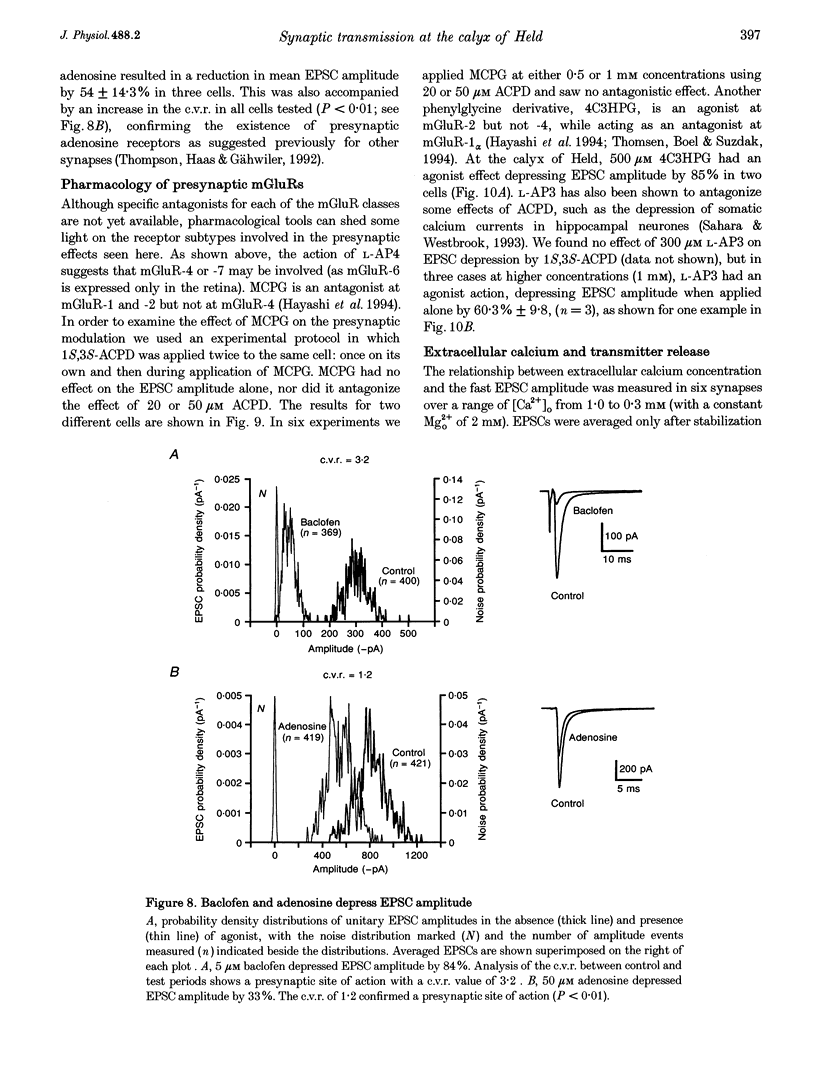
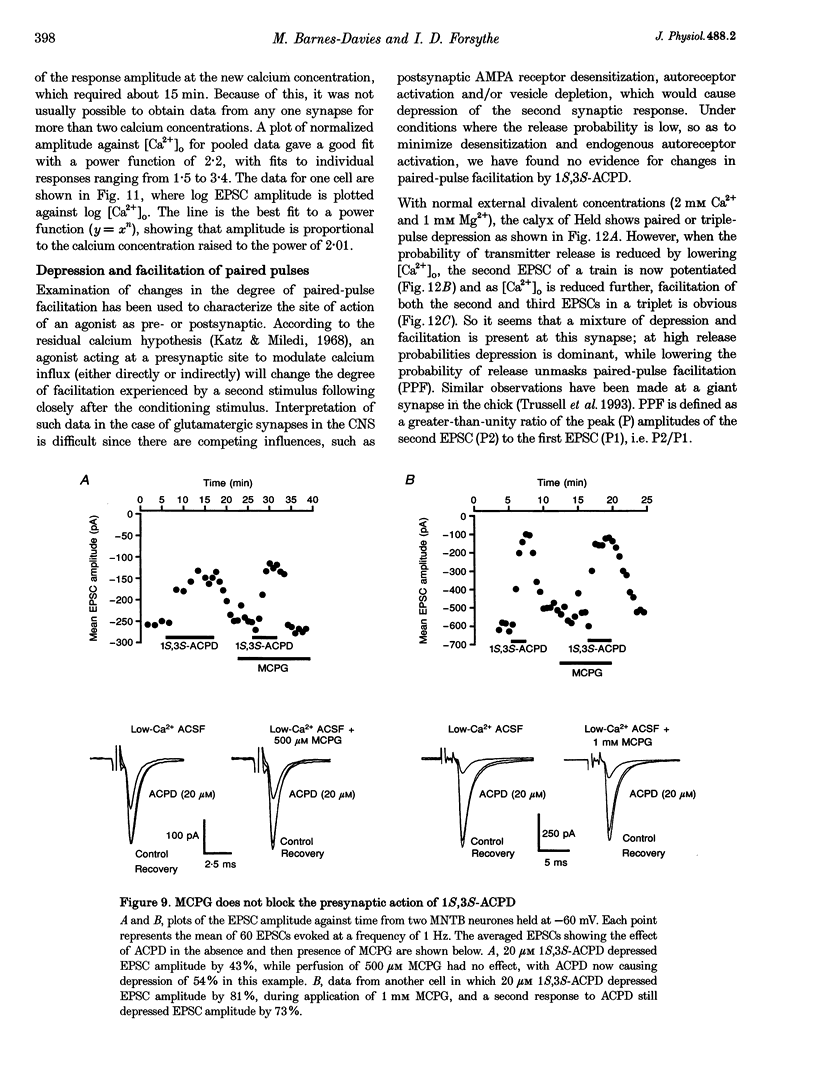
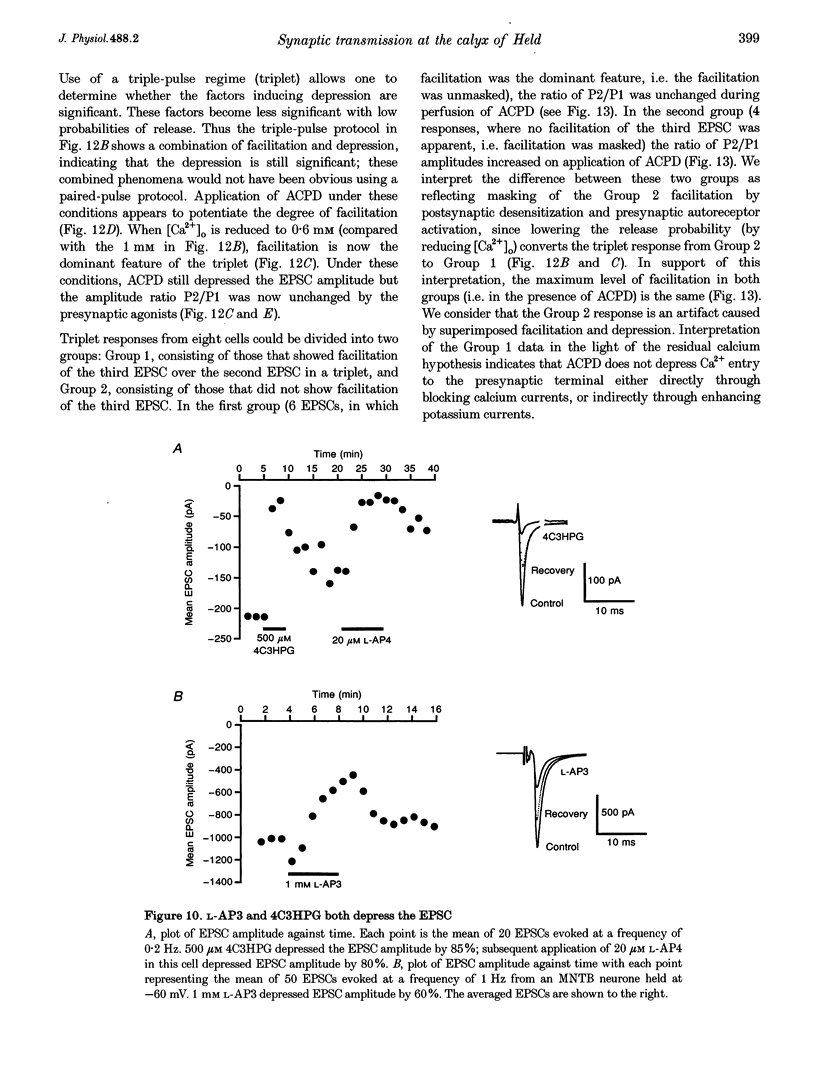
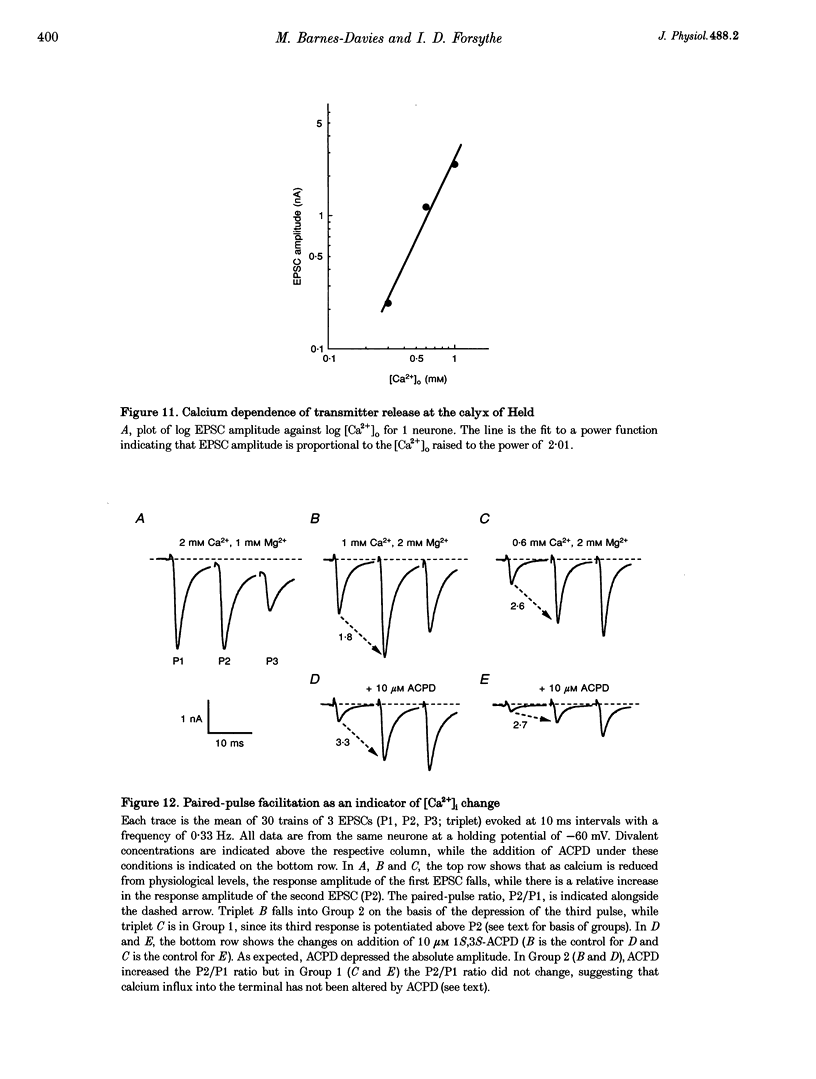
Abstract
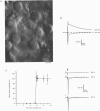
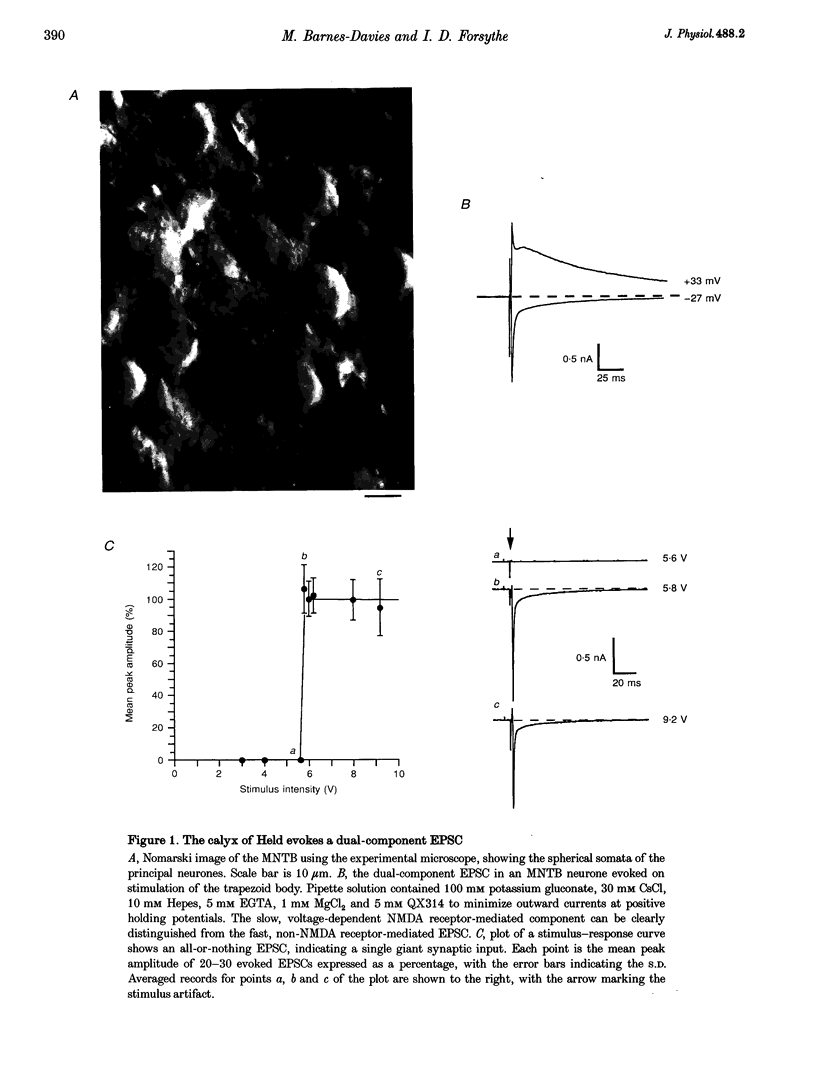
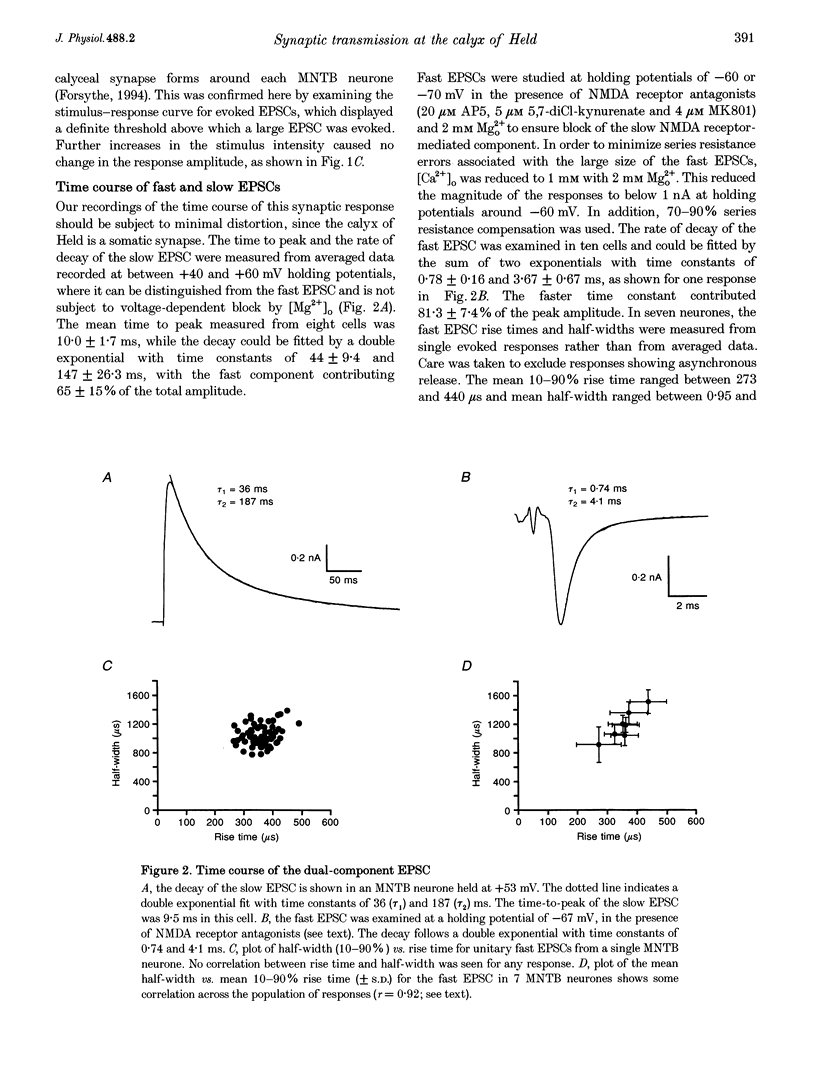
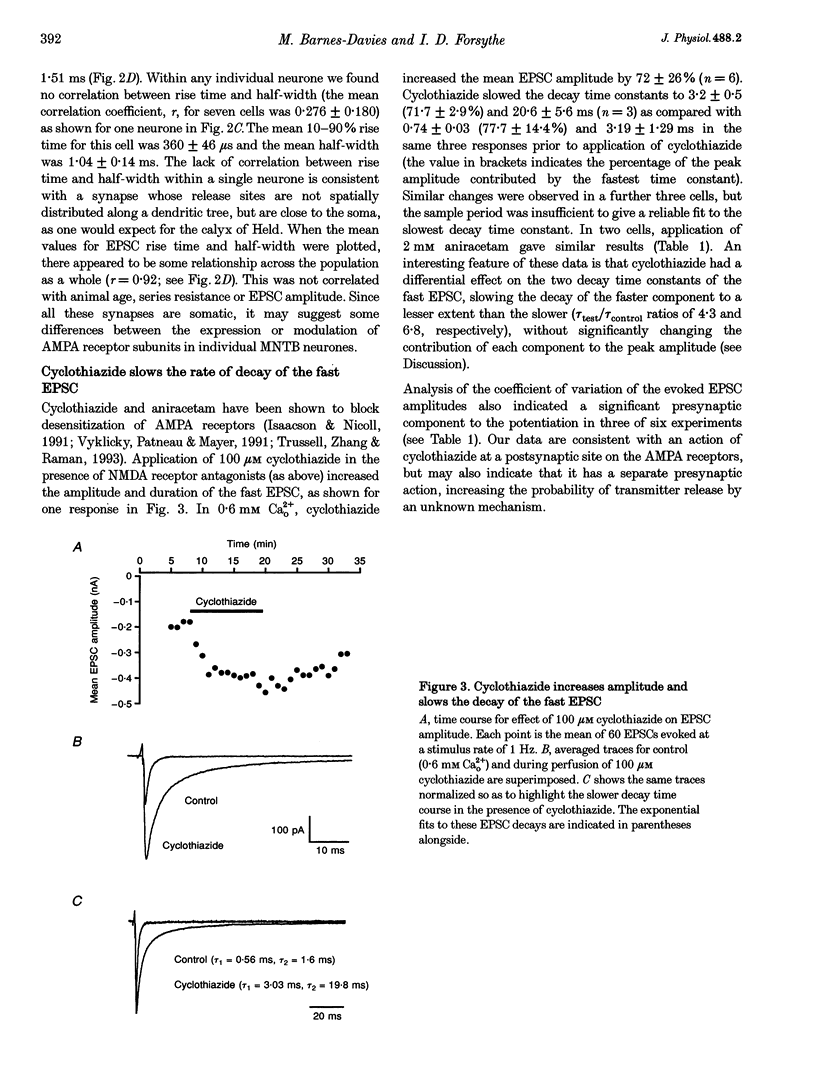
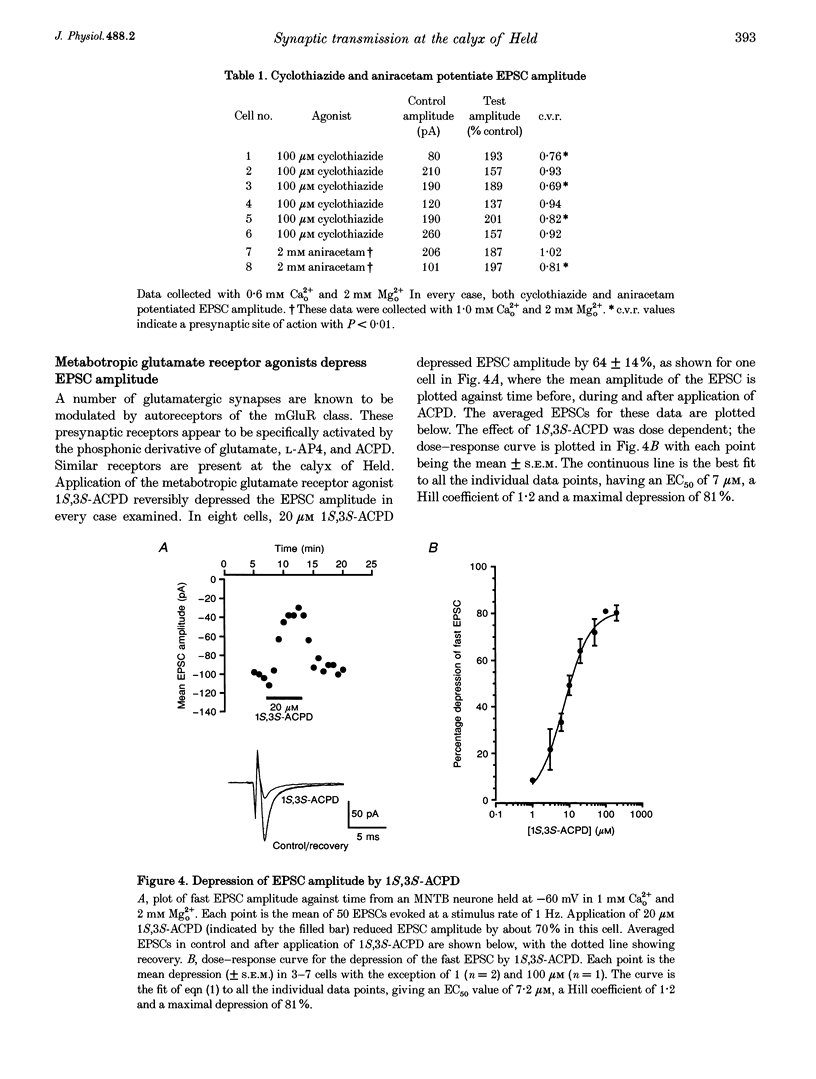
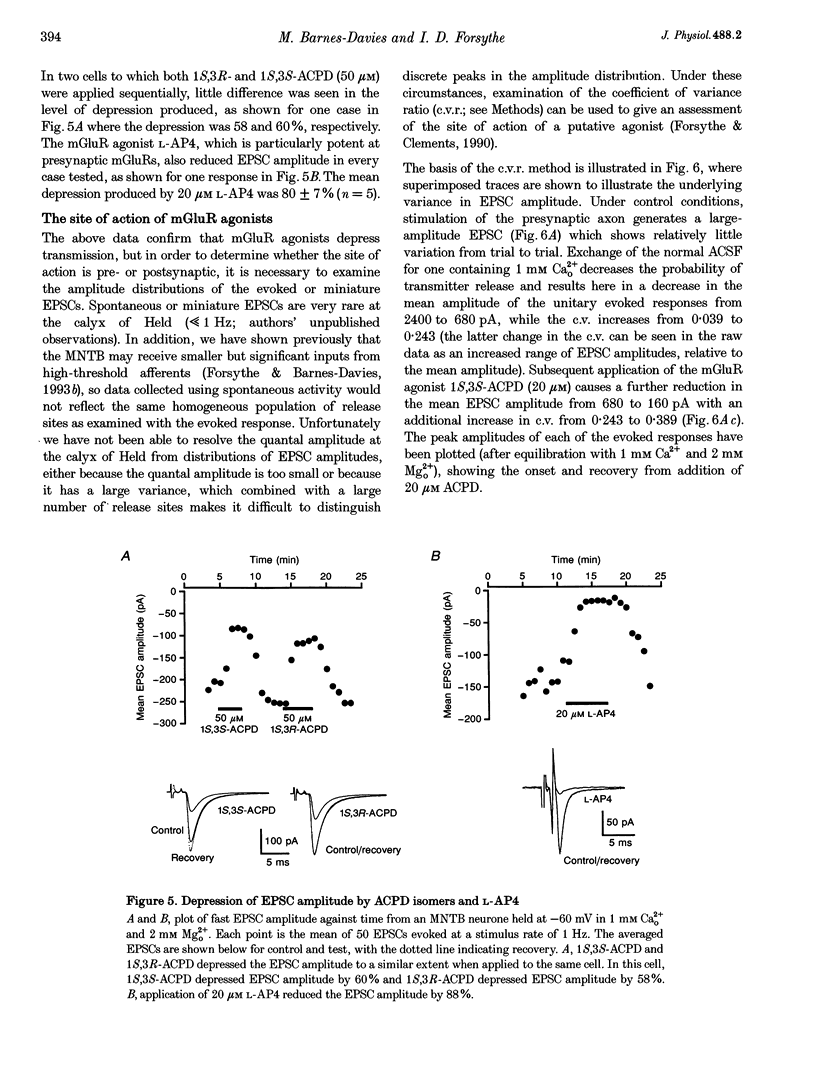
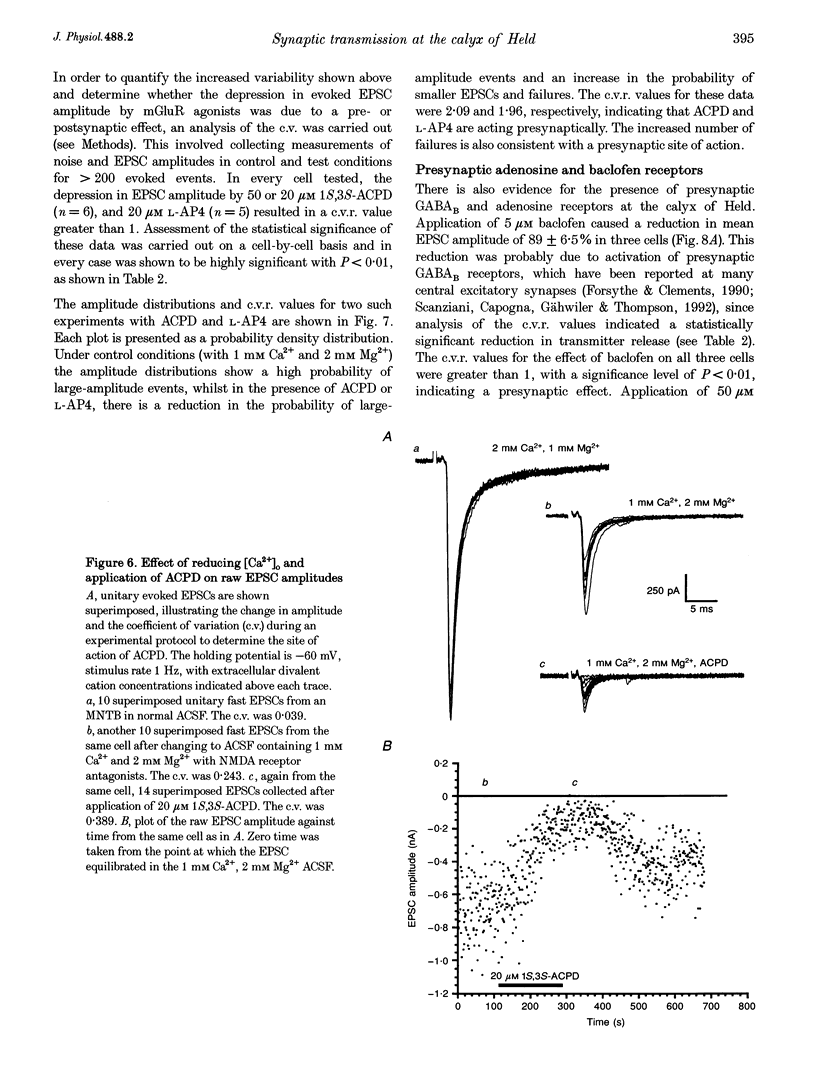
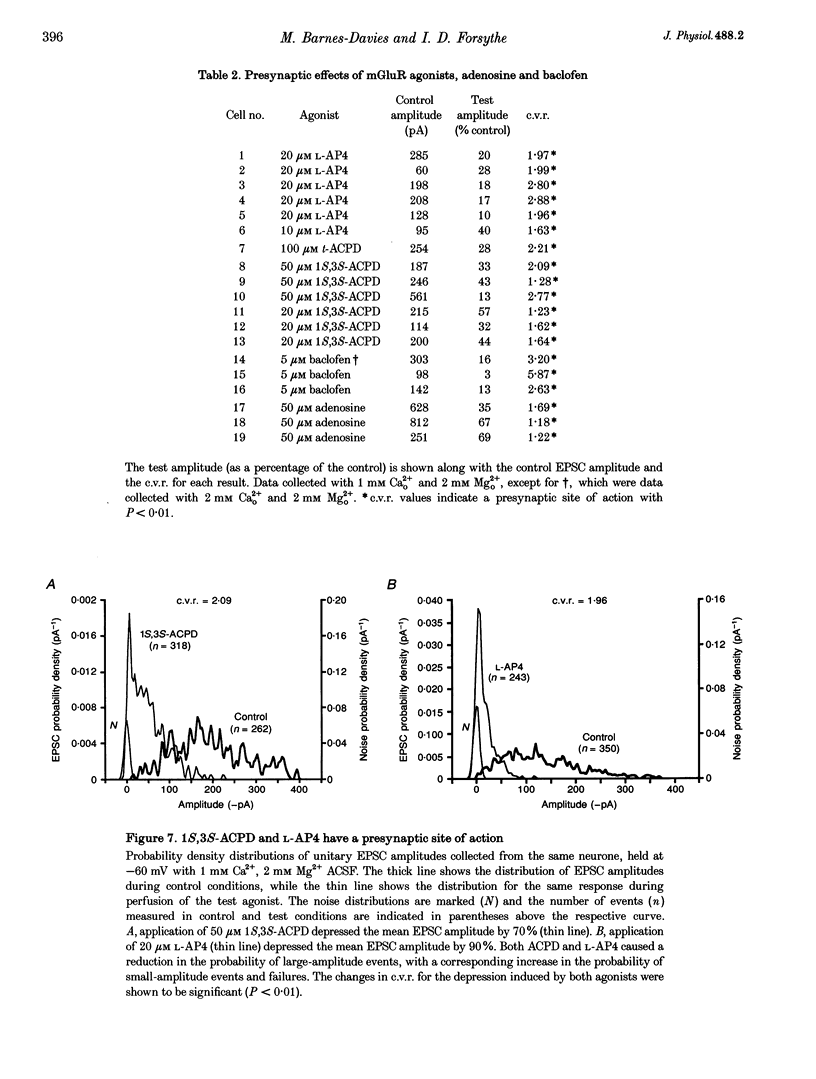
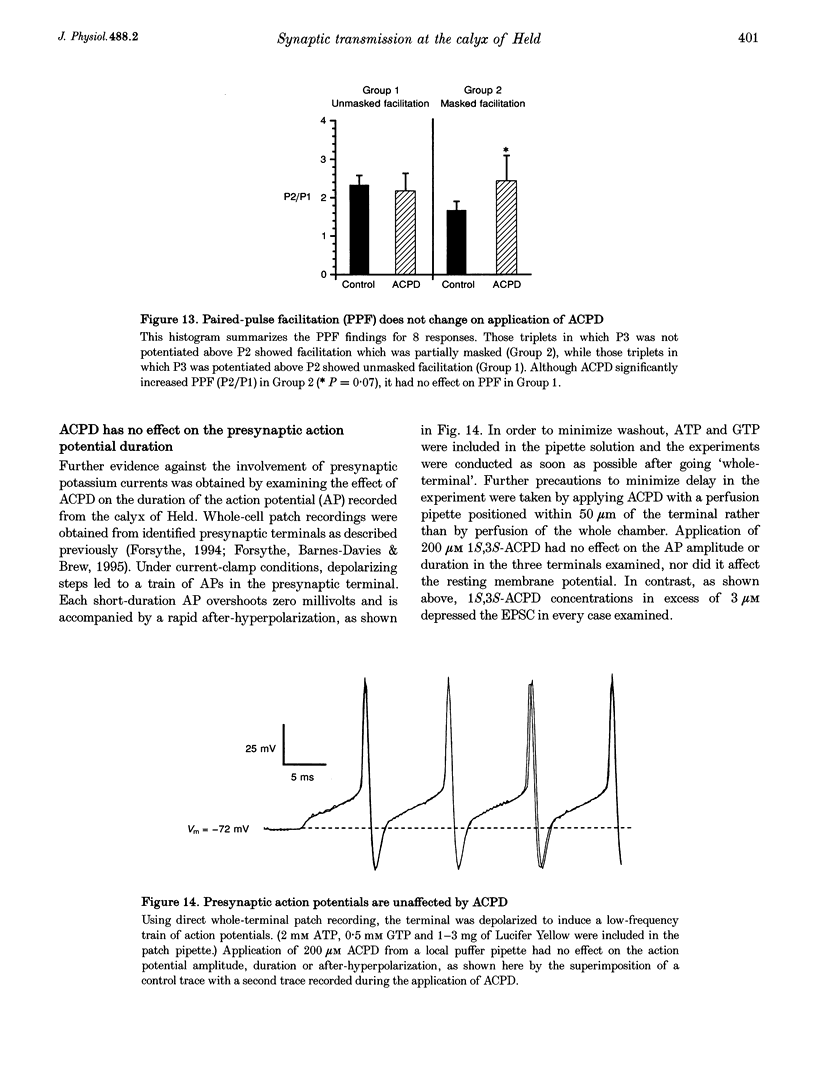
1. Whole-cell patch recordings were used to examine the EPSC generated by the calyx of Held in neurones of the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body (MNTB). Each neurone receives a somatic input from a single calyx (giant synapse). 2. A slow NMDA receptor-mediated EPSC peaked in 10 ms and decayed as a double exponential with time constants of 44 and 147 ms. A fast EPSC had a mean rise time of 356 microseconds (at 25 degrees C), while the decay was described by a double exponential with time constants of 0.70 and 3.43 ms. 3. Cyclothiazide slowed the decay of the fast EPSC, indicating that it is mediated by AMPA receptors. The slower time constant was slowed to a greater extent than the faster time constant. Cyclothiazide potentiated EPSC amplitude, partly by a presynaptic mechanism. 4. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) agonists, 1S,3S-ACPD, 1S,3R-ACPD and L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (L-AP4) reversibly depressed EPSC amplitude. A dose-response curve for 1S,3S-ACPD gave an EC50 of 7 microM and a Hill coefficient of 1.2. 5. Analysis of the coefficient of variation ratio showed that the above mGluR agonists acted presynaptically to reduce the probability of transmitter release. Adenosine and baclofen also depressed transmission by a presynaptic mechanism. 