Abstract
1. To examine the dependence of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptor gating on the alpha-subunit isoform, we studied the kinetics of GABA-gated currents (IGABA) of receptors that differed in the alpha-subunit subtype, alpha 1 beta 2 gamma 2S and alpha 3 beta 2 gamma 2S. cDNAs encoding rat brain subunits were co-expressed heterologously in HEK-293 cells and the resultant receptors studied with the whole-cell patch clamp technique and rapidly applied GABA pulses (5-10 s). 2. IGABA of both receptors showed a loosely similar dependence on GABA concentration over a wide range (1-5000 microM). Generally, IGABA manifested activation reaching an early current peak, subsequent slower spontaneous desensitization, and deactivation of open channels at pulse termination. Lowering GABA concentrations reduced peak currents and slowed activation and desensitization kinetics. 3. The presence of alpha 3 altered the peak IGABA concentration-response relationship by shifting the fitted Hill equation to tenfold greater GABA concentrations (GABA concentration at half amplitude: alpha 1, 7 microM; and alpha 3, 75 microM) without affecting Hill coefficients (alpha 1, 1.6; alpha 3, 1.5). These findings indicate a reduction in the apparent activating site affinity and are consistent with previous reports. 4. To investigate differences in gating, we normalized for apparent activating site affinities by analysing the time course of macroscopic gating at equi-activating GABA concentrations. The presence of alpha 3 slowed activation fourfold (time to current peak (means +/- S.E.M.): alpha 1, 1.2 +/- 0.06 s (2 microM); alpha 3, 4.7 +/- 0.5 s (20 microM)), desensitization nearly twofold (reciprocal of time to 80% decay: alpha 1, 2.5 +/- 0.48 s-1 (100 microM); alpha 3, 1.5 +/- 0.15 s-1 (1000 microM)) and deactivation threefold (monoexponential decay time constant: alpha 1, 0.22 +/- 0.026 s (2 microM); alpha 3, 0.68 +/- 0.1 s (20 microM)). 5. To gain an insight into the gating mechanisms underlying macroscopic desensitization, we extended a previous gating model of GABAA receptor single-channel activity to include a desensitization pathway. Such a mechanism reproduced empirical alpha 1 beta 2 gamma 2S activation, desensitization and deactivation kinetics. 6. To identify molecular transitions underlying the gating differences between alpha 1 beta 2 gamma 2S and alpha 3 beta 2 gamma 2S receptors, we explored parameter alterations of the alpha 1 beta 2 gamma 2S gating model that provided an accounting of alpha 3 beta 2 gamma 2S empirical responses. Remarkably, alteration of rates and rate constants involved in ligand binding alone allowed reproduction of alpha 3 beta 2 gamma 2S activation, desensitization and deactivation. 7. These results indicate that substitution of the alpha 3 subunit variant in an alpha 1 beta 2 gamma 2S receptor alters transition rates involved in ligand binding that underlie changes in apparent activating site affinity and macroscopic current gating. Furthermore, they argue strongly that the structural determinants of these functional features reside on the alpha-subunit.
