Abstract
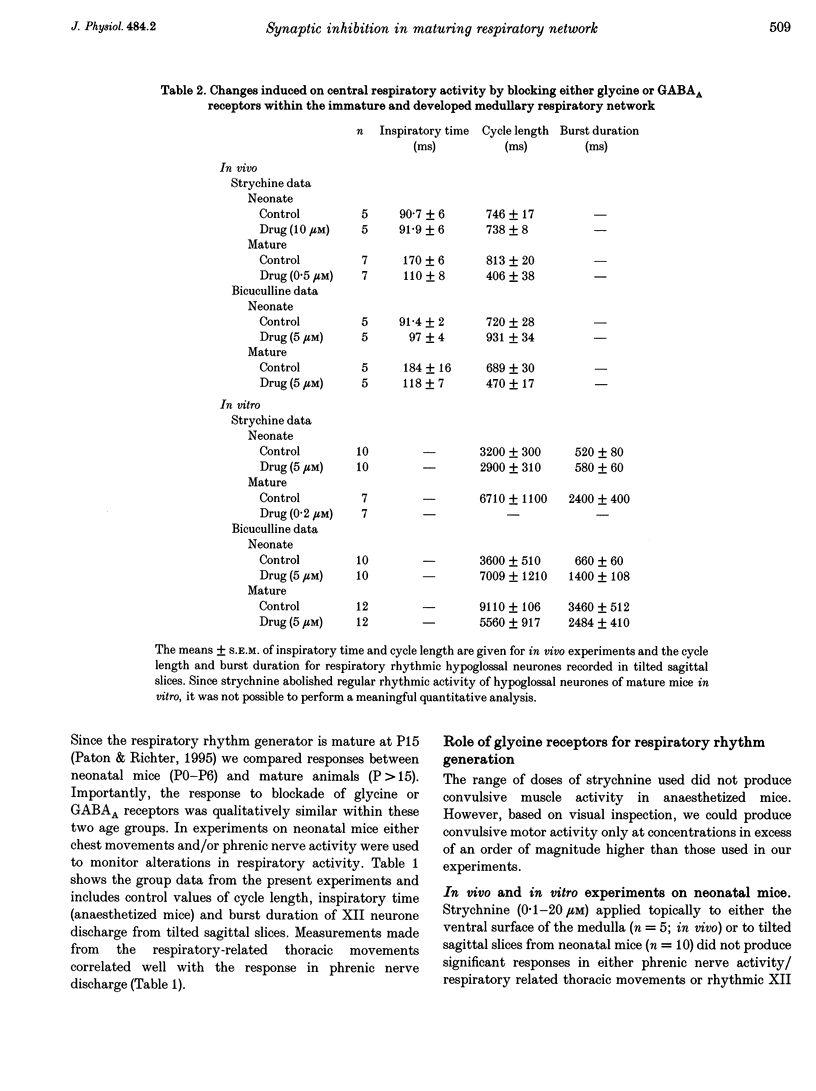
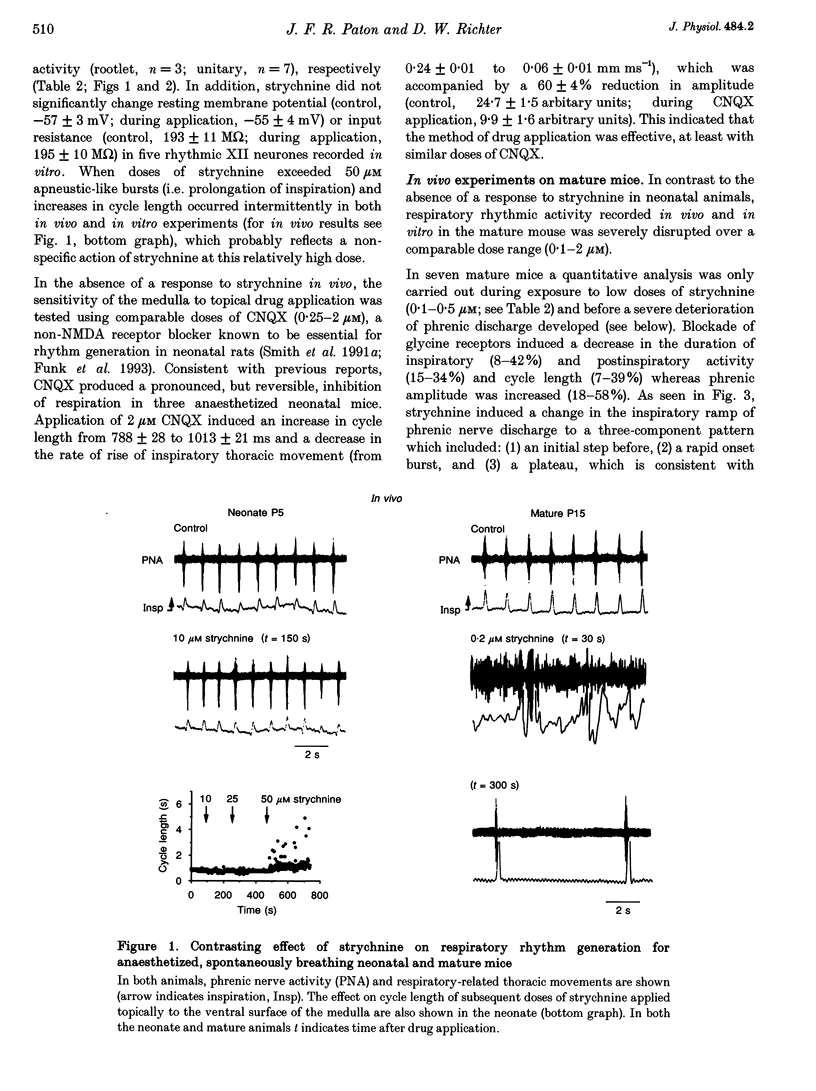
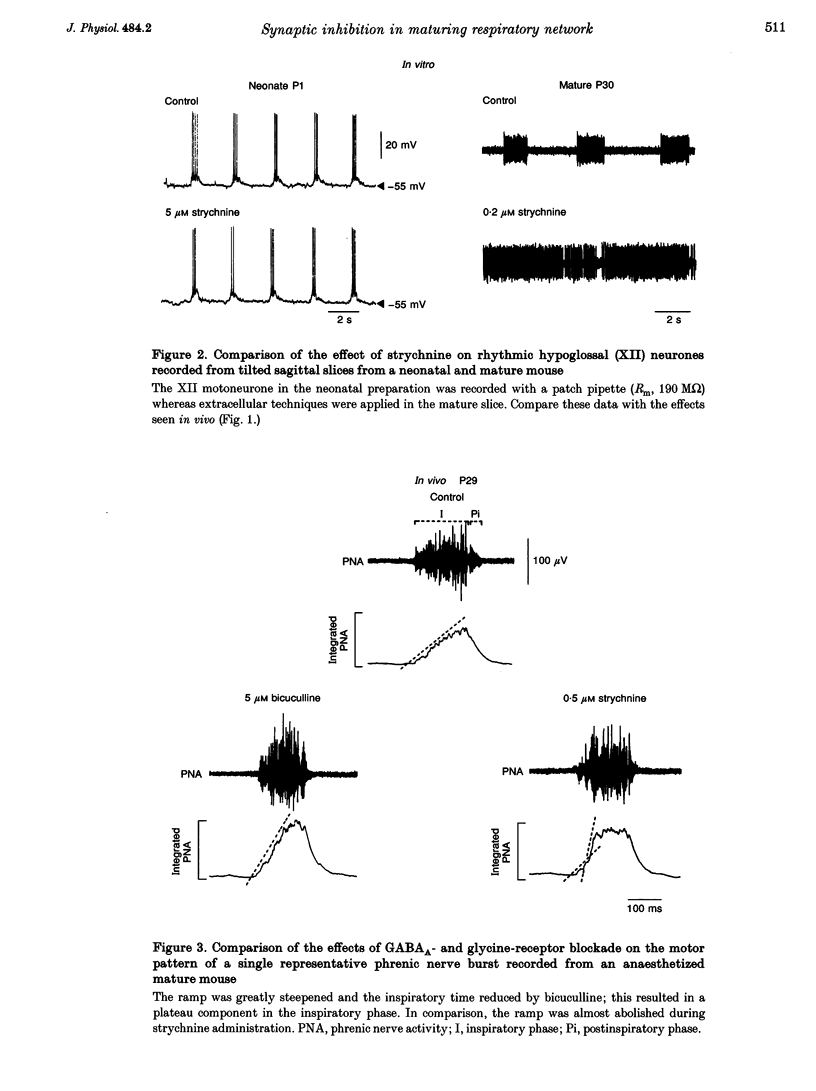
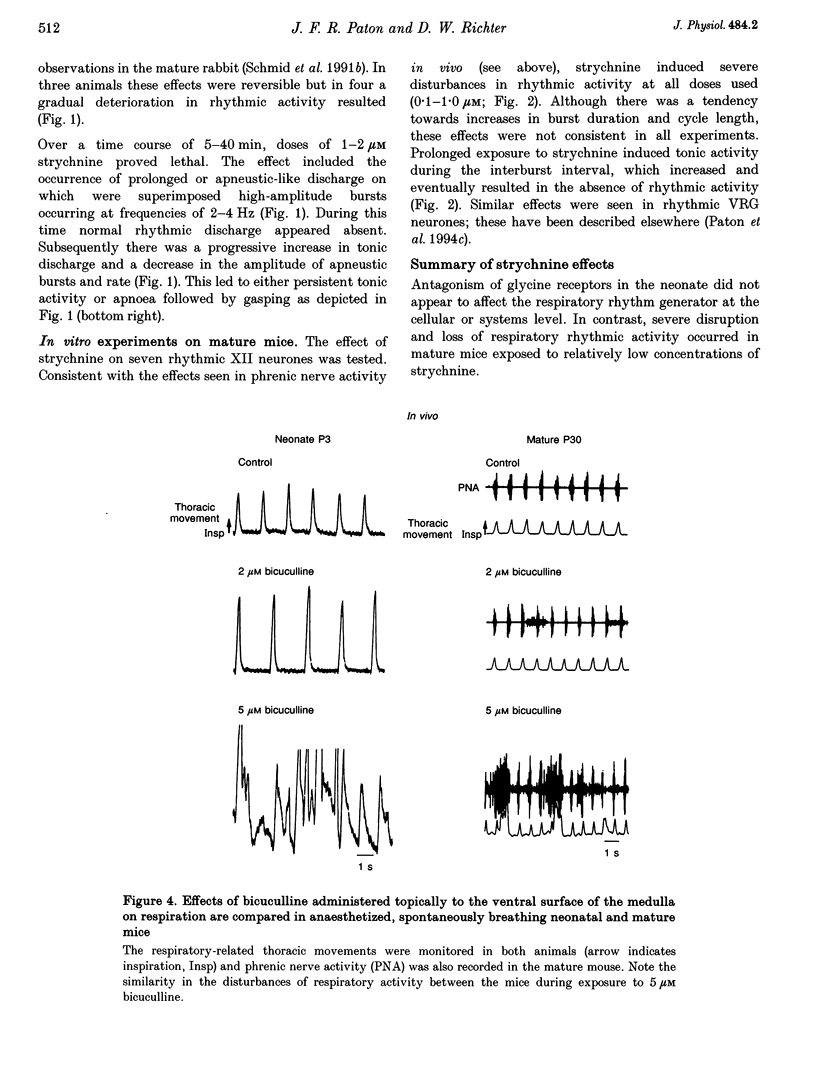
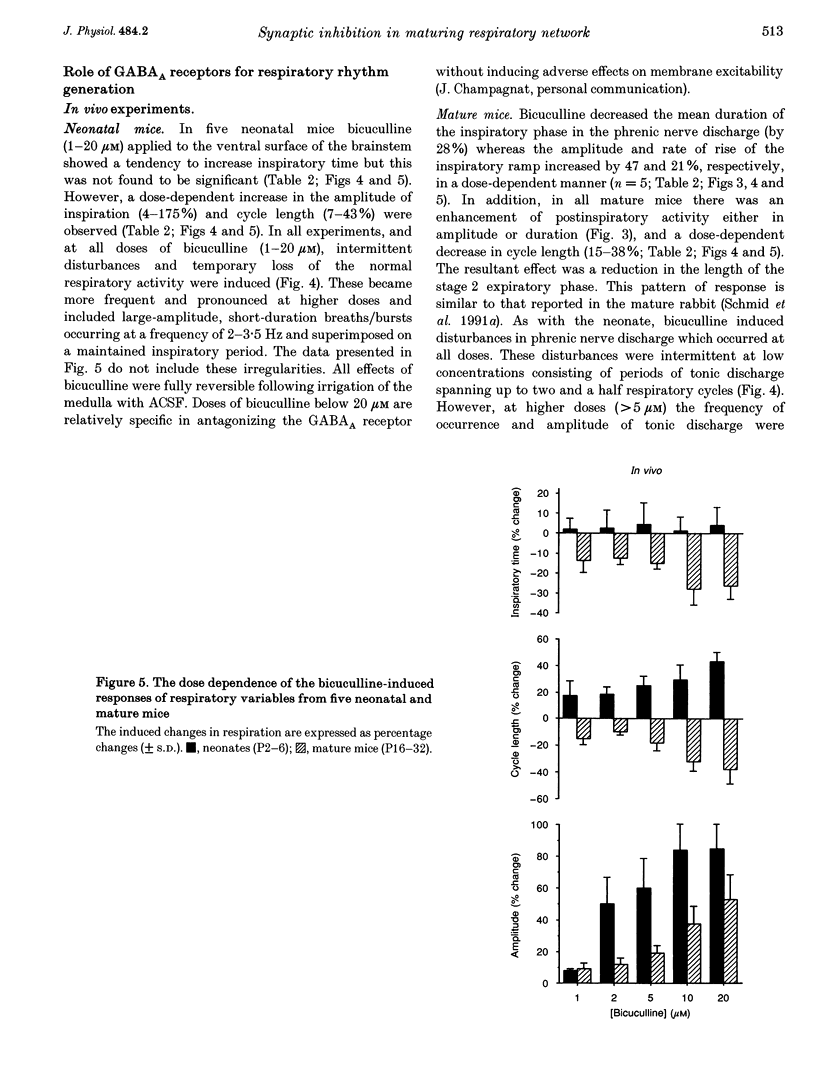
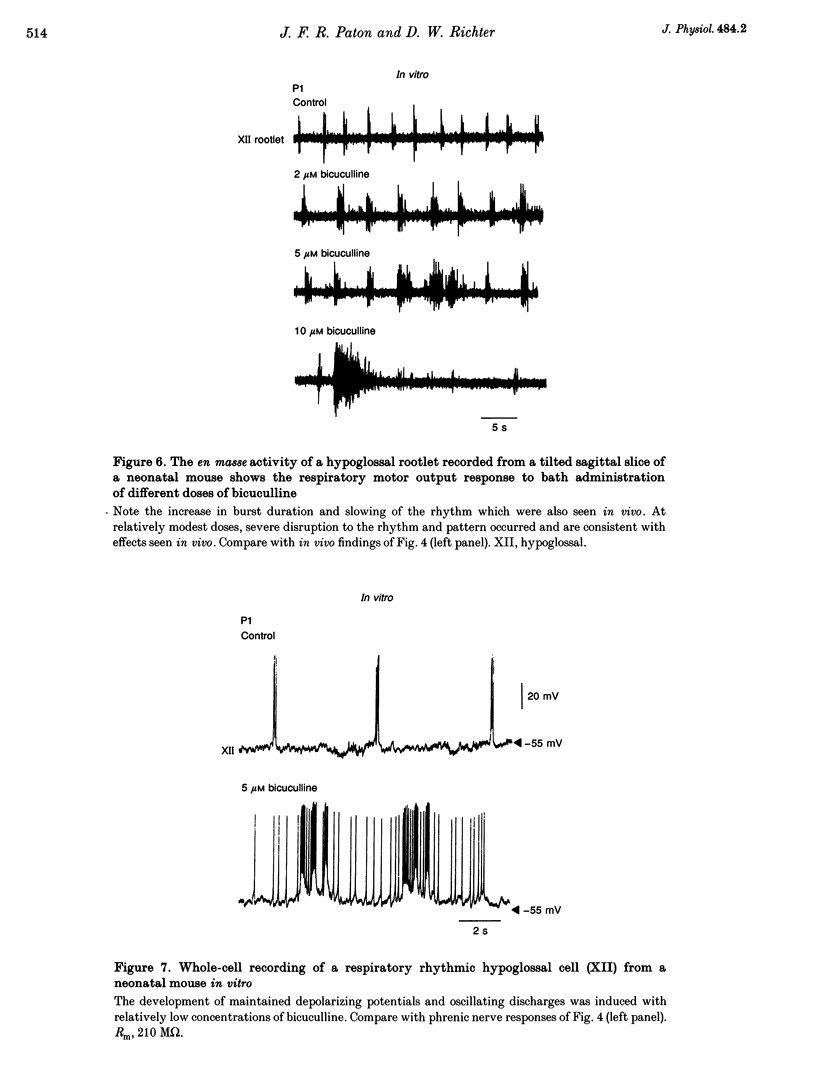
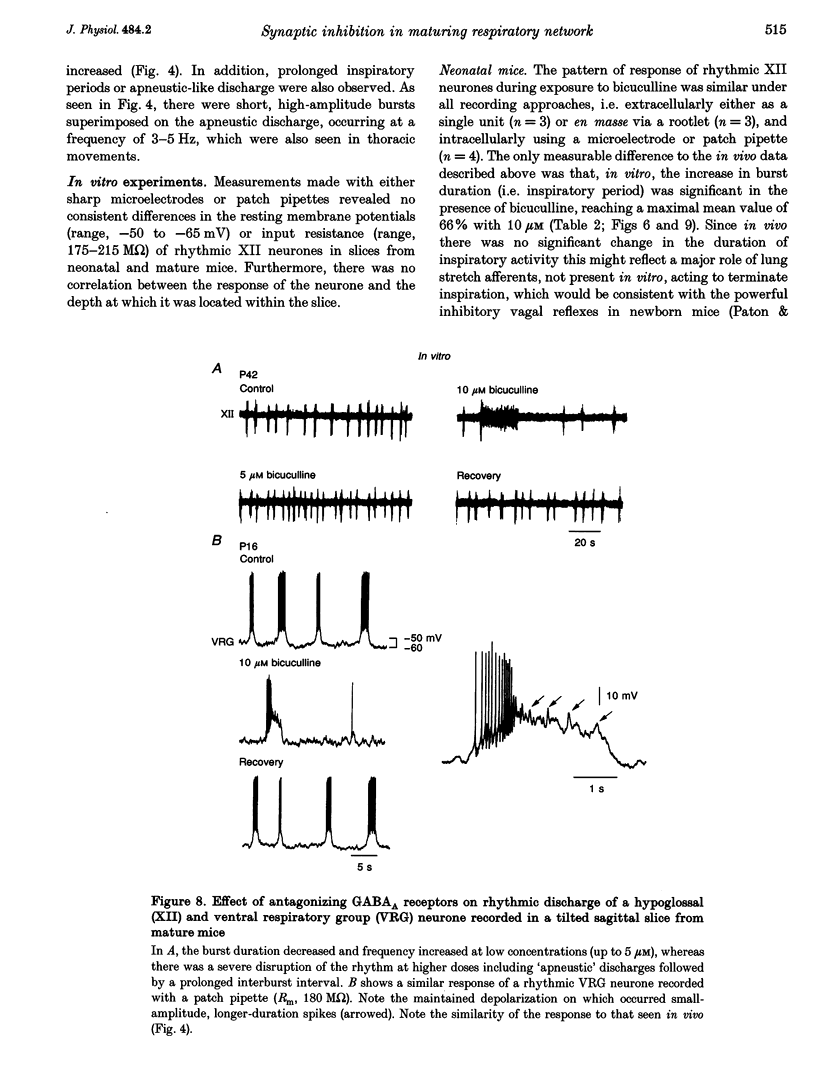
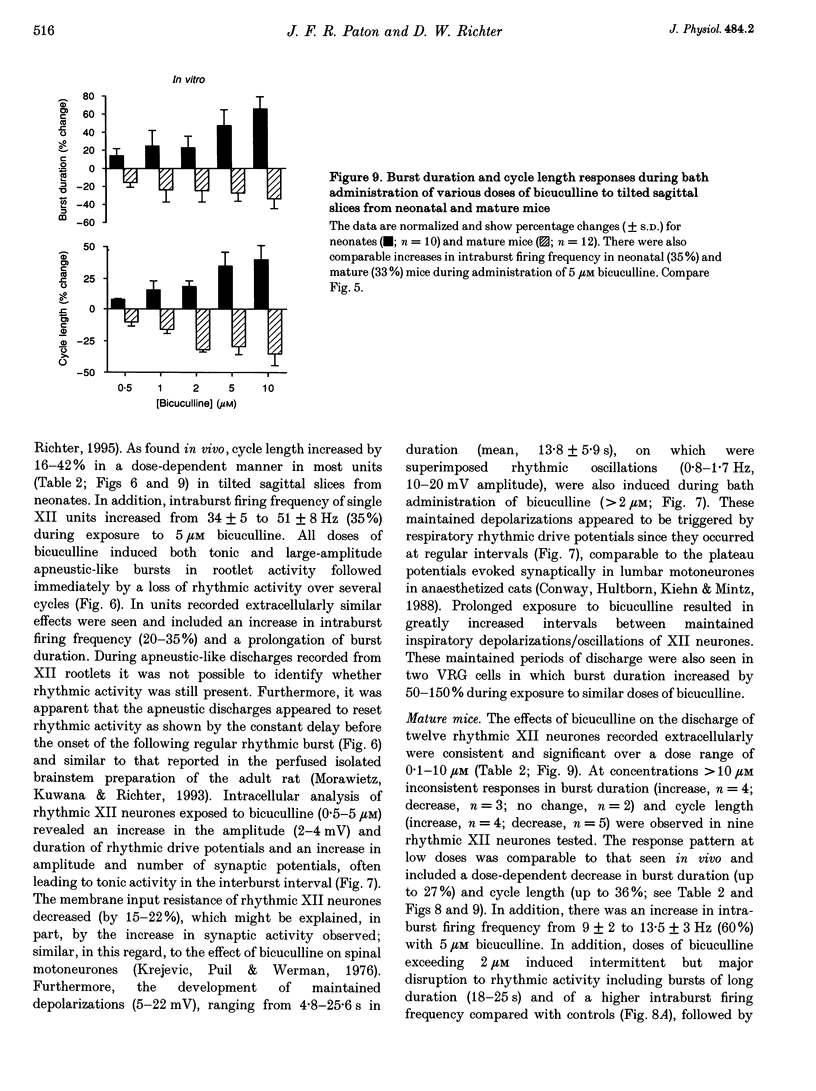
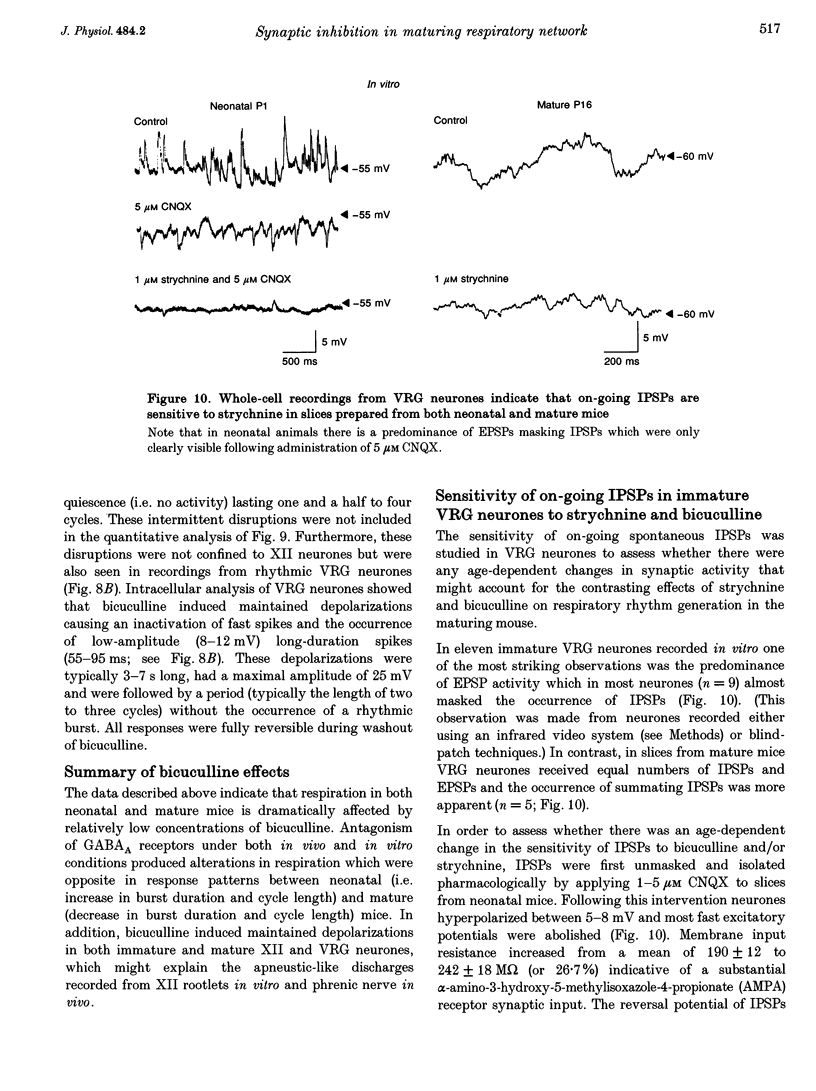
1. The importance of glycinergic and GABAAergic synaptic mechanisms for respiratory rhythm generation in the maturing mouse were investigated in vivo and in an in vitro slice preparation generating respiratory rhythmic activity spontaneously at all postnatal ages. 2. The effect on respiration of topical application of strychnine or bicuculline to the surface of the ventrolateral medulla was assessed in spontaneously breathing anaesthetized mice of different ages (postnatal (P) days 0 to > 56). Glycine receptor antagonization with concentrations of strychnine up to 25 microM was ineffective in altering the breathing pattern in neonates (P1-P8). However, in mature mice (P > 15), low doses of strychnine (0.2-2 microM) abolished regular rhythmic discharge in the phrenic nerve. Bicuculline (0.5-50 microM) produced dose-dependent increases in inspiratory time, amplitude and cycle length of phrenic nerve discharge in anaesthetized neonatal mice whereas both cycle length and duration of inspiratory activity were reduced in mature animals. In addition, in both neonates and mature mice low concentrations of bicuculline (0.5-5 microM) abolished phrenic nerve discharge intermittently. 