6. alpha-Methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG; 0.5-1 mM) did not antagonize the effects of 1S,3S-ACPD, while high concentrations of L-2-amino-3-phosphonopropionic acid (L-AP3; 1 mM) and 4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenyglycine (4C3HPG; 500 microM) depressed transmission. 7. There was a power relationship between [Ca2+]o and EPSC amplitude with co-operativity values ranging from 1.5 to 3.4. 8. The mechanism by which mGluRs modulate transmitter release appeared to be independent of presynaptic Ca2+ or K+ currents, since ACPD caused no change in the level of paired-pulse facilitation or the duration of the presynaptic action potential (observed by direct recording from the terminal), indicating that the presynaptic mGluR transduction mechanism may be coupled to part of the exocytotic machinery. 9. Our data are not consistent with the presence at the calyx of Held of any one known mGluR subtype. Comparison of the time course and pharmacology of the fast EPSC with data from cloned AMPA receptors is consistent with the idea that GluR-Do subunits dominate the postsynaptic channels.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P. Calcium dependence of presynaptic calcium current and post-synaptic response at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:619–640. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskys A., Malenka R. C. Agonists at metabotropic glutamate receptors presynaptically inhibit EPSCs in neonatal rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:687–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. P., Hablitz J. J. Presynaptic depression of synaptic transmission mediated by activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors in rat neocortex. J Neurosci. 1994 Aug;14(8):5120–5130. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-08-05120.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D. A statistical test for demonstrating a presynaptic site of action for a modulator of synaptic amplitude. J Neurosci Methods. 1990 Jan;31(1):75–88. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(90)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Lester R. A., Tong G., Jahr C. E., Westbrook G. L. The time course of glutamate in the synaptic cleft. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1498–1501. doi: 10.1126/science.1359647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds B., Colquhoun D. Rapid decay of averaged single-channel NMDA receptor activations recorded at low agonist concentration. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Dec 22;250(1329):279–286. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Barnes-Davies M. The binaural auditory pathway: excitatory amino acid receptors mediate dual timecourse excitatory postsynaptic currents in the rat medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Feb 22;251(1331):151–157. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Barnes-Davies M. The binaural auditory pathway: membrane currents limiting multiple action potential generation in the rat medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Feb 22;251(1331):143–150. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Clements J. D. Presynaptic glutamate receptors depress excitatory monosynaptic transmission between mouse hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D. Direct patch recording from identified presynaptic terminals mediating glutamatergic EPSCs in the rat CNS, in vitro. J Physiol. 1994 Sep 15;479(Pt 3):381–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by L-glutamate in cells dissociated from adult rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:143–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaum S. R., Sunter D. C., Udvarhelyi P. M., Watkins J. C., Miller R. J. The actions of phenylglycine derived metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists on multiple (1S,3R)-ACPD responses in the rat nucleus of the tractus solitarius. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Dec;32(12):1419–1425. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Momiyama A., Takahashi T., Ohishi H., Ogawa-Meguro R., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Role of a metabotropic glutamate receptor in synaptic modulation in the accessory olfactory bulb. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):687–690. doi: 10.1038/366687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Sekiyama N., Nakanishi S., Jane D. E., Sunter D. C., Birse E. F., Udvarhelyi P. M., Watkins J. C. Analysis of agonist and antagonist activities of phenylglycine derivatives for different cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3370–3377. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-03370.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C., Petralia R. S., Vu T., Wenthold R. J. Expression of AMPA-selective glutamate receptor subunits in morphologically defined neurons of the mammalian cochlear nucleus. J Neurosci. 1993 May;13(5):1932–1946. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-05-01932.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson J. S., Nicoll R. A. Aniracetam reduces glutamate receptor desensitization and slows the decay of fast excitatory synaptic currents in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10936–10940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson J. S., Walmsley B. Receptors underlying excitatory synaptic transmission in slices of the rat anteroventral cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Mar;73(3):964–973. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.3.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jane D. E., Jones P. L., Pook P. C., Tse H. W., Watkins J. C. Actions of two new antagonists showing selectivity for different sub-types of metabotropic glutamate receptor in the neonatal rat spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;112(3):809–816. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M., Roberts P., Pook P., Jane D., Jones A., Jones P., Sunter D., Udvarhelyi P., Watkins J. Antagonism of presynaptically mediated depressant responses and cyclic AMP-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 15;266(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. A., Clements J. D., Westbrook G. L., Jahr C. E. Channel kinetics determine the time course of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):565–567. doi: 10.1038/346565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M., Tyler E., Fidler S., Merritt A. Properties of a presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptor in rat neostriatal slices. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Apr;69(4):1236–1244. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.4.1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain C., Dingledine R. Dual-component miniature excitatory synaptic currents in rat hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jul;68(1):16–27. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbacher J., Schoepfer R., Monyer H., Burnashev N., Seeburg P. H., Ruppersberg J. P. A molecular determinant for submillisecond desensitization in glutamate receptors. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1059–1062. doi: 10.1126/science.7973663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: synaptic transmission, modulation, and plasticity. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi H., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S., Mizuno N. Distribution of the messenger RNA for a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR2, in the central nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1993 Apr;53(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90485-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otis T. S., Raman I. M., Trussell L. O. AMPA receptors with high Ca2+ permeability mediate synaptic transmission in the avian auditory pathway. J Physiol. 