Abstract
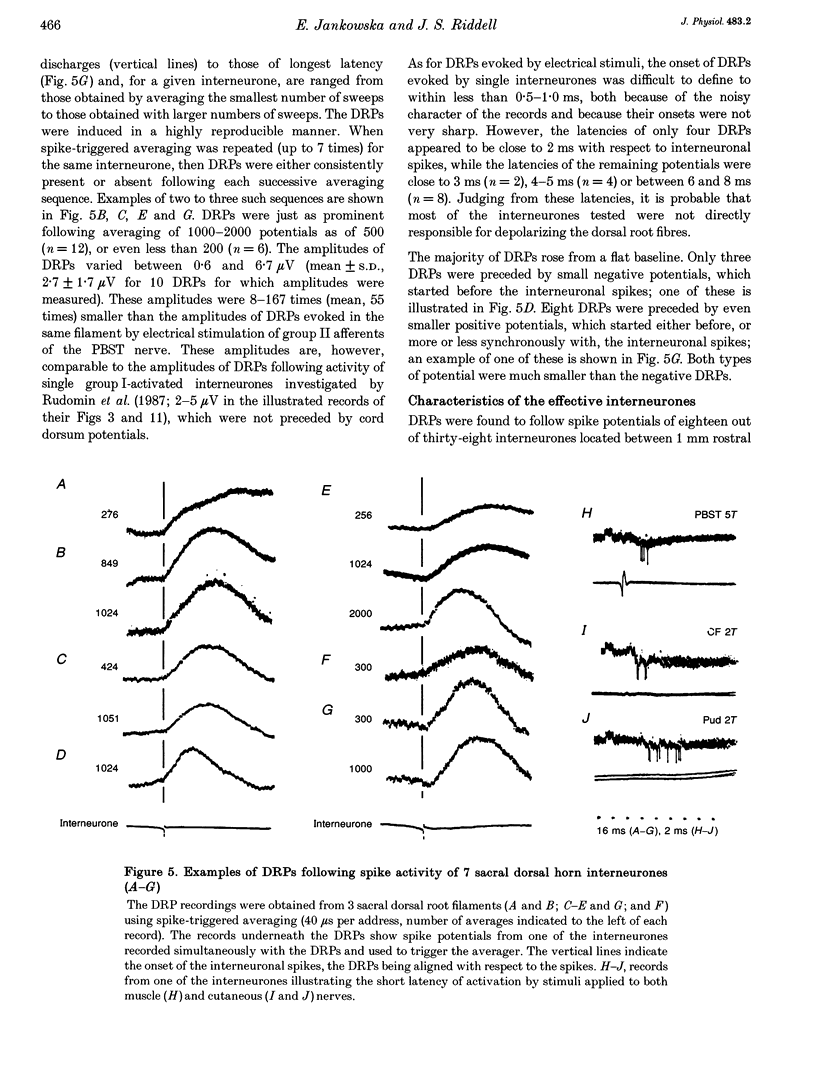
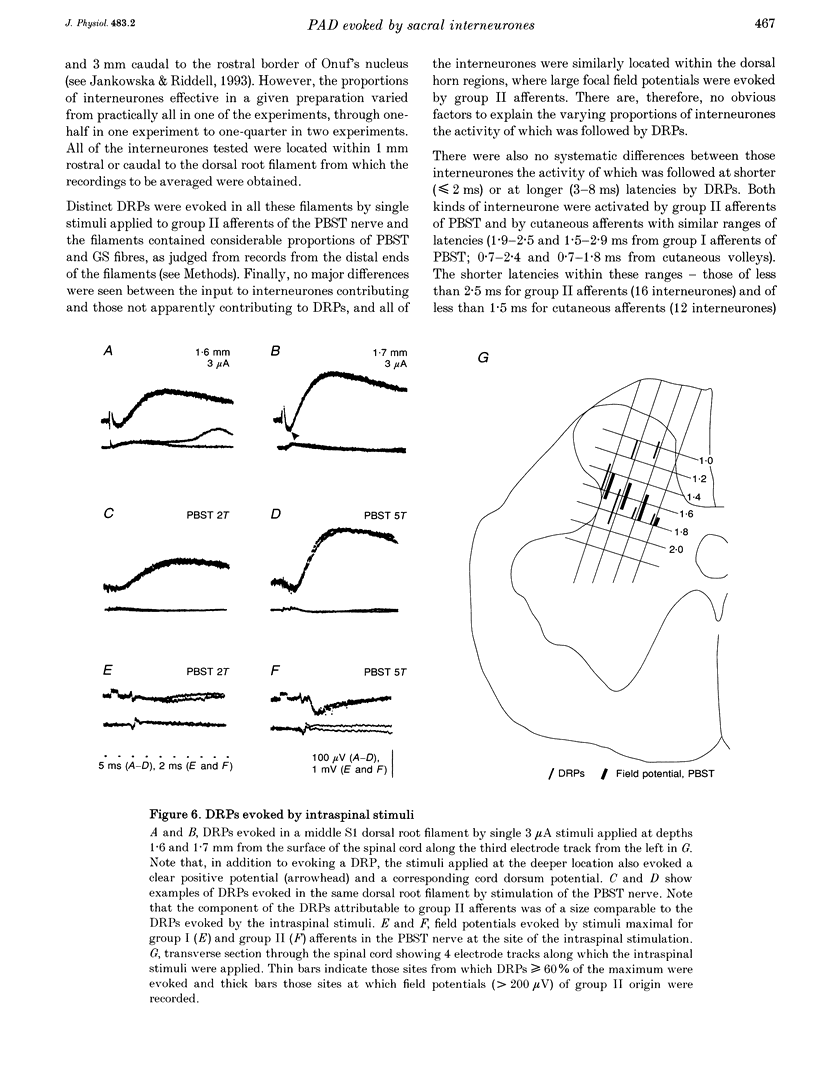
1. To investigate whether dorsal horn interneurones with input from group II muscle afferents induce depolarization of sensory fibres, simultaneous recordings were made from single interneurones in the sacral segments and from sacral dorsal root filaments using the spike-triggered averaging technique. 2. The spike potentials of eighteen out of thirty-eight interneurones tested were followed by dorsal root potentials (DRPs). The DRPs occurred at latencies of 2 and 6-8 ms. Interneurones evoking DRPs at latencies of up to 2 ms are considered likely to be last-order interneurones in pathways of presynaptic inhibition, while those inducing DRPs at longer latencies are considered likely to be first-order interneurones. The former were activated by peripheral afferents with somewhat longer latencies than the latter. However, all interneurones were co-activated by group II muscle and cutaneous afferents, indicating that the depolarization of group II muscle afferents, which these afferents induce, may be mediated by the same interneurones. 3. DRPs evoked by electrical stimulation of peripheral nerves were recorded from both sacral and midlumbar dorsal root filaments. The amplitudes of these DRPs were closely related to the potency with which group II afferents of various nerves activate dorsal horn interneurones in the sacral and midlumbar segments and group II afferents contributed to them more effectively than group I afferents. The second stimulus in a train was more effective than the first, while a third stimulus had little additional effect, indicating that the interneurones involved are relatively easily activated. 4. Intraspinal stimuli applied within the dorsal horn, at the sites where the largest field potentials of group II origin were recorded, evoked distinct DRPs. However, the location of the first- and last-order interneurones in pathways of primary afferent depolarization (PAD) could not be differentiated by this approach because the same stimuli induced positive potentials, which masked the onset of DRPs and precluded localization of the sites from which DRPs might be evoked monosynaptically.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bras H., Cavallari P., Jankowska E., Kubin L. Morphology of midlumbar interneurones relaying information from group II muscle afferents in the cat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Dec 1;290(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/cne.902900102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bras H., Jankowska E., Noga B., Skoog B. Comparison of Effects of Various Types of NA and 5-HT Agonists on Transmission from Group II Muscle Afferents in the Cat. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(12):1029–1039. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink E., Harrison P. J., Jankowska E., McCrea D. A., Skoog B. Post-synaptic potentials in a population of motoneurones following activity of single interneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:341–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink E., Jankowska E., Skoog B. Convergence onto interneurons subserving primary afferent depolarization of group I afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Mar;51(3):432–449. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter D., Engberg I., Lundberg A. Primary afferent depolarization evoked from the brain stem and the cerebellum. Arch Ital Biol. 1966 Mar;104(1):73–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari P., Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. Post-synaptic actions of midlumbar interneurones on motoneurones of hind-limb muscles in the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:675–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KOSTYUK P. G., SCHMIDT R. F. Presynaptic inhibition of the central actions of flexor reflex afferents. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:258–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Magni F., Willis W. D. Depolarization of central terminals of Group I afferent fibres from muscle. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160(1):62–93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T. C., Santini M., Schomburg E. D. Characteristics and distribution of spinal focal synaptic potentials generated by group II muscle afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jul;91(3):298–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Läckberg Z. S., Dyrehag L. E. Effects of monoamines on transmission from group II muscle afferents in sacral segments in the cat. Eur J Neurosci. 1994 Jun 1;6(6):1058–1061. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Rudomín P., Sykova E. Observations on neuronal pathways subserving primary afferent depolarization. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Sep;46(3):506–516. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.3.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Riddell J. S. A relay for input from group II muscle afferents in sacral segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:561–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Riddell J. S. Interneurones in pathways from group II muscle afferents in sacral segments of the feline spinal cord. J Physiol. 1994 Mar 15;475(3):455–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Riddell J. S., Szabo-Läckberg Z., Hammar I. Morphology of interneurones in pathways from group II muscle afferents in sacral segments of the cat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Nov 15;337(3):518–528. doi: 10.1002/cne.903370312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):623–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell J. S., Jankowska E., Huber J. Organization of neuronal systems mediating presynaptic inhibition of group II muscle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1995 Mar 1;483(Pt 2):443–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudomin P., Solodkin M., Jiménez I. Synaptic potentials of primary afferent fibers and motoneurons evoked by single intermediate nucleus interneurons in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1987 May;57(5):1288–1313. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.5.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt D. G., Stauffer E. K., Taylor A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 1. Spindle primary and tendon organ afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1375–1392. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