3. The response of respiratory-modulated hypoglossal (XII) neurones recorded in tilted sagittal slices from newborn and mature mice during blockade of glycine and GABAA receptors was similar to the phrenic nerve changes observed in vivo: in slices from neonates, the rhythmic activity of XII neurones was resistant to concentrations of strychnine up to 50 microM whereas low doses of strychnine (0.2-2 microM) abolished rhythmic activity in preparations from mature mice. Bicuculline (1-50 microM) produced a dose-dependent prolongation of burst duration and a slowing of rhythmic discharge in slices from neonatal mice whereas in mature mice rhythmic XII bursts were shortened and their frequency increased. At all maturational stages, bicuculline (1-50 microM) induced severe disruption of the regular rhythm of XII neurone activity causing maintained depolarizations and oscillations in membrane potential. 4. On-going inhibitory postsynaptic potentials of neurones located in the ventral respiratory group region of tilted sagittal slices from both immature and mature mice were sensitive to low concentrations of either bicuculline or strychnine (1-5 microM) indicating an absence of a maturational change in the sensitivity of GABAA and glycine receptors to their respective antagonists.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akagi H., Miledi R. Heterogeneity of glycine receptors and their messenger RNAs in rat brain and spinal cord. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):270–273. doi: 10.1126/science.2845580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne D., Richter D. W. Post-synaptic inhibition of bulbar inspiratory neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:67–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballanyi K., Kuwana S., Völker A., Morawietz G., Richter D. W. Developmental changes in the hypoxia tolerance of the in vitro respiratory network of rats. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Dec 14;148(1-2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90824-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. M., Hoch W., Betz H. Glycine receptor heterogeneity in rat spinal cord during postnatal development. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3717–3726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03255.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champagnat J., Denavit-Saubié M., Moyanova S., Rondouin G. Involvement of amino acids in periodic inhibitions of bulbar respiratory neurones. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 15;237(2):351–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90447-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway B. A., Hultborn H., Kiehn O., Mintz I. Plateau potentials in alpha-motoneurones induced by intravenous injection of L-dopa and clonidine in the spinal cat. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:369–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezure K. Synaptic connections between medullary respiratory neurons and considerations on the genesis of respiratory rhythm. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35(6):429–450. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90030-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. P. GABAergic effects on respiratory neuronal discharge during opossum development. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 2):R331–R336. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.264.2.R331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. L., Smith J. C. Cellular mechanisms underlying modulation of breathing pattern in mammals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;563:114–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb42194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk G. D., Smith J. C., Feldman J. L. Generation and transmission of respiratory oscillations in medullary slices: role of excitatory amino acids. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Oct;70(4):1497–1515. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.4.1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J. J., Smith J. C., Feldman J. L. Role of excitatory amino acids in the generation and transmission of respiratory drive in neonatal rat. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:727–749. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haji A., Remmers J. E., Connelly C., Takeda R. Effects of glycine and GABA on bulbar respiratory neurons of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1990 May;63(5):955–965. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.5.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haji A., Takeda R., Remmers J. E. Evidence that glycine and GABA mediate postsynaptic inhibition of bulbar respiratory neurons in the cat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Dec;73(6):2333–2342. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.6.2333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi F., Lipski J. The role of inhibitory amino acids in control of respiratory motor output in an arterially perfused rat. Respir Physiol. 1992 Jul;89(1):47–63. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(92)90070-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn O. Plateau potentials and active integration in the 'final common pathway' for motor behaviour. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90023-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klages S., Bellingham M. C., Richter D. W. Late expiratory inhibition of stage 2 expiratory neurons in the cat--a correlate of expiratory termination. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Oct;70(4):1307–1315. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.4.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraszewski K., Grantyn R. Development of GABAergic connections in vitro: increasing efficacy of synaptic transmission is not accompanied by changes in miniature currents. J Neurobiol. 1992 Aug;23(6):766–781. doi: 10.1002/neu.480230613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. Bicuculline, benzyl penicillin, and inhibitory amino acids in the spinal cord of the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;55(3):670–680. doi: 10.1139/y77-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeschcke H. H. Central chemosensitivity and the reaction theory. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:1–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malosio M. L., Marquèze-Pouey B., Kuhse J., Betz H. Widespread expression of glycine receptor subunit mRNAs in the adult and developing rat brain. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2401–2409. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie M. D., Gottschalk A., Anders K., Richter D. W., Pack A. I. A network model of respiratory rhythmogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 2):R962–R975. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.263.4.R962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onimaru H., Arata A., Homma I. Inhibitory synaptic inputs to the respiratory rhythm generator in the medulla isolated from newborn rats. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Dec;417(4):425–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00370663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onimaru H., Homma I. Whole cell recordings from respiratory neurons in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparations isolated from newborn rats. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Mar;420(3-4):399–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00374476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. F., Ramirez J. M., Richter D. W. Functionally intact in vitro preparation generating respiratory activity in neonatal and mature mammals. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Oct;428(3-4):250–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00724504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. F., Ramirez J. M., Richter D. W. Mechanisms of respiratory rhythm generation change profoundly during early life in mice and rats. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Mar 28;170(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D., Lichtman J. W. Formation and maintenance of synaptic connections in autonomic ganglia. Physiol Rev. 1978 Oct;58(4):821–862. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.4.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W., Ballantyne D., Remmers J. E. The differential organization of medullary post-inspiratory activities. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Nov;410(4-5):420–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00586520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W., Ballanyi K., Schwarzacher S. Mechanisms of respiratory rhythm generation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Dec;2(6):788–793. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Böhmer G., Gebauer K. GABAA receptor mediated fast synaptic inhibition in the rabbit brain-stem respiratory system. Acta Physiol Scand. 1991 Jul;142(3):411–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1991.tb09175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Böhmer G., Gebauer K. Glycine receptor-mediated fast synaptic inhibition in the brainstem respiratory system. Respir Physiol. 1991 Jun;84(3):351–361. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(91)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Prince D. A. Changes in excitatory and inhibitory synaptic potentials leading to epileptogenic activity. Brain Res. 1980 Feb 3;183(1):61–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindt P. C., Spain W. J., Crill W. E. Calcium-dependent potassium currents in neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jan;67(1):216–226. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.1.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Ballanyi K., Richter D. W. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from respiratory neurons in neonatal rat brainstem in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Jan 6;134(2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90504-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Ellenberger H. H., Ballanyi K., Richter D. W., Feldman J. L. Pre-Bötzinger complex: a brainstem region that may generate respiratory rhythm in mammals. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):726–729. doi: 10.1126/science.1683005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John P. A., Stephens S. L. Adult-type glycine receptors form clusters on embryonic rat spinal cord neurons developing in vitro. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):2749–2757. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-02749.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Momiyama A., Hirai K., Hishinuma F., Akagi H. Functional correlation of fetal and adult forms of glycine receptors with developmental changes in inhibitory synaptic receptor channels. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90073-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


