Abstract
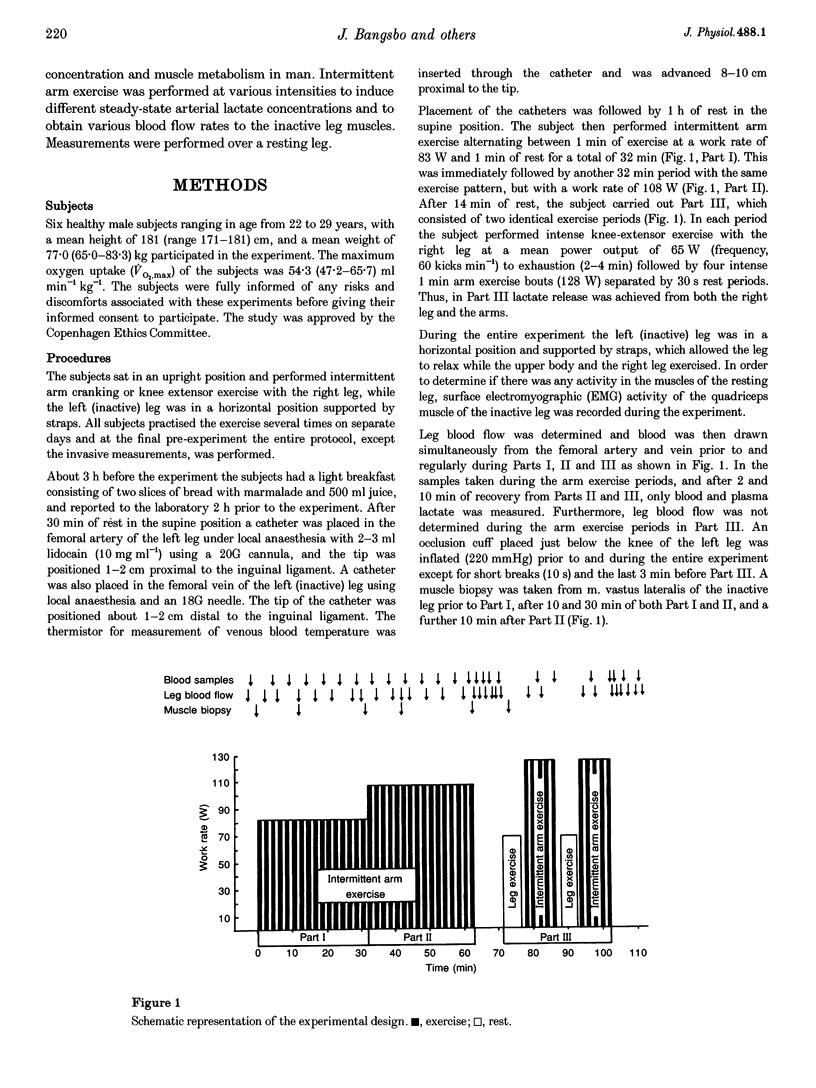
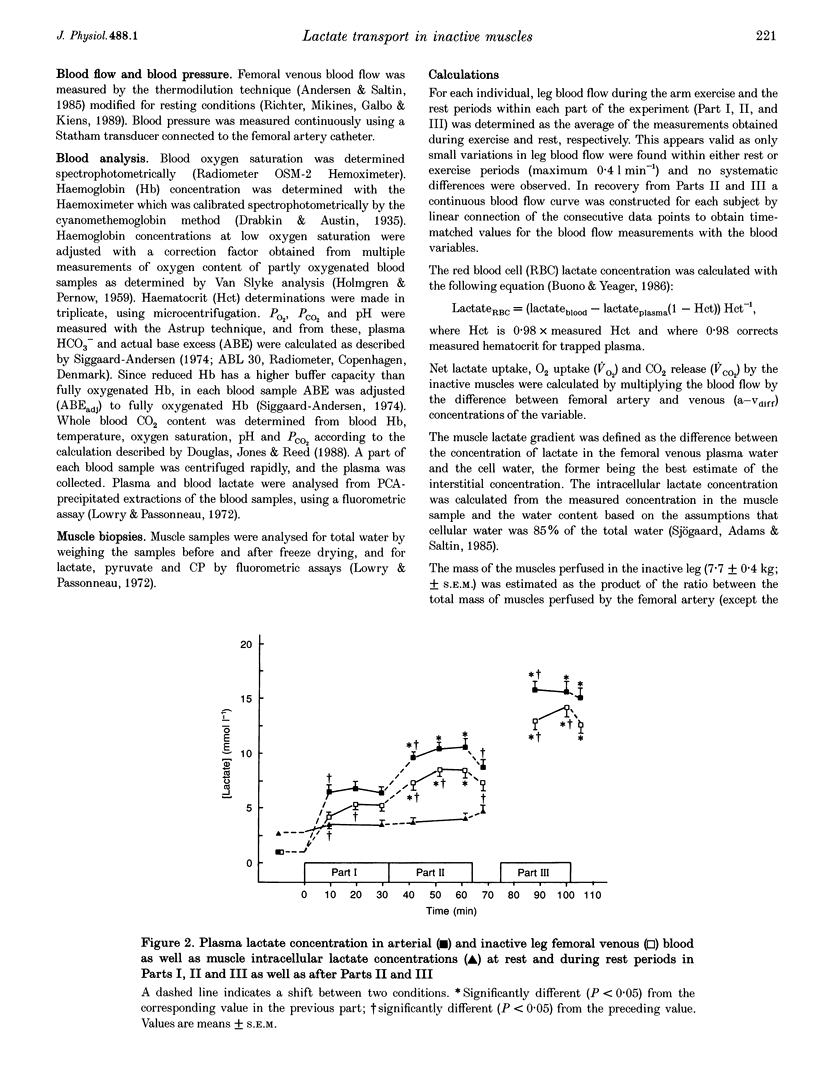
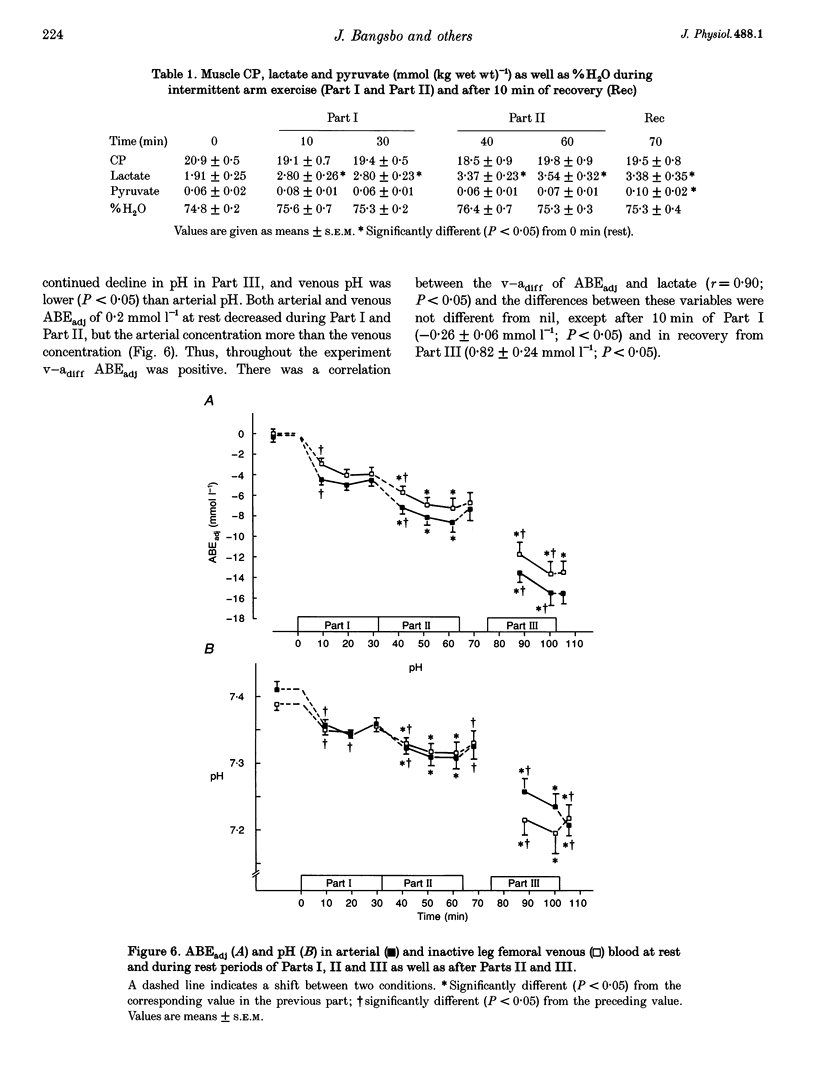
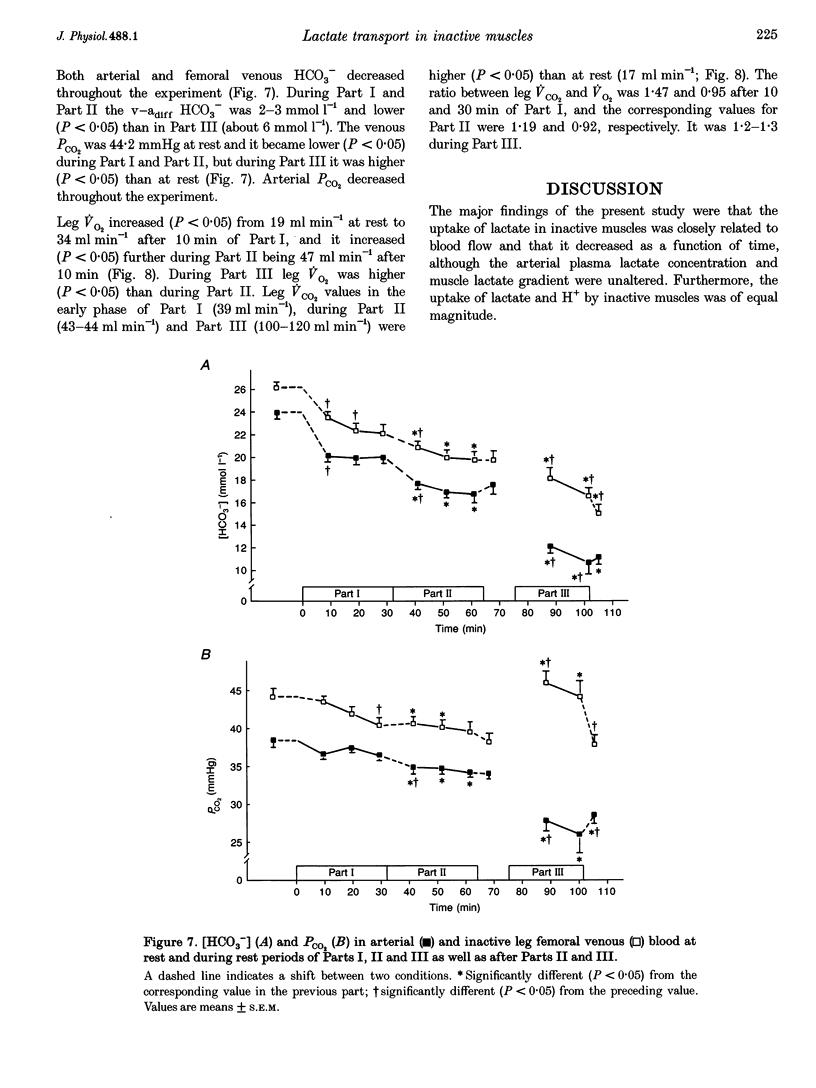
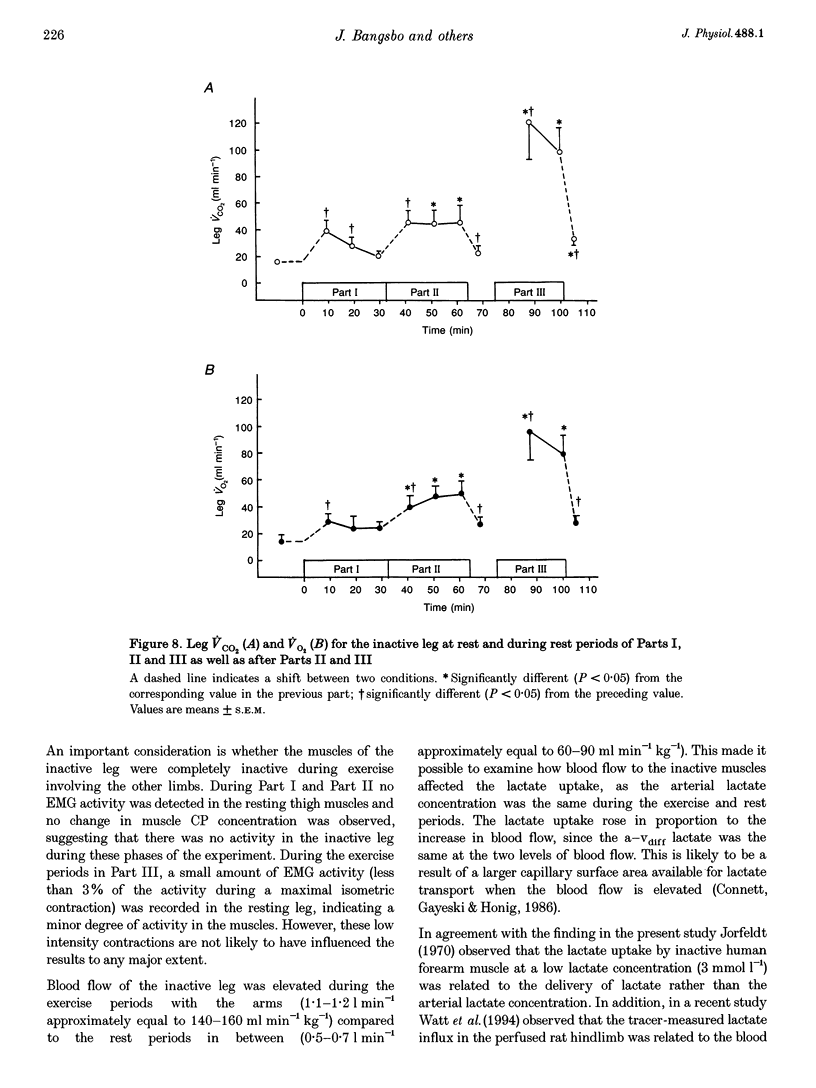
1. The present study examined how uptake of lactate and H+ in resting muscle is affected by blood flow, arterial lactate concentration and muscle metabolism. 2. Six males subjects performed intermittent arm exercise in two separate 32 min periods (Part I and Part II) and in one subsequent 20 min period