Correction: BMC Medical Research Methodology 24, 254 (2024)
10.1186/s12874-024-02379-z
Following publication of the original article [1], the authors noticed errors in equations.
Page 4, Incorrect equation:
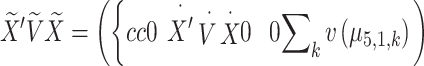 |
Corrected equation:
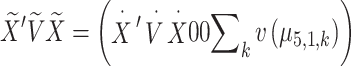 |
Page 4, Incorrect equation:
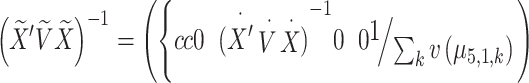 |
Corrected equation:
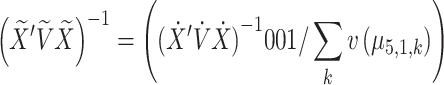 |
Page 4, Incorrect equation:
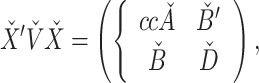 |
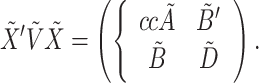 |
Corrected equation:
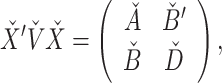 |
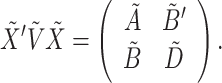 |
The original article [1] has been updated.
Footnotes
The online version of the original article can be found at 10.1186/s12874-024-02379-z.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Lee KM, Yang GM, Cheung YB. Inclusion of unexposed clusters improves the precision of fixed effects analysis of stepped-wedge cluster randomized trials with binary and count outcomes. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2024;24:254. 10.1186/s12874-024-02379-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


