Abstract
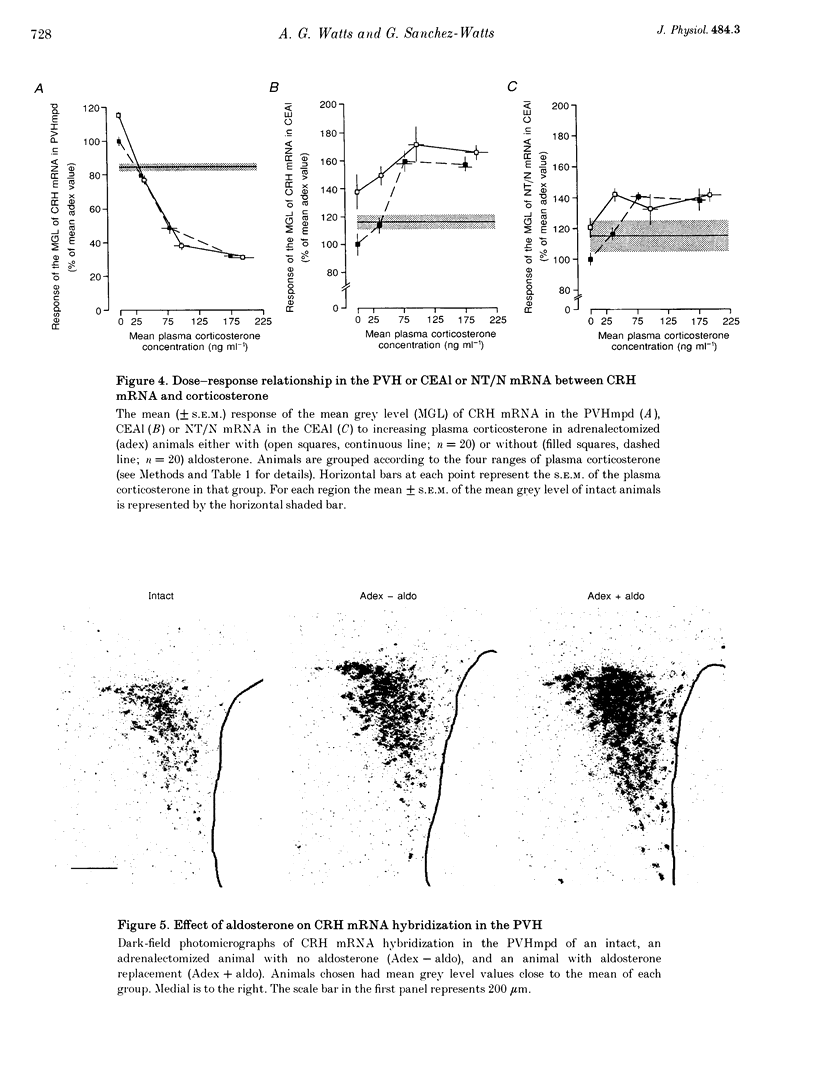
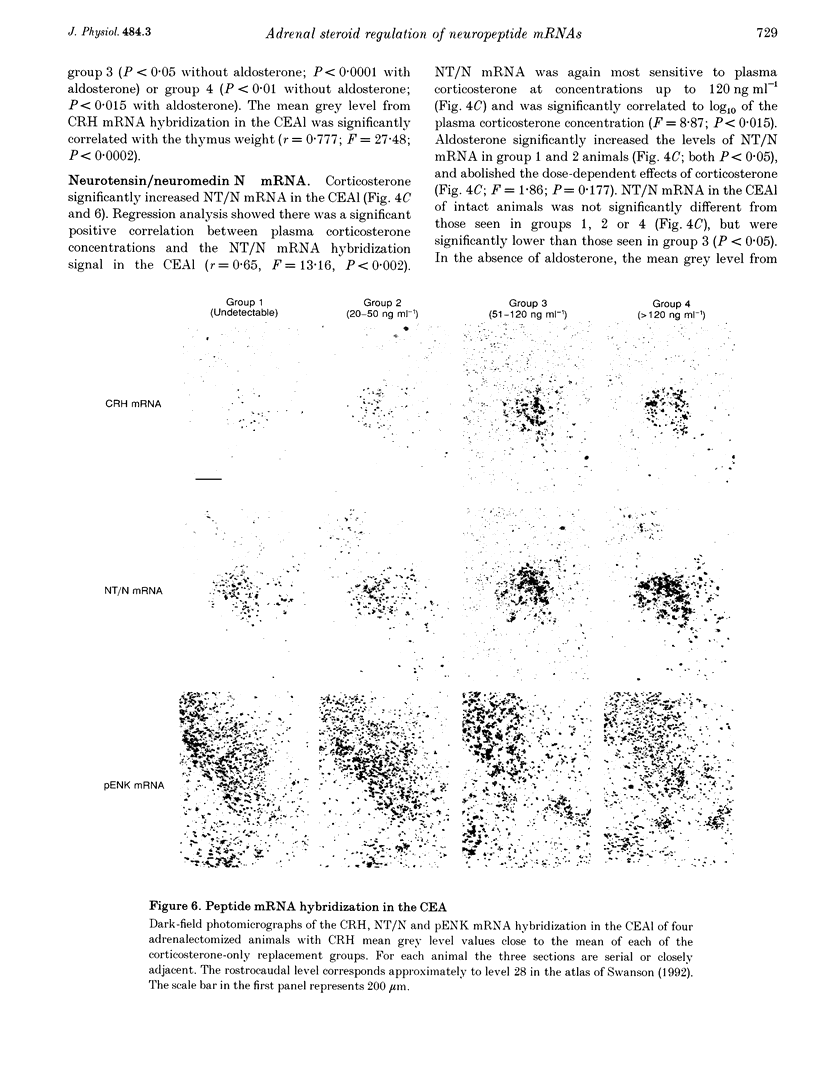
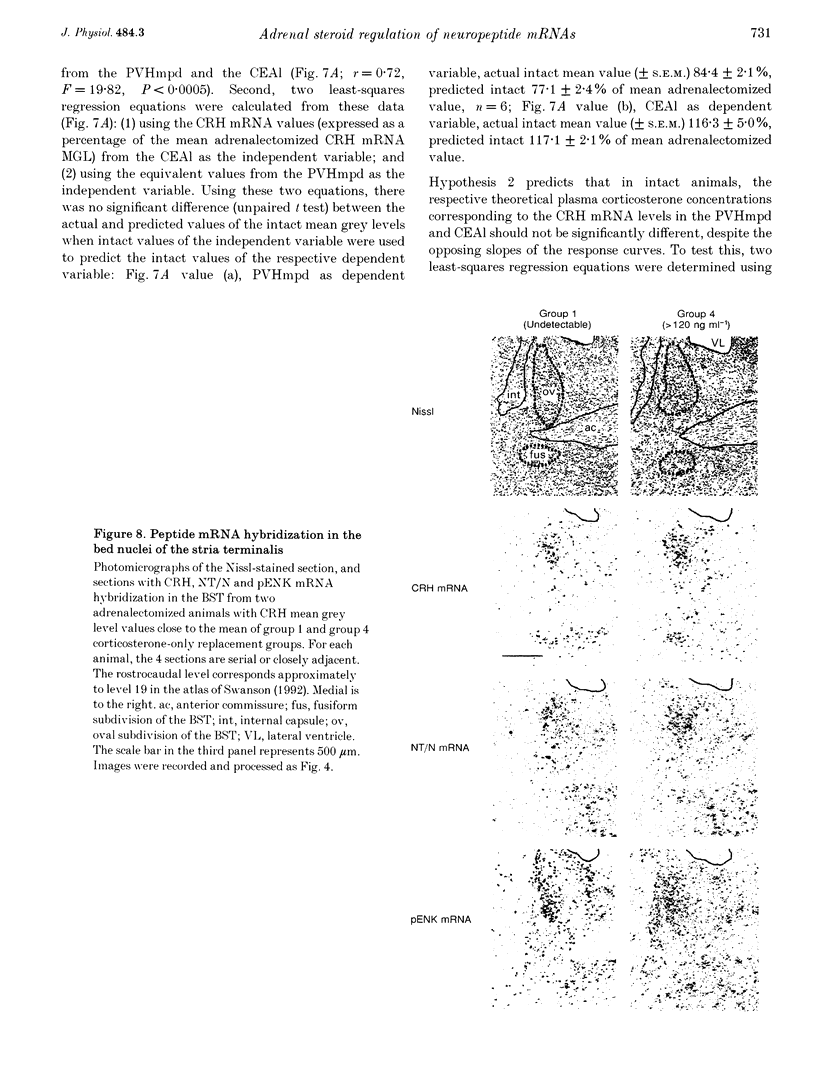
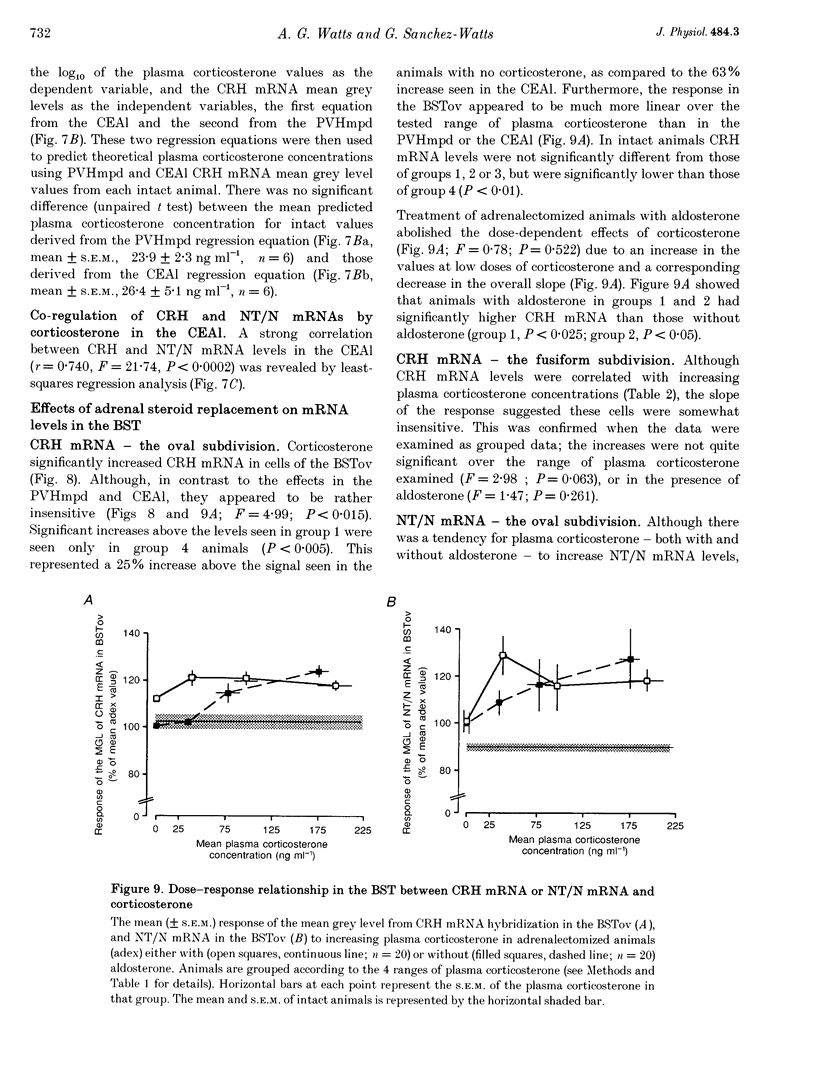
1. We have determined in adrenalectomized male rats the effects of clamping plasma corticosterone and aldosterone at various concentrations on corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), neurotensin/neuromedin N (NT/N) and proenkephalin (pENK) mRNAs in the hypothalamus and amygdala using semi-quantitative in situ hybridization. 2. Corticosterone differentially regulated the levels of CRH and NT/N but not pENK mRNA. These effects were cell specific. CRH mRNA was reduced in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVH), but increased in the central nucleus of the amygdala and bed nuclei of the stria terminalis. NT/N mRNA was never seen in the PVH, whereas levels increased in the central nucleus of the amygdala, but were unaffected in the lateral hypothalamic area. In those regions expressing pENK mRNA, levels were unaffected in all treatment groups. 3. CRH mRNA in both the central nucleus of the amygdala and PVH, and NT/N mRNA in the central nucleus of the amygdala were most sensitive to plasma corticosterone concentrations of less than 120 ng ml-1, i.e. those seen away from the peak of the diurnal rhythm. In adrenalectomized animals CRH mRNA in both the central nucleus of the amygdala and PVH could be set at levels usually seen in intact animals by the same plasma concentration of corticosterone. 4. The levels of CRH mRNA in the PVH and the central nucleus of the amygdala were closely correlated, while CRH and NT/N mRNA levels were similarly correlated in the central nucleus of the amygdala suggesting the existence of a common regulatory mechanism. The ED50 of their responses to corticosterone and correlations with thymus weight suggested the operation of glucocorticoid (type II) receptor mechanisms. 