Abstract
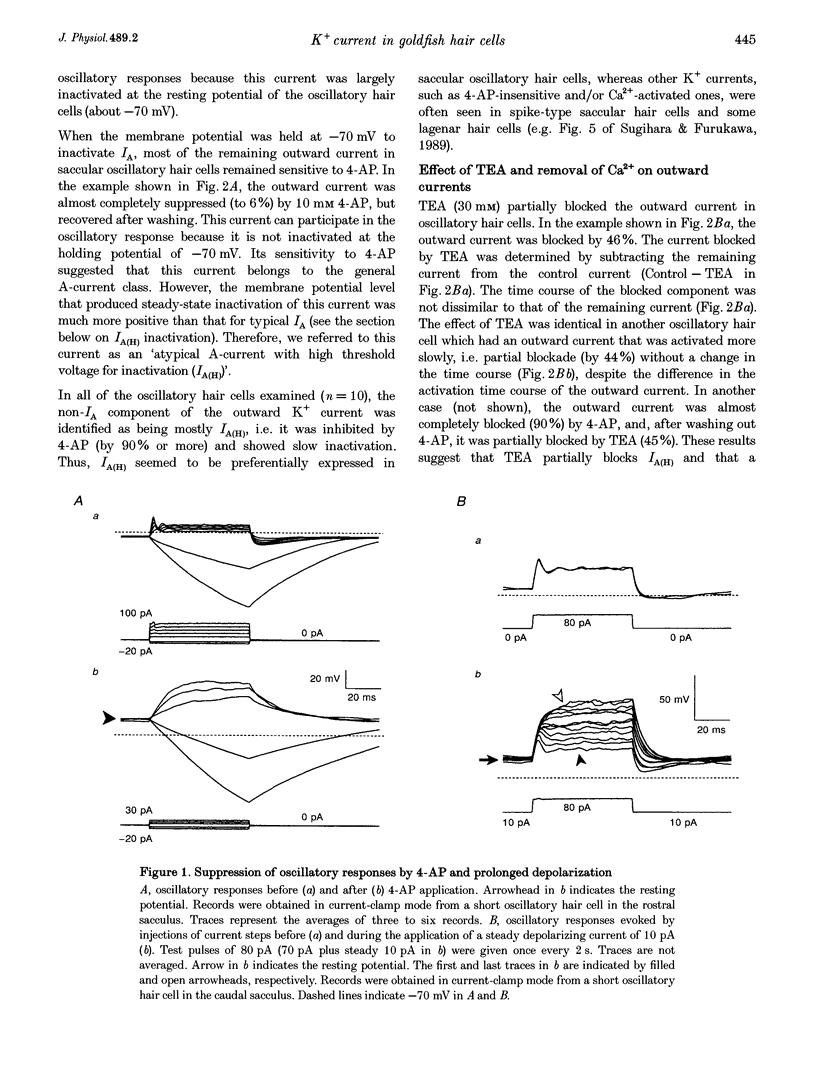
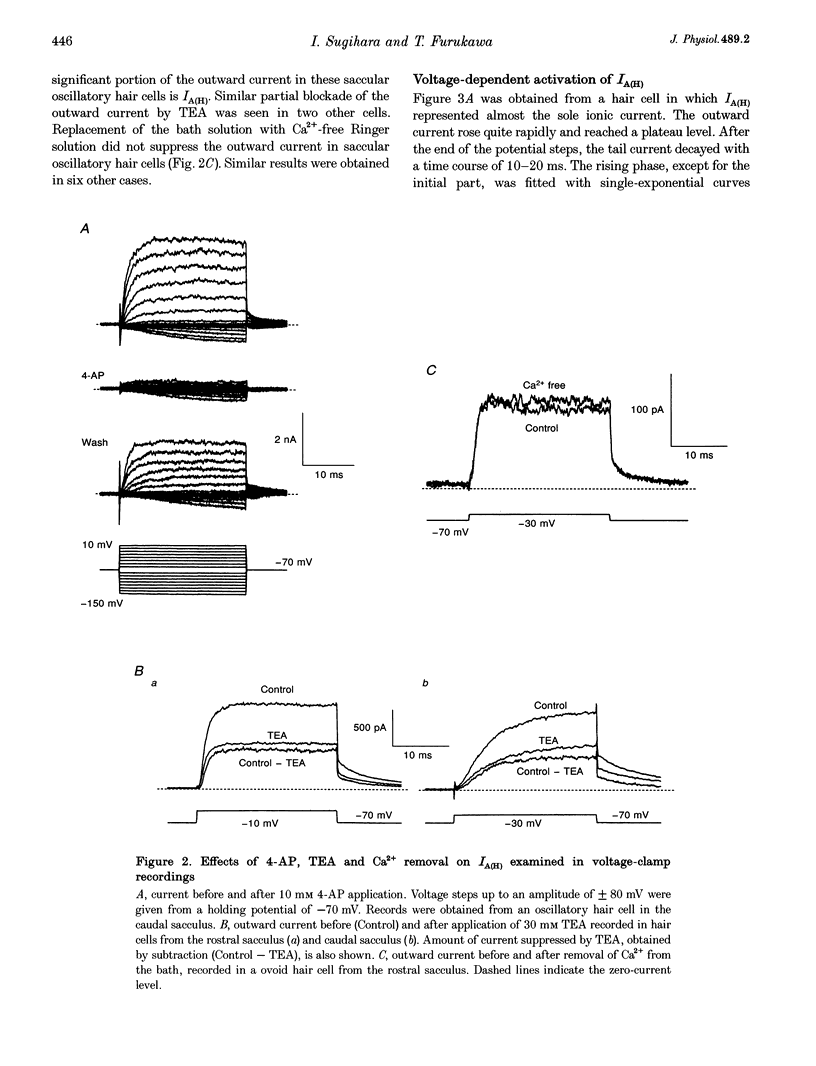
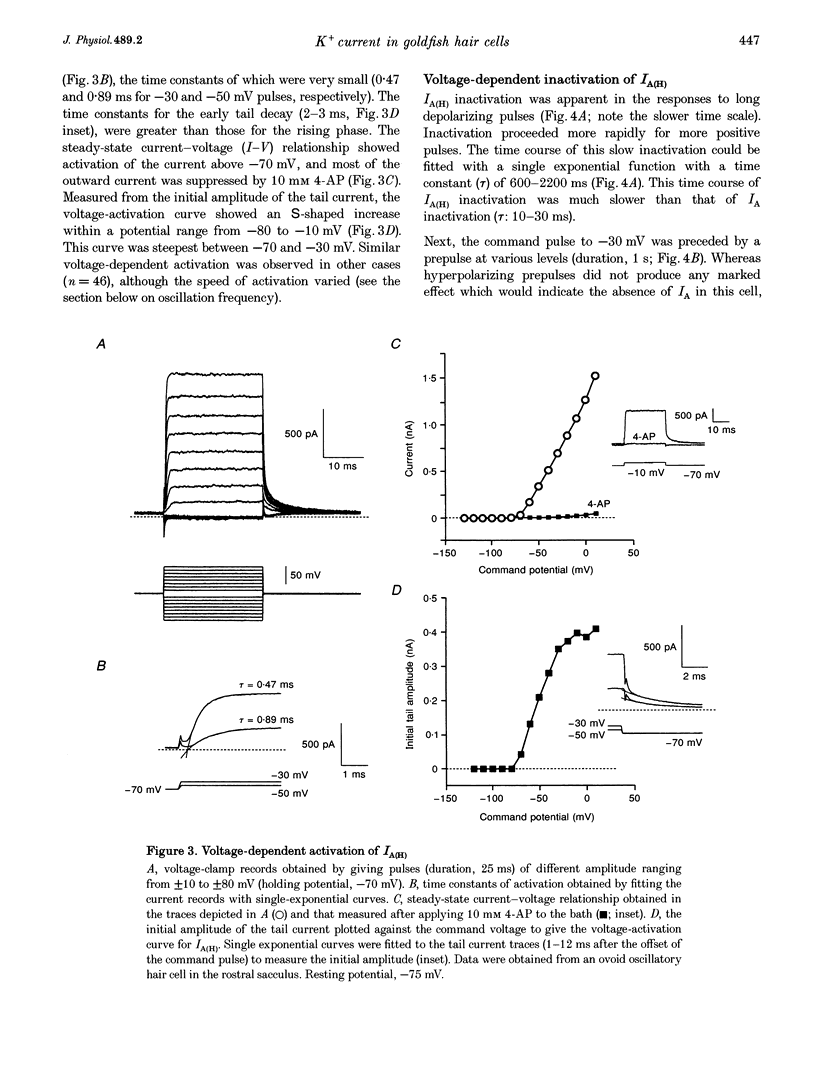
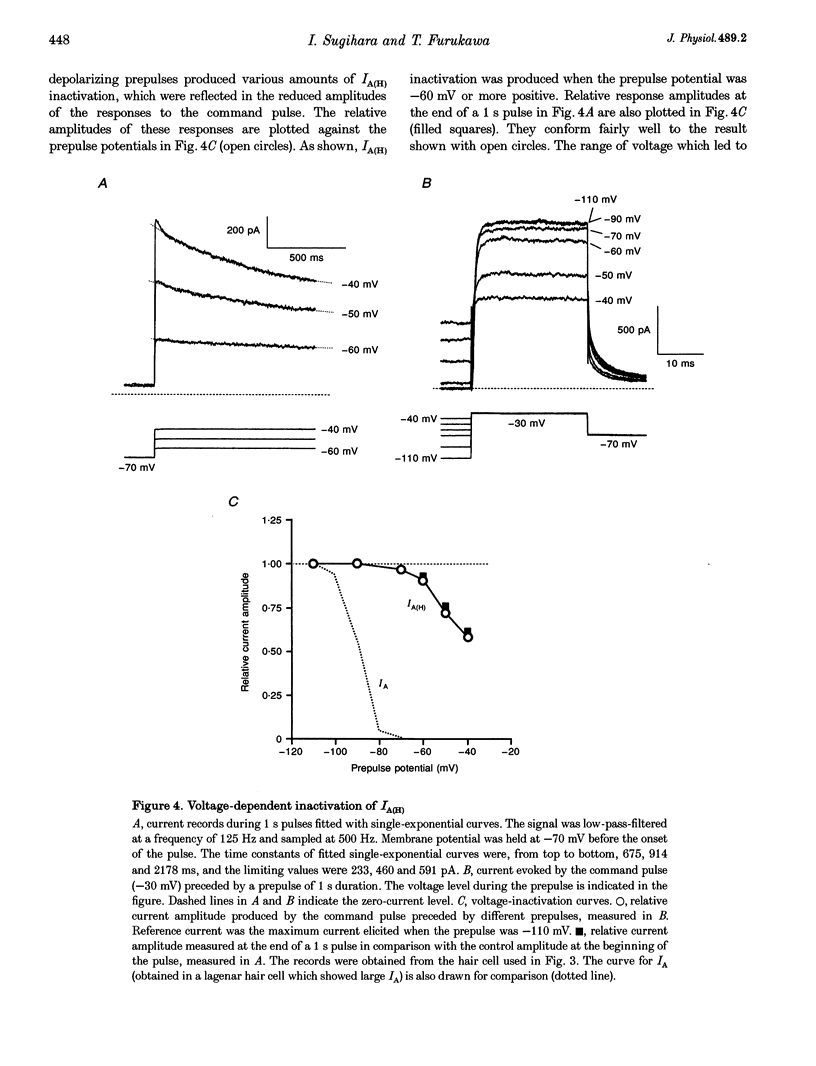
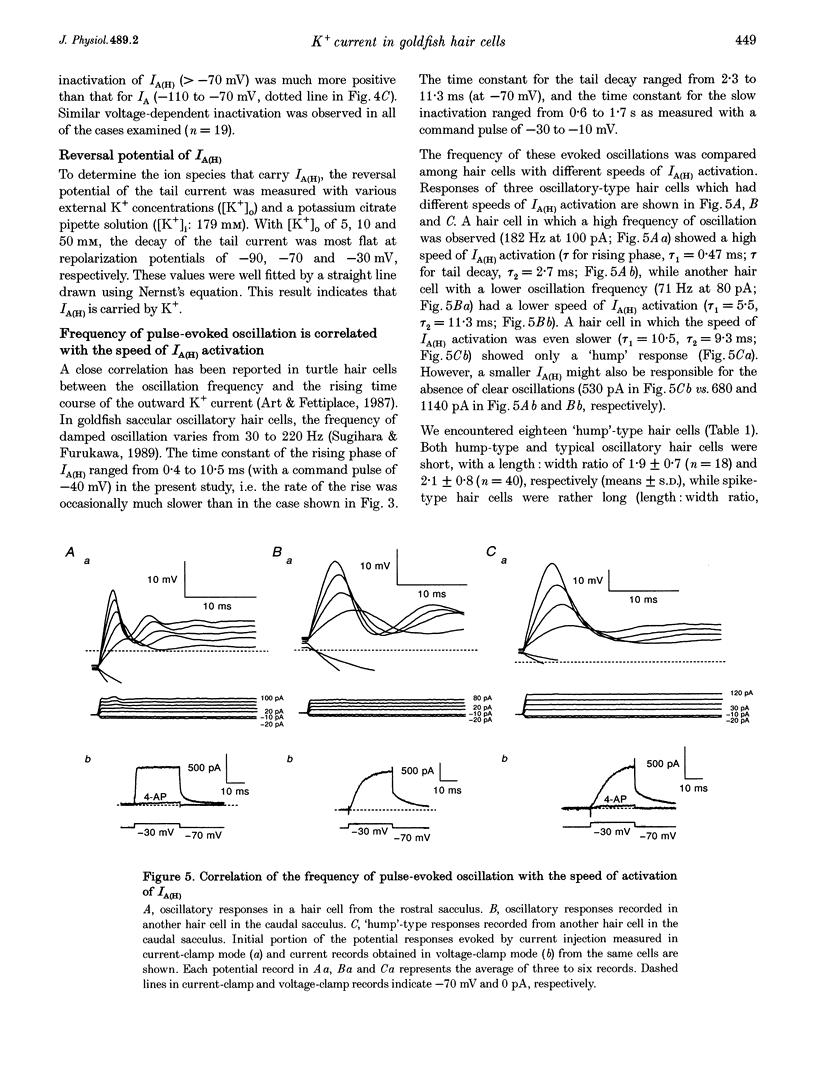
1. Ionic currents underlying the oscillatory response of membrane potential were studied in oscillatory-type hair cells isolated from the goldfish sacculus with the whole-cell recording method using a patch pipette. 2. Bath application of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP; 10 mM) reversibly produced moderate depolarization of the resting potential along with complete suppression of the oscillatory response. Sustained injection of a small depolarizing current also suppressed the oscillatory response. 3. A 4-AP-sensitive atypical A-type K+ current which had a high threshold voltage for inactivation (IA(H)) was found to be a major outward current underlying the oscillatory response. 4. IA(H) was activated with a time constant of 0.4-10 ms and was inactivated slowly with a time constant of 0.6-2 s. IA(H) activation and inactivation occurred mostly at membrane potentials more positive than -70 mV. 5. There was a clear correlation between activation speed of IA(H) and the frequency of pulse-evoked oscillation. A 'hump'-type response was produced in about one-quarter of the oscillatory-type hair cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Art J. J., Fettiplace R. Variation of membrane properties in hair cells isolated from the turtle cochlea. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:207–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Art J. J., Fettiplace R., Wu Y. C. The effects of low calcium on the voltage-dependent conductances involved in tuning of turtle hair cells. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:109–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore J. F. Frequency tuning in a frog vestibular organ. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):536–538. doi: 10.1038/304536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Bertrand D. Effect of changes in intra- and extracellular sodium on the inward (anomalous) rectification in salamander photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:611–631. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs S., Fay R. R. Response dynamics of goldfish saccular fibers: effects of stimulus frequency and intensity on fibers with different tuning, sensitivity, and spontaneous activity. J Acoust Soc Am. 1987 Apr;81(4):1025–1035. doi: 10.1121/1.395113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correia M. J., Christensen B. N., Moore L. E., Lang D. G. Studies of solitary semicircular canal hair cells in the adult pigeon. I. Frequency- and time-domain analysis of active and passive membrane properties. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Oct;62(4):924–934. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.4.924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. C., Fettiplace R. An electrical tuning mechanism in turtle cochlear hair cells. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:377–412. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eatock R. A., Saeki M., Hutzler M. J. Electrical resonance of isolated hair cells does not account for acoustic tuning in the free-standing region of the alligator lizard's cochlea. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1767–1783. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01767.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay R. R. Phase-locking in goldfish saccular nerve fibres accounts for frequency discrimination capacities. Nature. 1978 Sep 28;275(5678):320–322. doi: 10.1038/275320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay R. R., Ream T. J. Acoustic response and tuning in saccular nerve fibers of the goldfish (Carassius auratus). J Acoust Soc Am. 1986 Jun;79(6):1883–1895. doi: 10.1121/1.393196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. A., Evans M. G., Murrow B. W. Calcium currents in hair cells isolated from the cochlea of the chick. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:553–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. A., Evans M. G. Potassium currents in hair cells isolated from the cochlea of the chick. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:529–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. A., Nagai T., Evans M. G. Electrical tuning in hair cells isolated from the chick cochlea. J Neurosci. 1988 Jul;8(7):2460–2467. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-07-02460.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Ishii Y. Neurophysiological studies on hearing in goldfish. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Nov;30(6):1377–1403. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.6.1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Sugihara I. Multiplicity of ionic currents underlying the oscillatory-type activity of isolated goldfish hair cells. Neurosci Res Suppl. 1990;12:S27–S38. doi: 10.1016/0921-8696(90)90006-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S. The properties and function of inward rectification in rod photoreceptors of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:319–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J., Lewis R. S. A model for electrical resonance and frequency tuning in saccular hair cells of the bull-frog, Rana catesbeiana. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:275–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J., Lewis R. S. Kinetic analysis of voltage- and ion-dependent conductances in saccular hair cells of the bull-frog, Rana catesbeiana. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:237–274. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kros C. J., Crawford A. C. Potassium currents in inner hair cells isolated from the guinea-pig cochlea. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:263–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. G., Correia M. J. Studies of solitary semicircular canal hair cells in the adult pigeon. II. Voltage-dependent ionic conductances. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Oct;62(4):935–945. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.4.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. S., Hudspeth A. J. Voltage- and ion-dependent conductances in solitary vertebrate hair cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):538–541. doi: 10.1038/304538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris C. H., Ricci A. J., Housley G. D., Guth P. S. The inactivating potassium currents of hair cells isolated from the crista ampullaris of the frog. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Nov;68(5):1642–1653. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.5.1642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie K. J., Ashmore J. F. Ionic currents in isolated vestibular hair cells from the guinea-pig crista ampullaris. Hear Res. 1991 Feb;51(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(91)90044-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):729–749. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinacker A., Romero A. Voltage-gated potassium current and resonance in the toadfish saccular hair cell. Brain Res. 1992 Mar 6;574(1-2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90821-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara I. Calcium-activated potassium channels in goldfish hair cells. J Physiol. 1994 May 1;476(3):373–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
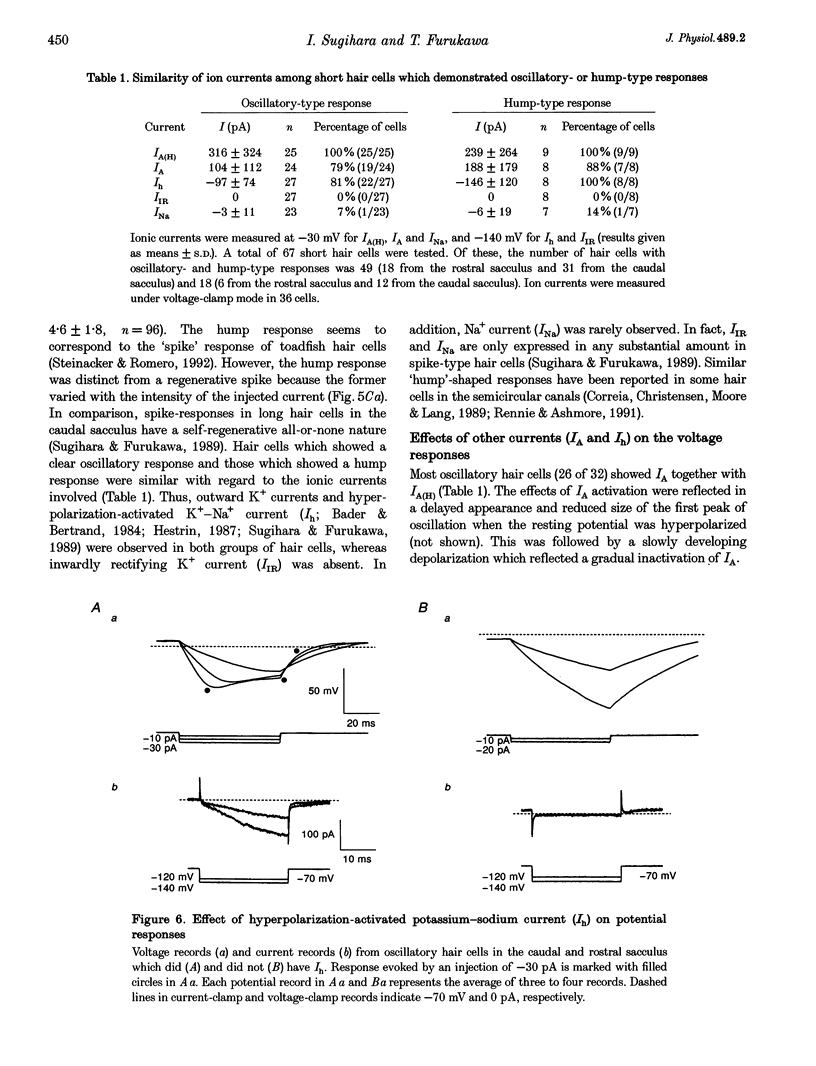
- Sugihara I., Furukawa T. Morphological and functional aspects of two different types of hair cells in the goldfish sacculus. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Dec;62(6):1330–1343. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



