Abstract
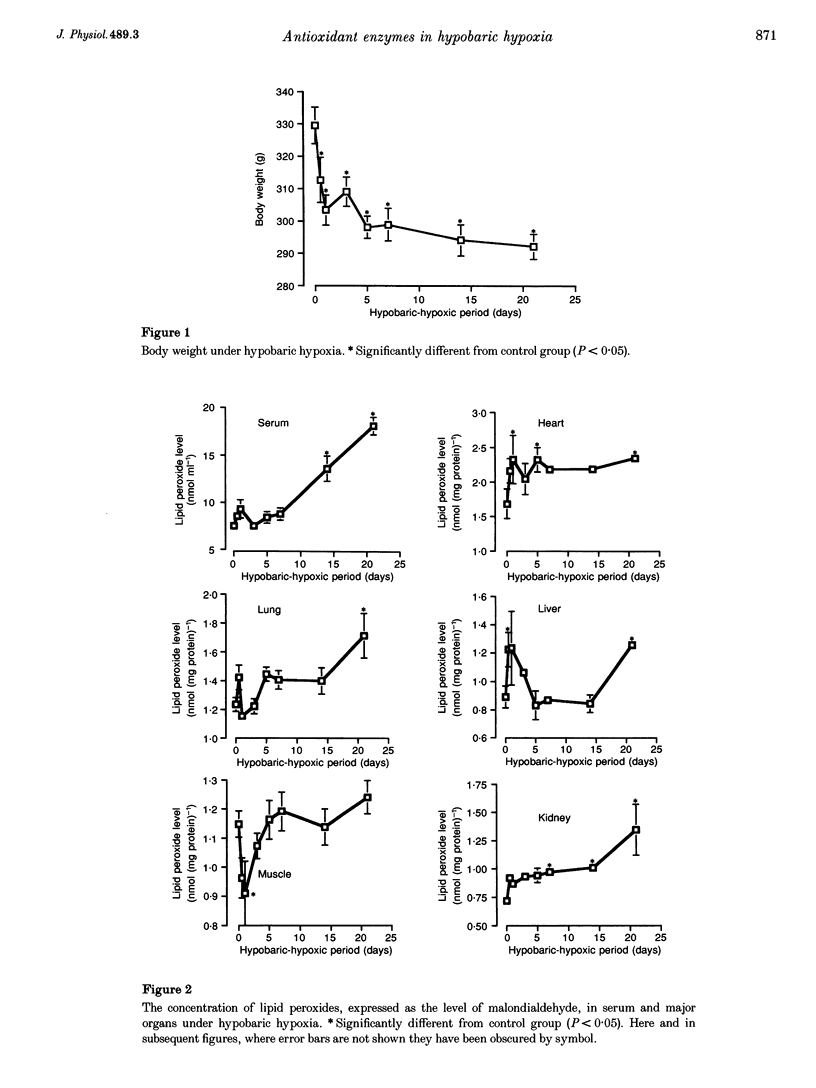
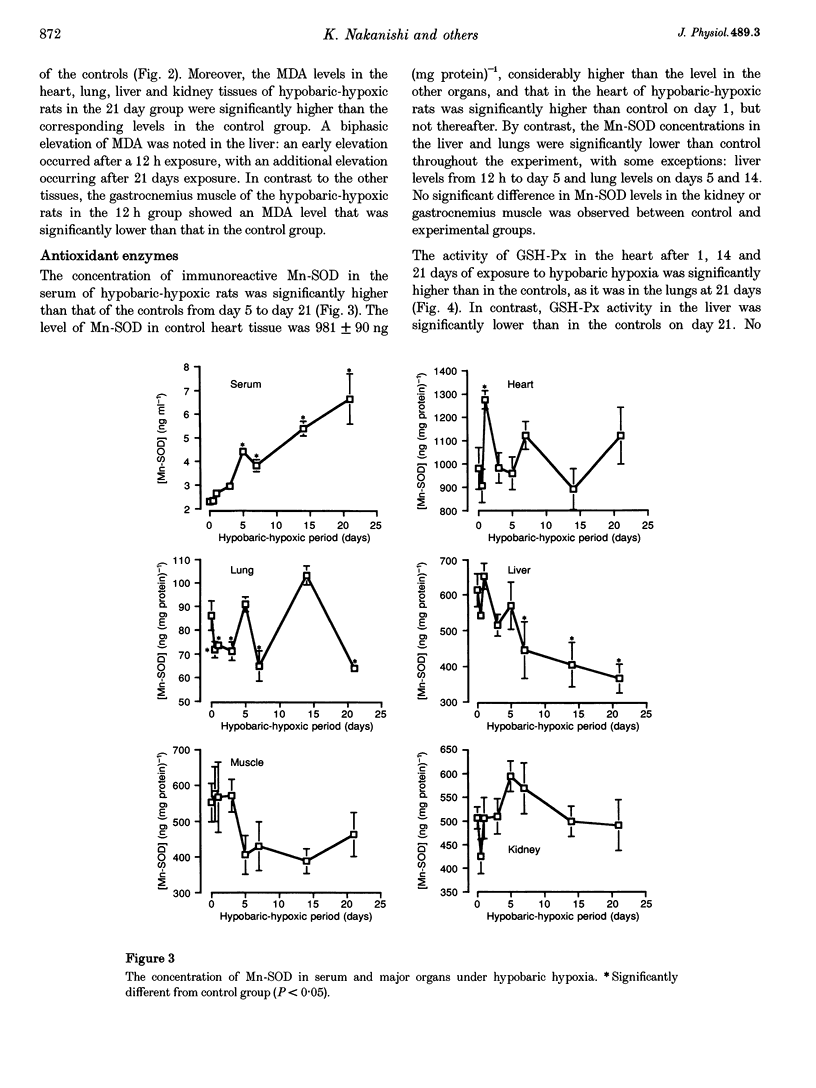
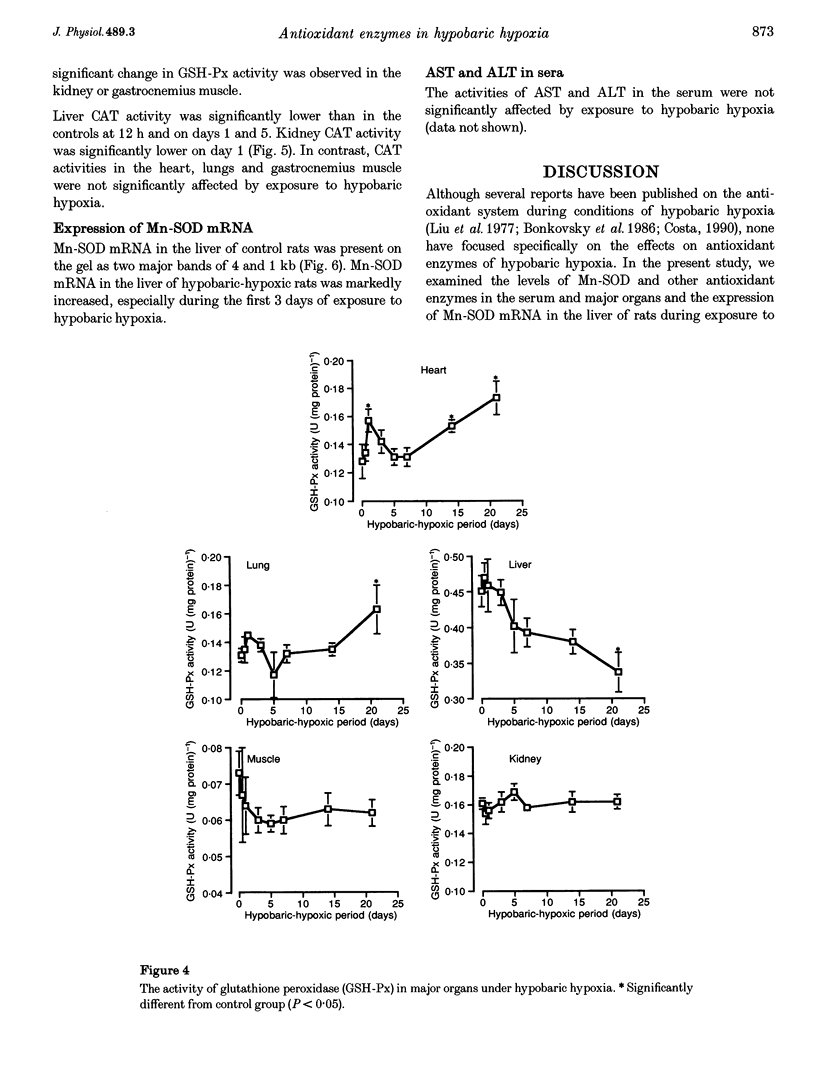
1. The present study was undertaken to investigate the effects of hypobaric hypoxia, equivalent to an altitude of 5500 m, on antioxidant enzymes in rats. 2. Malondialdehyde levels in serum, heart, lung, liver and kidney of hypobaric-hypoxic rats were all significantly higher than in control rats by day 21 of exposure (P < 0.05), indicating increased oxidative stress. 3. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalyses the conversion of the superoxide anion to H2O2 and O2. The concentration of immunoreactive Mn-SOD in the serum of hypobaric-hypoxic rats was raised significantly from day 5 onwards, whereas in liver and lung, it had decreased significantly by day 21 (P < 0.05). 4. Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) catalyses H2O2 and certain lipid peroxides. By day 21, GSH-Px activity had increased significantly in the heart and lungs, but decreased significantly in the liver (P < 0.05). 5. Catalase catalyses H2O2. Catalase activity in the liver and kidney of hypobaric-hypoxic rats was significantly decreased on day 1 (P < 0.05) though levels then recovered. 6. Mn-SOD mRNA in the liver of hypobaric-hypoxic rats was induced during the experiment, the effect being exceptionally marked, especially during the first 3 days of exposure to hypobaric hypoxia. 7. These results suggest that the liver may be more vulnerable than the other organs tested to oxidative stress under hypobaric hypoxia.