5. In the absence of corticosterone, aldosterone increased CRH and NT/N mRNA accumulation in the central nucleus of the amygdala, and increased CRH but not NT/N mRNA accumulation in the PVH. Aldosterone also blunted the dose-response effects of corticosterone on CRH and NT/N mRNA levels in the central nucleus of the amygdala, but not in the PVH. 6. These results suggest that, in intact animals, adrenal steroids play a major role in maintaining the levels of neuropeptide mRNAs in the PVH, bed nuclei of the stria terminalis and central nucleus of the amygdala. The results underscore the importance of cell-specific mechanisms operating to regulate the expression of neuropeptide genes in different cell types in response to diverse physiological conditions.
Full text
PDF


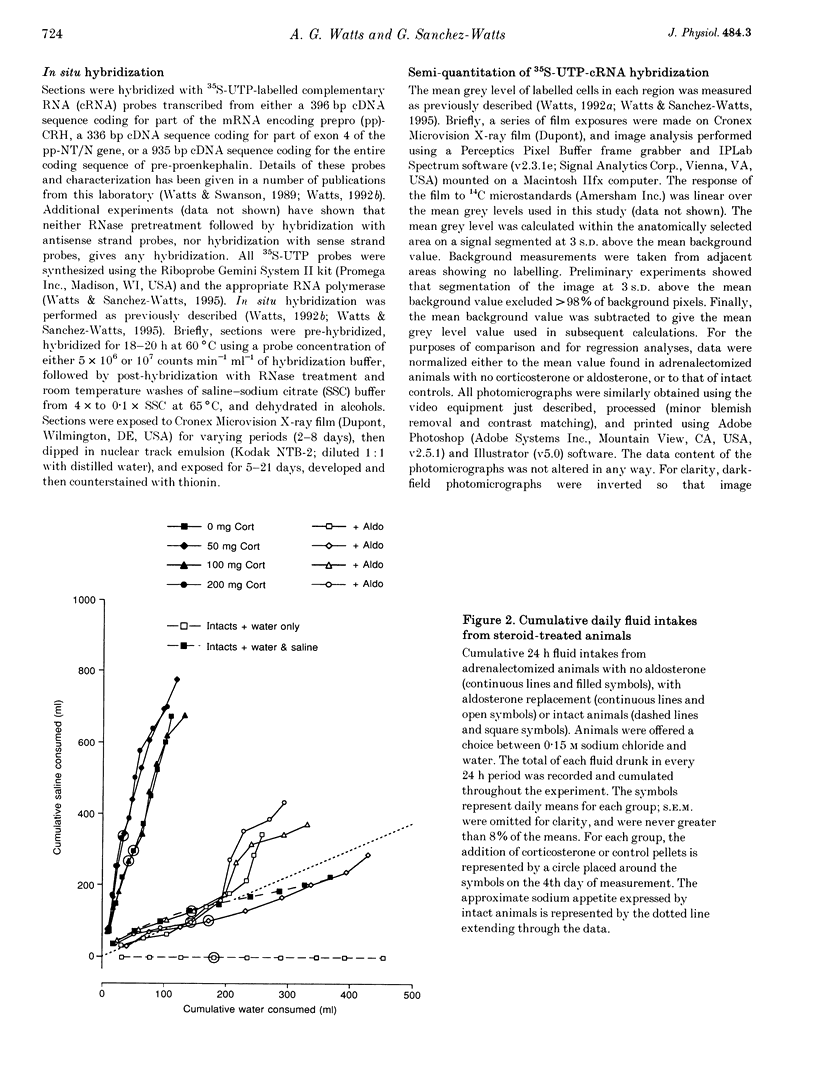

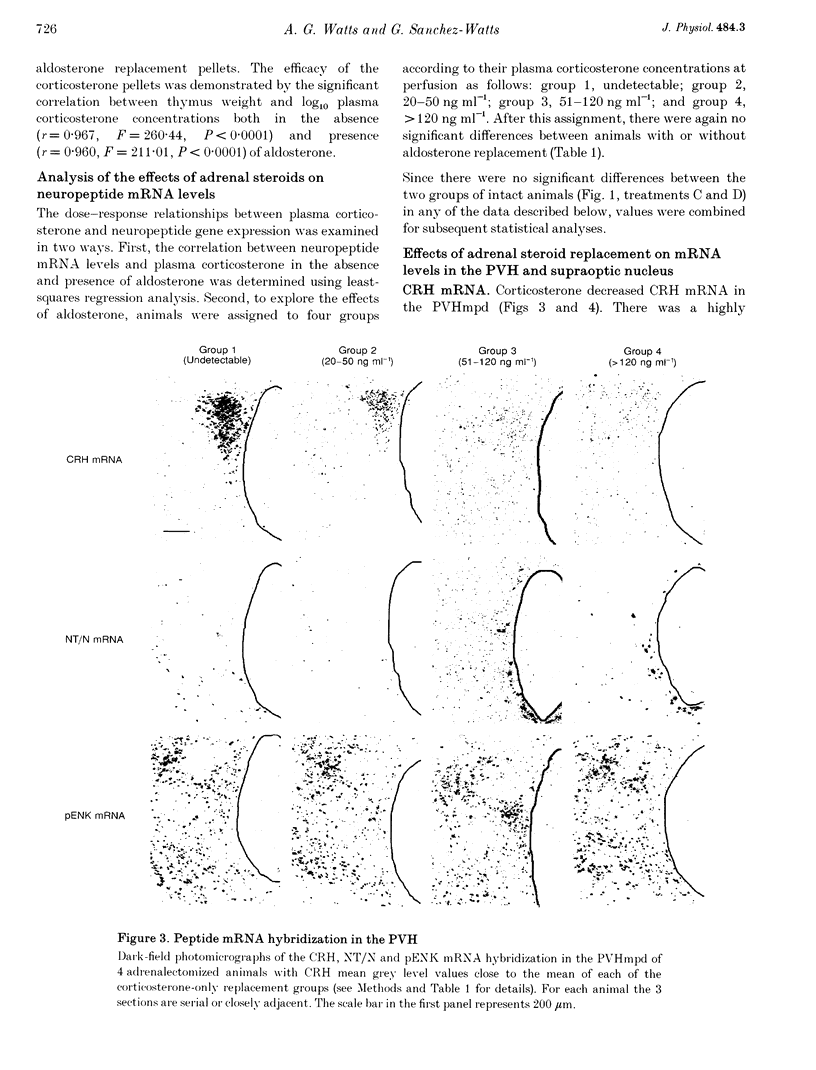






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler G. K., Smas C. M., Majzoub J. A. Expression and dexamethasone regulation of the human corticotropin-releasing hormone gene in a mouse anterior pituitary cell line. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5846–5852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahima R. S., Harlan R. E. Charting of type II glucocorticoid receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1990;39(3):579–604. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90244-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriza J. L., Simerly R. B., Swanson L. W., Evans R. M. The neuronal mineralocorticoid receptor as a mediator of glucocorticoid response. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):887–900. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenbosch F., Tilders F. J. Effect of axonal transport blockade on corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactivity in the median eminence of intact and adrenalectomized rats: relationship between depletion rate and secretory activity. