Abstract
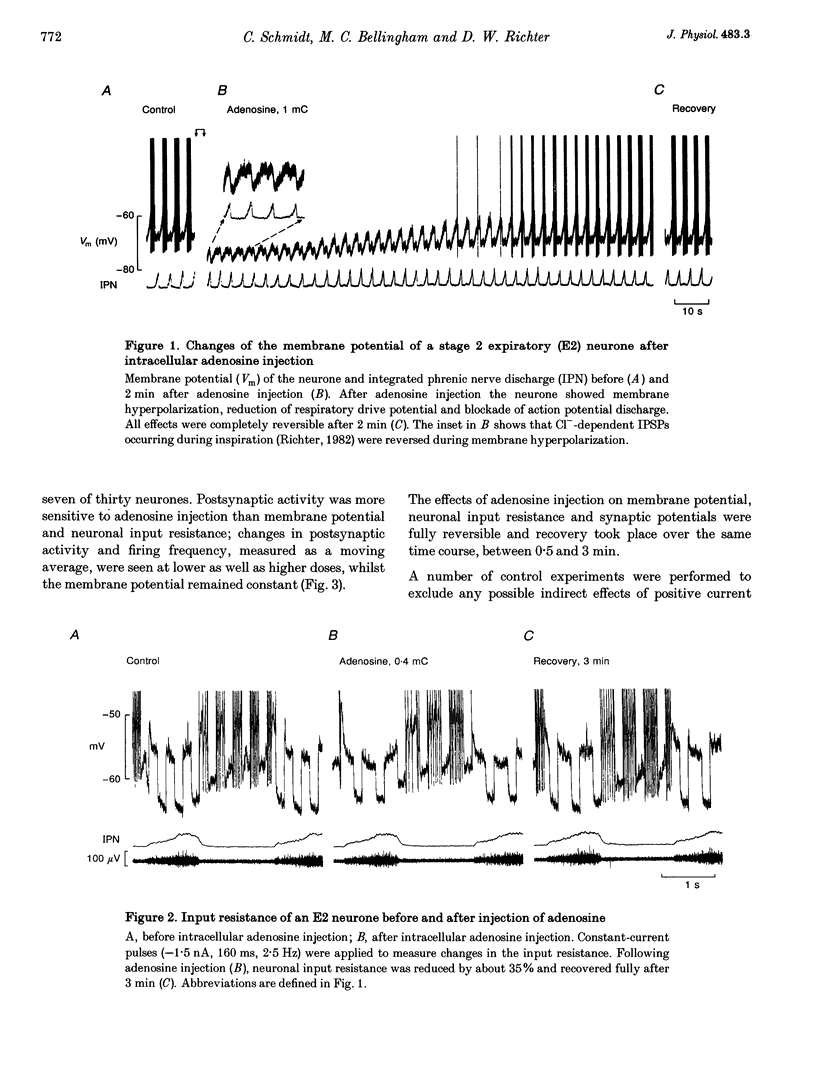
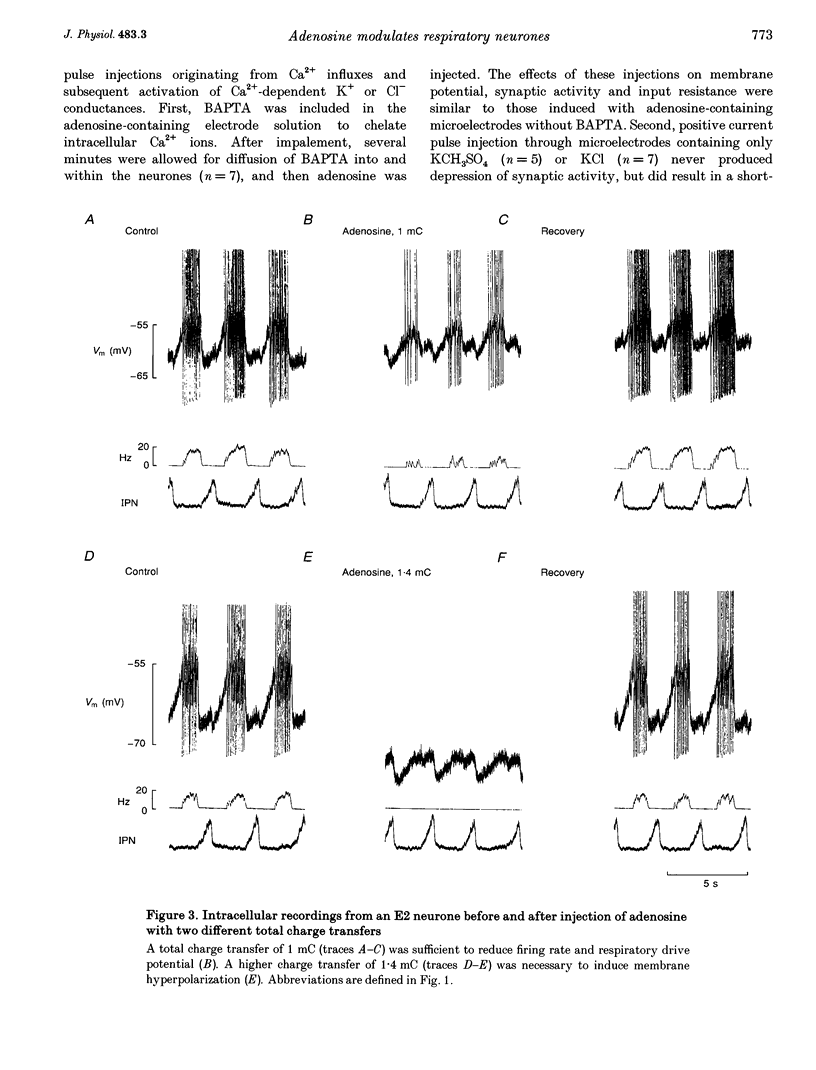
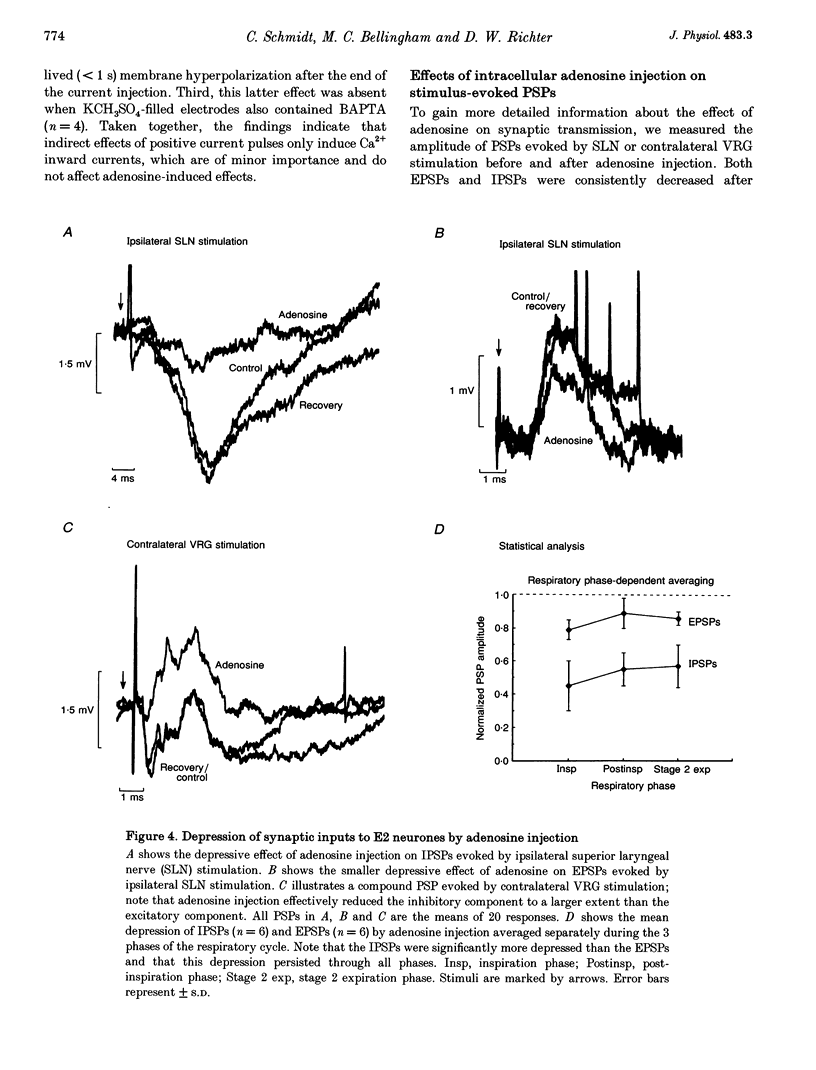
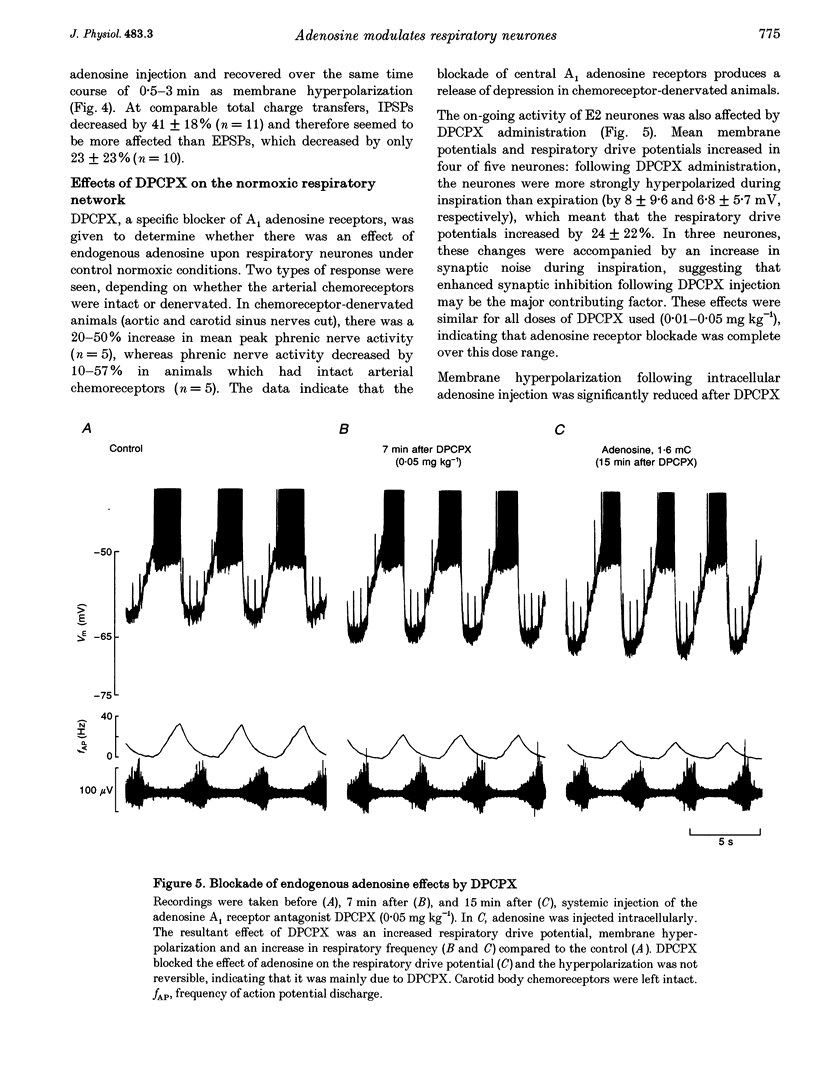
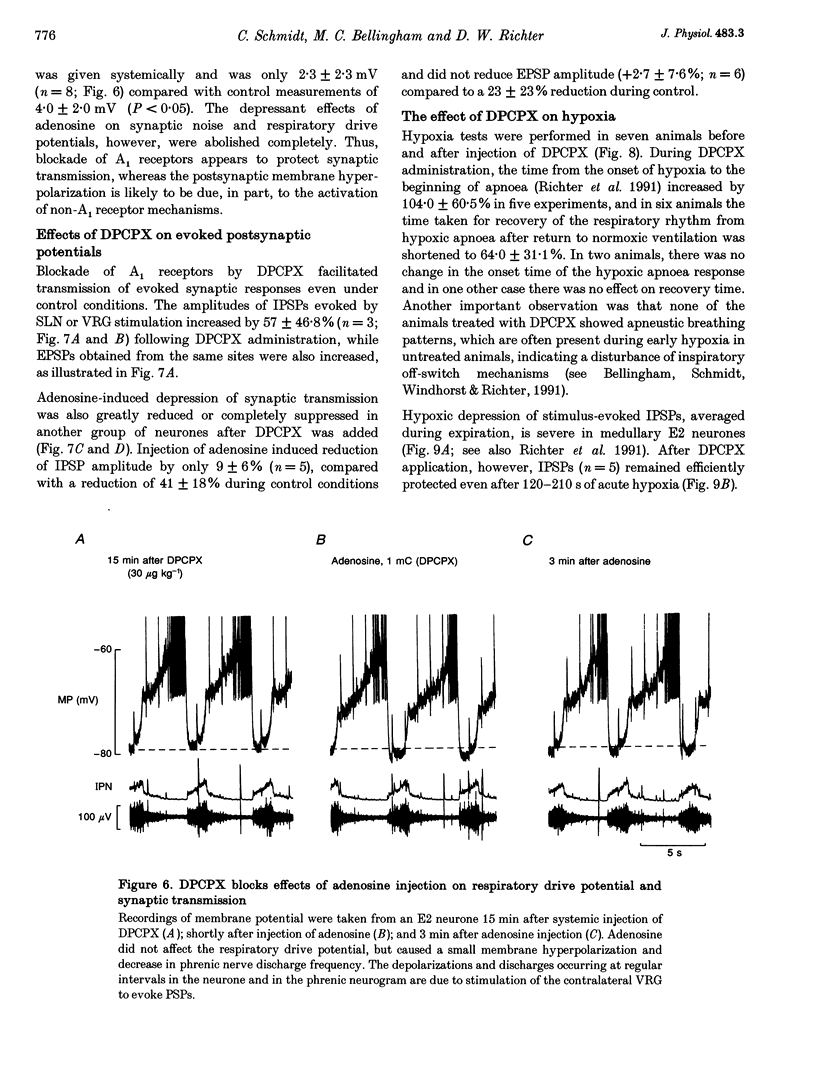
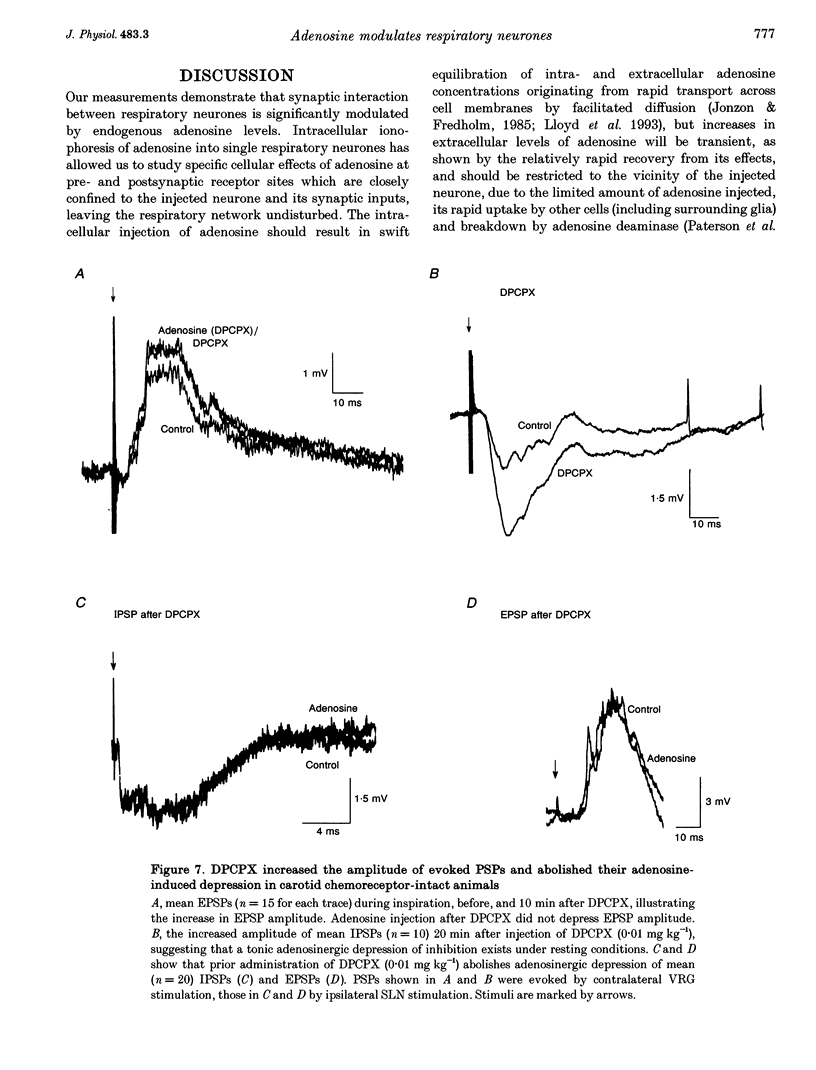
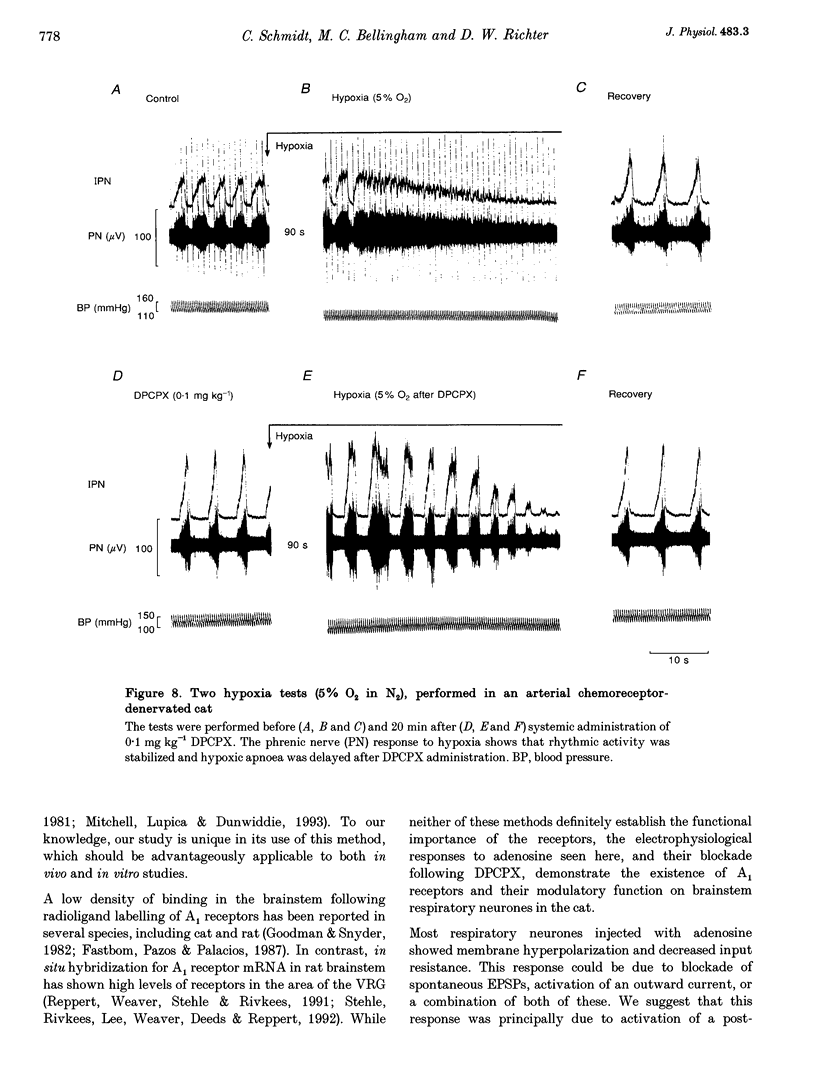
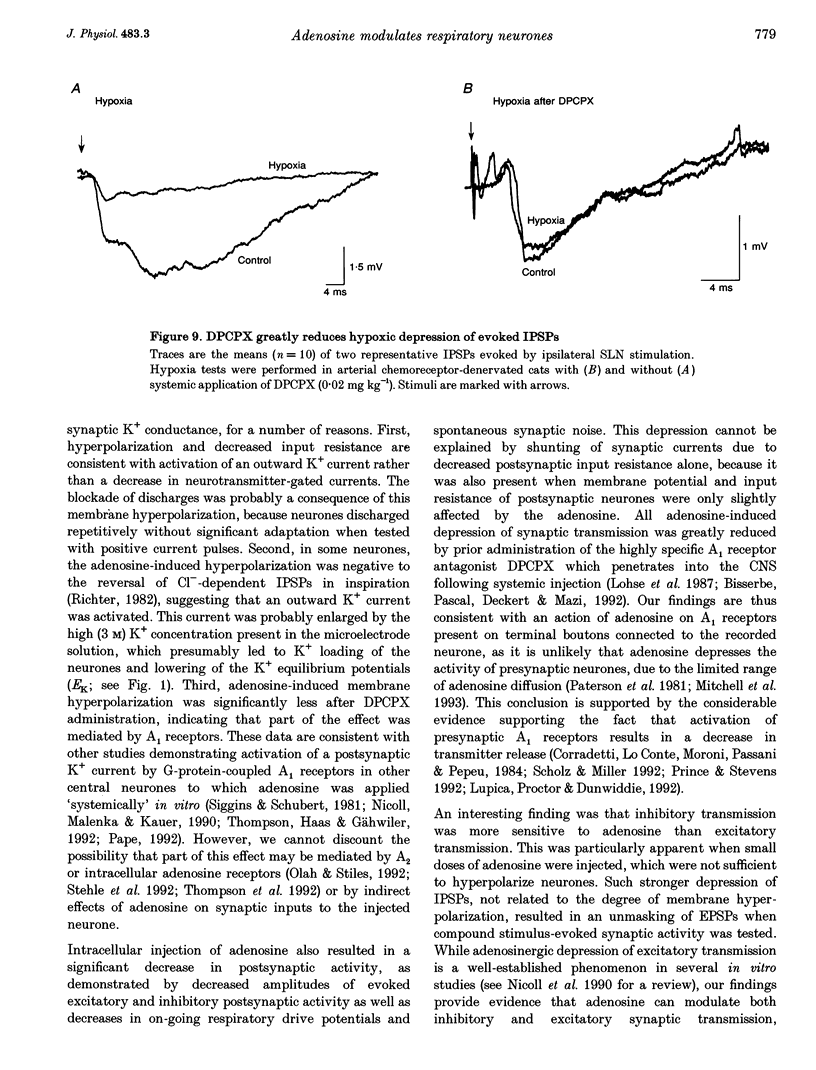
1. The modulatory effects of intracellularly injected adenosine on membrane potential, input resistance and spontaneous or evoked synaptic activity were determined in respiratory neurones of the ventral respiratory group. 2. The membrane potential hyperpolarized and sometimes reached values which were beyond the equilibrium potential of Cl(-)-dependent IPSPs. At the same time, neuronal input resistance decreased. 3. Spontaneous and stimulus-evoked postsynaptic activities were decreased, as were mean respiratory drive potentials. 4. Systemic injection of the A1 adenosine receptor antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX; 0.01-0.05 mg kg-1) resulted in an increase in mean peak phrenic nerve activity when arterial chemoreceptors were denervated. In contrast, phrenic nerve activity decreased when arterial chemoreceptors were left intact. 5. The depressant effect of adenosine on synaptic activity was abolished after systemic DPCPX administration. DPCPX caused an increase in respiratory drive potentials, increased the amplitude of stimulus-evoked IPSPs, and hyperpolarized membrane potential. 