Abstract
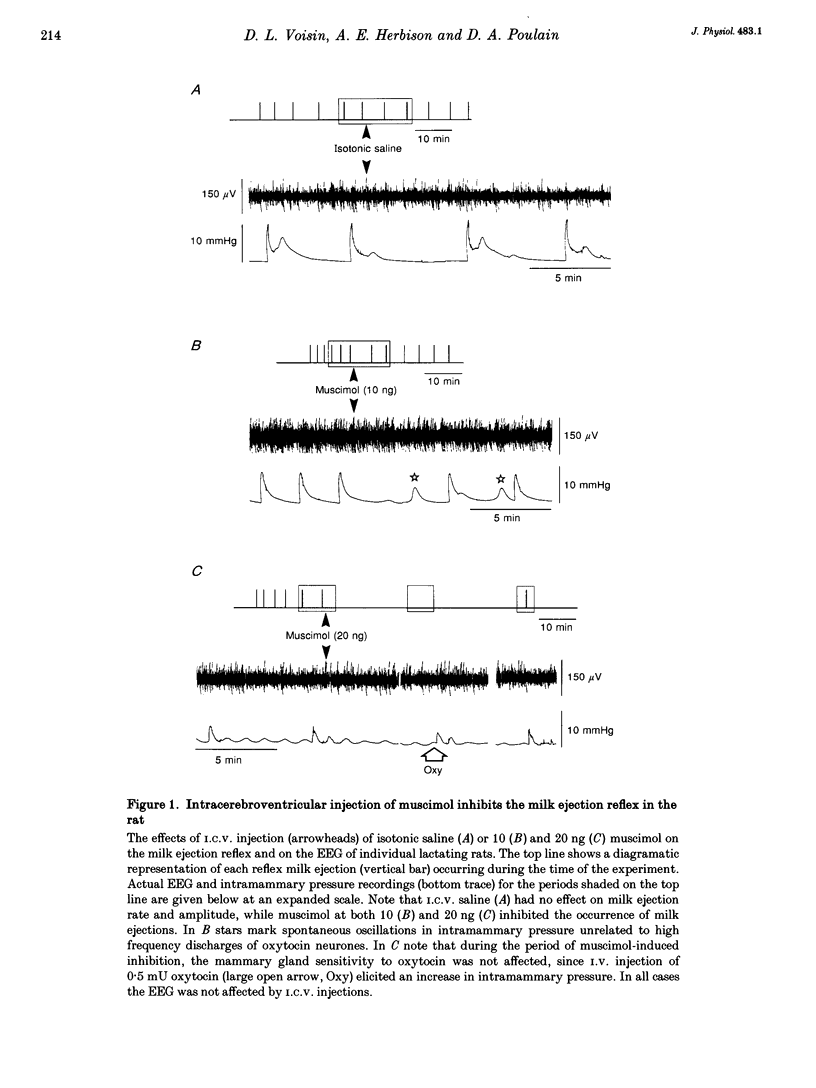
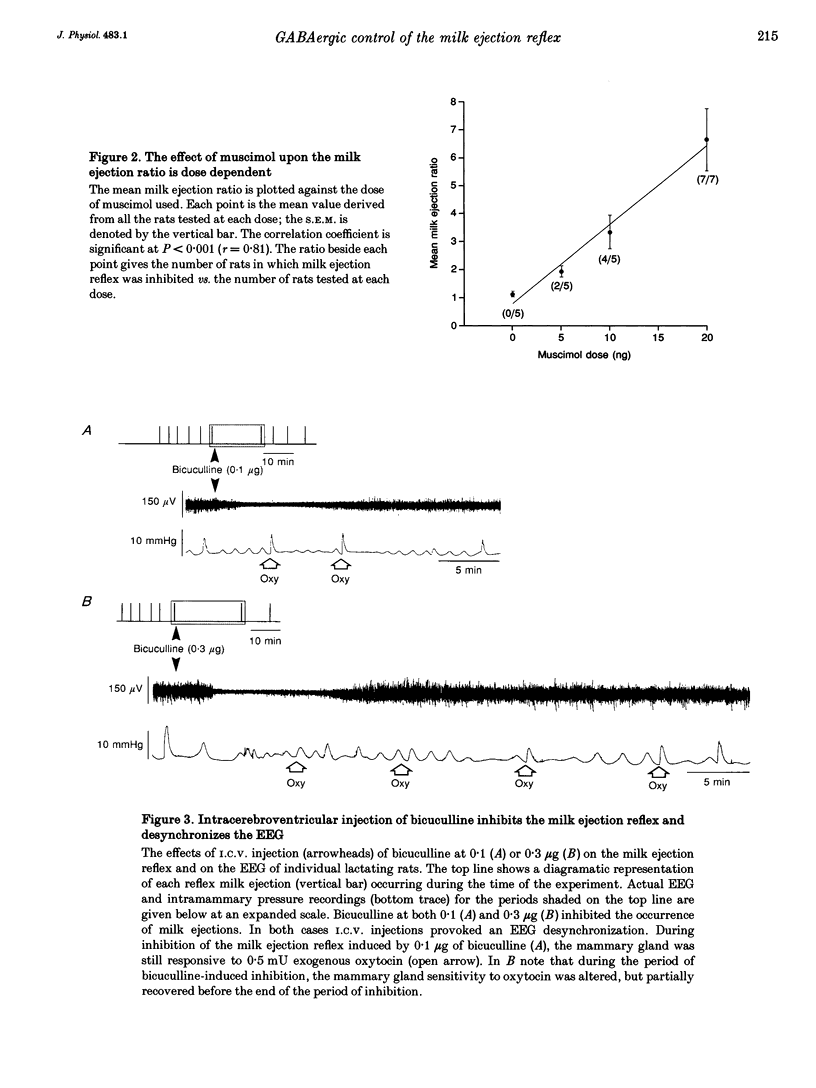
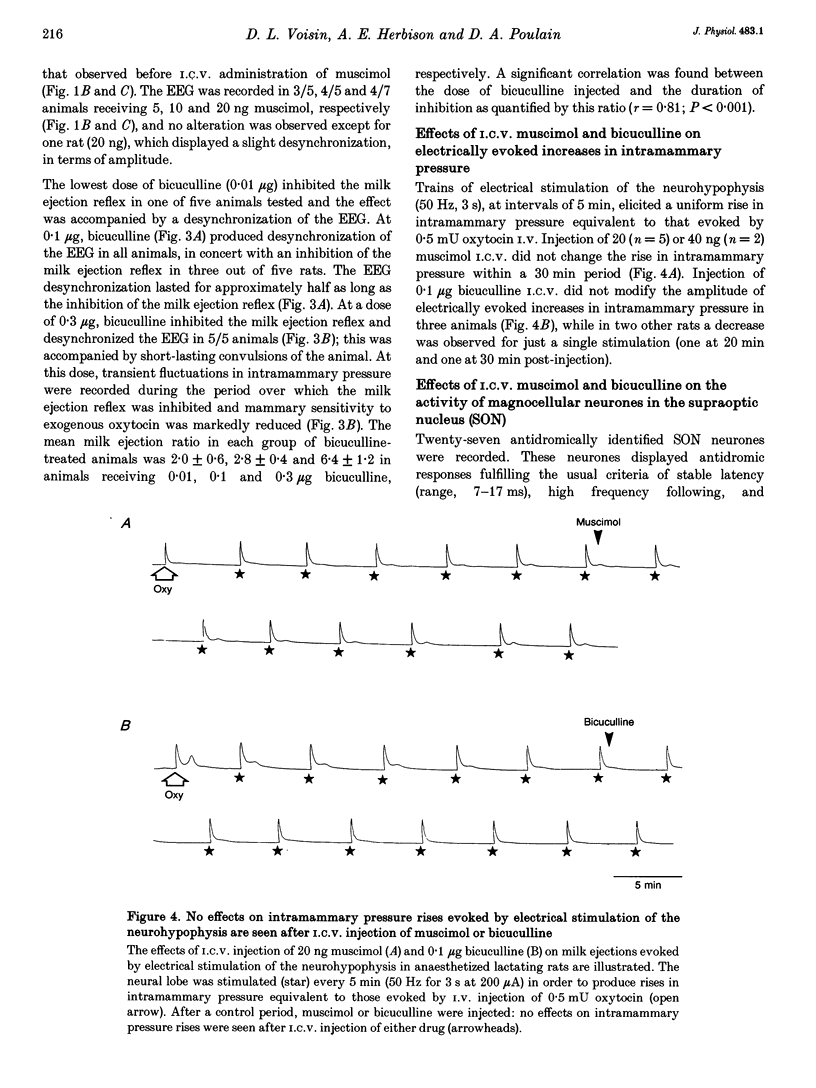
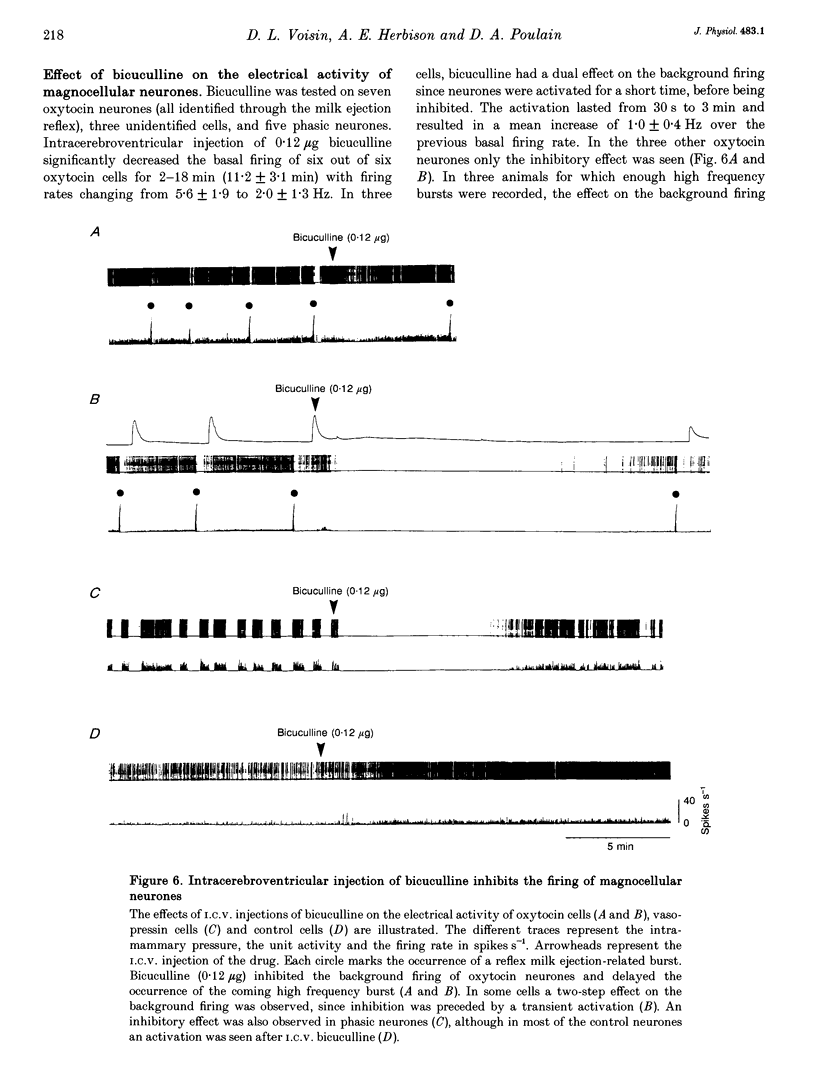
1. In order to determine whether GABAergic mechanisms are involved in the control of the milk ejection reflex in the rat, we examined the effects of central administration of a GABAA receptor agonist (muscimol) and antagonist (bicuculline) on the milk ejection reflex in the urethane-anaesthetized rat. 2. Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of both muscimol (n = 17), at doses of 5, 10 and 20 ng, and bicuculline (n = 15), at doses of 0.01, 0.1 and 0.3 microgram, inhibited the milk ejection reflex in a dose-dependent manner. The bicuculline-induced inhibition was accompanied by desynchronization of the electroencephalogram and, at the highest dose, by alteration in the sensitivity of the mammary gland to oxytocin. No significant effect on the milk ejection reflex was seen with i.c.v. isotonic saline (n = 5). 3. Injection of 20 (n = 5) or 40 ng (n = 2) muscimol or 0.1 microgram bicuculline (n = 5) i.c.v. did not significantly alter the rise in intramammary pressure evoked by electrical stimulation of the neurohypophysis. 4. Bilateral 400 nl microinfusions directly into the supraoptic nuclei of either muscimol (20-100 ng microliter(-1); n = 10) or bicuculline (0.15 micrograms microliter(-1); n = 5) [corrected] resulted in an inhibition of the milk ejection reflex, which was not accompanied by desynchronization of the electroencephalogram. 5. The effects of i.c.v. injections of muscimol (15 and 20 ng) and bicuculline (0.01, 0.12 and 0.3 microgram) on the electrical activity of twenty-seven antidromically identified supraoptic magnocellular neurones were examined. Both compounds resulted in an inhibition of the background firing of oxytocinergic and vasopressinergic cells, and delayed the occurrence of high frequency bursts in oxytocin neurones. In five supraoptic neurones, bicuculline induced a transient activation before inhibition. 6. The powerful inhibitory action on the milk ejection reflex of both muscimol and bicuculline provides evidence for the importance of GABA neurones in maintaining the functional integrity of the mechanisms which allow the intermittent and pulsatile release of oxytocin during suckling.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnauld E., Cirino M., Layton B. S., Renaud L. P. Contrasting actions of amino acids, acetylcholine, noradrenaline and leucine enkephalin on the excitability of supraoptic vasopressin-secreting neurons. A microiontophoretic study in the rat. Neuroendocrinology. 