Abstract
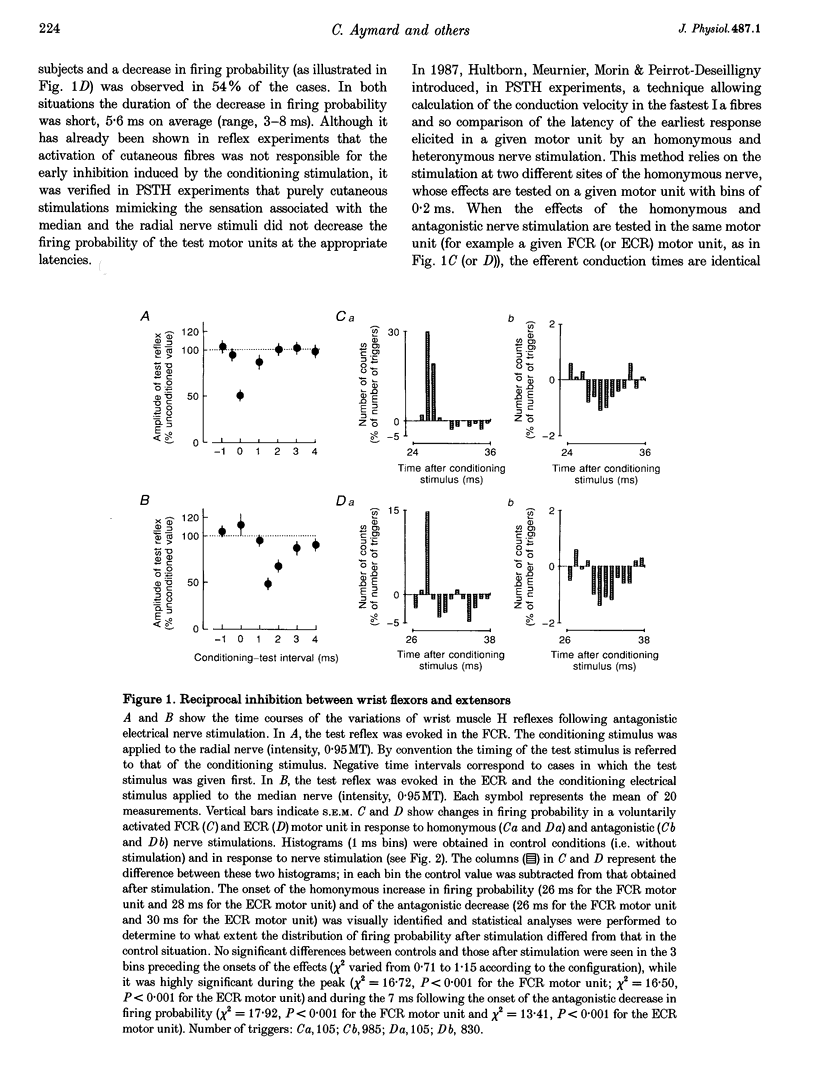
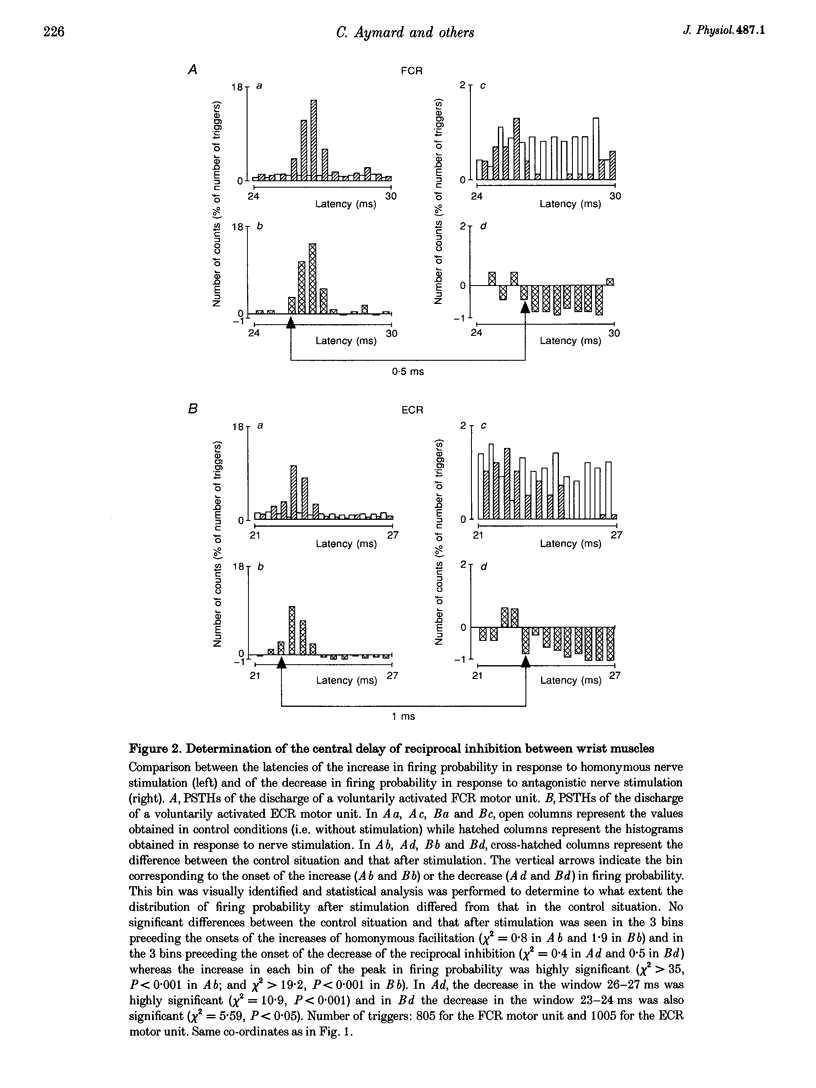
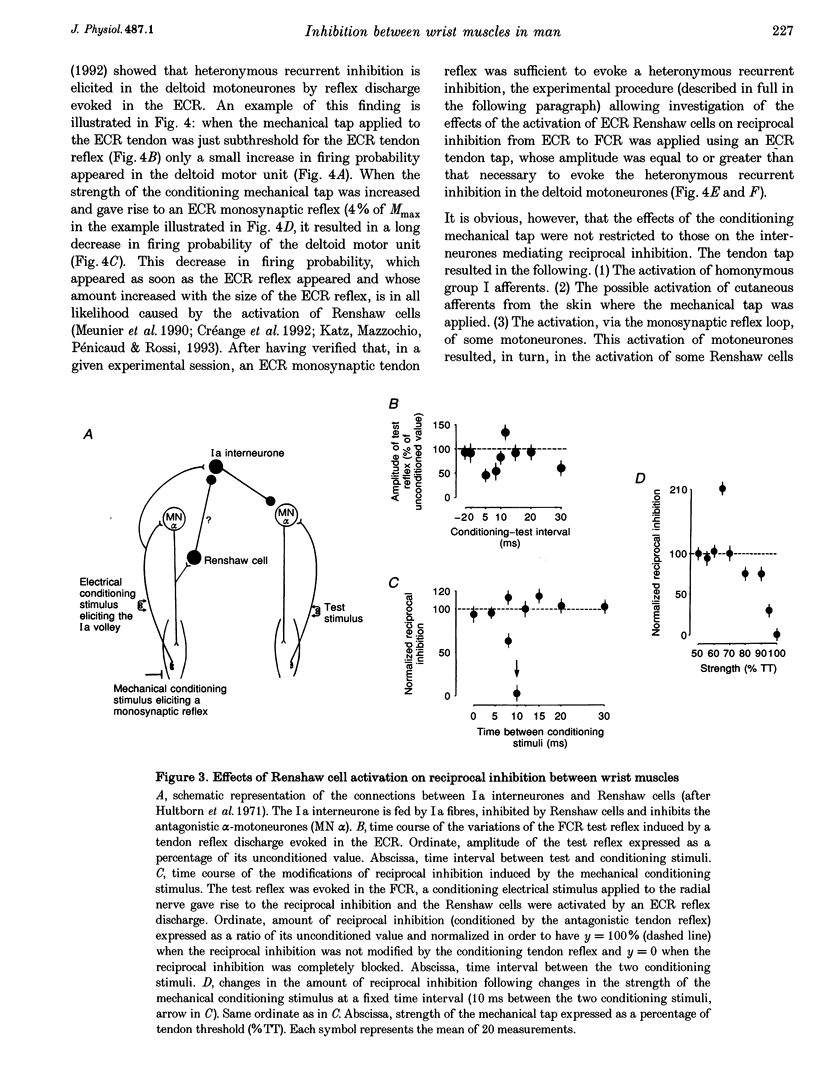
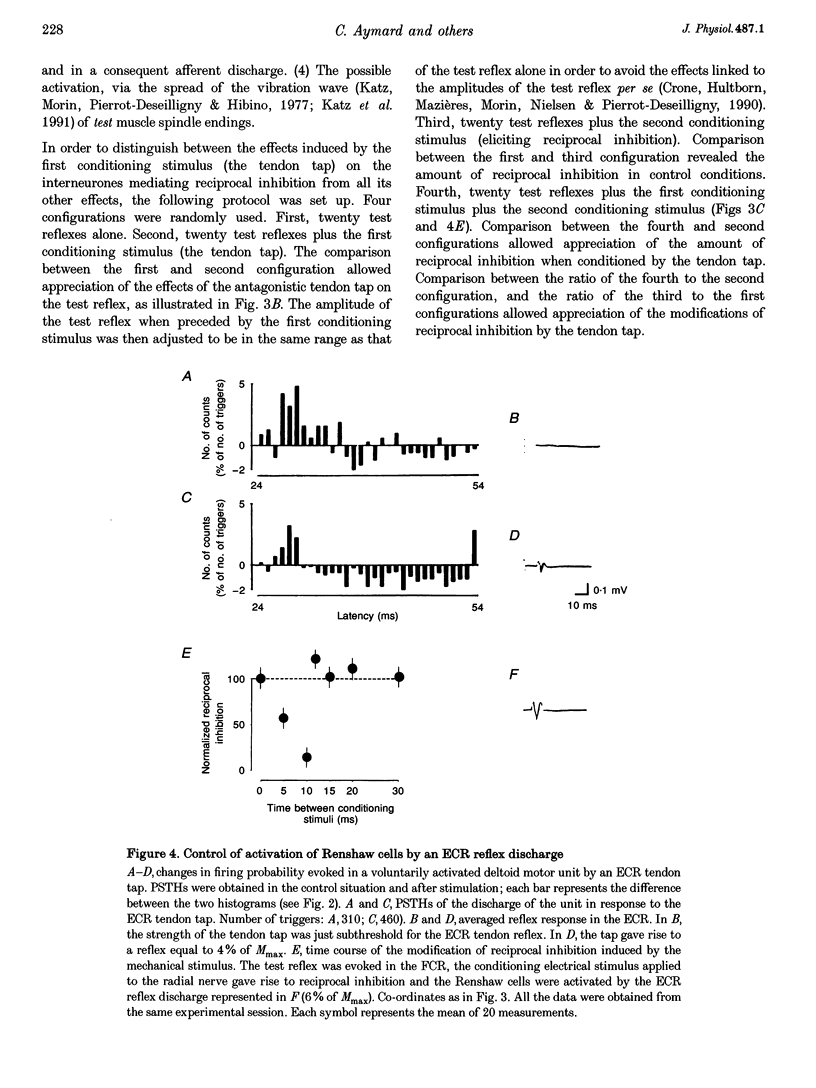
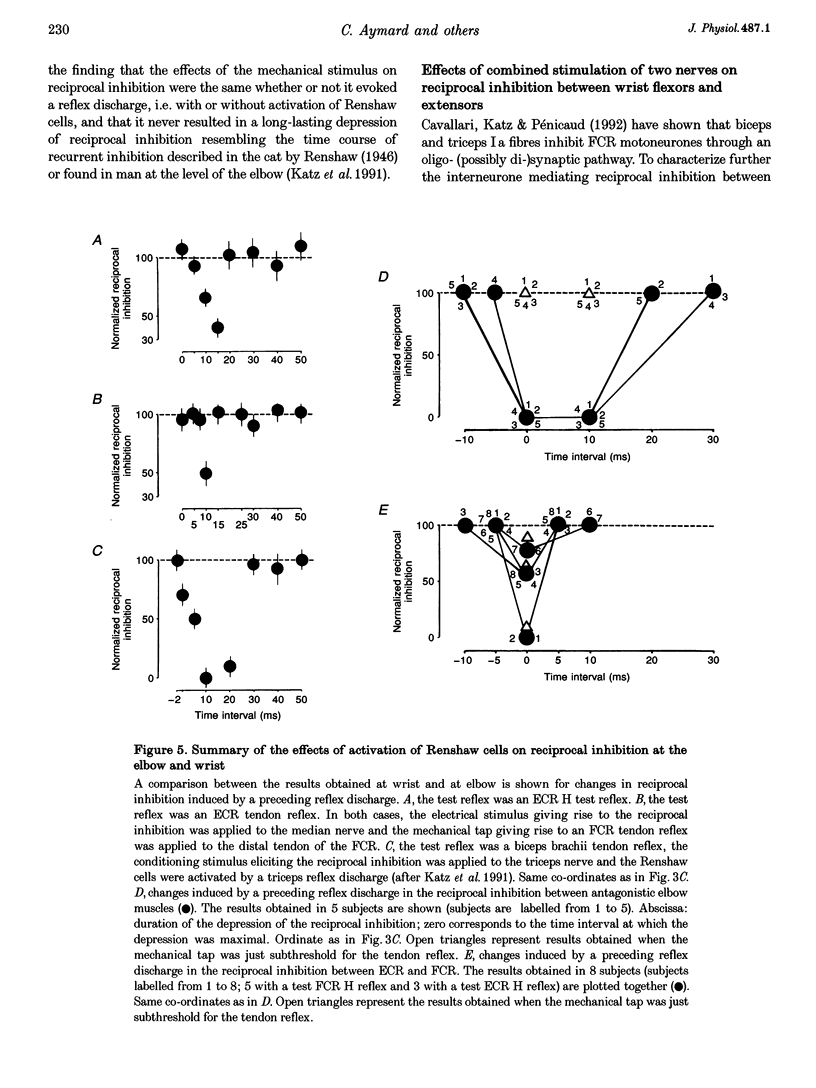
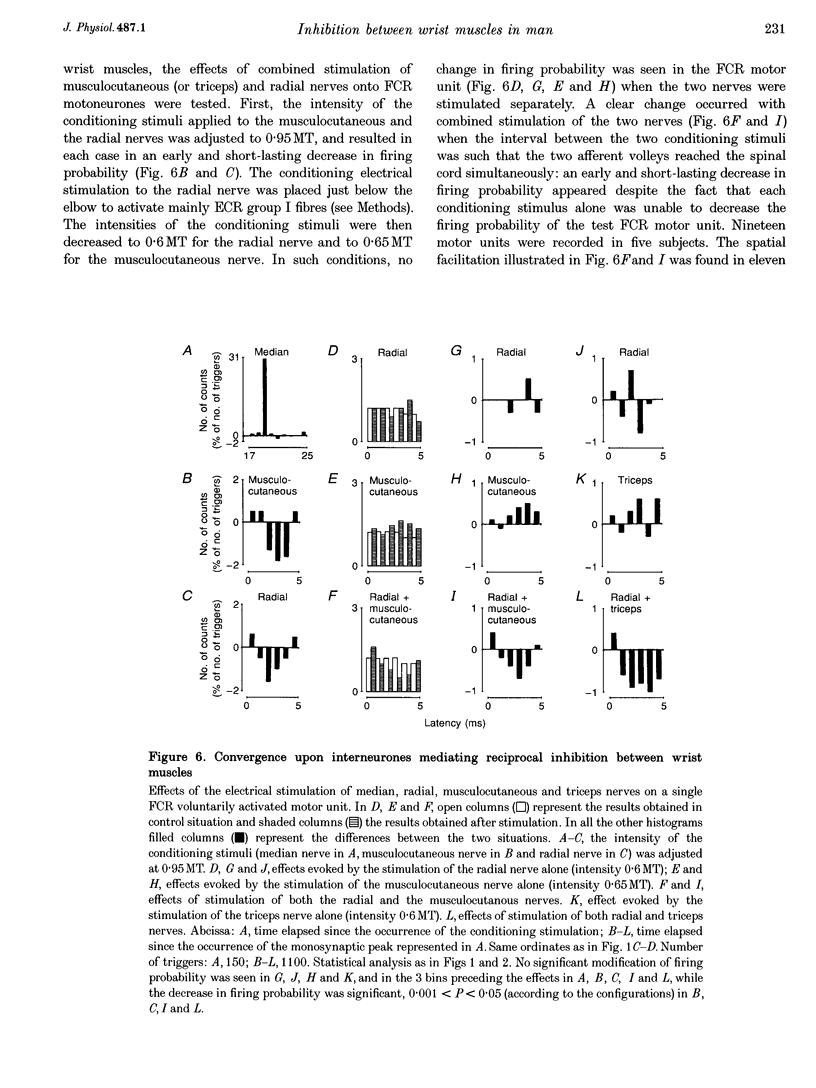
1. Interneurones mediating reciprocal inhibition between wrist flexors and extensors in man are characterized using both Renshaw cells and transarticular group I afferent activation. 2. Renshaw cells were activated by reflex discharges evoked by a tendon tap. The tendon tap was applied to the tendon of the muscles from which the Ia fibres responsible for the reciprocal inhibition originated. Contrary to what was observed both in the cat hindlimb and in human elbow muscles, this Renshaw cell activation never resulted in a long depression of the reciprocal inhibition between wrist flexors and extensors. 3. Convergence from group I elbow muscle afferents and antagonistic group I afferents onto interneurones mediating reciprocal inhibition between wrist muscles was revealed in post-stimulus time histogram (PSTH) experiments using the technique of spatial facilitation. 4. The characteristics of the interneurones mediating reciprocal inhibition between wrist flexors and extensors could therefore be summarized as follows: (a) they are fed by antagonistic group I afferents and group I afferents originating from both flexor and extensor elbow muscles; (b) they are not inhibited by Renshaw cells; (c) they are not excited by low threshold cutaneous afferents; and (d) they are probably interposed in a disynaptic pathway. 