1995 Jan 15;482(Pt 2):309–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partin K. M., Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Cyclothiazide differentially modulates desensitization of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor splice variants. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;46(1):129–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partin K. M., Patneau D. K., Winters C. A., Mayer M. L., Buonanno A. Selective modulation of desensitization at AMPA versus kainate receptors by cyclothiazide and concanavalin A. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1069–1082. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90220-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raman I. M., Zhang S., Trussell L. O. Pathway-specific variants of AMPA receptors and their contribution to neuronal signaling. J Neurosci. 1994 Aug;14(8):4998–5010. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-08-04998.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahara Y., Westbrook G. L. Modulation of calcium currents by a metabotropic glutamate receptor involves fast and slow kinetic components in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):3041–3050. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-03041.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarantis M., Ballerini L., Miller B., Silver R. A., Edwards M., Attwell D. Glutamate uptake from the synaptic cleft does not shape the decay of the non-NMDA component of the synaptic current. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):541–549. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90158-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saugstad J. A., Kinzie J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Segerson T. P., Westbrook G. L. Cloning and expression of a new member of the L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid-sensitive class of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayer R. J., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated suppression of L-type calcium current in acutely isolated neocortical neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Sep;68(3):833–842. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.3.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanziani M., Capogna M., Gähwiler B. H., Thompson S. M. Presynaptic inhibition of miniature excitatory synaptic currents by baclofen and adenosine in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):919–927. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Miller R. J. Inhibition of quantal transmitter release in the absence of calcium influx by a G protein-linked adenosine receptor at hippocampal synapses. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1139–1150. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90134-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. A., Traynelis S. F., Cull-Candy S. G. Rapid-time-course miniature and evoked excitatory currents at cerebellar synapses in situ. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):163–166. doi: 10.1038/355163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Momiyama A., Takahashi T. Presynaptic inhibitory action of a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist on excitatory transmission in visual cortical neurons. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Sep 22;253(1338):297–303. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P., Edwards F. A., Sakmann B. Fast and slow components of unitary EPSCs on stellate cells elicited by focal stimulation in slices of rat visual cortex. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:247–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90118-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Nomura A., Masu M., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Signal transduction, pharmacological properties, and expression patterns of two rat metabotropic glutamate receptors, mGluR3 and mGluR4. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1372–1378. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01372.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Haas H. L., Gähwiler B. H. Comparison of the actions of adenosine at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1992;451:347–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen C., Boel E., Suzdak P. D. Actions of phenylglycine analogs at subtypes of the metabotropic glutamate receptor family. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Mar 15;267(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoreson W. B., Miller R. F. Actions of (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (1S,3R-ACPD) in retinal ON bipolar cells indicate that it is an agonist at L-AP4 receptors. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Jun;103(6):1019–1034. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.6.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Zhang S., Raman I. M. Desensitization of AMPA receptors upon multiquantal neurotransmitter release. Neuron. 1993 Jun;10(6):1185–1196. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90066-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklicky L., Jr, Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission by drugs that reduce desensitization at AMPA/kainate receptors. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):971–984. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90342-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. H., Kelly J. B. Response of neurons in the lateral superior olive and medial nucleus of the trapezoid body to repetitive stimulation: intracellular and extracellular recordings from mouse brain slice. Hear Res. 1993 Aug;68(2):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(93)90123-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S., Trussell L. O. Voltage clamp analysis of excitatory synaptic transmission in the avian nucleus magnocellularis. J Physiol. 1994 Oct 1;480(Pt 1):123–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]