Full text
PDF

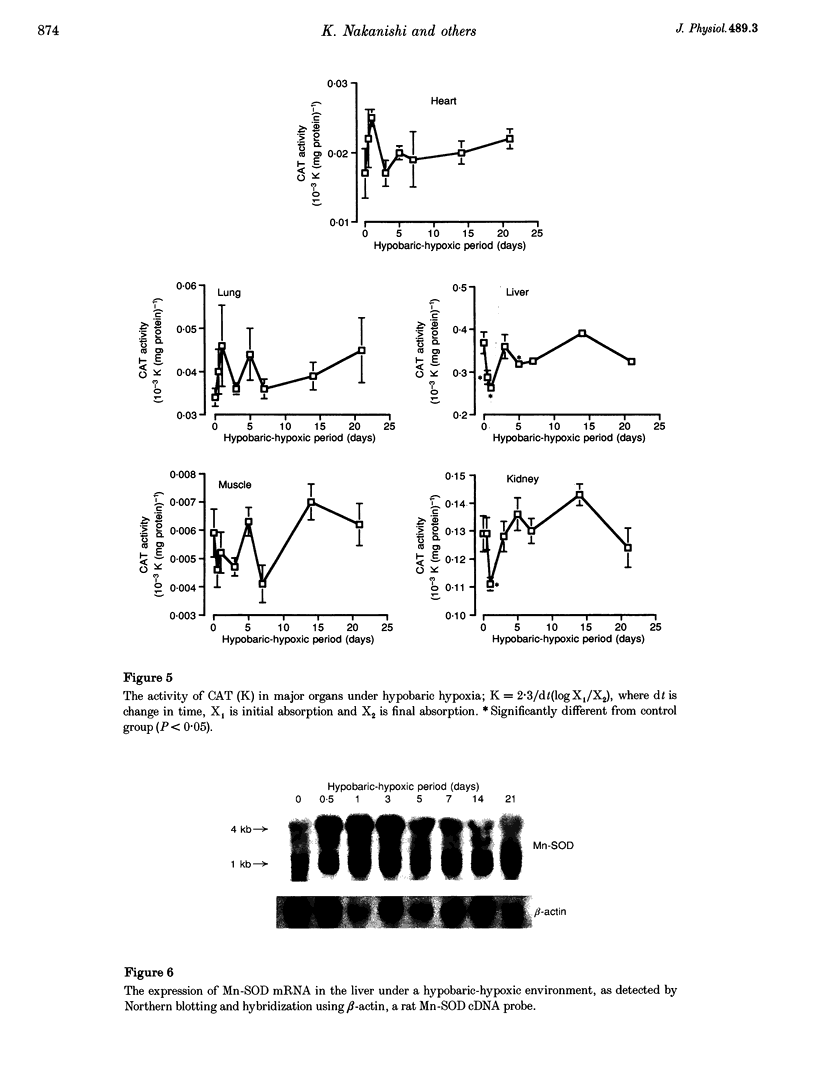


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonkovsky H. L., Lincoln B., Healey J. F., Ou L. C., Sinclair P. R., Muller-Eberhard U. Hepatic heme and drug metabolism in rats with chronic mountain sickness. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):G467–G474. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.4.G467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa L. E. Hepatic cytochrome P-450 in rats submitted to chronic hypobaric hypoxia. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):C654–C659. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.4.C654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal H., Kirshenbaum L. A., Randhawa A. K., Singal P. K. Correlation between antioxidant changes during hypoxia and recovery on reoxygenation. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):H632–H638. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.3.H632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Simon L. M., Phillips J. R., Robin E. D. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in hypoxic mammalian systems. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Jan;42(1):107–110. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.42.