5. It is therefore concluded that interneurones mediating reciprocal inhibition between wrist flexors and extensors in man differ both from Ia interneurones and from interneurones interposed in the Ib reflex pathways and these characteristics are related to the complex circumduction movements developed in the wrist.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldissera F., Campadelli P., Cavallari P. Inhibition from radial group I afferents of H-reflex in wrist flexors. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1983 Mar-Apr;23(3):187–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera F., Cavallari P., Fournier E., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Evidence for mutual inhibition of opposite Ia interneurones in the human upper limb. Exp Brain Res. 1987;66(1):106–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00236207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussel B., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Inhibition of human motoneurons, probably of Renshaw origin, elicited by an orthodromic motor discharge. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):319–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari P., Fournier E., Katz R., Malmgren K., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in Ib reflex pathways in the human upper limb. Exp Brain Res. 1985;60(1):197–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00237033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari P., Katz R. Pattern of projections of group I afferents from forearm muscles to motoneurones supplying biceps and triceps muscles in man. Exp Brain Res. 1989;78(3):465–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00230235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari P., Katz R., Penicaud A. Pattern of projections of group I afferents from elbow muscles to motoneurones supplying wrist muscles in man. Exp Brain Res. 1992;91(2):311–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00231664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C., Hultborn H., Mazières L., Morin C., Nielsen J., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Sensitivity of monosynaptic test reflexes to facilitation and inhibition as a function of the test reflex size: a study in man and the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1990;81(1):35–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00230098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Créange A., Faist M., Katz R., Pénicaud A. Distribution of heteronymous Ia facilitation and recurrent inhibition in the human deltoid motor nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1992;90(3):620–624. doi: 10.1007/BF00230946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day B. L., Marsden C. D., Obeso J. A., Rothwell J. C. Reciprocal inhibition between the muscles of the human forearm. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:519–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Gustafsson B. Relation between shapes of post-synaptic potentials and changes in firing probability of cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:387–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Evidence for interneuronally mediated Ia excitatory effects to human quadriceps motoneurones. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:143–169. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Illert M., Santini M. Convergence on interneurones mediating the reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. I. Disynaptic Ia inhibition of Ia inhibitory interneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Feb;96(2):193–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition from motor axon collaterals of transmission in the Ia inhibitory pathway to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):591–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Meunier S., Morin C., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Assessing changes in presynaptic inhibition of I a fibres: a study in man and the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:729–756. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Wigström H. Recurrent inhibition and afterhyperpolarization following motoneuronal discharge in the cat. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Udo M. Convergence of large muscle spindle (Ia) afferents at interneuronal level in the reciprocal Ia inhibitory pathway to motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Apr;84(4):493–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E. Interneuronal relay in spinal pathways from proprioceptors. Prog Neurobiol. 1992;38(4):335–378. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(92)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D. A. Shared reflex pathways from Ib tendon organ afferents and Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:99–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R., Mazzocchio R., Pénicaud A., Rossi A. Distribution of recurrent inhibition in the human upper limb. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993 Oct;149(2):183–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R., Morin C., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Hibino R. Conditioning of H reflex by a preceding subthreshold tendon reflex stimulus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Jun;40(6):575–580. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.6.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R., Penicaud A., Rossi A. Reciprocal Ia inhibition between elbow flexors and extensors in the human. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:269–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzocchio R., Rossi A. Further evidence for Renshaw inhibition in man. A combined electrophysiological and pharmacological approach. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Nov 20;106(1-2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier S., Penicaud A., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Rossi A. Monosynaptic Ia excitation and recurrent inhibition from quadriceps to ankle flexors and extensors in man. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:661–675. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno Y., Tanaka R., Yanagisawa N. Reciprocal group I inhibition on triceps surae motoneurons in man. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Nov;34(6):1010–1017. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.6.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Pattern of cutaneous inhibition of the propriospinal-like excitation to human upper limb motoneurones. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:169–182. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryall R. W. Renshaw cell mediated inhibition of Renshaw cells: patterns of excitation and inhibition from impulses in motor axon collaterals. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Mar;33(2):257–270. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


