Abstract
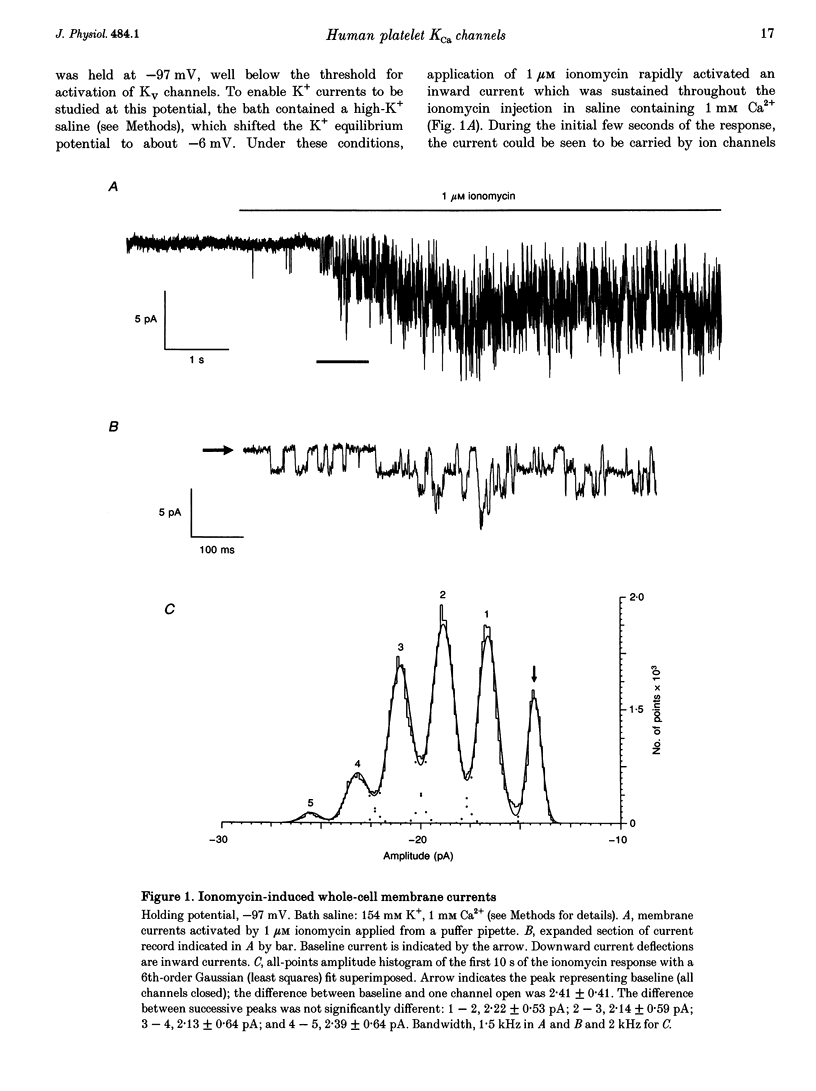
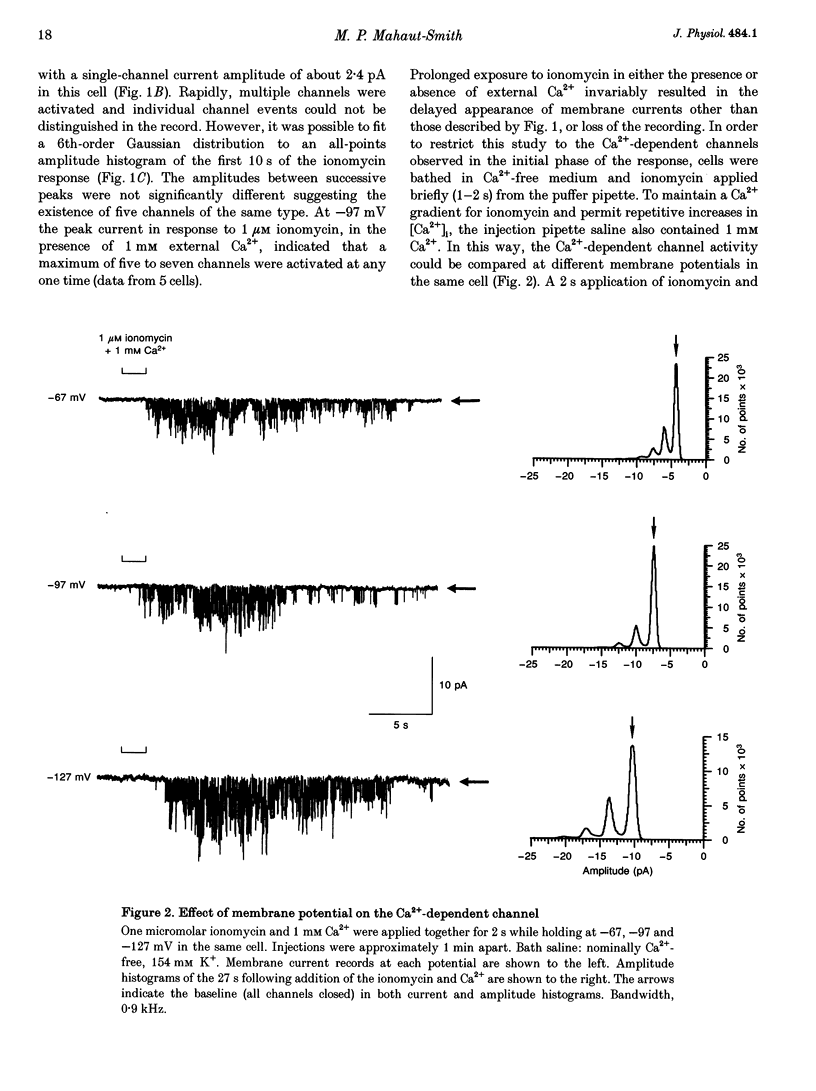
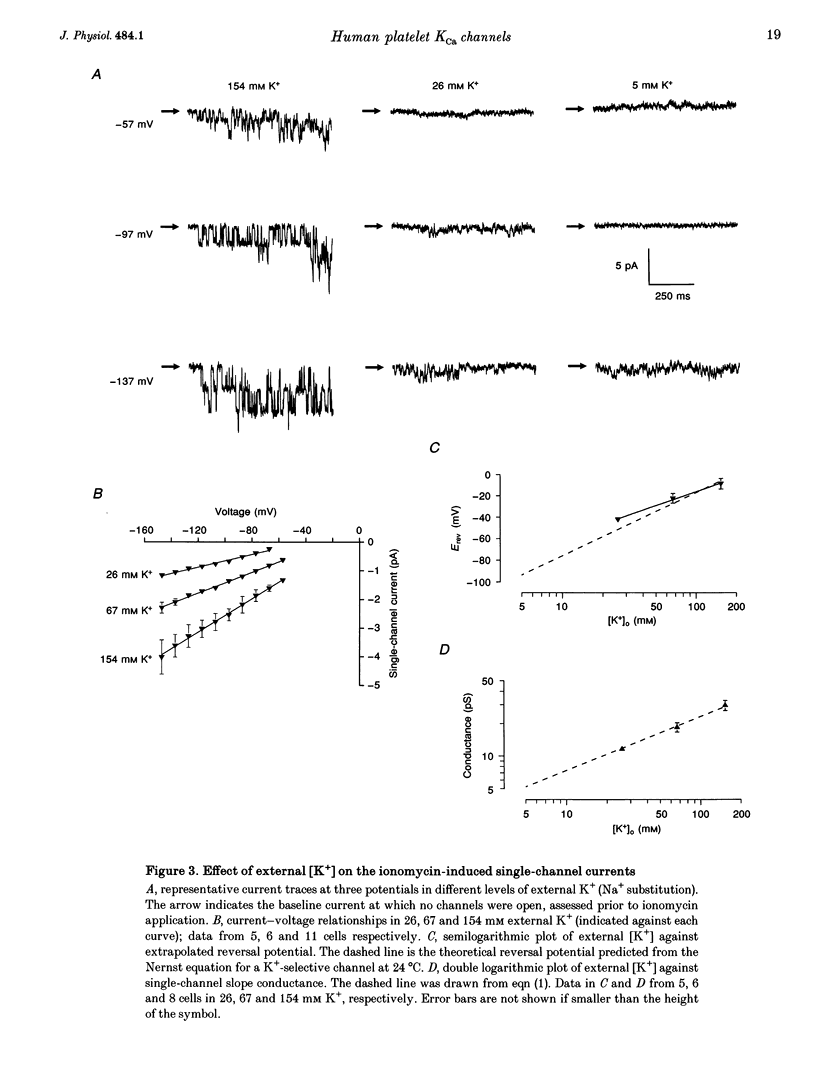
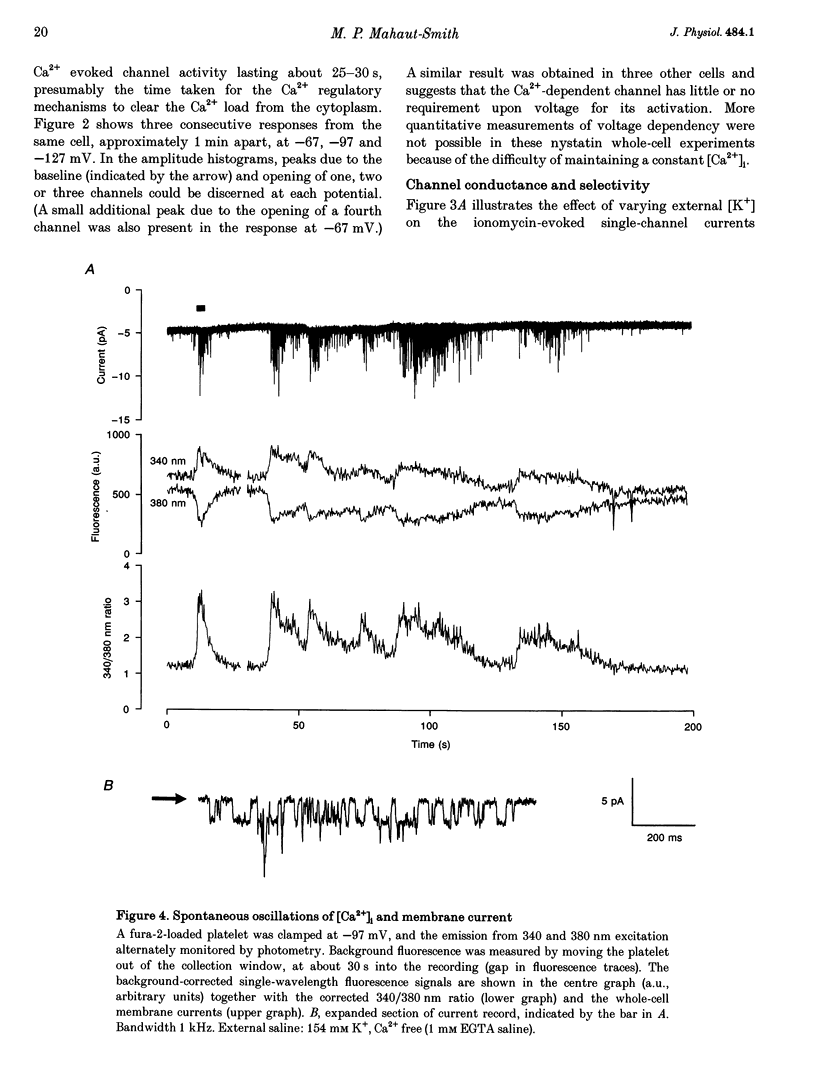
1. The effect of intracellular [Ca2+] ([Ca2+]i) on human platelet ion channels was studied using the nystatin whole-cell patch clamp recording technique. 2. Ionomycin-induced increases in [Ca2+]i rapidly activated a voltage-independent K(+)-selective channel with a slope conductance of 30 pS in 154 mM K+ saline. The single-channel conductance decreased in proportion to the square root of the external K+ concentration such that the estimated conductance in 5 mM K+ was approximately 5 pS. 3. The peak current under conditions expected to increase [Ca2+]i to micromolar levels indicated that each platelet possesses a small number (5-7) of 30 pS Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels (KCa channels). 4. Spontaneous [Ca2+]i spiking was observed in many patch-clamped platelets using fura-2 fluorescence measurements. Each Ca2+ spike triggered up to five KCa channels at any one time. KCa channels were not active at resting levels of [Ca2+]i. 5. The results suggest that platelet KCa channels are not active under resting conditions but may have an important role in determining the membrane potential during Ca2+ signalling.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bregestovski P., Redkozubov A., Alexeev A. Elevation of intracellular calcium reduces voltage-dependent potassium conductance in human T cells. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):776–778. doi: 10.1038/319776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S. The pharmacology of potassium channels and their therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies T. A., Drotts D. L., Weil G. J., Simons E. R. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ is necessary for thrombin-induced platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19600–19606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine B. P., Hansen K. A., Salcedo J. R., Aviv A. Calcium-activated potassium channels in human platelets. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Nov;192(2):109–113. doi: 10.3181/00379727-192-42963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y. Blocking kinetics of the anomalous potassium rectifier of tunicate egg studied by single channel recording. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:311–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K. Evidence for a Ca-activated inwardly rectifying K channel in human macrophages. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 1):C77–C85. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.1.C77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grissmer S., Lewis R. S., Cahalan M. D. Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in human leukemic T cells. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jan;99(1):63–84. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grissmer S., Nguyen A. N., Cahalan M. D. Calcium-activated potassium channels in resting and activated human T lymphocytes. Expression levels, calcium dependence, ion selectivity, and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Oct;102(4):601–630. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. The anomalous rectification and cation selectivity of the membrane of a starfish egg cell. J Membr Biol. 1974;18(1):61–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01870103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Responses to adenosine diphosphate in human platelets loaded with the fluorescent calcium indicator quin2. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:131–146. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk J. W., Hoyland J., Mason W. T., Sage S. O. Spiking in cytosolic calcium concentration in single fibrinogen-bound fura-2-loaded human platelets. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):379–383. doi: 10.1042/bj2830379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. C., Simons E. R. Probes of transmembrane potentials in platelets: changes in cyanine dye fluorescence in response to aggregation stimuli. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):741–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Oberhauser A., Labarca P., Alvarez O. Varieties of calcium-activated potassium channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:385–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livne A., Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Volume-regulating behavior of human platelets. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jun;131(3):354–363. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., Rink T. J. The role of platelet membrane potential in the initiation of platelet aggregation. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Feb 26;47(1):22–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut-Smith M. P. Chloride channels in human platelets: evidence for activation by internal calcium. J Membr Biol. 1990 Oct;118(1):69–75. doi: 10.1007/BF01872205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut-Smith M. P., Mason M. J. Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in rat thymic lymphocytes: activation by concanavalin A. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:513–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut-Smith M. P., Rink T. J., Collins S. C., Sage S. O. Voltage-gated potassium channels and the control of membrane potential in human platelets. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:723–735. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut-Smith M. P., Schlichter L. C. Ca2(+)-activated K+ channels in human B lymphocytes and rat thymocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:69–83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y. A patch-clamp study of mammalian platelets and their voltage-gated potassium current. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:467–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio H., Ikegami Y., Segawa T. Fluorescence digital image analysis of serotonin-induced calcium oscillations in single blood platelets. Cell Calcium. 1991 Feb-Mar;12(2-3):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90019-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partiseti M., Choquet D., Diu A., Korn H. Differential regulation of voltage- and calcium-activated potassium channels in human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3361–3368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipili E. Platelet membrane potential: simultaneous measurement of diSC3(5) fluorescence and optical density. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):645–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sage S. O. Calcium signaling in human platelets. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:431–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Trube G. Conductance properties of single inwardly rectifying potassium channels in ventricular cells from guinea-pig heart. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:641–657. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauvé R., Simoneau C., Monette R., Roy G. Single-channel analysis of the potassium permeability in HeLa cancer cells: evidence for a calcium-activated potassium channel of small unitary conductance. J Membr Biol. 1986;92(3):269–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01869395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki T. Conductance and kinetics of delayed rectifier potassium channels in nodal cells of the rabbit heart. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:227–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vostal J. G., Jackson W. L., Shulman N. R. Cytosolic and stored calcium antagonistically control tyrosine phosphorylation of specific platelet proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16911–16916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


