Abstract
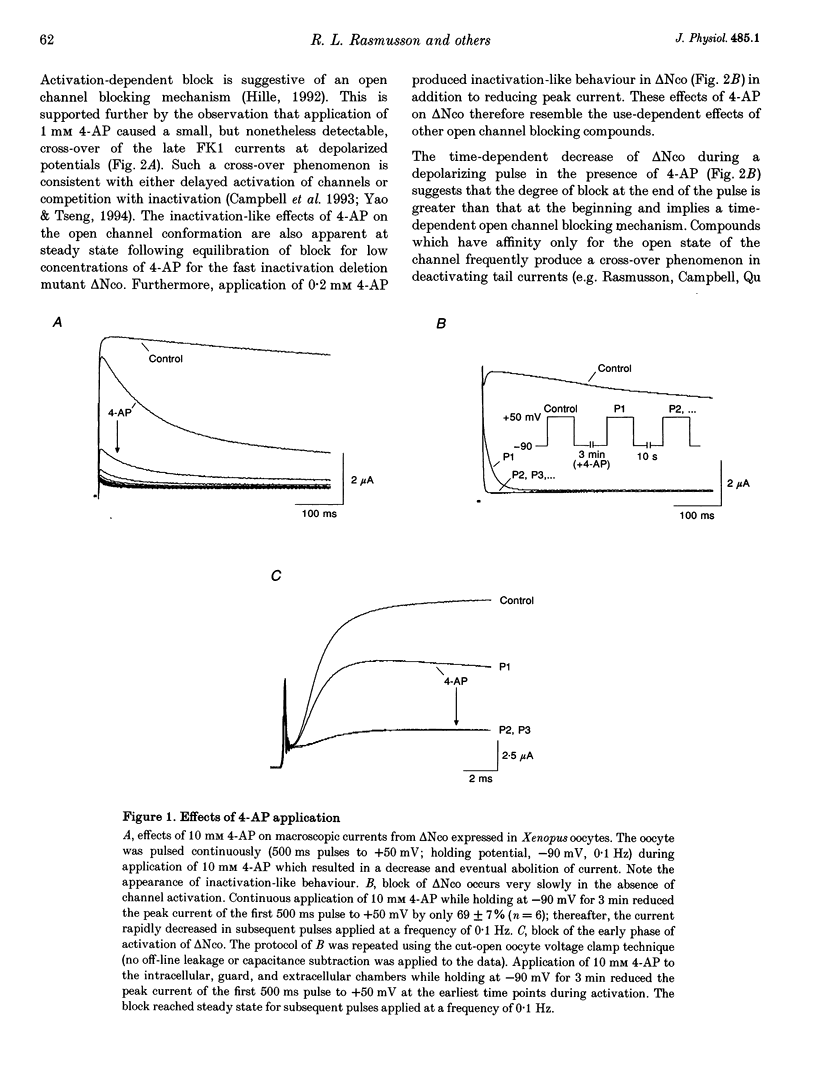
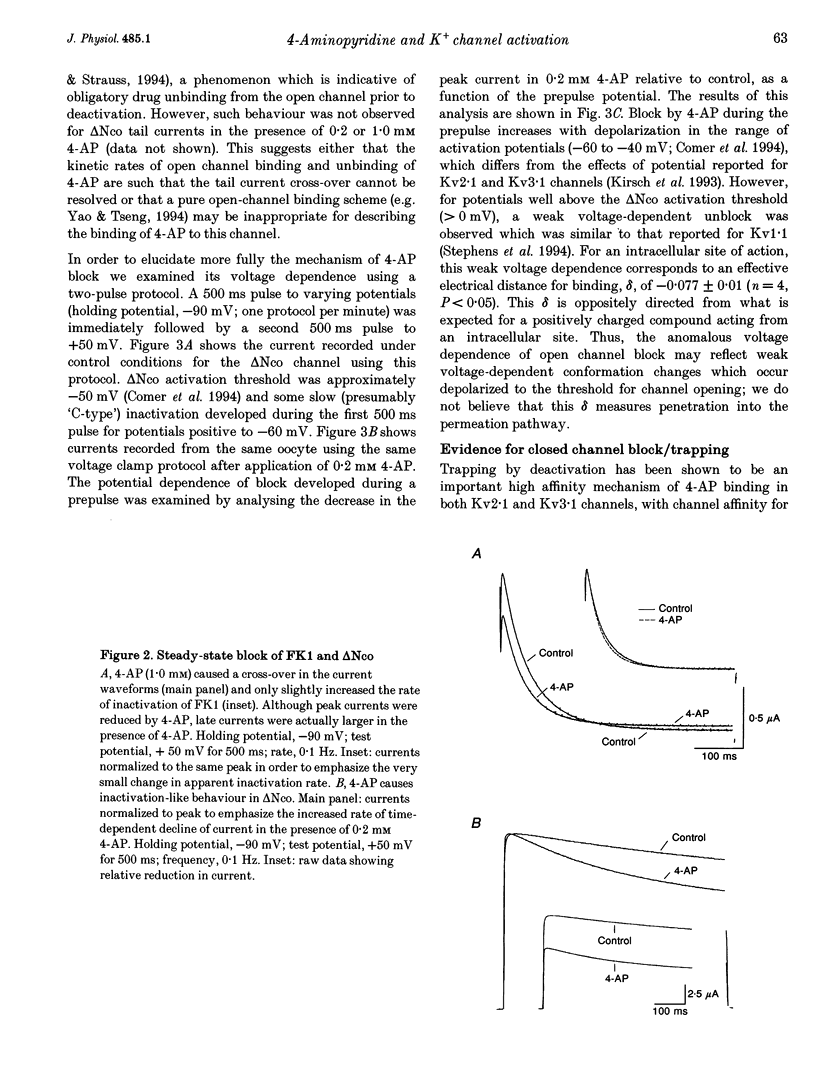
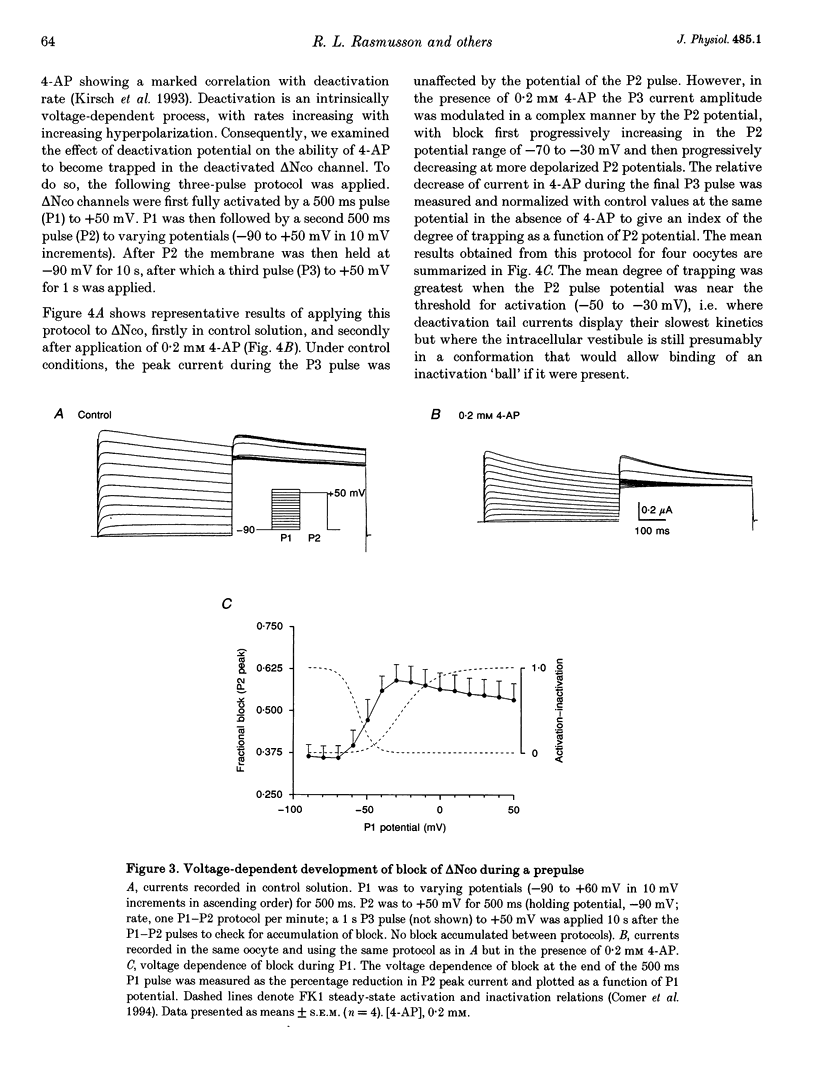
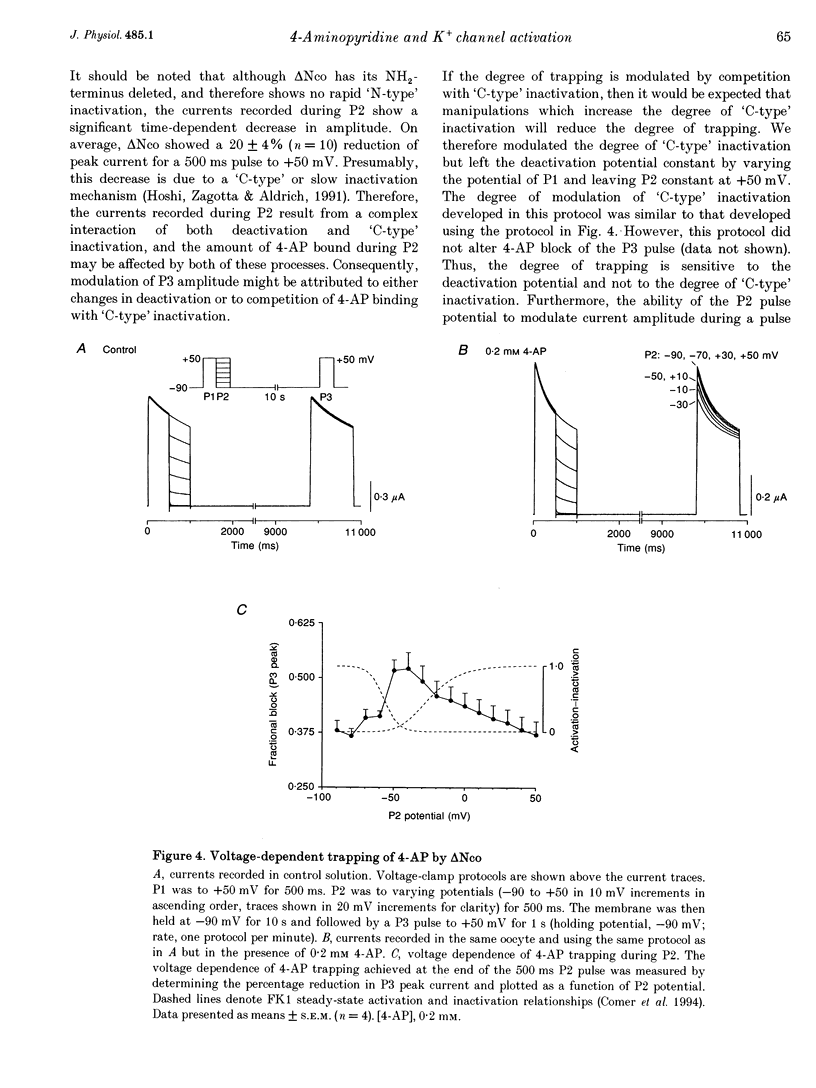
1. Using the two-microelectrode, 'cut open' oocyte, and 'torn off' macropatch voltage clamp techniques, we studied the blocking effects of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) on two cloned K+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes, an inactivating K+ channel isolated from ferret ventricle (FK1), and its NH2-terminal deletion mutant (delta NCO) which lacks fast N-type inactivation. 