Abstract
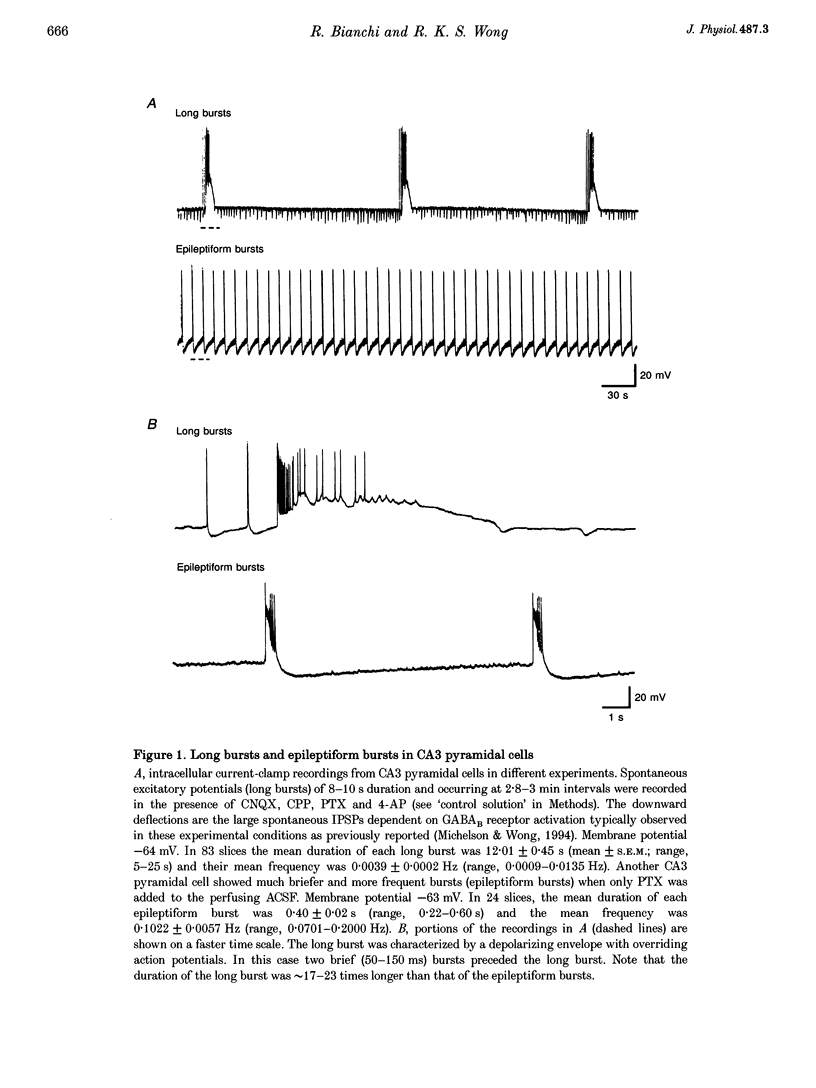
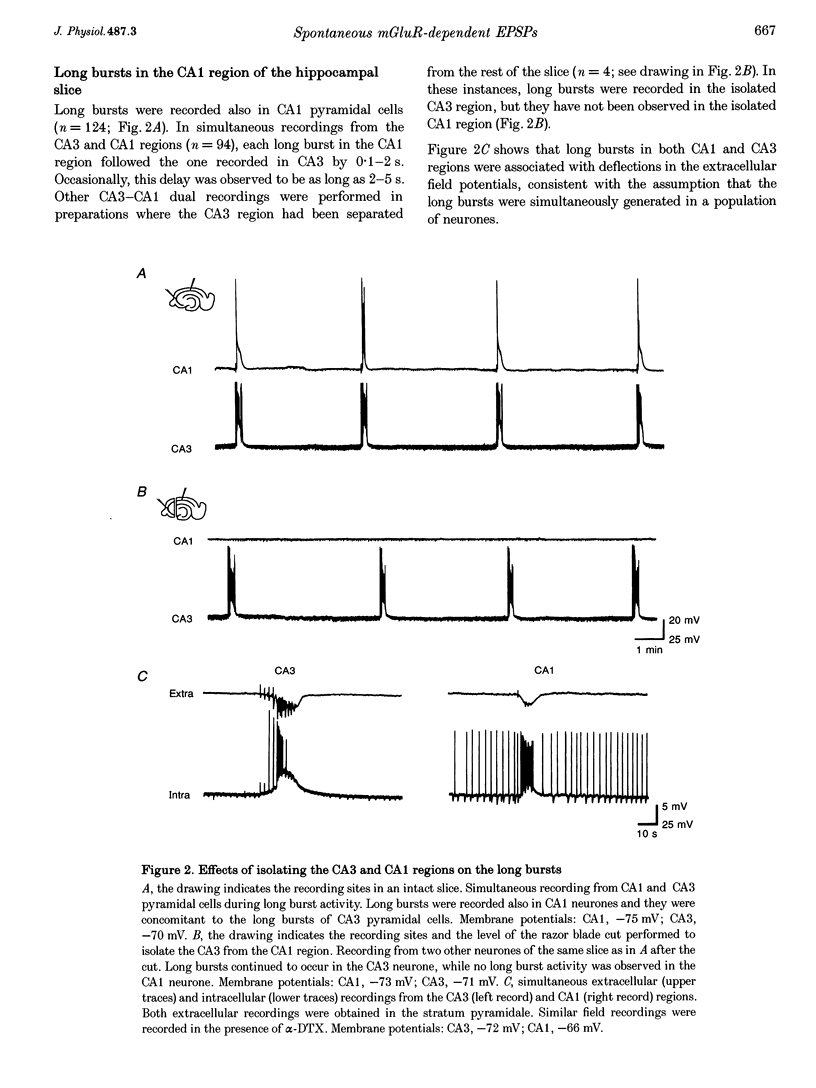
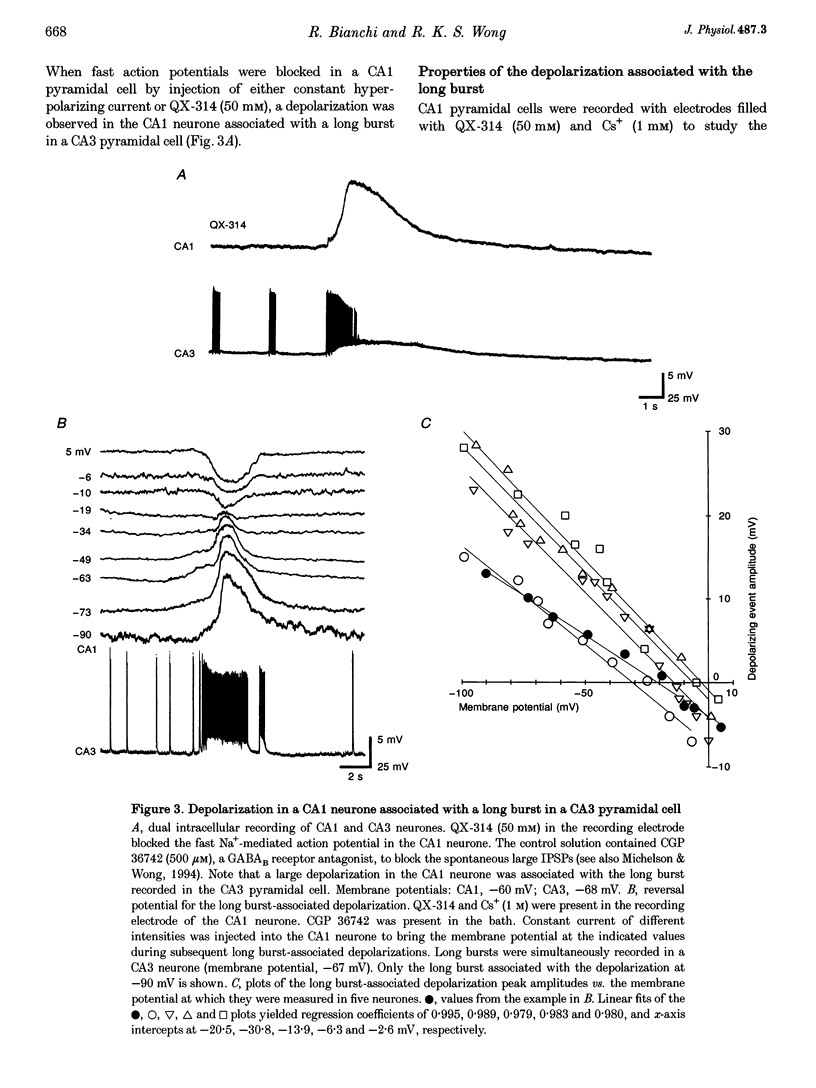
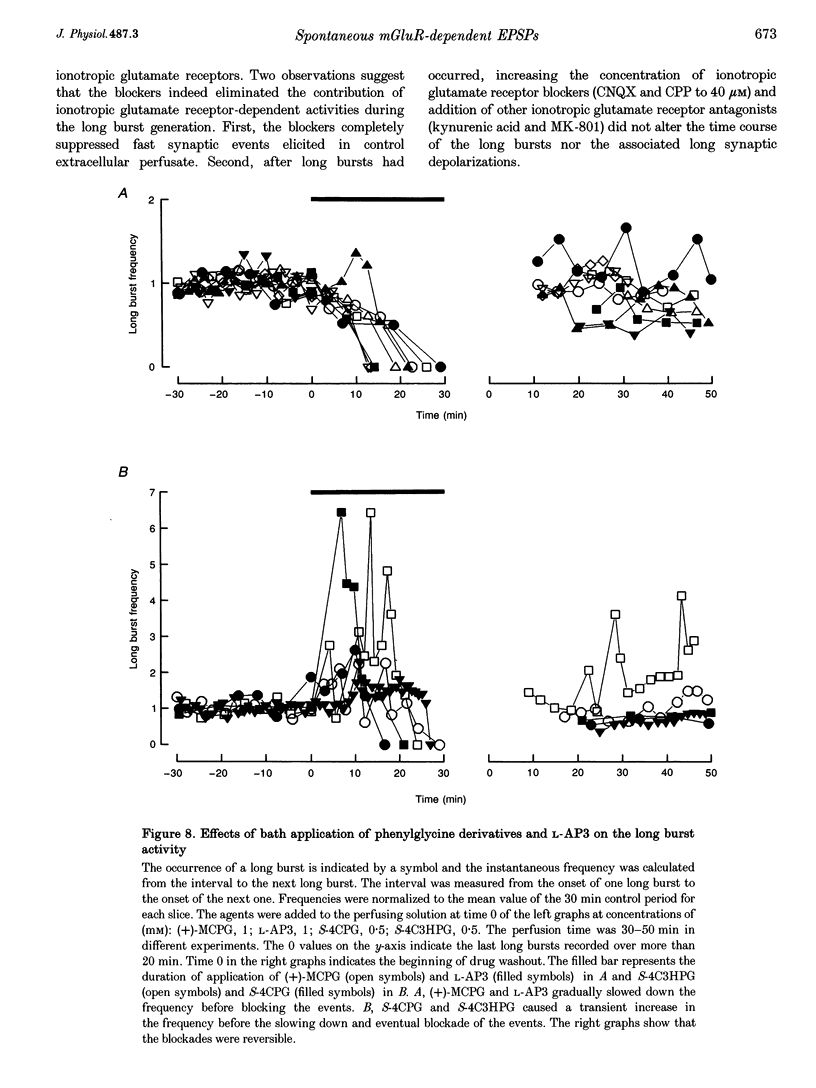
1. Intracellular and extracellular recordings of CA1 and CA3 neurones were performed in guinea-pig hippocampal slices to examine synaptic activities dependent on metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). 2. Long burst activities were elicited by 4-aminopyridine in the presence of ionotropic glutamate receptor and GABAA receptor blockers (6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione and 3-(RS-2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)-propyl-1-phosphonic acid, and picrotoxin). Long bursts were also elicited by alpha-dendrotoxin. 3. Long bursts consisted of a 5-25 s depolarization with overriding action potentials and occurred rhythmically at intervals ranging from 1 to 20 min. Long bursts were generated in a population of CA3 neurones and the synchronized output elicited long bursts in CA1 cells. Depolarizing potentials underlying long bursts in CA1 cells had a reversal potential of -14.8 +/- 5.1 mV. 4. Long burst-associated depolarizations in CA1 neurones were suppressed by local application of L-(+)-2-amino-3-phosphonopropionic acid (L-AP3) and of the phenylglycine derivatives (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine ((+)-MCPG), S-4-carboxyphenylglycine (S-4CPG) and S-4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine (S-4C3HPG). (-)-MCPG or atropine application did not affect the long burst-associated depolarization. 