Full text
PDF


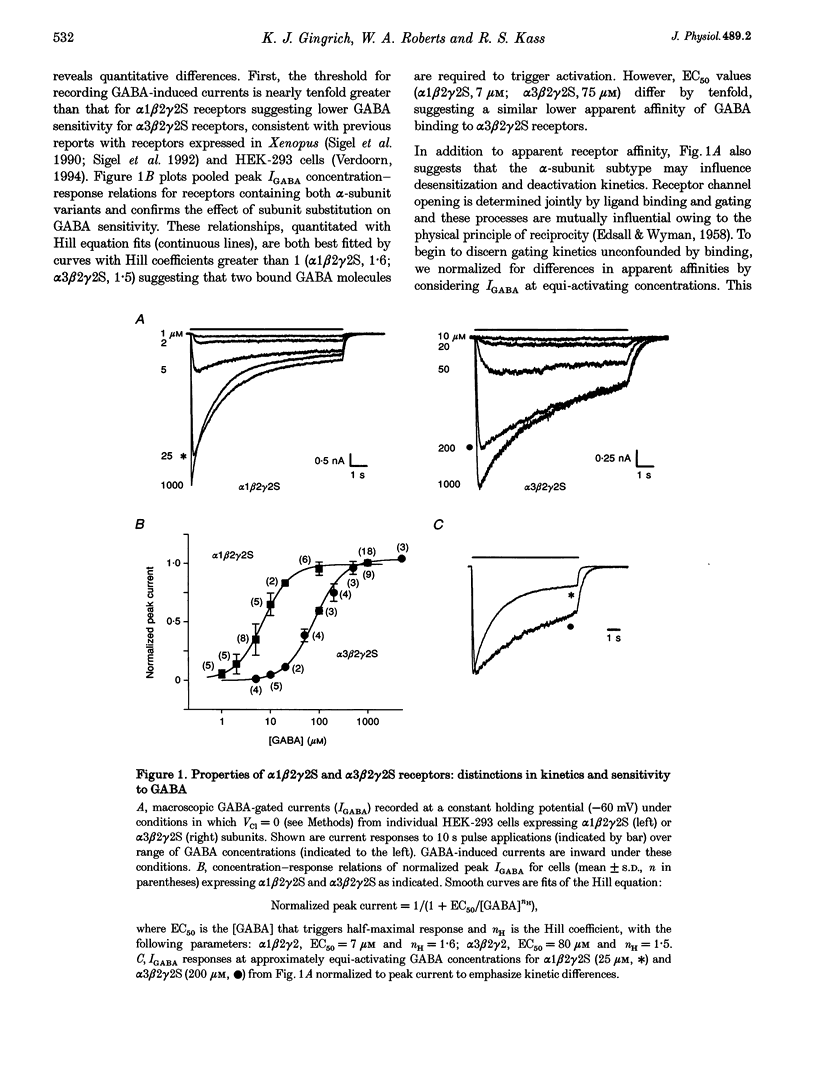

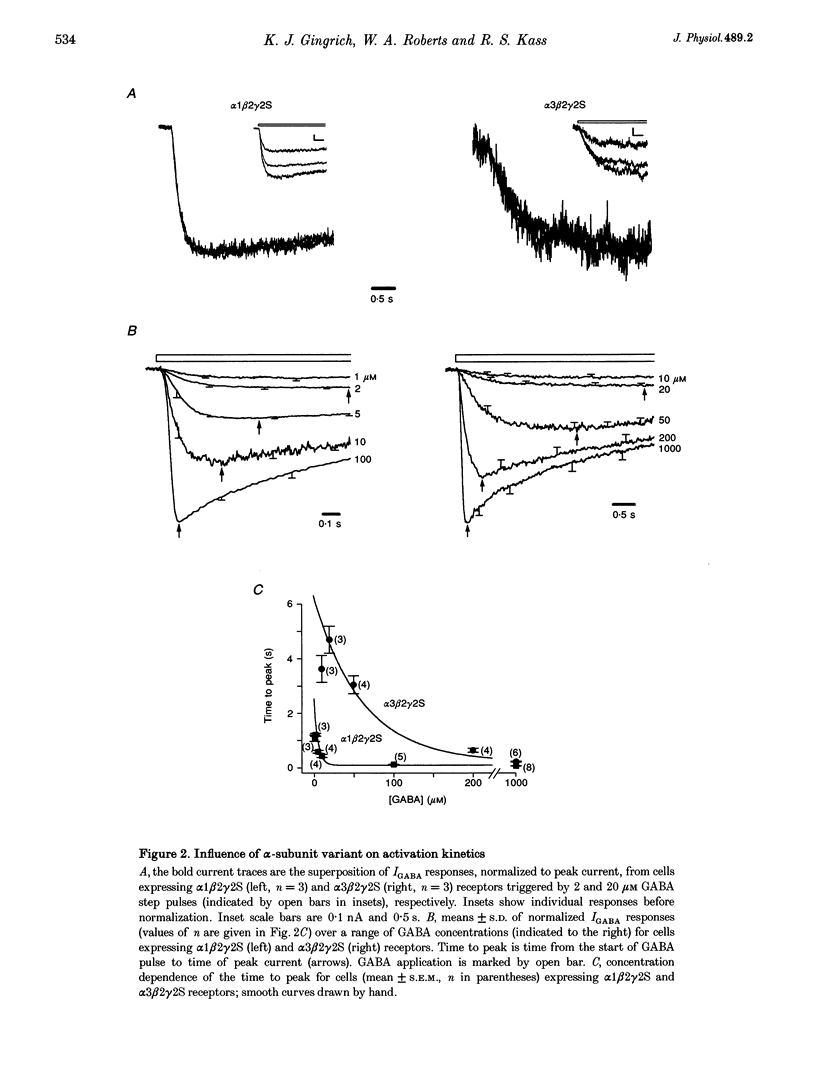
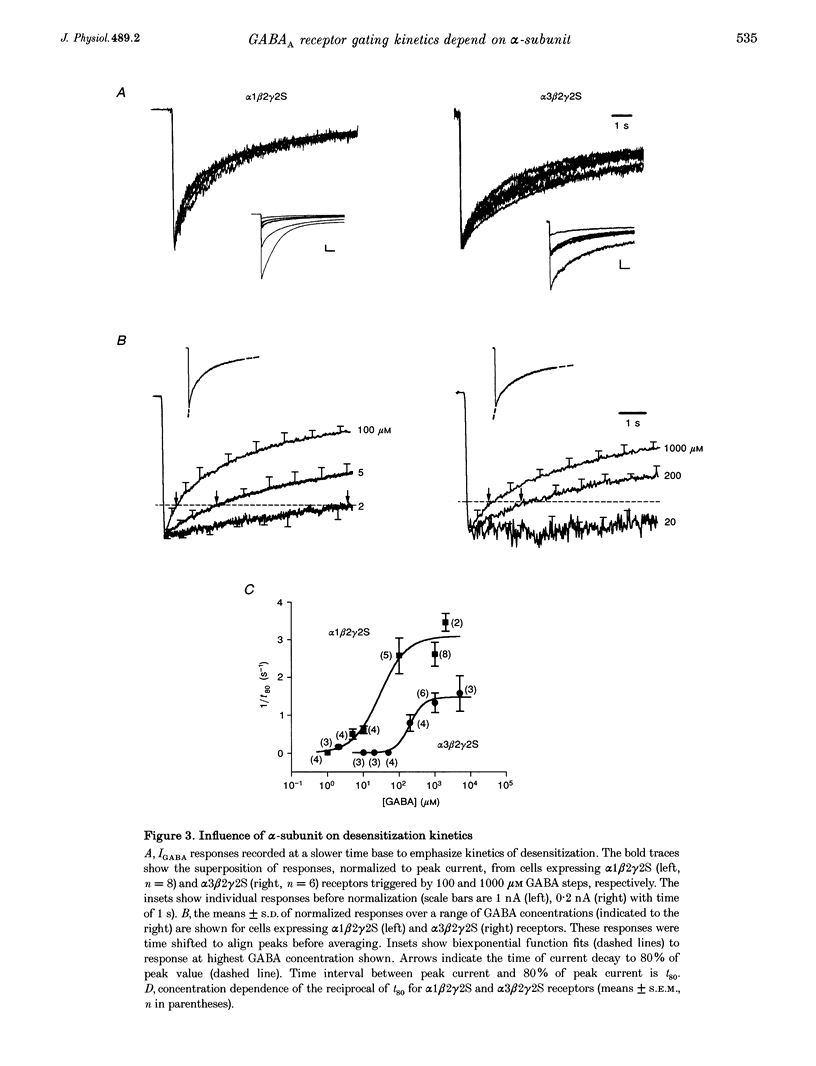
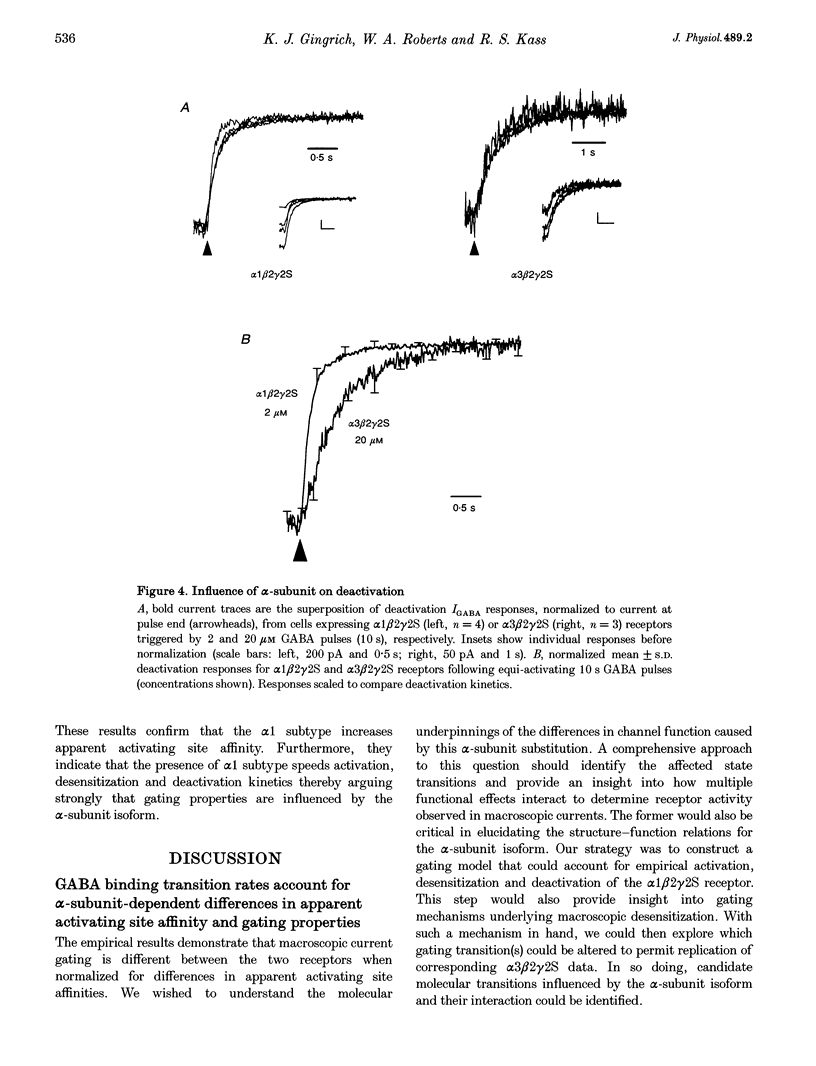
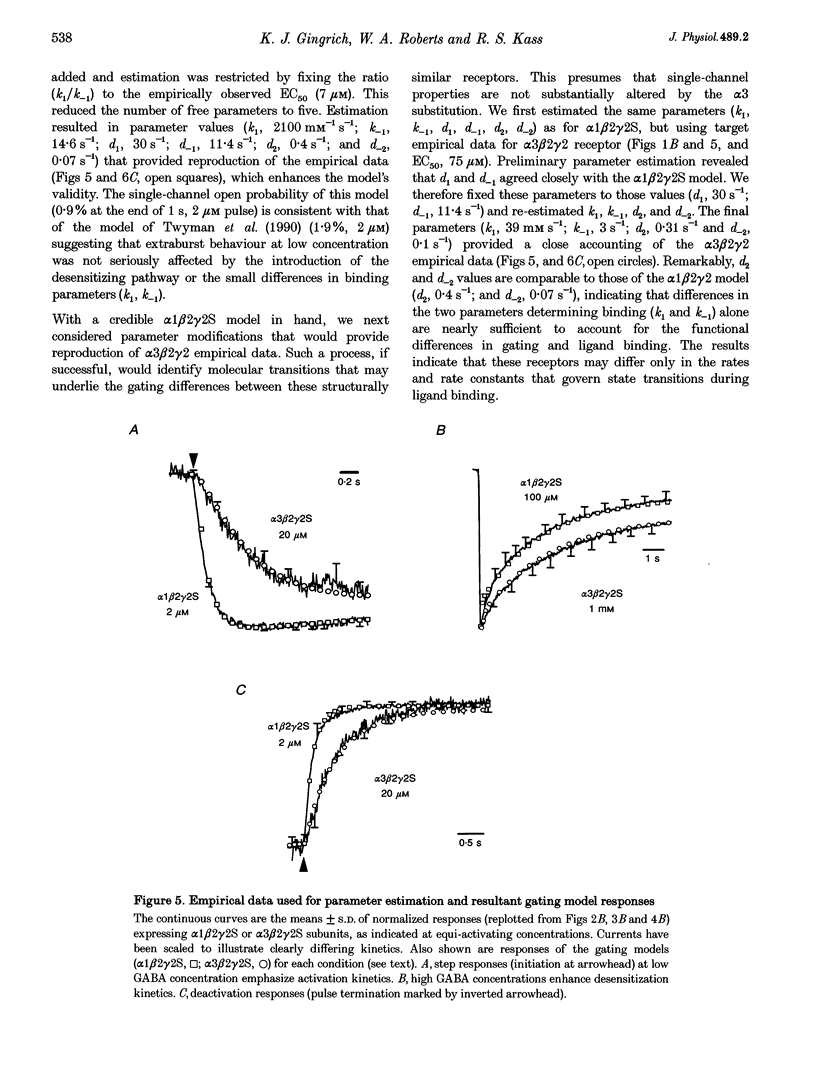
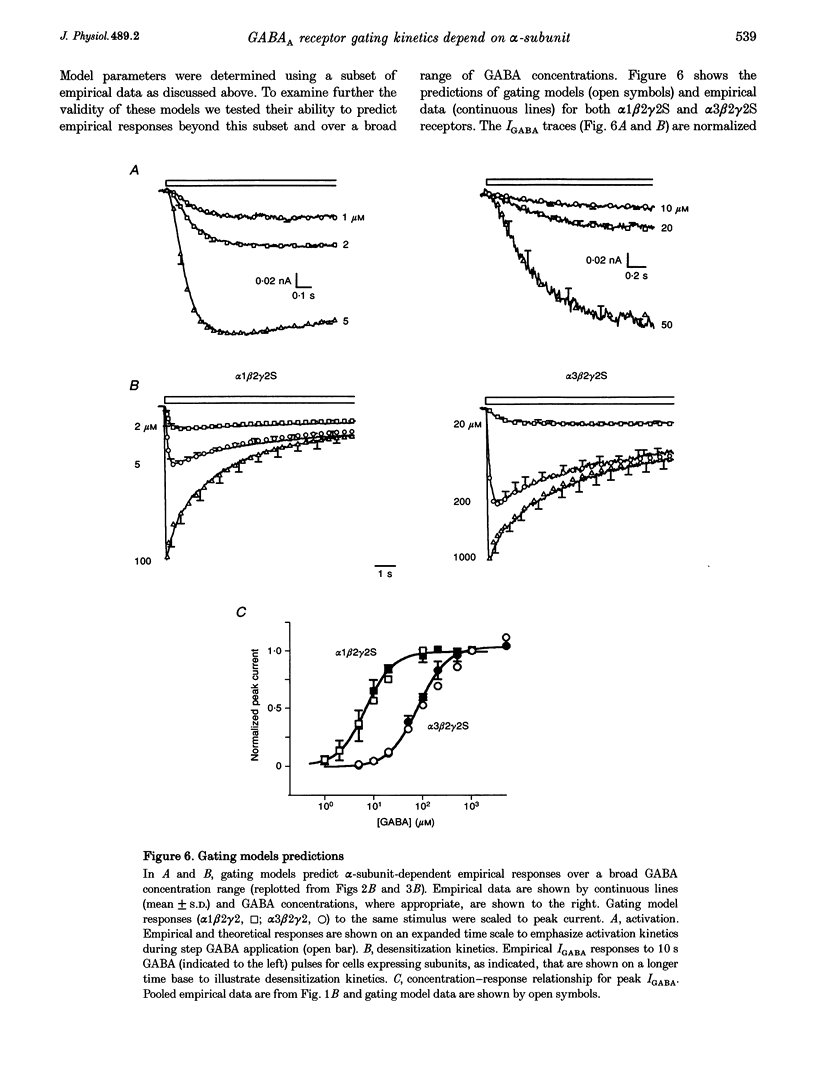

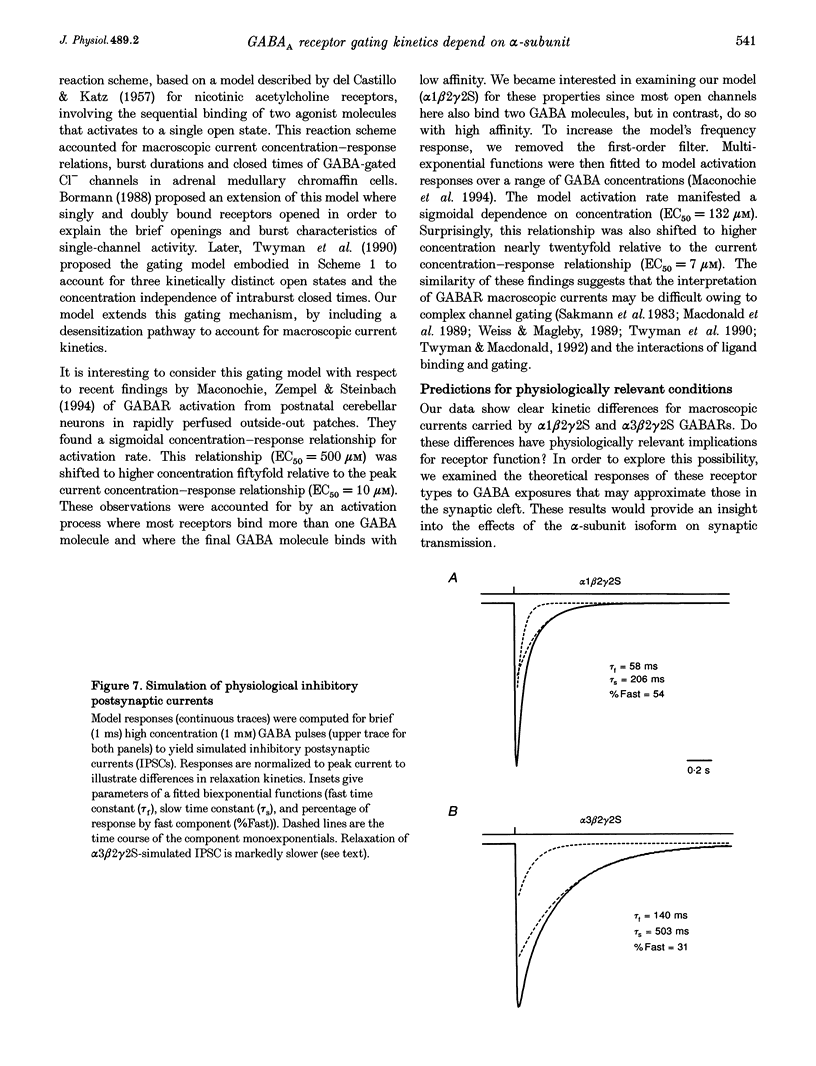


Selected References
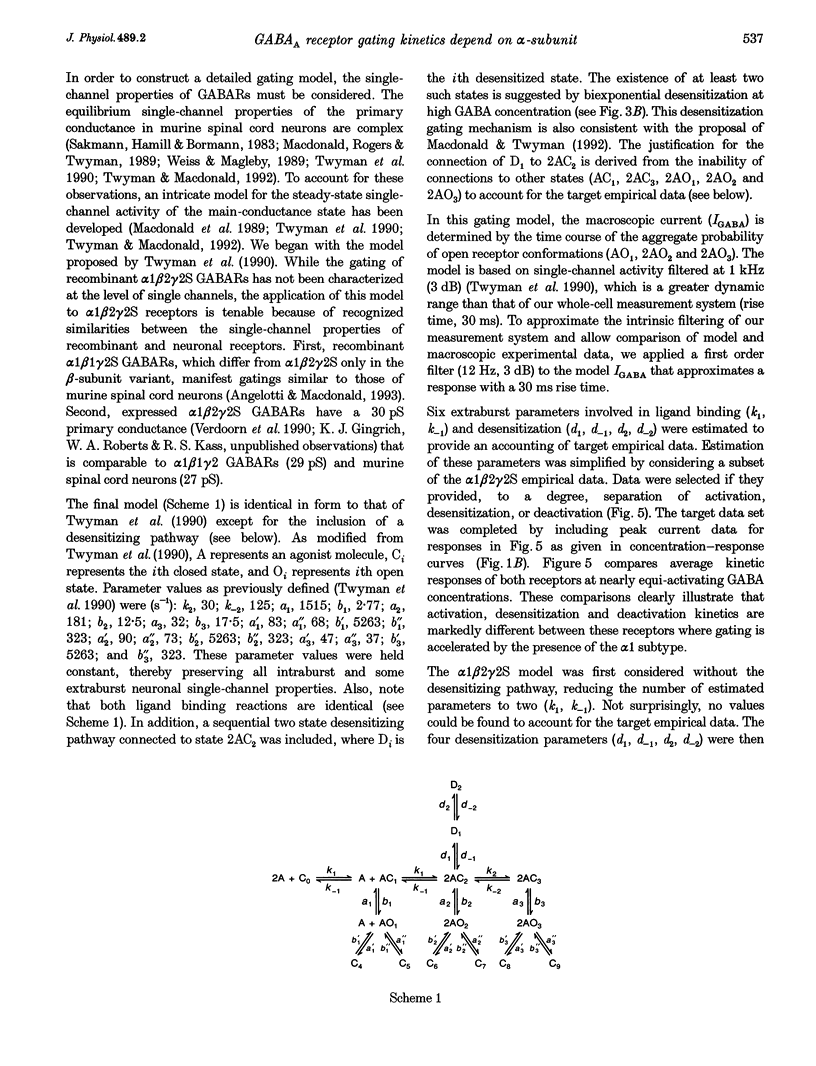
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Inoue M., Krishtal O. A. 'Concentration-clamp' study of gamma-aminobutyric-acid-induced chloride current kinetics in frog sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:171–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin J., Weiss D. S. GABAA receptor needs two homologous domains of the beta-subunit for activation by GABA but not by pentobarbital. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):565–569. doi: 10.1038/366565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelotti T. P., Macdonald R. L. Assembly of GABAA receptor subunits: alpha 1 beta 1 and alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 2S subunits produce unique ion channels with dissimilar single-channel properties. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1429–1440. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01429.