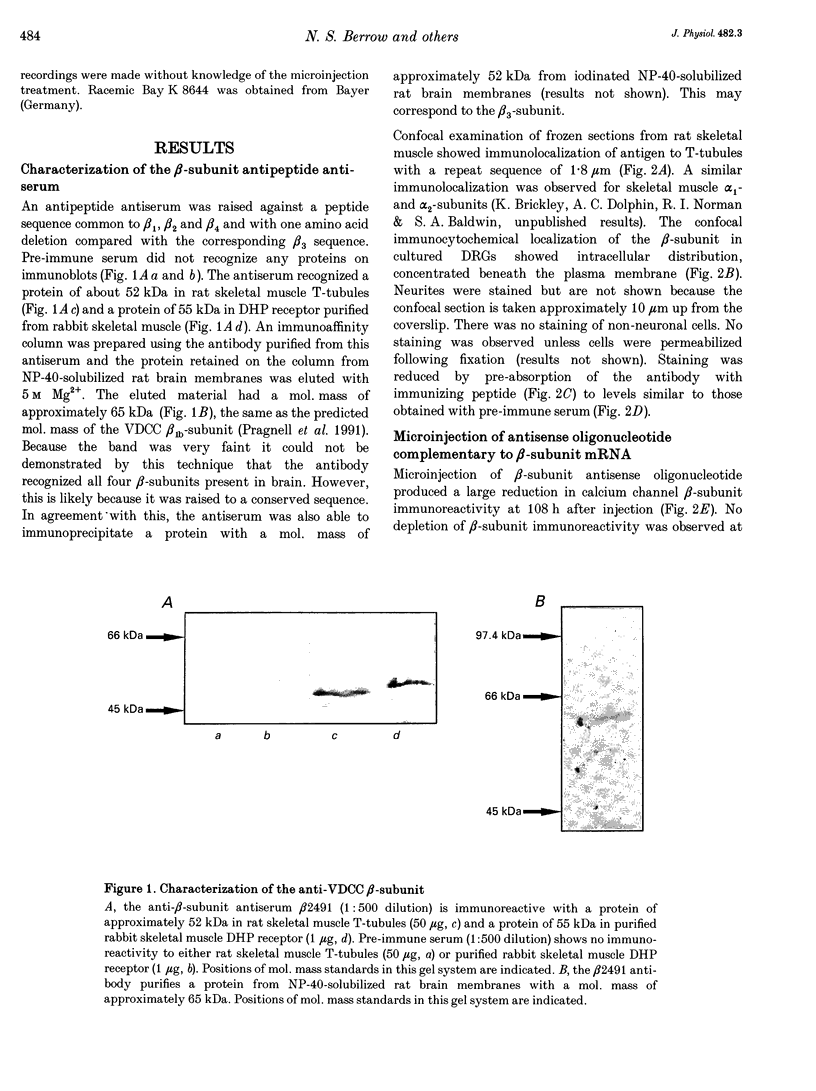
Abstract
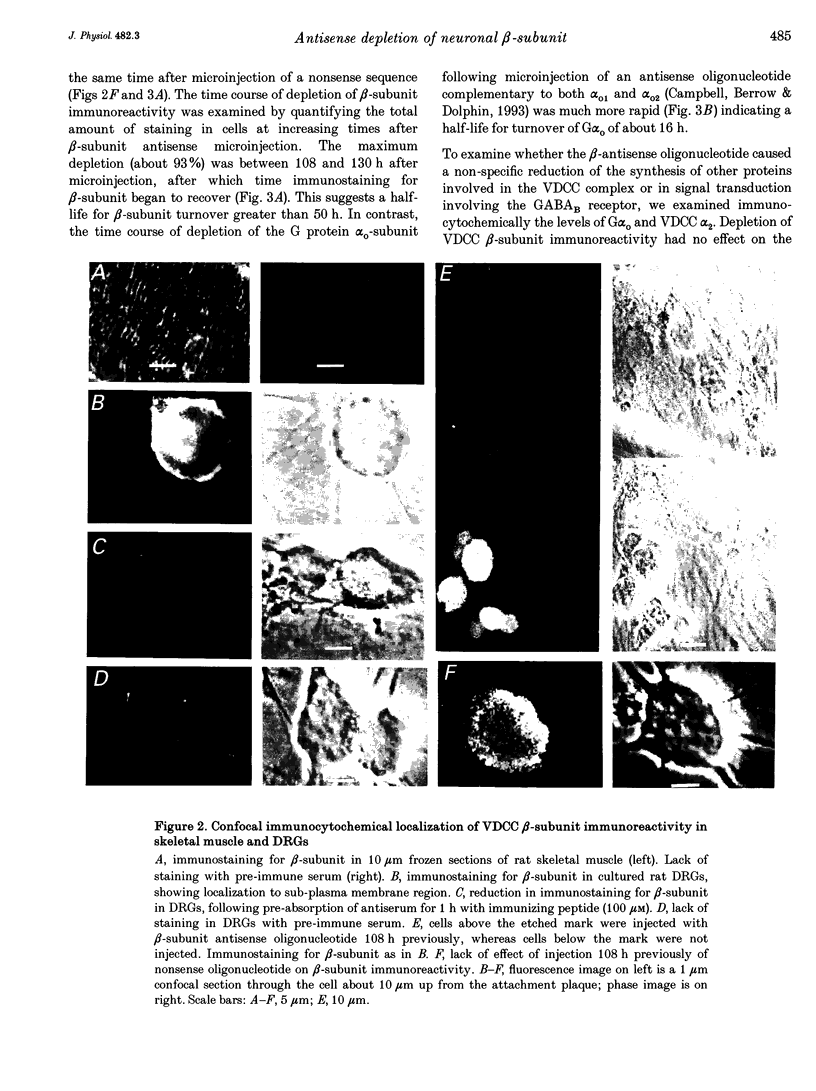
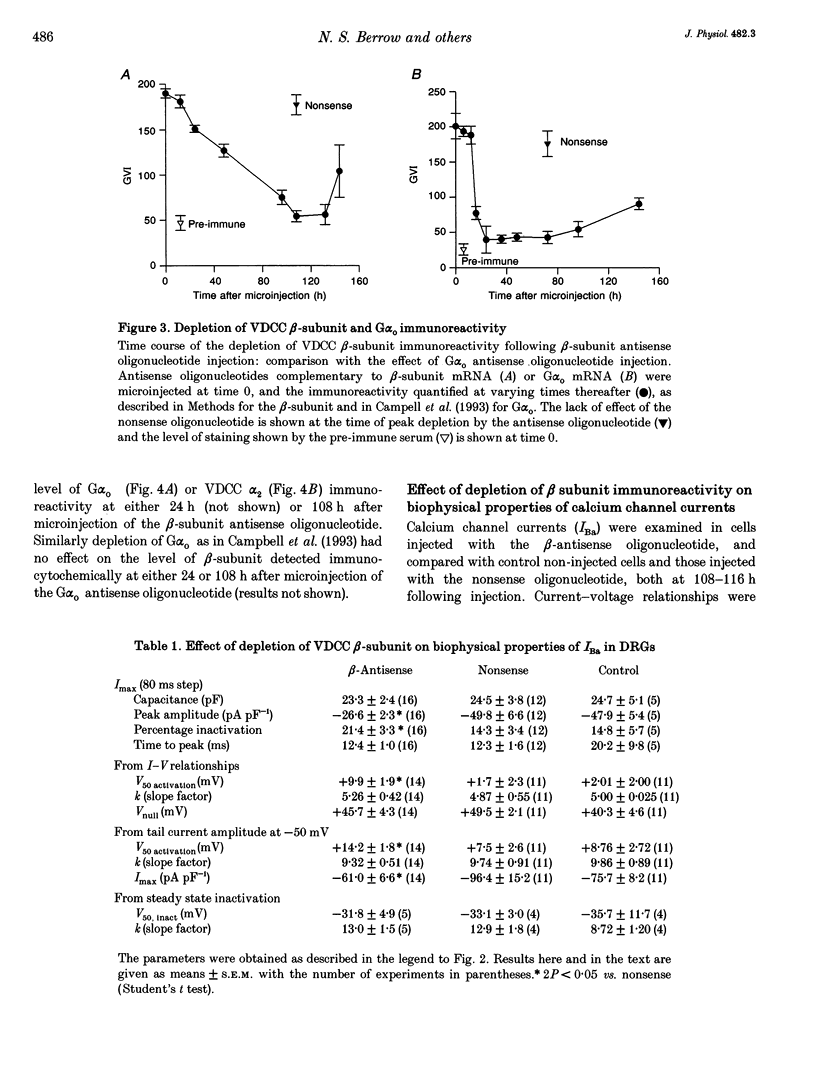
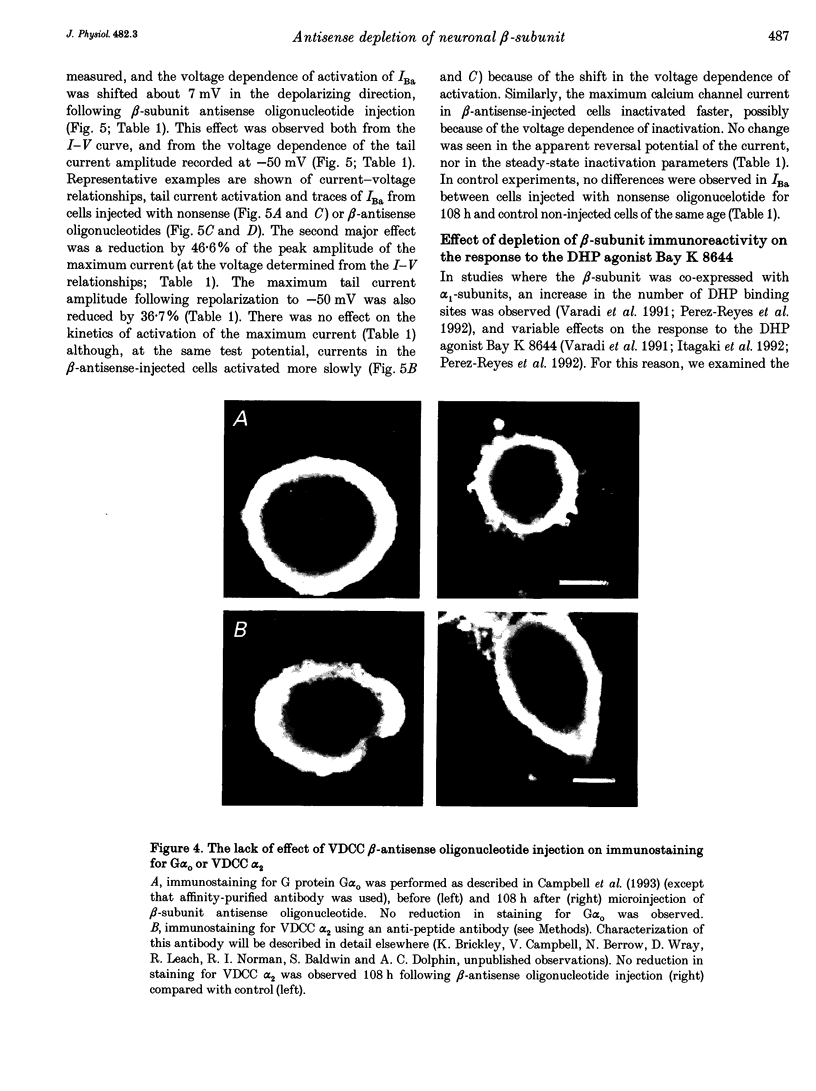
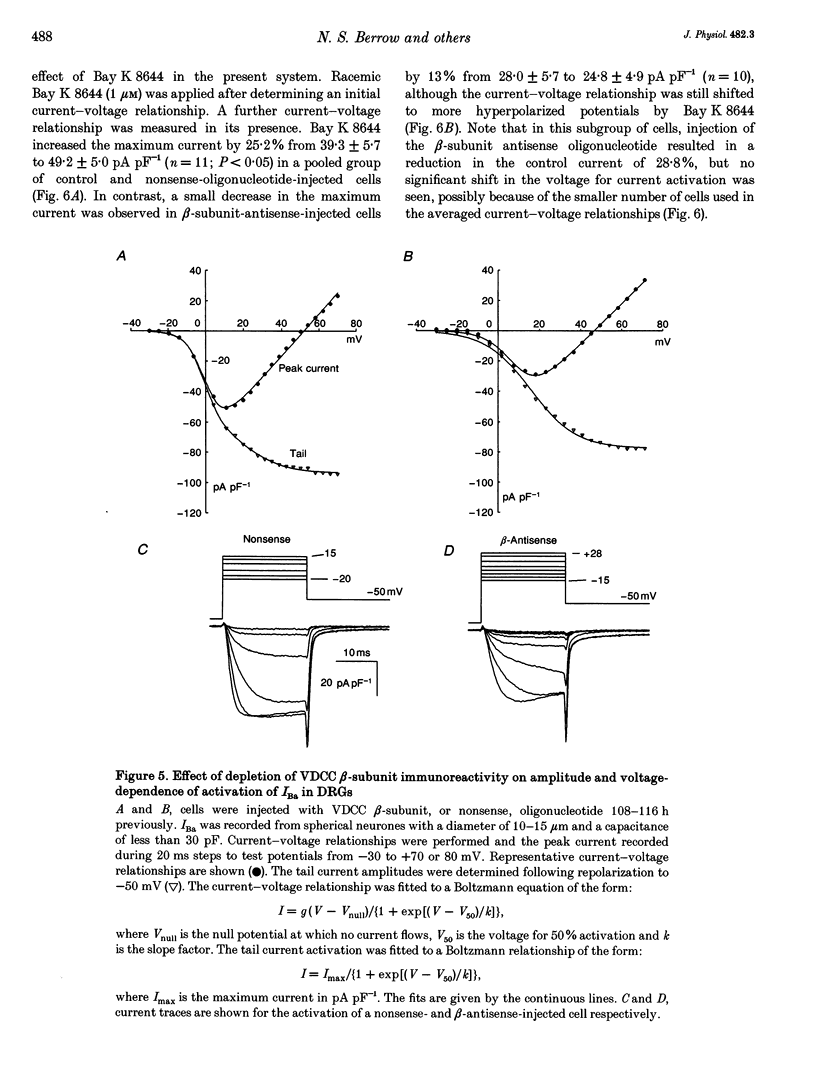
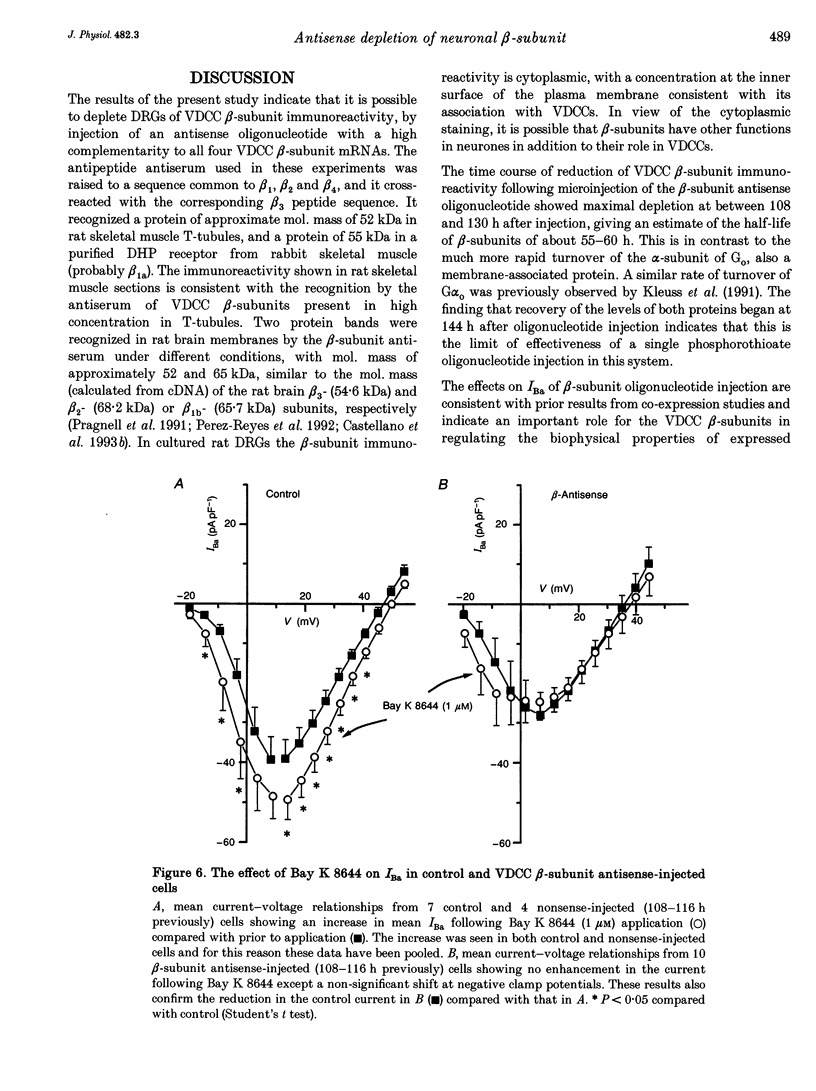
1. The role of the voltage-dependent calcium channel (VDCC) beta-subunit has been examined in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurones (DRGs). An antipeptide antibody was raised and this recognized proteins corresponding to beta-subunits in a number of preparations. Immunoreactivity for the VDCC beta-subunit in DRGs was concentrated on the internal side of the plasma membrane but was also present in the cytoplasm. 2. A twenty-six-mer antisense oligonucleotide with homology to all published VDCC beta-subunit sequences was microinjected into individual cells, and maximal depletion of VDCC beta-subunit immunoreactivity was observed after 108 h suggesting a half-life for the turnover of the beta-subunit greater than 50 h. No depletion was obtained with nonsense oligonucleotide. 3. The effect of depletion of VDCC beta-subunit immunoreactivity on calcium channel currents in these cells was a reduction in amplitude of the maximum current of about 47%, and a shift in the voltage dependence of current activation of about +7 mV. These effects are the converse of those observed following co-expression of cloned beta- with alpha 1-subunits in oocytes and other expression systems. 4. The ability of the 1,4-dihydropyridine (DHP) agonist Bay K 8644 to enhance calcium channel currents was greatly reduced following depletion of beta-subunit immunoreactivity. This result is in agreement with the finding in several systems that co-expression of the beta-subunit with alpha 1-subunits results in an increased number of DHP binding sites. 