6. Administration of DPCPX blocked the early hypoxic depression of stimulus-evoked IPSPs, doubled the delay of onset of hypoxic apnoea and shortened the time necessary for recovery of the respiratory rhythm. 7. The data indicate that adenosine acts on pre- and postsynaptic A1 receptors resulting in postsynaptic membrane hyperpolarization and depression of synaptic transmission. Blockade of A1 receptors increases respiratory activity, indicating that adenosine A1 receptors are tonically activated under control conditions. Further activation contributes to the hypoxic depression of synaptic transmission in the respiratory network.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballarín M., Fredholm B. B., Ambrosio S., Mahy N. Extracellular levels of adenosine and its metabolites in the striatum of awake rats: inhibition of uptake and metabolism. Acta Physiol Scand. 1991 May;142(1):97–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1991.tb09133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisserbe J. C., Pascal O., Deckert J., Mazière B. Potential use of DPCPX as probe for in vivo localization of brain A1 adenosine receptors. Brain Res. 1992 Dec 18;599(1):6–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90845-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherniack N. S., Edelman N. H., Lahiri S. Hypoxia and hypercapnia as respiratory stimulants and depressants. Respir Physiol. 1970;11(1):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(70)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradetti R., Lo Conte G., Moroni F., Passani M. B., Pepeu G. Adenosine decreases aspartate and glutamate release from rat hippocampal slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 3;104(1-2):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90364-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L., Millhorn D. E., Kiley J. P. Antagonism by theophylline of respiratory inhibition induced by adenosine. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Nov;59(5):1428–1433. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.5.1428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fastbom J., Pazos A., Palacios J. M. The distribution of adenosine A1 receptors and 5'-nucleotidase in the brain of some commonly used experimental animals. Neuroscience. 1987 Sep;22(3):813–826. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)92961-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Synder S. H. Autoradiographic localization of adenosine receptors in rat brain using [3H]cyclohexyladenosine. J Neurosci. 1982 Sep;2(9):1230–1241. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-09-01230.