in which one leg knee-extensor exercise was also performed (Part III). The exercise was performed at various intensities in order to obtain different steady-state arterial blood lactate concentrations. In the inactive leg, femoral venous blood flow (draining about 7.7 kg of muscles) was measured and femoral arterial and venous blood was collected frequently. Biopsies were taken from m. vastus lateralis of the inactive leg at rest and 10 and 30 min into both Part I and Part II as well as 10 min into recovery from Part II. 3. The arterial plasma lactate concentrations were 7, 9 and 16 mmol l-1 after 10 min of Parts I, II and III, respectively, and the corresponding arterial-venous difference (a-vdiff) for lactate in the resting leg was 1.3, 1.4 and 2.0 mmol l-1. The muscle lactate concentration was 2.8 mmol (kg wet wt)-1 after 10 min of Part I and remained constant throughout the experiment. During Parts I and II, a-vdiff lactate decreased although the arterial lactate concentration and plasma-muscle lactate gradient were unaltered throughout each period. Thus, membrane transport of lactate decreased during each period. 4. Blood flow in the inactive leg was about 2-fold higher during arm exercise compared to the rest periods, resulting in a 2-fold higher lactate uptake. Thus, lactate uptake by inactive muscles was closely related to blood flow. 5. Throughout the experiment a-vdiff for actual base excess and for lactate were of similar magnitude. Thus, in inactive muscles lactate uptake appears to be coupled to the transport of H+.