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 1;442(2):312–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91517-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer H. S., Matta S. G., Sharp B. M. Regulation of the messenger ribonucleic acid for corticotropin-releasing factor in the paraventricular nucleus and other brain sites of the rat. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):2117–2123. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-2117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. F., Akana S. F., Cascio C. S., Darlington D. N., Jacobson L., Levin N. Regulation of ACTH secretion: variations on a theme of B. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1987;43:113–173. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571143-2.50010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. F., Levin N., Cascio C. S., Akana S. F., Jacobson L., Kuhn R. W. Pharmacological evidence that the inhibition of diurnal adrenocorticotropin secretion by corticosteroids is mediated via type I corticosterone-preferring receptors. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):2844–2850. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-6-2844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink G., Robinson I. C., Tannahill L. A. Effects of adrenalectomy and glucocorticoids on the peptides CRF-41, AVP and oxytocin in rat hypophysial portal blood. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:329–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbuz M. S., Lightman S. L. Responses of hypothalamic and pituitary mRNA to physical and psychological stress in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1989 Sep;122(3):705–711. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman J. P., Schäfer M. K., Young E. A., Thompson R., Douglass J., Akil H., Watson S. J. Evidence for hippocampal regulation of neuroendocrine neurons of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. J Neurosci. 1989 Sep;9(9):3072–3082. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-09-03072.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honkaniemi J., Pelto-Huikko M., Rechardt L., Isola J., Lammi A., Fuxe K., Gustafsson J. A., Wikström A. C., Hökfelt T. Colocalization of peptide and glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactivities in rat central amygdaloid nucleus. Neuroendocrinology. 1992 Apr;55(4):451–459. doi: 10.1159/000126156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaki T., Nahan J. L., Rivier C., Sawchenko P. E., Vale W. Differential regulation of corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA in rat brain regions by glucocorticoids and stress. J Neurosci. 1991 Mar;11(3):585–599. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-03-00585.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Swanson L. W., Simerly R. B. Studies on the cellular architecture of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis in the rat: II. Chemoarchitecture. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Feb 22;280(4):603–621. doi: 10.1002/cne.902800410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislauskis E., Dobner P. R. Mutually dependent response elements in the cis-regulatory region of the neurotensin/neuromedin N gene integrate environmental stimuli in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):783–795. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90205-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács K. J., Mezey E. Dexamethasone inhibits corticotropin-releasing factor gene expression in the rat paraventricular nucleus. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Oct;46(4):365–368. doi: 10.1159/000124846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwak S. P., Morano M. I., Young E. A., Watson S. J., Akil H. Diurnal CRH mRNA rhythm in the hypothalamus: decreased expression in the evening is not dependent on endogenous glucocorticoids. Neuroendocrinology. 