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. W., Haas H. L. Adenosine actions on CA1 pyramidal neurones in rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1985 Sep;366:119–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribkoff V. K., Bauman L. A., VanderMaelen C. P. The adenosine antagonist 8-cyclopentyltheophylline reduces the depression of hippocampal neuronal responses during hypoxia. Brain Res. 1990 Apr 2;512(2):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90648-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. M., Hazinski T. A., Schlueter M. A. Respiratory control during hypoxia in newborn rabbits: implied action of endorphins. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jul;51(1):122–130. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen K., Hedner T., Lundborg P. GABA concentrations and turnover in neonatal rat brain during asphyxia and recovery. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 May;118(1):91–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonzon B., Fredholm B. B. Release of purines, noradrenaline, and GABA from rat hippocampal slices by field stimulation. J Neurochem. 1985 Jan;44(1):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd H. G., Lindström K., Fredholm B. B. Intracellular formation and release of adenosine from rat hippocampal slices evoked by electrical stimulation or energy depletion. Neurochem Int. 1993 Aug;23(2):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(93)90095-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Klotz K. N., Lindenborn-Fotinos J., Reddington M., Schwabe U., Olsson R. A. 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX)--a selective high affinity antagonist radioligand for A1 adenosine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;336(2):204–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00165806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupica C. R., Proctor W. R., Dunwiddie T. V. Presynaptic inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission by adenosine in rat hippocampus: analysis of unitary EPSP variance measured by whole-cell recording. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):3753–3764. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-03753.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S., Ribeiro J. A. Effect of adenosine on carotid chemoreceptor activity in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;74(1):129–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. B., Lupica C. R., Dunwiddie T. V. Activity-dependent release of endogenous adenosine modulates synaptic responses in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1993 Aug;13(8):3439–3447. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-08-03439.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newby A. C., Worku Y., Holmquist C. A. Adenosine formation. Evidence for a direct biochemical link with energy metabolism. Adv Myocardiol. 