Abstract
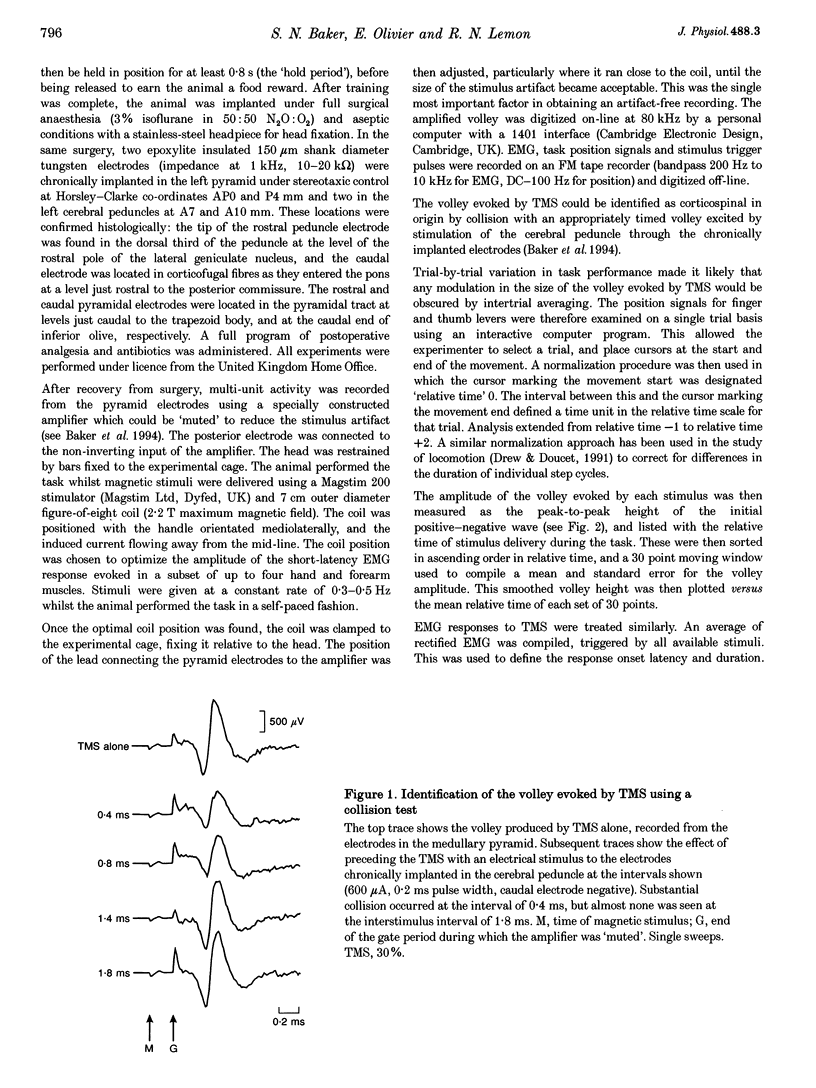
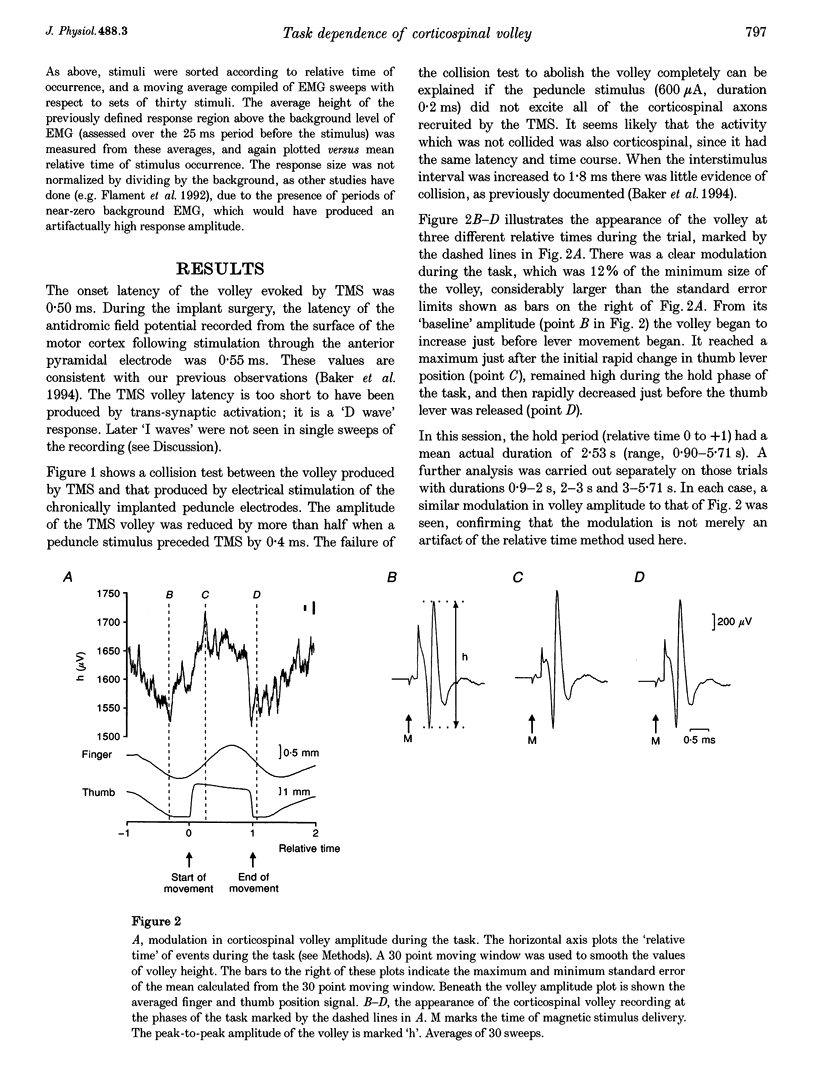
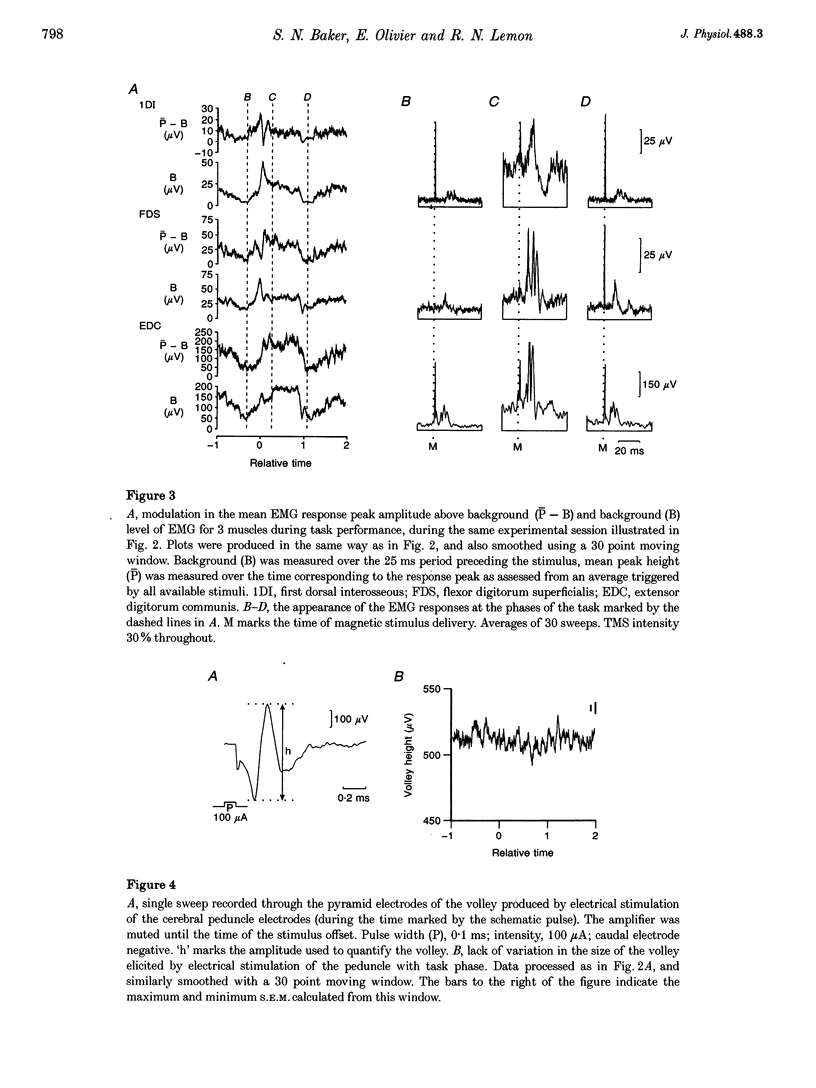
1. A volley evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) over the motor cortex was recorded from the medullary pyramid in an awake monkey performing a precision grip task. It was identified as corticospinal using a collision test. 2. The volley latency was 0.50 ms, indicating that it was produced by direct activation of corticospinal neurones. 3. A mean modulation of 13% in the amplitude of this volley was seen during task performance, with the largest volley occurring during the hold phase of the task. A similar pattern of modulation was seen in the EMG responses of hand and forearm muscles to TMS. 4. No comparable modulation was observed in a volley evoked by electrical stimulation of the corticospinal fibres via chronically implanted electrodes in the cerebral peduncle. 5. The results are compatible with direct activation of the corticospinal neurones by TMS at a site close to the soma, with the probability of activation by TMS depending on the current level of cortical excitability.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amassian V. E., Quirk G. J., Stewart M. A comparison of corticospinal activation by magnetic coil and electrical stimulation of monkey motor cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1990 Sep-Oct;77(5):390–401. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(90)90061-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amassian V. E., Stewart M., Quirk G. J., Rosenthal J. L. Physiological basis of motor effects of a transient stimulus to cerebral cortex. Neurosurgery. 1987 Jan;20(1):74–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. N., Olivier E., Lemon R. N. Recording an identified pyramidal volley evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation in a conscious macaque monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1994;99(3):529–532. doi: 10.1007/BF00228989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker A. T., Jalinous R., Freeston I. L. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet. 1985 May 11;1(8437):1106–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92413-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. M., Lemon R. N. The influence of single monkey cortico-motoneuronal cells at different levels of activity in target muscles. J Physiol. 1994 Jun 1;477(Pt 2):291–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Hicks R., Gandevia S. C., Stephen J., Woodforth I., Crawford M. Direct comparison of corticospinal volleys in human subjects to transcranial magnetic and electrical stimulation. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:383–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day B. L., Riescher H., Struppler A., Rothwell J. C., Marsden C. D. Changes in the response to magnetic and electrical stimulation of the motor cortex following muscle stretch in man. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:41–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day B. L., Thompson P. D., Dick J. P., Nakashima K., Marsden C. D. Different sites of action of electrical and magnetic stimulation of the human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Mar 20;75(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew T., Doucet S. Application of circular statistics to the study of neuronal discharge during locomotion. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Jul;38(2-3):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Eyre J. A., Lemon R. N., Miller S. Excitation of the corticospinal tract by electromagnetic and electrical stimulation of the scalp in the macaque monkey. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:301–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flament D., Goldsmith P., Buckley C. J., Lemon R. N. Task dependence of responses in first dorsal interosseous muscle to magnetic brain stimulation in man. J Physiol. 1993 May;464:361–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess C. W., Mills K. R., Murray N. M. Responses in small hand muscles from magnetic stimulation of the human brain. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:397–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. R., Corrie W. S. Properties of pyramidal tract neuron system within a functionally defined subregion of primate motor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Jan;41(1):216–243. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.1.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inghilleri M., Berardelli A., Cruccu G., Priori A., Manfredi M. Corticospinal potentials after transcranial stimulation in humans. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Aug;52(8):970–974. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.8.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson R. S., Lemon R. N., Westling G. Time-varying enhancement of human cortical excitability mediated by cutaneous inputs during precision grip. J Physiol. 1994 Dec 15;481(Pt 3):761–775. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. N., Mantel G. W., Muir R. B. Corticospinal facilitation of hand muscles during voluntary movement in the conscious monkey. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:497–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Petersen N., Ballegaard M. Latency of effects evoked by electrical and magnetic brain stimulation in lower limb motoneurones in man. J Physiol. 1995 May 1;484(Pt 3):791–802. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Petersen N., Deuschl G., Ballegaard M. Task-related changes in the effect of magnetic brain stimulation on spinal neurones in man. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:223–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werhahn K. J., Fong J. K., Meyer B. U., Priori A., Rothwell J. C., Day B. L., Thompson P. D. The effect of magnetic coil orientation on the latency of surface EMG and single motor unit responses in the first dorsal interosseous muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1994 Apr;93(2):138–146. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(94)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