Full text
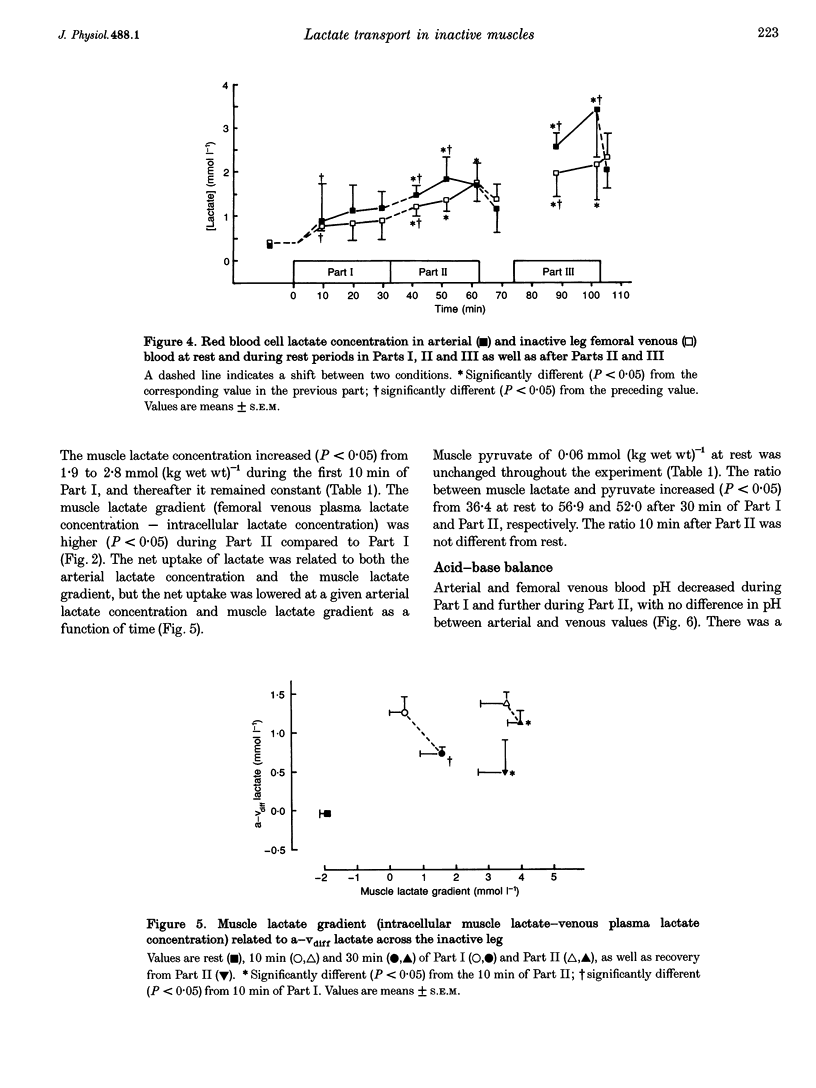
PDF
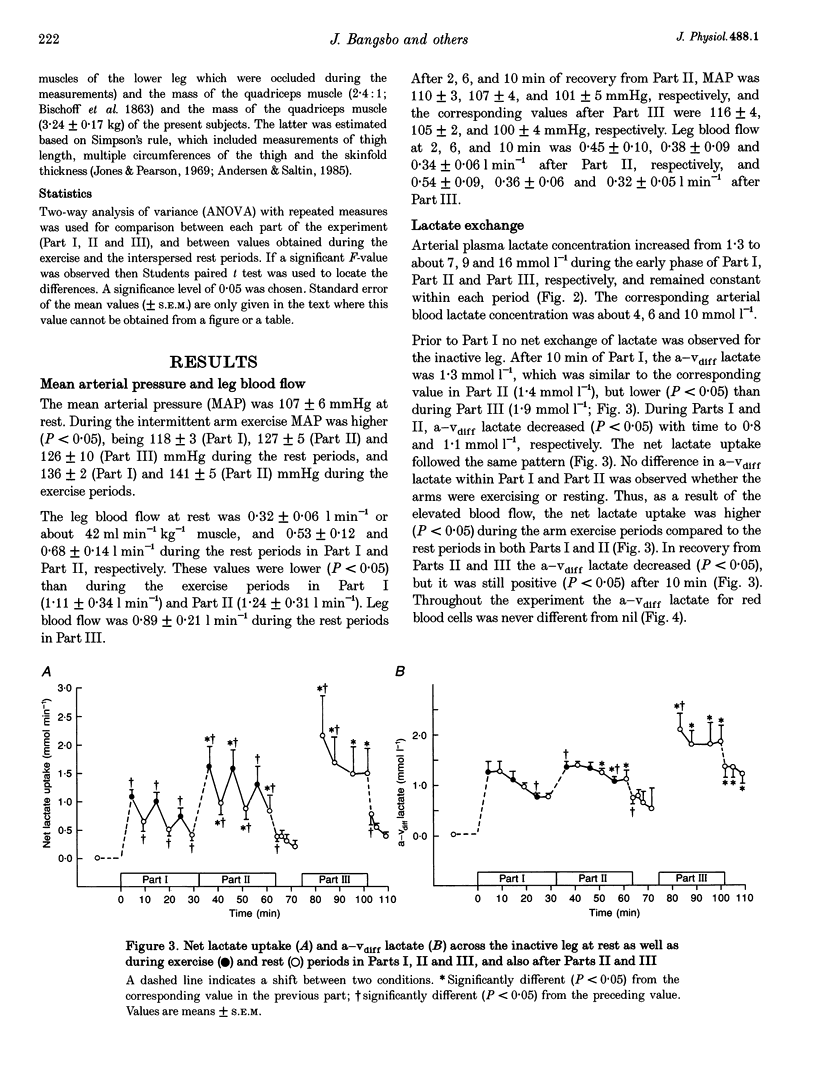



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlborg G., Hagenfeldt L., Wahren J. Influence of lactate infusion on glucose and FFA metabolism in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 Mar;36(2):193–201. doi: 10.1080/00365517609055248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlborg G., Hagenfeldt L., Wahren J. Substrate utilization by the inactive leg during one-leg or arm exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Nov;39(5):718–723. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.5.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Saltin B. Maximal perfusion of skeletal muscle in man. J Physiol. 1985 Sep;366:233–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangsbo J., Gollnick P. D., Graham T. E., Juel C., Kiens B., Mizuno M., Saltin B. Anaerobic energy production and O2 deficit-debt relationship during exhaustive exercise in humans. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:539–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangsbo J., Gollnick P. D., Graham T. E., Saltin B. Substrates for muscle glycogen synthesis in recovery from intense exercise in man. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:423–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangsbo J., Johansen L., Graham T., Saltin B. Lactate and H+ effluxes from human skeletal muscles during intense, dynamic exercise. J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buono M. J., Yeager J. E. Intraerythrocyte and plasma lactate concentrations during exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1986;55(3):326–329. doi: 10.1007/BF02343807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas A. R., Jones N. L., Reed J. W. Calculation of whole blood CO2 content. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jul;65(1):473–477. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.1.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden L. B., Crawford R. E., Webster M. J. Effect of blood flow on net lactate uptake during steady-level contractions in canine skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 May;72(5):1826–1830. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.5.1826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden L. B., Crawford R. E., Webster M. J. Effect of lactate concentration and metabolic rate on net lactate uptake by canine skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 2):R1095–R1101. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.4.R1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden L. B. Lactate uptake by skeletal muscle. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1989;17:115–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden L. B., Yates J. W. Lactic acid infusion in dogs: effects of varying infusate pH. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 May;54(5):1254–1260. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.5.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez G., Fernandez E., Hurtado F. J., Kiiski R., Chakravarthy S., Ronco J. J., Arbelaez G. Hydroxymalonate inhibits lactate uptake by the rabbit hindlimb. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994 Jun;76(6):2735–2741. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.6.2735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirche H. J., Hombach V., Langohr H. D., Wacker U., Busse J. Lactic acid permeation rate in working gastrocnemii of dogs during metabolic alkalosis and acidosis. Pflugers Arch. 1975;356(3):209–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00583833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig C. R., Odoroff C. L., Frierson J. L. Active and passive capillary control in red muscle at rest and in exercise. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):H196–H206. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.243.2.H196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorfeldt L. Metabolism of L(plus)-lactate in human skeletal muscle during exercise. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1970;338:1–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juel C., Bangsbo J., Graham T., Saltin B. Lactate and potassium fluxes from human skeletal muscle during and after intense, dynamic, knee extensor exercise. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 Oct;140(2):147–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juel C. Intracellular pH recovery and lactate efflux in mouse soleus muscles stimulated in vitro: the involvement of sodium/proton exchange and a lactate carrier. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Mar;132(3):363–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juel C., Wibrand F. Lactate transport in isolated mouse muscles studied with a tracer technique--kinetics, stereospecificity, pH dependency and maximal capacity. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Sep;137(1):33–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A., Webster B., Lowell S. Cellular uptake of L-lactate in mouse diaphragm. Biophys J. 1981 Dec;36(3):775–796. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84765-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalchuk J. M., Heigenhauser G. J., Lindinger M. I., Obminski G., Sutton J. R., Jones N. L. Role of lungs and inactive muscle in acid-base control after maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Nov;65(5):2090–2096. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.5.2090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindinger M. I., Heigenhauser G. J., McKelvie R. S., Jones N. L. Role of nonworking muscle on blood metabolites and ions with intense intermittent exercise. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 2):R1486–R1494. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.258.6.R1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. J., Thomas R. C. A microelectrode study of the mechanisms of L-lactate entry into and release from frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:459–479. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKelvie R. S., Lindinger M. I., Jones N. L., Heigenhauser G. J. Erythrocyte ion regulation across inactive muscle during leg exercise. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;70(12):1625–1633. doi: 10.1139/y92-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poortmans J. R., Delescaille-Vanden Bossche J., Leclercq R. Lactate uptake by inactive forearm during progressive leg exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Dec;45(6):835–839. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.6.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter E. A., Mikines K. J., Galbo H., Kiens B. Effect of exercise on insulin action in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Feb;66(2):876–885. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.2.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjøgaard G., Adams R. P., Saltin B. Water and ion shifts in skeletal muscle of humans with intense dynamic knee extension. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):R190–R196. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1985.248.2.R190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley W. C., Gertz E. W., Wisneski J. A., Neese R. A., Morris D. L., Brooks G. A. Lactate extraction during net lactate release in legs of humans during exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Apr;60(4):1116–1120. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.4.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. W., Gladden L. B., Hundal H. S., Crawford R. E. Effects of flow and contraction on lactate transport in the perfused rat hindlimb. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jul;267(1 Pt 1):E7–13. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.267.1.E7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. W., MacLennan P. A., Hundal H. S., Kuret C. M., Rennie M. J. L(+)-lactate transport in perfused rat skeletal muscle: kinetic characteristics and sensitivity to pH and transport inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 6;944(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