5. Bath perfusion of (+)-MCPG (0.5 mM), S-4CPG (0.5 mM), S-4C3HPG (0.5 mM) or L-AP3 (1 mM) blocked the occurrence of long bursts. 6. The results suggest that the long burst-associated depolarizations are synaptic potentials dependent on mGluR activation. Activation of mGluRs may also be involved in the generation of synchronized long bursts in the CA3 region.
Full text
PDF


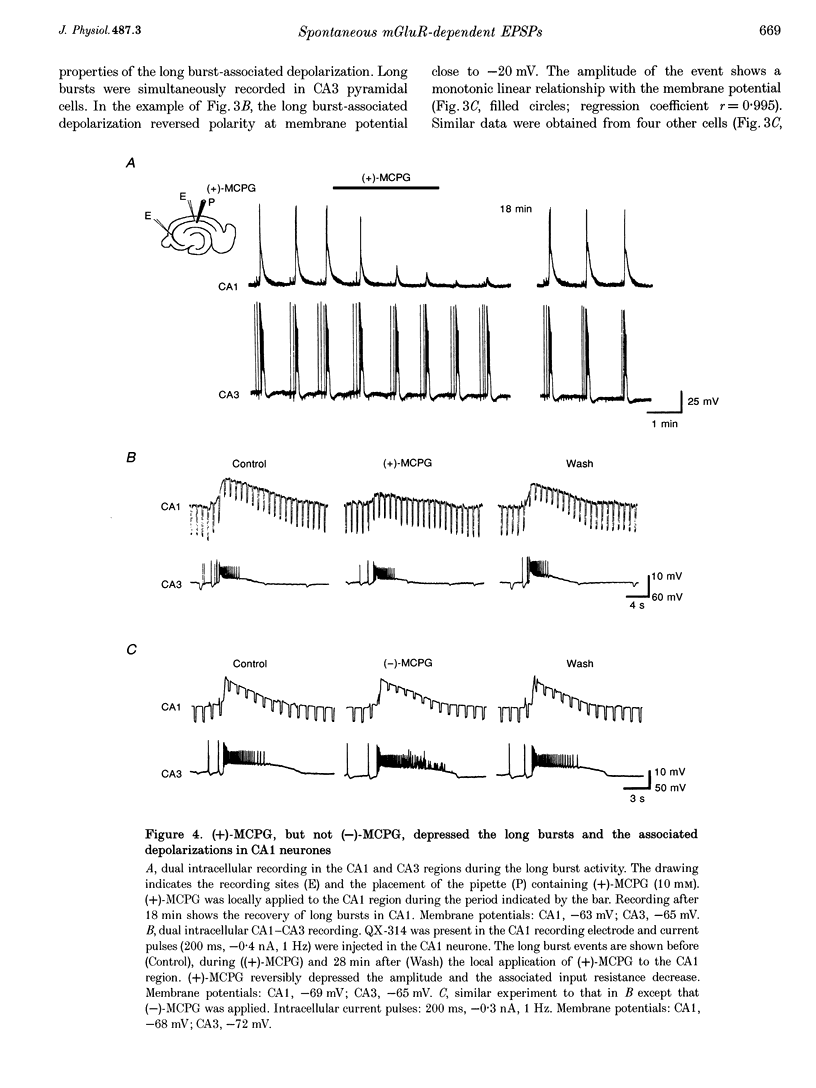
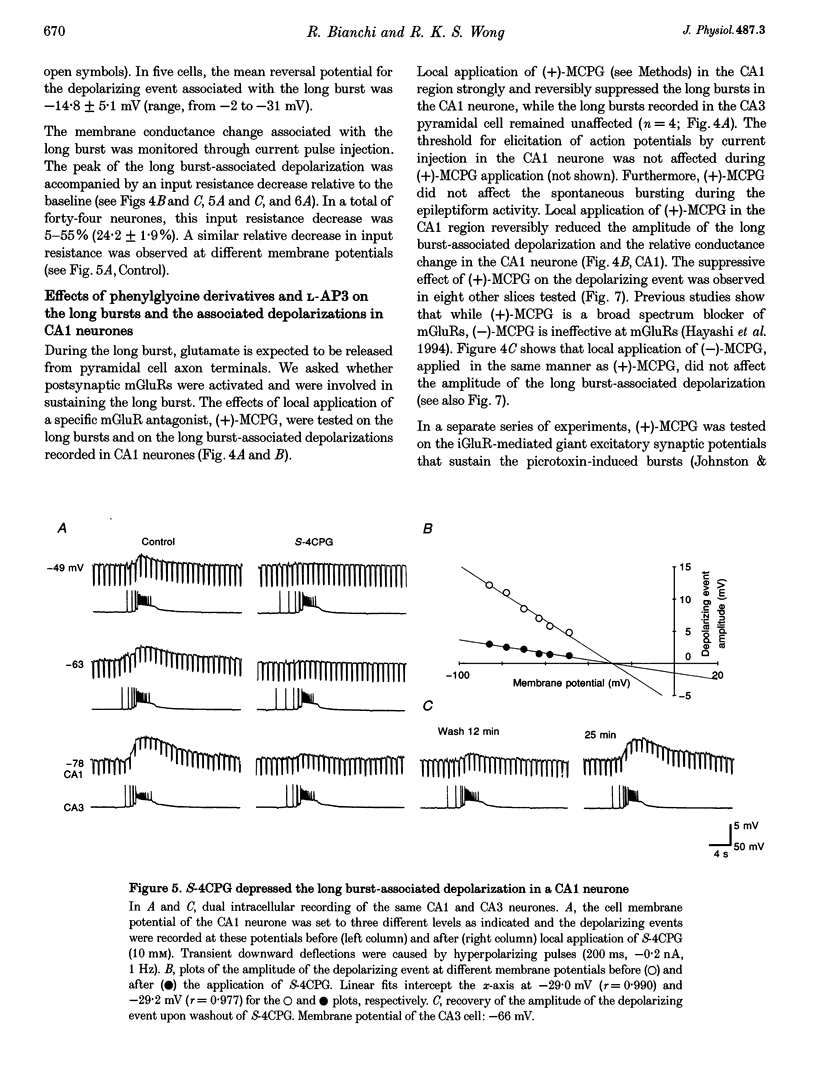
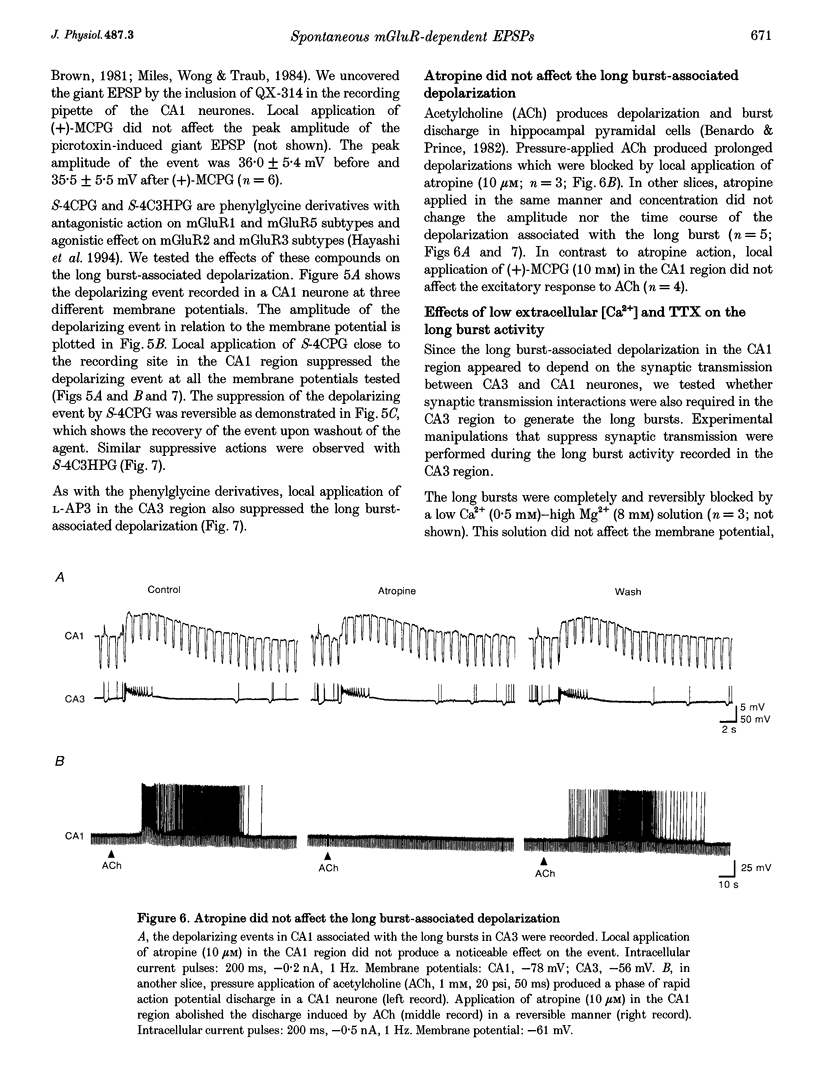
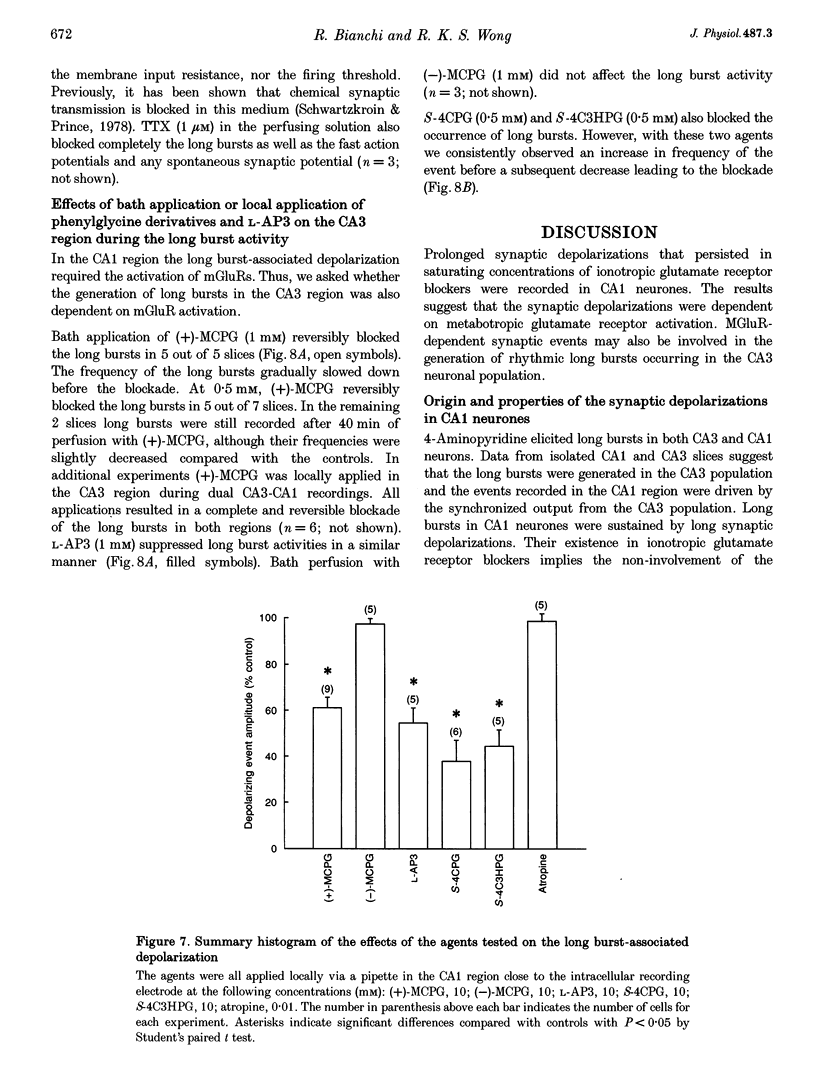



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aniksztejn L., Bregestovski P., Ben-Ari Y. Selective activation of quisqualate metabotropic receptor potentiates NMDA but not AMPA responses. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 3;205(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90921-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashir Z. I., Bortolotto Z. A., Davies C. H., Berretta N., Irving A. J., Seal A. J., Henley J. M., Jane D. E., Watkins J. C., Collingridge G. L. Induction of LTP in the hippocampus needs synaptic activation of glutamate metabotropic receptors. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):347–350. doi: 10.1038/363347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskys A., Malenka R. C. Agonists at metabotropic glutamate receptors presynaptically inhibit EPSCs in neonatal rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:687–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor A. M., Madge D. J., Garthwaite J. Synaptic activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the parallel fibre-Purkinje cell pathway in rat cerebellar slices. Neuroscience. 1994 Dec;63(4):911–915. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90558-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baude A., Nusser Z., Roberts J. D., Mulvihill E., McIlhinney R. A., Somogyi P. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1 alpha) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):771–787. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benardo L. S., Prince D. A. Cholinergic excitation of mammalian hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi R., Wong R. K. Carbachol-induced synchronized rhythmic bursts in CA3 neurons of guinea pig hippocampus in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Jul;72(1):131–138. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpak S., Gähwiler B. H., Do K. Q., Knöpfel T. Potassium conductances in hippocampal neurons blocked by excitatory amino-acid transmitters. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):765–767. doi: 10.1038/347765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpak S., Gähwiler B. H. Glutamate mediates a slow synaptic response in hippocampal slice cultures. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Mar 22;243(1308):221–226. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinestra P., Aniksztejn L., Diabira D., Ben-Ari Y. (RS)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine neither prevents induction of LTP nor antagonizes metabotropic glutamate receptors in CA1 hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Dec;70(6):2684–2689. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.6.2684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crépel V., Aniksztejn L., Ben-Ari Y., Hammond C. Glutamate metabotropic receptors increase a Ca(2+)-activated nonspecific cationic current in CA1 hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Oct;72(4):1561–1569. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.4.1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaum S. R., Miller R. J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors mediate excitatory transmission in the nucleus of the solitary tract. J Neurosci. 1992 Jun;12(6):2251–2258. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-06-02251.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guérineau N. C., Bossu J. L., Gähwiler B. H., Gerber U. Activation of a nonselective cationic conductance by metabotropic glutamatergic and muscarinic agonists in CA3 pyramidal neurons of the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1995 Jun;15(6):4395–4407. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-06-04395.