1985;6:273–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Malenka R. C., Kauer J. A. Functional comparison of neurotransmitter receptor subtypes in mammalian central nervous system. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):513–565. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olah M. E., Stiles G. L. Adenosine receptors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:211–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.001235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape H. C. Adenosine promotes burst activity in guinea-pig geniculocortical neurones through two different ionic mechanisms. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:729–753. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. R., Kolassa N., Cass C. E. Transport of nucleoside drugs in animal cells. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;12(3):515–536. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A., Stevens C. F. Adenosine decreases neurotransmitter release at central synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8586–8590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reppert S. M., Weaver D. R., Stehle J. H., Rivkees S. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of a rat A1-adenosine receptor that is widely expressed in brain and spinal cord. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1037–1048. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-8-1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W., Ballanyi K., Schwarzacher S. Mechanisms of respiratory rhythm generation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Dec;2(6):788–793. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W., Bischoff A., Anders K., Bellingham M., Windhorst U. Response of the medullary respiratory network of the cat to hypoxia. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:231–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W. Generation and maintenance of the respiratory rhythm. J Exp Biol. 1982 Oct;100:93–107. doi: 10.1242/jeb.100.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runold M., Lagercrantz H., Prabhakar N. R., Fredholm B. B. Role of adenosine in hypoxic ventilatory depression. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Aug;67(2):541–546. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.2.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Miller R. J. Inhibition of quantal transmitter release in the absence of calcium influx by a G protein-linked adenosine receptor at hippocampal synapses. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1139–1150. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90134-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siggins G. R., Schubert P. Adenosine depression of hippocampal neurons in vitro: an intracellular study of dose-dependent actions on synaptic and membrane potentials. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Apr 9;23(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehle J. H., Rivkees S. A., Lee J. J., Weaver D. R., Deeds J. D., Reppert S. M. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel A2-adenosine receptor subtype. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;6(3):384–393. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1584214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Haas H. L., Gähwiler B. H. Comparison of the actions of adenosine at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1992;451:347–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchimura N., North R. A. Baclofen and adenosine inhibit synaptic potentials mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate release in rat nucleus accumbens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Aug;258(2):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström T., Vernet L., Ungerstedt U., Tossman U., Jonzon B., Fredholm B. B. Purine levels in the intact rat brain. Studies with an implanted perfused hollow fibre. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Apr 16;29(2):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu P. J., Krnjević K. Adenosine release is a major cause of failure of synaptic transmission during hypoglycaemia in rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Jun 11;155(2):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90689-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