1983;36(3):187–196. doi: 10.1159/000123455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin V., Moos F. Paired recordings from supraoptic and paraventricular oxytocin cells in suckled rats: recruitment and synchronization. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:369–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bioulac B., Gaffori O., Harris M., Vincent J. D. Effects of acetylcholine, sodium glutamate and GABA on the discharge of supraoptic neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 6;154(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisset G. W., Chowdrey H. S., Fairhall K. M., Gunn L. K. Central inhibition by gamma-aminobutyric acid and muscimol of the release of vasopressin and oxytocin by an osmotic stimulus in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):529–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12963.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bureau M. H., Olsen R. W. GABAA receptor subtypes: ligand binding heterogeneity demonstrated by photoaffinity labeling and autoradiography. J Neurochem. 1993 Oct;61(4):1479–1491. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb13643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G., Fall C. H., Lincoln D. W., Merrick L. P. Effects of cholinoceptor antagonists on the suckling-induced and experimentally evoked release of oxytocin. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;63(3):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07807.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decavel C., Van den Pol A. N. GABA: a dominant neurotransmitter in the hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Dec 22;302(4):1019–1037. doi: 10.1002/cne.903020423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyball R. E., Shaw F. D. Inhibition by GABA of hormone release from the neurohypophysis in the rat [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:78P–79P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gies U., Theodosis D. T. Synaptic plasticity in the rat supraoptic nucleus during lactation involves GABA innervation and oxytocin neurons: a quantitative immunocytochemical analysis. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 1):2861–2869. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-02861.