5. These results show that calcium channel beta-subunits form part of native neuronal calcium channels and modify their biophysical and pharmacological properties.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlijanian M. K., Westenbroek R. E., Catterall W. A. Subunit structure and localization of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in mammalian brain, spinal cord, and retina. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):819–832. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell V., Berrow N., Dolphin A. C. GABAB receptor modulation of Ca2+ currents in rat sensory neurones by the G protein G(0): antisense oligonucleotide studies. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:1–11. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellano A., Wei X., Birnbaumer L., Perez-Reyes E. Cloning and expression of a neuronal calcium channel beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellano A., Wei X., Birnbaumer L., Perez-Reyes E. Cloning and expression of a third calcium channel beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3450–3455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Seagar M. J., Takahashi M. Molecular properties of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3535–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jongh K. S., Warner C., Catterall W. A. Subunits of purified calcium channels. Alpha 2 and delta are encoded by the same gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14738–14741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubel S. J., Starr T. V., Hell J., Ahlijanian M. K., Enyeart J. J., Catterall W. A., Snutch T. P. Molecular cloning of the alpha-1 subunit of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5058–5062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Oeken H. J., Hofmann F. Purification of a functional receptor for calcium-channel blockers from rabbit skeletal-muscle microsomes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., Ellinor P. T., Krizanova O., Wang J. J., Diebold R. J., Schwartz A. Molecular cloning of multiple subtypes of a novel rat brain isoform of the alpha 1 subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hullin R., Singer-Lahat D., Freichel M., Biel M., Dascal N., Hofmann F., Flockerzi V. Calcium channel beta subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNA from heart, aorta and brain. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):885–890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki K., Koch W. J., Bodi I., Klöckner U., Slish D. F., Schwartz A. Native-type DHP-sensitive calcium channel currents are produced by cloned rat aortic smooth muscle and cardiac alpha 1 subunits expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes and are regulated by alpha 2- and beta-subunits. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 10;297(3):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80542-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Ewel C., Rosenthal W., Schultz G., Wittig B. Assignment of G-protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):43–48. doi: 10.1038/353043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Mechti N., Degols G., Gagnor C., Lebleu B. Intracellular distribution of microinjected antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2702–2706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lledo P. M., Vernier P., Vincent J. D., Mason W. T., Zorec R. Inhibition of Rab3B expression attenuates Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis in rat anterior pituitary cells. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):540–544. doi: 10.1038/364540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory P., Varadi G., Slish D. F., Varadi M., Schwartz A. Characterization of beta subunit modulation of a rabbit cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel alpha 1 subunit as expressed in mouse L cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 4;315(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81156-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEnery M. W., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Evidence for subtypes of the omega-conotoxin GVIA receptor. Identification of the properties intrinsic to the high-affinity receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:435–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Adams M. E., Bean B. P. P-type calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90223-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely A., Wei X., Olcese R., Birnbaumer L., Stefani E. Potentiation by the beta subunit of the ratio of the ionic current to the charge movement in the cardiac calcium channel. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):575–578. doi: 10.1126/science.8211185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S., Takeshima H., Hofmann F., Flockerzi V., Imoto K. Requirement of the calcium channel beta subunit for functional conformation. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 21;324(3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80135-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Reyes E., Castellano A., Kim H. S., Bertrand P., Baggstrom E., Lacerda A. E., Wei X. Y., Birnbaumer L. Cloning and expression of a cardiac/brain beta subunit of the L-type calcium channel. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1792–1797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell M., Sakamoto J., Jay S. D., Campbell K. P. Cloning and tissue-specific expression of the brain calcium channel beta-subunit. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 21;291(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81296-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemblatt M., Hidalgo C., Vergara C., Ikemoto N. Immunological and biochemical properties of transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8140–8148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth P., Röhrkasten A., Biel M., Bosse E., Regulla S., Meyer H. E., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Primary structure of the beta subunit of the DHP-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1115–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.2549640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto J., Campbell K. P. A monoclonal antibody to the beta subunit of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor immunoprecipitates the brain omega-conotoxin GVIA receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18914–18919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D., Biel M., Lotan I., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F., Dascal N. The roles of the subunits in the function of the calcium channel. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1553–1557. doi: 10.1126/science.1716787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Rat brain expresses a heterogeneous family of calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Reiner P. B. Ca2+ channels: diversity of form and function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Jun;2(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90111-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea A., Dubel S. J., Pragnell M., Leonard J. P., Campbell K. P., Snutch T. P. A beta-subunit normalizes the electrophysiological properties of a cloned N-type Ca2+ channel alpha 1-subunit. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1103–1116. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90005-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Seagar M. J., Jones J. F., Reber B. F., Catterall W. A. Subunit structure of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Third J. SOME CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS ON ARTERIO-SCLEROSIS. Can Med Assoc J. 1913 Apr;3(4):261–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varadi G., Lory P., Schultz D., Varadi M., Schwartz A. Acceleration of activation and inactivation by the beta subunit of the skeletal muscle calcium channel. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):159–162. doi: 10.1038/352159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Brust P. F., Feldman D. H., Patthi S., Simerson S., Maroufi A., McCue A. F., Veliçelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive human N-type calcium channel. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):389–395. doi: 10.1126/science.1321501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witcher D. R., De Waard M., Campbell K. P. Characterization of the purified N-type Ca2+ channel and the cation sensitivity of omega-conotoxin GVIA binding. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1127–1139. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90007-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. F., Randall A. D., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A., Sather W. A., Tanabe T., Schwarz T. L., Tsien R. W. Distinctive pharmacology and kinetics of cloned neuronal Ca2+ channels and their possible counterparts in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1075–1088. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90003-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]