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. Hypoxia and incorporation of 3H-thymidine by cells of the rat pulmonary arteries and alveolar wall. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jul;96(1):51–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. The effect of continued hypoxia on rat pulmonary arterial circulation. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1978 Feb;38(2):188–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa H., Ohishi N., Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno H., Kayashima S., Nagata N., Yamashita H., Ookawara T., Taniguchi N. Changes in immunoreactive manganese-superoxide dismutase concentration in human serum after 93 h strenuous physical exercise. Clin Chim Acta. 1993 Jun 16;215(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(93)90127-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno H., Sato Y., Yamashita K., Doi R., Arai K., Kondo T., Taniguchi N. The effect of brief physical exercise on free radical scavenging enzyme systems in human red blood cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;64(9):1263–1265. doi: 10.1139/y86-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno H., Yahata T., Sato Y., Yamamura K., Taniguchi N. Physical training and fasting erythrocyte activities of free radical scavenging enzyme systems in sedentary men. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1988;57(2):173–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00640658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon-Schnass I. M. Nutrition at high altitude. J Nutr. 1992 Mar;122(3 Suppl):778–781. doi: 10.1093/jn/122.suppl_3.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kinoshita N., Matsuda Y., Higashiyama S., Kuzuya T., Minamino T., Tada M., Taniguchi N. Elevation of immunoreactive serum Mn-superoxide dismutase in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Free Radic Res Commun. 1992;15(6):325–334. doi: 10.3109/10715769209049148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi N. Clinical significances of superoxide dismutases: changes in aging, diabetes, ischemia, and cancer. Adv Clin Chem. 1992;29:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tappel A. L. Glutathione peroxidase and hydroperoxides. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:506–513. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa T., Furukawa Y., Wakamatsu Y., Takemura S., Tanaka H., Kondo M. Experimental hypoxia and lipid peroxide in rats. Biochem Med. 1982 Apr;27(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(82)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot H., Littauer A. Hypoxia, reactive oxygen, and cell injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 1989;6(5):541–551. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(89)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