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guérineau N. C., Gähwiler B. H., Gerber U. Reduction of resting K+ current by metabotropic glutamate and muscarinic receptors in rat CA3 cells: mediation by G-proteins. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 1;474(1):27–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp019999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Sekiyama N., Nakanishi S., Jane D. E., Sunter D. C., Birse E. F., Udvarhelyi P. M., Watkins J. C. Analysis of agonist and antagonist activities of phenylglycine derivatives for different cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3370–3377. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-03370.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Brown T. H. Giant synaptic potential hypothesis for epileptiform activity. Science. 1981 Jan 16;211(4479):294–297. doi: 10.1126/science.7444469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. A., Jahr C. E. Quisqualate receptor-mediated depression of calcium currents in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):741–749. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90200-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. G., Somogyi P., Ylinen A., Buzsáki G. The hippocampal CA3 network: an in vivo intracellular labeling study. J Comp Neurol. 1994 Jan 8;339(2):181–208. doi: 10.1002/cne.903390204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden D. J., Smeyne M., Connor J. A. Trans-ACPD, a metabotropic receptor agonist, produces calcium mobilization and an inward current in cultured cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1994 May;71(5):1992–1998. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.5.1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson H. B., Wong R. K. Synchronization of inhibitory neurones in the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1994 May 15;477(Pt 1):35–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Poncer J. C. Metabotropic glutamate receptors mediate a post-tetanic excitation of guinea-pig hippocampal inhibitory neurones. J Physiol. 1993 Apr;463:461–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K., Traub R. D. Synchronized afterdischarges in the hippocampus: contribution of local synaptic interactions. Neuroscience. 1984 Aug;12(4):1179–1189. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler J. V., Vaca K. W., White W. F., Lynch G. S., Cotman C. W. Aspartate and glutamate as possible transmitters of excitatory hippocampal afferents. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):538–540. doi: 10.1038/260538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: synaptic transmission, modulation, and plasticity. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A. Neurophysiology of epilepsy. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:395–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutecki P. A., Lebeda F. J., Johnston D. 4-Aminopyridine produces epileptiform activity in hippocampus and enhances synaptic excitation and inhibition. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jun;57(6):1911–1924. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.6.1911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D., Conn P. J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in brain function and pathology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jan;14(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90107-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Prince D. A. Cellular and field potential properties of epileptogenic hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1978 May 19;147(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90776-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Pin J. P., Récasens M., Bockaert J., Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):717–719. doi: 10.1038/317717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub C., Vranesic I., Knöpfel T. Responses to Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Activation in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells: Induction of an Inward Current. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4(9):832–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton K. R., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M. Excitation of hippocampal neurons by stimulation of glutamate Qp receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 7;173(2-3):235–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. L., Barish M. E. Two pharmacologically and kinetically distinct transient potassium currents in cultured embryonic mouse hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1992 Jun;12(6):2235–2246. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-06-02235.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng F., Gallagher J. P. Metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists potentiate a slow afterdepolarization in CNS neurons. Neuroreport. 1992 Jul;3(7):622–624. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199207000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng F., Gallagher J. P. Pharmacologically distinct, pertussis toxin-resistant inward currents evoked by metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) agonists in dorsolateral septal nucleus (DLSN) neurons. J Neurosci. 1995 Jan;15(1 Pt 2):504–510. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00504.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng F., Gallagher J. P. Trans-ACPD (trans-D,L-1-amino-1,3-cyclopentanedicarboxylic acid) elicited oscillation of membrane potentials in rat dorsolateral septal nucleus neurons recorded intracellularly in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Apr 29;125(2):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90013-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