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Clapham D. E. gamma-Aminobutyric acid receptor channels in adrenal chromaffin cells: a patch-clamp study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2168–2172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. R., Kamatchi G. L. GABAA receptor subtypes: from pharmacology to molecular biology. FASEB J. 1991 Nov;5(14):2916–2923. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.14.1661244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casalotti S. O., Stephenson F. A., Barnard E. A. Separate subunits for agonist and benzodiazepine binding in the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor oligomer. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15013–15016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Interaction at end-plate receptors between different choline derivatives. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):369–381. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng L., Ransom R. W., Olsen R. W. [3H]muscimol photolabels the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding site on a peptide subunit distinct from that labeled with benzodiazepines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1308–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draguhn A., Verdorn T. A., Ewert M., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional and molecular distinction between recombinant rat GABAA receptor subtypes by Zn2+. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):781–788. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90337-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Konnerth A., Sakmann B. Quantal analysis of inhibitory synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus of rat hippocampal slices: a patch-clamp study. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:213–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs K., Möhler H., Sieghart W. Various proteins from rat brain, specifically and irreversibly labeled by [3H]flunitrazepam, are distinct alpha-subunits of the GABA-benzodiazepine receptor complex. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 1;90(3):314–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs K., Sieghart W. Evidence for the existence of several different alpha- and beta-subunits of the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor complex from rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Feb 27;97(3):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90619-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré E., Attali B., Romey G., Lesage F., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Different types of K+ channel current are generated by different levels of a single mRNA. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2465–2471. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khrestchatisky M., MacLennan A. J., Chiang M. Y., Xu W. T., Jackson M. B., Brecha N., Sternini C., Olsen R. W., Tobin A. J. A novel alpha subunit in rat brain GABAA receptors. Neuron. 