1993 Jan;57(1):96–105. doi: 10.1159/000126347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin N., Shinsako J., Dallman M. F. Corticosterone acts on the brain to inhibit adrenalectomy-induced adrenocorticotropin secretion. Endocrinology. 1988 Feb;122(2):694–701. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-2-694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Influence of steroids on the hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor and preproenkephalin mRNA responses to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4306–4310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Vasopressin, oxytocin, dynorphin, enkephalin and corticotrophin-releasing factor mRNA stimulation in the rat. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:23–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liposits Z., Uht R. M., Harrison R. W., Gibbs F. P., Paull W. K., Bohn M. C. Ultrastructural localization of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in hypothalamic paraventricular neurons synthesizing corticotropin releasing factor (CRF). Histochemistry. 1987;87(5):407–412. doi: 10.1007/BF00496811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Gold P. W., Schulkin J. Corticosterone effects on corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA in the central nucleus of the amygdala and the parvocellular region of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1994 Mar 21;640(1-2):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moga M. M., Gray T. S. Evidence for corticotropin-releasing factor, neurotensin, and somatostatin in the neural pathway from the central nucleus of the amygdala to the parabrachial nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Nov 15;241(3):275–284. doi: 10.1002/cne.902410304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moga M. M., Saper C. B., Gray T. S. Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: cytoarchitecture, immunohistochemistry, and projection to the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1989 May 15;283(3):315–332. doi: 10.1002/cne.902830302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moga M. M., Saper C. B., Gray T. S. Neuropeptide organization of the hypothalamic projection to the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1990 May 22;295(4):662–682. doi: 10.1002/cne.902950409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reul J. M., de Kloet E. R. Two receptor systems for corticosterone in rat brain: microdistribution and differential occupation. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2505–2511. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckl J. R., Dow R. C., Low S. C., Edwards C. R., Fink G. The 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitor glycyrrhetinic acid affects corticosteroid feedback regulation of hypothalamic corticotrophin-releasing peptides in rats. J Endocrinol. 1993 Mar;136(3):471–477. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1360471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada S., Inagaki S., Kubota Y., Ogawa N., Shibasaki T., Takagi H. Coexistence of peptides (corticotropin releasing factor/neurotensin and substance P/somatostatin) in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and central amygdaloid nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience. 1989;30(2):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Simmons D. M. Differential steroid hormone and neural influences on peptide mRNA levels in CRH cells of the paraventricular nucleus: a hybridization histochemical study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jul 22;285(4):413–435. doi: 10.1002/cne.902850402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A. G. Disturbance of fluid homeostasis leads to temporally and anatomically distinct responses in neuropeptide and tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA levels in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the rat. Neuroscience. 1992;46(4):859–879. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90190-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A. G. Osmotic stimulation differentially affects cellular levels of corticotropin-releasing hormone and neurotensin/neuromedin N mRNAs in the lateral hypothalamic area and central nucleus of the amygdala. Brain Res. 1992 May 29;581(2):208–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90710-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A. G., Sanchez-Watts G. Physiological regulation of peptide messenger RNA colocalization in rat hypothalamic paraventricular medial parvicellular neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1995 Feb 20;352(4):501–514. doi: 10.1002/cne.903520403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A. G., Swanson L. W. Diurnal variations in the content of preprocorticotropin-releasing hormone messenger ribonucleic acids in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of rats of both sexes as measured by in situ hybridization. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1734–1738. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Mezey E., Siegel R. E. Quantitative in situ hybridization histochemistry reveals increased levels of corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA after adrenalectomy in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Oct 8;70(2):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90463-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kloet E. R., Oitzl M. S., Joëls M. Functional implications of brain corticosteroid receptor diversity. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1993 Aug;13(4):433–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00711582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]