Abstract
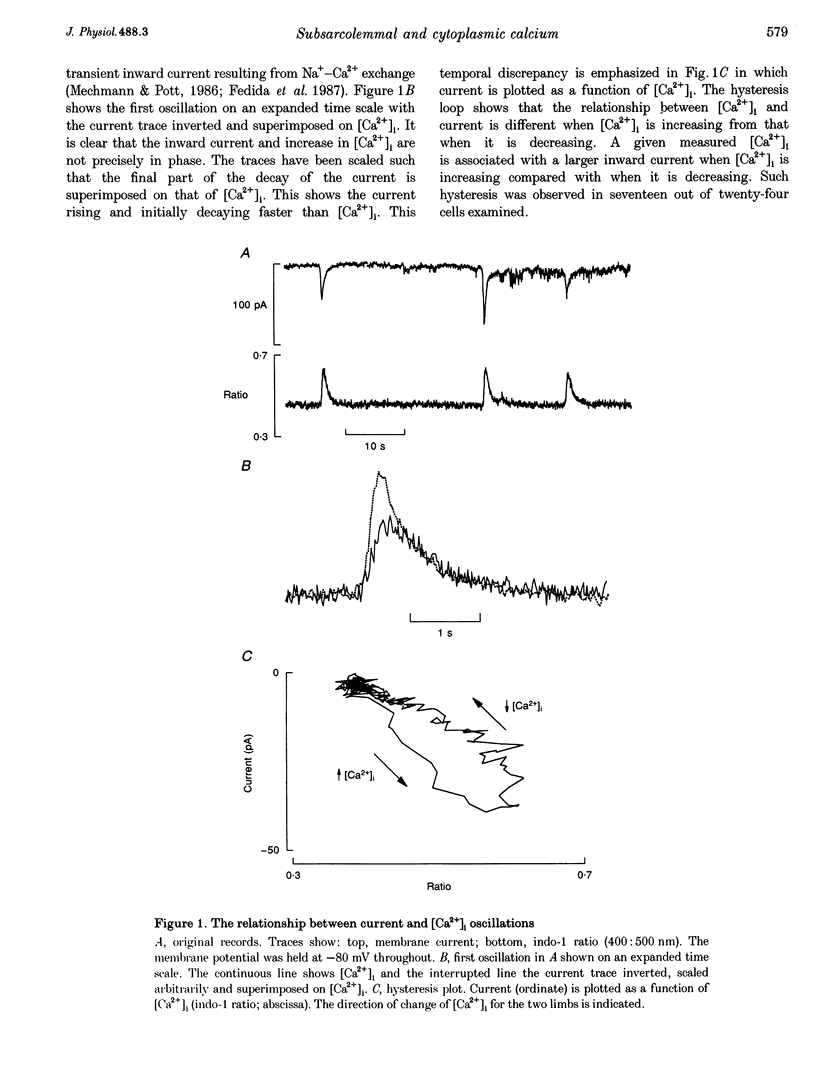
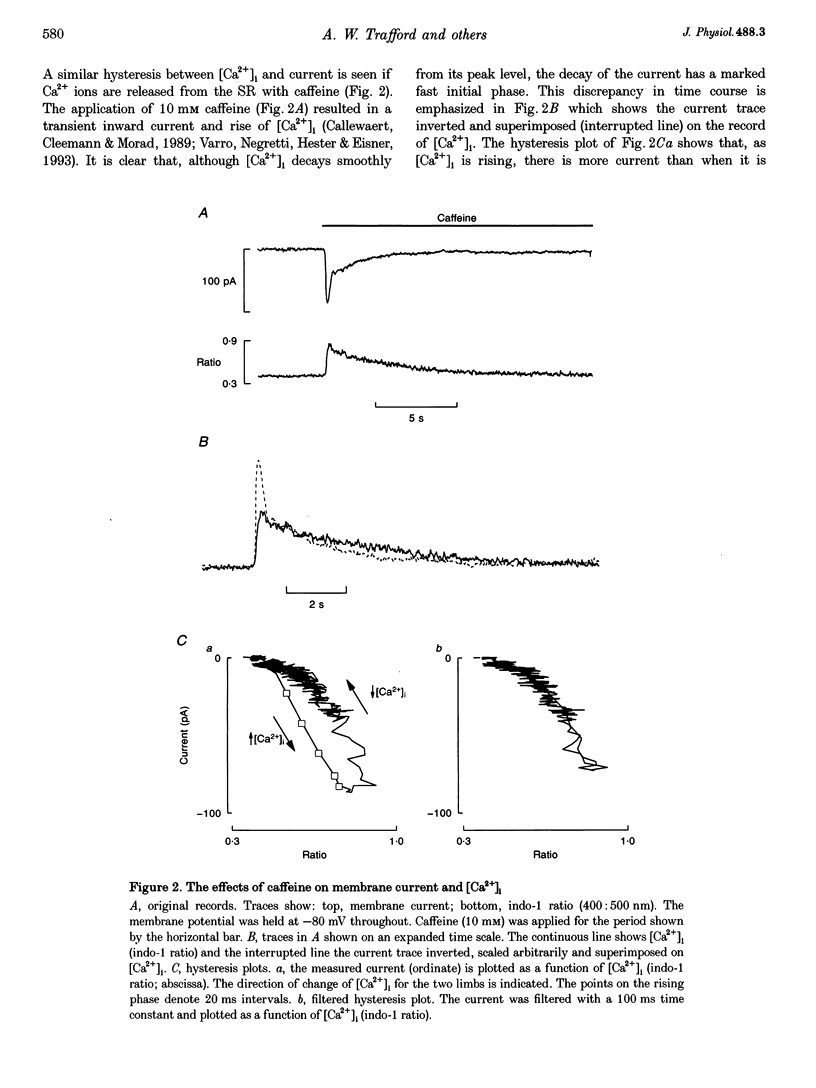
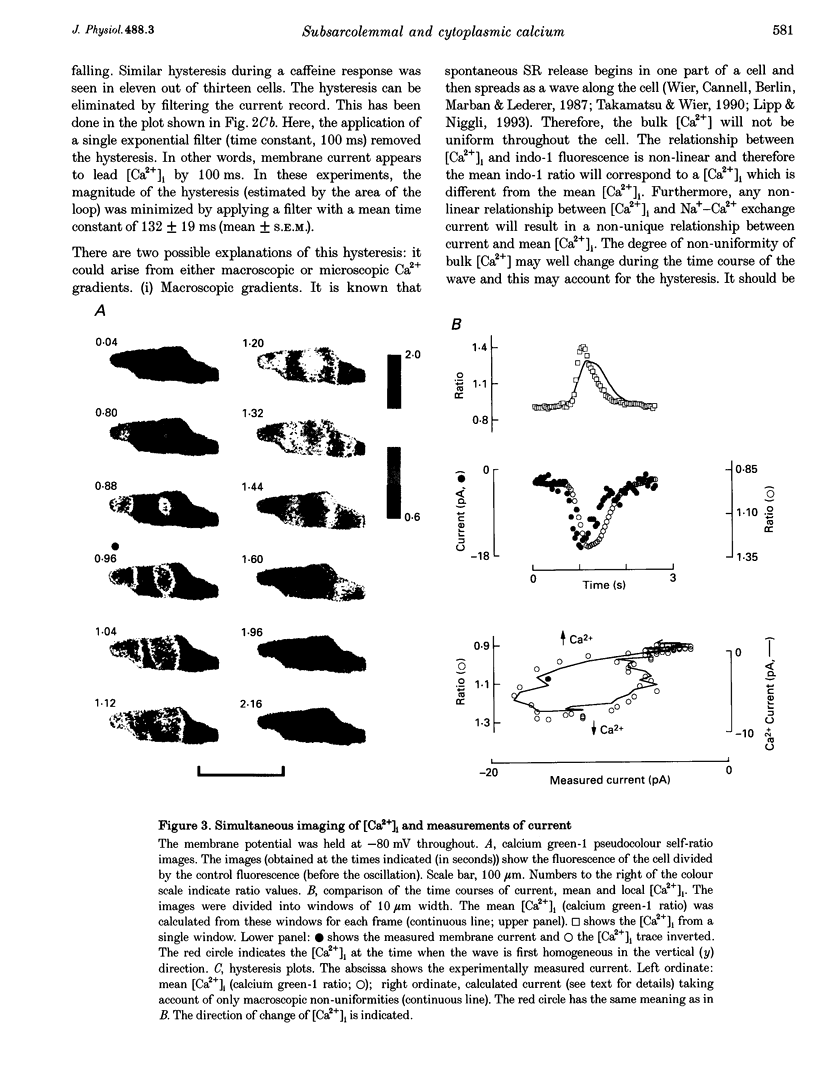
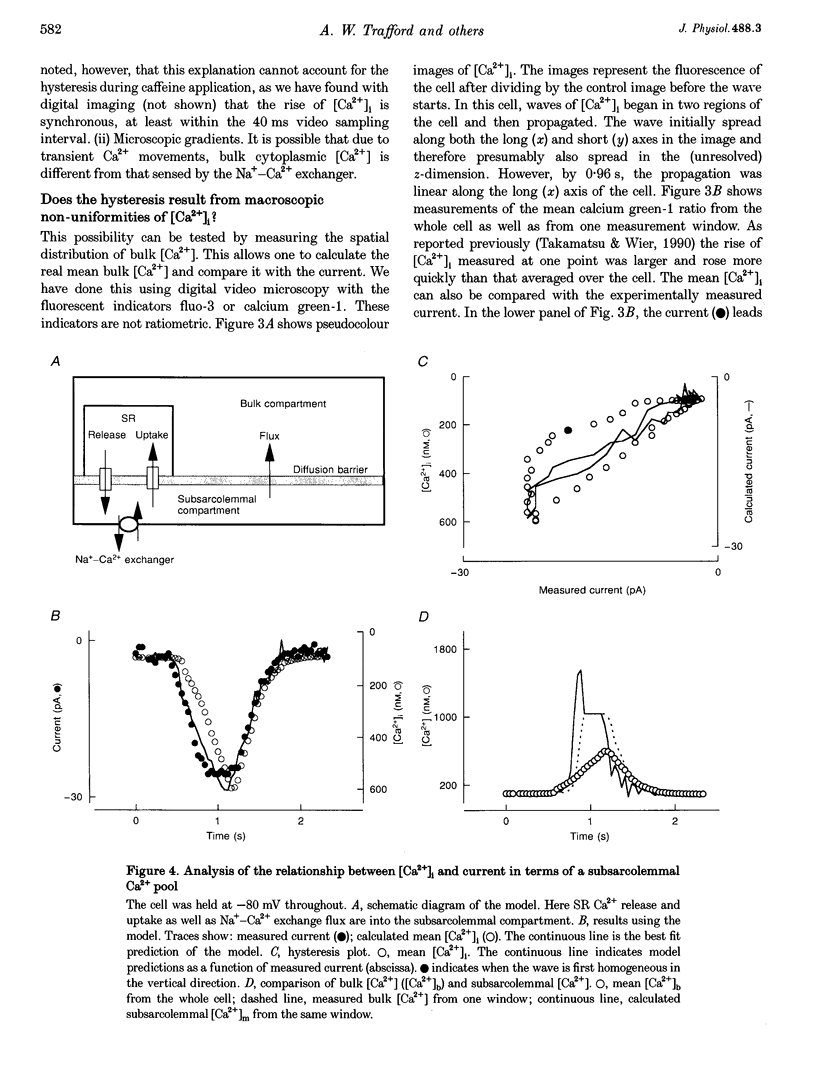
1. The aim of these experiments was to compare the time course of changes in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) measured in the bulk cytoplasm with those estimated to occur near the sarcolemma. Sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange current and [Ca2+]i were measured in single, voltage-clamped ventricular myocytes. 2. Spontaneous Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) resulted in a transient inward current. This current developed and decayed more quickly than the accompanying changes in [Ca2+]i (measured with indo-1) resulting in a hysteresis between [Ca2+]i and current. A similar hysteresis was also observed if [Ca2+]i was elevated with caffeine and was removed if the current was low pass filtered with a time constant of 132 ms. 3. Digital video imaging (using fluo-3 or calcium green-1 to measure [Ca2+]i) allowed measurement of [Ca2+]i at all points in the cell during the wave of spontaneous Ca2+ release. The hysteresis between [Ca2+]i and current remained, even after allowing for the spatial and temporal properties of this wave. 4. The hysteresis can be accounted for if there is a barrier to diffusion of Ca2+ ions separating the bulk cytoplasm from the space under the sarcolemma (into which Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum). The calculated subsarcolemmal [Ca2+] rises and falls more quickly (and reaches a higher peak) than does the bulk [Ca2+]. The delay introduced by this barrier is equivalent to a time constant of 133 ms. 5. The subsarcolemmal space described in this paper may be equivalent to the 'fuzzy space' previously suggested to be important in controlling SR Ca2+ release.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S. Fura-2 calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:151–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. R., Bassani J. W., Bers D. M. Intrinsic cytosolic calcium buffering properties of single rat cardiac myocytes. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1775–1787. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80652-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. R., Cannell M. B., Lederer W. J. Cellular origins of the transient inward current in cardiac myocytes. Role of fluctuations and waves of elevated intracellular calcium. Circ Res. 1989 Jul;65(1):115–126. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuckelmann D. J., Wier W. G. Sodium-calcium exchange in guinea-pig cardiac cells: exchange current and changes in intracellular Ca2+. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:499–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert G., Cleemann L., Morad M. Caffeine-induced Ca2+ release activates Ca2+ extrusion via Na+-Ca2+ exchanger in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 1):C147–C152. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.1.C147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Berlin J. R., Lederer W. J. Intracellular calcium in cardiac myocytes: calcium transients measured using fluorescence imaging. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1987;42:201–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Lederer W. J., Cannell M. B. Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):740–744. doi: 10.1126/science.8235594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Nichols C. G., O'Neill S. C., Smith G. L., Valdeolmillos M. The effects of metabolic inhibition on intracellular calcium and pH in isolated rat ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:393–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Valdeolmillos M. A study of intracellular calcium oscillations in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres measured at the single cell level. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:539–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etter E. F., Kuhn M. A., Fay F. S. Detection of changes in near-membrane Ca2+ concentration using a novel membrane-associated Ca2+ indicator. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10141–10149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedida D., Noble D., Rankin A. C., Spindler A. J. The arrhythmogenic transient inward current iTI and related contraction in isolated guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:523–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S., Bloebaum P., Snowdowne K. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum interacts with the Ca(2+) indicator precursor fura-2-am. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1153–1162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kargacin G. J. Calcium signaling in restricted diffusion spaces. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):262–272. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80477-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Lederer W. J., Tsien R. W., Weingart R. Role of calcium ions in transient inward currents and aftercontractions induced by strophanthidin in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:187–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattanzio F. A., Jr, Bartschat D. K. The effect of pH on rate constants, ion selectivity and thermodynamic properties of fluorescent calcium and magnesium indicators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):184–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91966-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Niggli E., Hadley R. W. Sodium-calcium exchange in excitable cells: fuzzy space. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):283–283. doi: 10.1126/science.2326638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Niggli E. Microscopic spiral waves reveal positive feedback in subcellular calcium signaling. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2272–2276. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81316-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Pott L., Callewaert G., Carmeliet E. Simultaneous recording of Indo-1 fluorescence and Na+/Ca2+ exchange current reveals two components of Ca2(+)-release from sarcoplasmic reticulum of cardiac atrial myocytes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81467-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechmann S., Pott L. Identification of Na-Ca exchange current in single cardiac myocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):597–599. doi: 10.1038/319597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Requena J. Calcium measurement in the periphery of an axon. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Sep;74(3):393–413. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill S. C., Donoso P., Eisner D. A. The role of [Ca2+]i and [Ca2+] sensitization in the caffeine contracture of rat myocytes: measurement of [Ca2+]i and [caffeine]i. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:55–70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osipchuk Y. V., Wakui M., Yule D. I., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations evoked by receptor stimulation, G-protein activation, internal application of inositol trisphosphate or Ca2+: simultaneous microfluorimetry and Ca2+ dependent Cl- current recording in single pancreatic acinar cells. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):697–704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipido K. R., Wier W. G. Flux of Ca2+ across the sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells during excitation-contraction coupling. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehno-Bittel L., Sturek M. Spontaneous sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release and extrusion from bovine, not porcine, coronary artery smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1992;451:49–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. Theory of excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):497–517. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81615-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamatsu T., Wier W. G. Calcium waves in mammalian heart: quantification of origin, magnitude, waveform, and velocity. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1519–1525. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2307330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varro A., Negretti N., Hester S. B., Eisner D. A. An estimate of the calcium content of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in rat ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Apr;423(1-2):158–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00374975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Cannell M. B., Berlin J. R., Marban E., Lederer W. J. Cellular and subcellular heterogeneity of [Ca2+]i in single heart cells revealed by fura-2. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):325–328. doi: 10.1126/science.3798114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]