Abstract
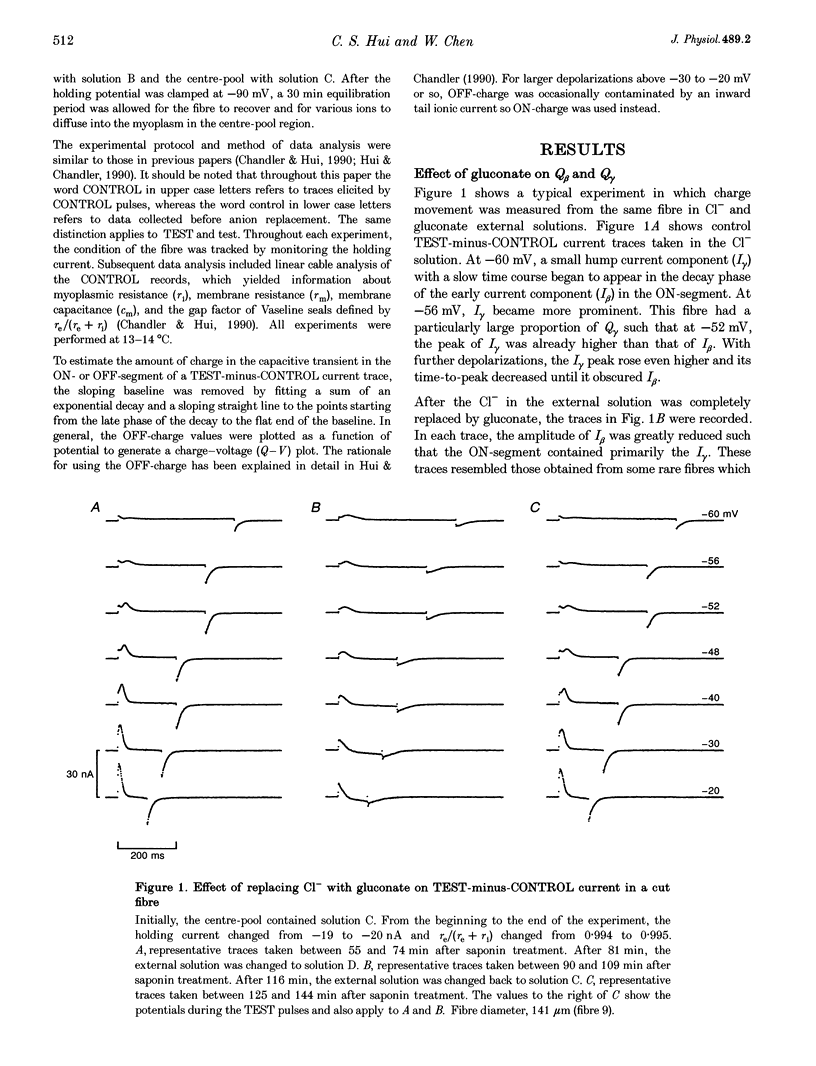
1. Charge movement was studied in cut twitch fibres of Rana temporaria using a double Vaseline-gap voltage-clamp technique. 2. Replacement of Cl- by gluconate in the external solution reduced the magnitude of the early current component (I beta) substantially but affected the magnitude and slowed the kinetics of the hump current component (I gamma) slightly. 3. The early (Q beta) and hump (Q gamma) charge components in the gluconate solution were 11.8 +/- 2.3 and 88.0 +/- 4.8% (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 9), respectively, of those in the Cl- solution. 4. These results suggest that Q beta cannot be a precursor of Q gamma. Moreover, since fibres bathed in a gluconate solution can release calcium, Q beta is probably not involved in triggering calcium release.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Peres A. R. A gating signal for the potassium channel? Nature. 1977 Jun 30;267(5614):800–804. doi: 10.1038/267800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peres A. Charge movement and membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:83–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Hui C. S. Membrane capacitance in frog cut twitch fibers mounted in a double vaseline-gap chamber. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Aug;96(2):225–256. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Hui C. S. Existence of Q gamma in frog cut twitch fibers with little Q beta. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):503–507. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82243-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csernoch L., Pizarro G., Uribe I., Rodríguez M., Ríos E. Interfering with calcium release suppresses I gamma, the "hump" component of intramembranous charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1991 May;97(5):845–884. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. 'Off' tails of intramembrane charge movements in frog skeletal muscle in perchlorate-containing solutions. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:491–509. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Charge conservation in intact frog skeletal muscle fibres in gluconate-containing solutions. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 1;474(1):161–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:375–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. The differential effects of twitch potentiators on charge movements in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S., Chandler W. K. Intramembranous charge movement in frog cut twitch fibers mounted in a double vaseline-gap chamber. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Aug;96(2):257–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S., Chandler W. K. Q beta and Q gamma components of intramembranous charge movement in frog cut twitch fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Sep;98(3):429–464. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Comparison of charge movement components in intact and cut twitch fibers of the frog. Effects of stretch and temperature. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Aug;98(2):287–314. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Differential properties of two charge components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:531–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Factors affecting the appearance of the hump charge movement component in frog cut twitch fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Aug;98(2):315–347. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Pharmacological dissection of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1982 Jul;39(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84498-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M., Maylie J., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Intrinsic optical and passive electrical properties of cut frog twitch fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):1–40. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs L., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Measurement and modification of free calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres by a metallochromic indicator dye. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:161–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape P. C., Jong D. S., Chandler W. K. Calcium release and its voltage dependence in frog cut muscle fibers equilibrated with 20 mM EGTA. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Aug;106(2):259–336. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J., Caputo C. Effects of tetracaine on charge movements and calcium signals in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1477–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