1989 Dec;3(6):745–753. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkness E. F., Turner A. J. Antibodies directed against a nonapeptide sequence of the gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA)/benzodiazepine receptor alpha-subunit. Detection of a distinct alpha-like subunit in pig cerebral cortex but not cerebellum. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):291–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2560291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. J., Seeburg P. H., Wisden W. The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. II. Olfactory bulb and cerebellum. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1063–1076. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01063.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan E. S., Schofield P. R., Burt D. R., Rhee L. M., Wisden W., Köhler M., Fujita N., Rodriguez H. F., Stephenson A., Darlison M. G. Structural and functional basis for GABAA receptor heterogeneity. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):76–79. doi: 10.1038/335076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. L., Twyman R. E. Kinetic properties and regulation of GABAA receptor channels. Ion Channels. 1992;3:315–343. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3328-3_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Rogers C. J., Twyman R. E. Kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor main conductance state of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:479–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconochie D. J., Zempel J. M., Steinbach J. H. How quickly can GABAA receptors open? Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce R. A. Physiological evidence for two distinct GABAA responses in rat hippocampus. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90310-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Lüddens H., Seeburg P. H. Type I and type II GABAA-benzodiazepine receptors produced in transfected cells. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1389–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2551039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Sontheimer H., Shivers B. D., Ymer S., Kettenmann H., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Importance of a novel GABAA receptor subunit for benzodiazepine pharmacology. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):582–585. doi: 10.1038/338582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Costa E., Vicini S. Functional diversity of GABA-activated Cl- currents in Purkinje versus granule neurons in rat cerebellar slices. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Hamill O. P., Bormann J. Patch-clamp measurements of elementary chloride currents activated by the putative inhibitory transmitter GABA and glycine in mammalian spinal neurons. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1983;18:83–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Wisden W., Verdoorn T. A., Pritchett D. B., Werner P., Herb A., Lüddens H., Sprengel R., Sakmann B. The GABAA receptor family: molecular and functional diversity. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:29–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R., Kellenberger S., Malherbe P. Point mutations affecting antagonist affinity and agonist dependent gating of GABAA receptor channels. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2017–2023. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R., Trube G., Möhler H., Malherbe P. The effect of subunit composition of rat brain GABAA receptors on channel function. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivilotti L., Nistri A. GABA receptor mechanisms in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36(1):35–92. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90036-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Macdonald R. L. Neurosteroid regulation of GABAA receptor single-channel kinetic properties of mouse spinal cord neurons in culture. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:215–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Rogers C. J., Macdonald R. L. Intraburst kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor main conductance state of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:193–220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Draguhn A., Ymer S., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional properties of recombinant rat GABAA receptors depend upon subunit composition. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A. Formation of heteromeric gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors containing two different alpha subunits. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):475–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathey J. C., Nass M. M., Lester H. A. Numerical reconstruction of the quantal event at nicotinic synapses. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):145–164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85208-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Magleby K. L. Gating scheme for single GABA-activated Cl- channels determined from stability plots, dwell-time distributions, and adjacent-interval durations. J Neurosci. 1989 Apr;9(4):1314–1324. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-04-01314.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Laurie D. J., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H. The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. I. Telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1040–1062. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01040.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