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbison A. E., Chapman C., Dyer R. G. Role of medial preoptic GABA neurones in regulating luteinising hormone secretion in the ovariectomised rat. Exp Brain Res. 1991;87(2):345–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00231851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbison A. E. Immunocytochemical evidence for oestrogen receptors within GABA neurones located in the perinuclear zone of the supraoptic nucleus and GABAA receptor beta 2/beta 3 subunits on supraoptic oxytocin neurones. J Neuroendocrinol. 1994 Feb;6(1):5–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.1994.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isherwood K. M., Cross B. A. Effect of the suckling stimulus on secretion of prolactin and luteinizing hormone in conscious and anaesthetized rats. J Endocrinol. 1980 Dec;87(3):437–444. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0870437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Way S., Dyball R. E. Identification of oxytoxin cells in the rat supraoptic nucleus by their response to cholecystokinin injection. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jan 28;122(2):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90847-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln D. W., Hentzen K., Hin T., van der Schoot P., Clarke G., Summerlee A. J. Sleep: a prerequisite for reflex milk ejection in the rat. Exp Brain Res. 1980 Jan;38(2):151–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00236736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln D. W., Hill A., Wakerley J. B. The milk-ejection reflex of the rat: an intermittent function not abolished by surgical levels of anaesthesia. J Endocrinol. 1973 Jun;57(3):459–476. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0570459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. T., Poulain D., Cobbett P. gamma-Aminobutyric acid as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the rat supraoptic nucleus: intracellular recordings in the hypothalamic slice. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 27;73(3):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90255-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison R. D., Dreifuss J. J. Structure-activity relationships of a neurohypophysial GABA receptor. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 14;187(2):476–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKernan R. M., Quirk K., Prince R., Cox P. A., Gillard N. P., Ragan C. I., Whiting P. GABAA receptor subtypes immunopurified from rat brain with alpha subunit-specific antibodies have unique pharmacological properties. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90379-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Barker J. L. The pharmacology of recurrent inhibition in the supraoptic neurosecretory system. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 24;35(2):501–511. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90491-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel W. H., Mugnaini E., Tappaz M. L., Weise V. K., Dahl A. L., Schmechel D. E., Kopin I. J. Central GABAergic innervation of neurointermediate pituitary lobe: biochemical and immunocytochemical study in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):675–679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne P. G., Mataga N., Onoe H., Watanabe Y. Behavioral activation by stimulation of a GABAergic mechanism in the preoptic area of rat. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Aug 20;158(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90264-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otis T. S., Staley K. J., Mody I. Perpetual inhibitory activity in mammalian brain slices generated by spontaneous GABA release. Brain Res. 1991 Apr 5;545(1-2):142–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91280-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Tasker J. G. Recurrent mammary gland contractions induced by a low tonic release of oxytocin in rats. J Endocrinol. 1985 Oct;107(1):89–96. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1070089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B., Dyball R. E. Electrophysiological differentiation of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr;196(1125):367–384. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B. Electrophysiology of hypothalamic magnocellular neurones secreting oxytocin and vasopressin. Neuroscience. 1982 Apr;7(4):773–808. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle J. C., Bourque C. W., Renaud L. P. Characterization of spontaneous and evoked inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in rat supraoptic neurosecretory neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Dec;56(6):1703–1717. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.6.1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle J. C., Renaud L. P. Actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on rat supraoptic nucleus neurosecretory neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:629–647. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland B. L., Sawchenko P. E. Local origins of some GABAergic projections to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Jun 1;332(1):123–143. doi: 10.1002/cne.903320109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivilotti L., Nistri A. GABA receptor mechanisms in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36(1):35–92. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90036-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodosis D. T., Paut L., Tappaz M. L. Immunocytochemical analysis of the GABAergic innervation of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurons in the rat supraoptic nucleus. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):207–222. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga K., Shibata S., Hamada T., Watanabe S. GABAA receptor agonist muscimol can reset the phase of neural activity rhythm in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Jan 17;166(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90845-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribollet E., Armstrong W. E., Dubois-Dauphin M., Dreifuss J. J. Extra-hypothalamic afferent inputs to the supraoptic nucleus area of the rat as determined by retrograde and anterograde tracing techniques. Neuroscience. 1985 May;15(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voisin D. L., Chapman C., Poulain D. A., Herbison A. E. Extracellular GABA concentrations in rat supraoptic nucleus during lactation and following haemodynamic changes: an in vivo microdialysis study. Neuroscience. 1994 Nov;63(2):547–558. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90549-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakerley J. B., Juss T. S., Farrington R., Ingram C. D. Role of the paraventricular nucleus in controlling the frequency of milk ejection and the facilitatory effect of centrally administered oxytocin in the suckled rat. J Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;125(3):467–475. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1250467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin L. D., Mitchell L. D., Ganten D., Johnson A. K. The supraoptic nucleus: afferents from areas involved in control of body fluid homeostasis. Neuroscience. 1989;28(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J. P., Dudek F. E. Patch-clamp analysis of spontaneous synaptic currents in supraoptic neuroendocrine cells of the rat hypothalamus. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2323–2331. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02323.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. J., Jackson M. B. GABA-activated chloride channels in secretory nerve endings. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):531–534. doi: 10.1126/science.8380942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]