oct;61(4):1329–1336. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.4.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L. Organ and cellular development in mice growing at simulated high altitude. Lab Invest. 1966 Apr;15(4):700–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon M., Marshall J. M. The role of adenosine in the respiratory and cardiovascular response to systemic hypoxia in the rat. J Physiol. 1991;440:529–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. B., Jr, Dempsey J. A. Rat as a model for humanlike ventilatory adaptation to chronic hypoxia. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 May;44(5):763–769. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.44.5.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Pearson J. D. Cardiovascular purinoceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):761–845. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STICKNEY J. C., VAN LIERE E. J. Acclimatization to low oxygen tension. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jan;33(1):13–34. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner N. S., Jr, Powell W. J., Jr Action of oxygen and potassium on vascular resistance of dog skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1967 Mar;212(3):533–540. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.3.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder G. K., Byers R. L., Kayar S. R. Effects of hypoxia on tissue capillarity in geese. Respir Physiol. 1984 Nov;58(2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90144-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Studies of the unitary properties of adenosine-5'-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:213–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Elnazir B. K., Marshall J. M. Differentiation of the peripherally mediated from the centrally mediated influences of adenosine in the rat during systemic hypoxia. Exp Physiol. 1994 Sep;79(5):809–822. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1994.sp003809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Marshall J. M. Interdependence of respiratory and cardiovascular changes induced by systemic hypoxia in the rat: the roles of adenosine. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 1;480(Pt 3):627–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