2. Experiments with a permanently charged, impermeant 4-AP derivative, 4-aminopyridine-methyliodide, indicated that the cationic form of 4-AP blocks at an intracellular site. 3. Block accumulated from pulse to pulse and was sensitive to the applied potential during hyperpolarizing deactivating pulses, indicating trapping of 4-AP in deactivated channels. For long trains of depolarizing pulses (-90 to +50 mV, 0.1 Hz), 4-AP block increased with decreasing pulse duration. Block of FK1 was much more sensitive to pulse duration than was block of delta NCO, consistent with competition between N-type inactivation and 4-AP binding. 4. To elucidate these mechanisms further, in the absence of fast N-type inactivation the following results were obtained on delta NCO channels: (1) application of 4-AP caused the appearance of apparent inactivation; (2) 4-AP, however, did not cause cross-over of deactivating tail currents; (3) 4-AP block developed with time for potentials positive to -40 mV; and (4) trapping of 4-AP by delta NCO was insensitive to the degree of C-type inactivation. 5. We conclude that the kinetics of 4-AP block of FK1 and delta NCO channels cannot be accounted for by either a pure open channel or closed channel blocking scheme.
Full text
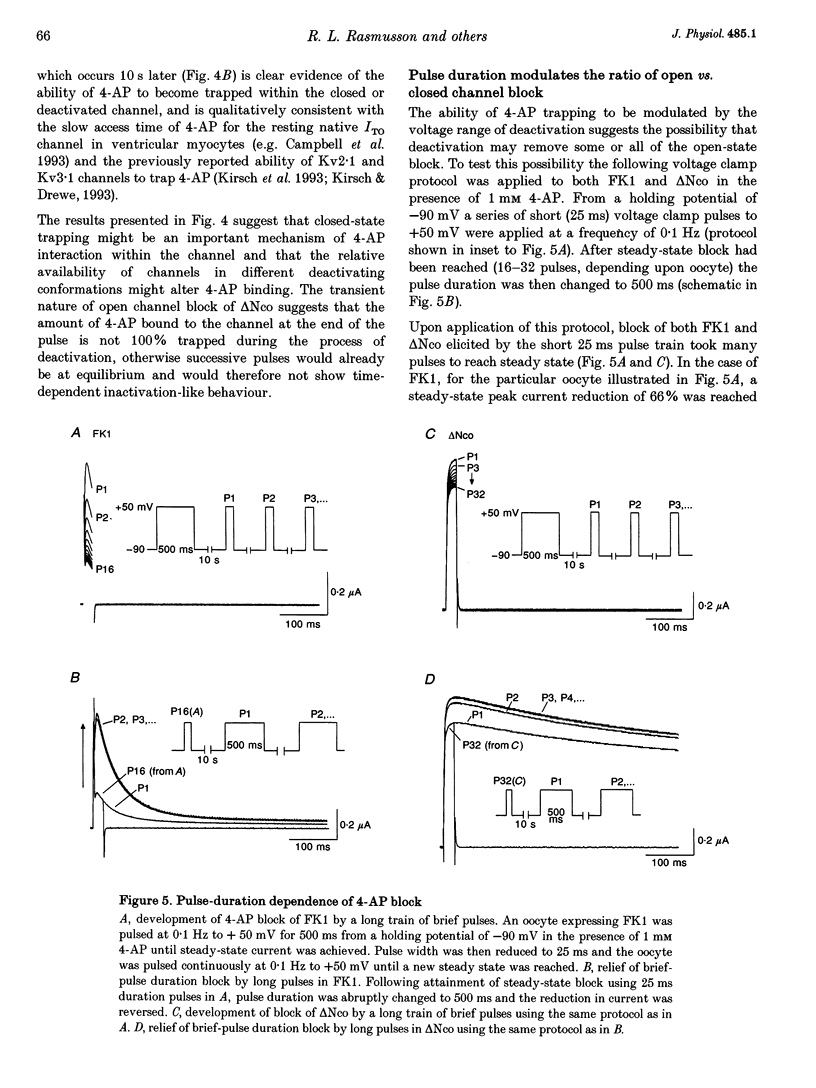
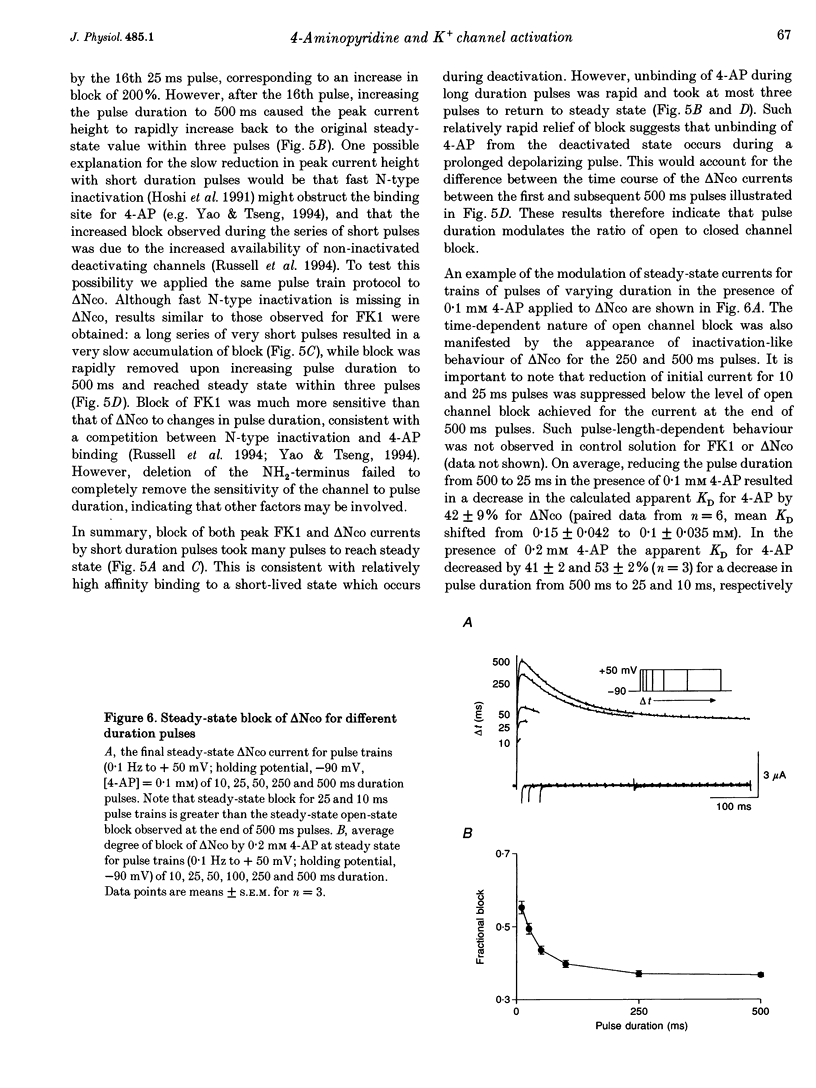
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell D. L., Qu Y., Rasmusson R. L., Strauss H. C. The calcium-independent transient outward potassium current in isolated ferret right ventricular myocytes. II. Closed state reverse use-dependent block by 4-aminopyridine. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Apr;101(4):603–626. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.4.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choquet D., Korn H. Mechanism of 4-aminopyridine action on voltage-gated potassium channels in lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Feb;99(2):217–240. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comer M. B., Campbell D. L., Rasmusson R. L., Lamson D. R., Morales M. J., Zhang Y., Strauss H. C. Cloning and characterization of an Ito-like potassium channel from ferret ventricle. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 2):H1383–H1395. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.267.4.H1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., MacKinnon R. The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90276-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh J. K., Quandt F. N. Aminopyridine block of potassium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Nov;267(2):604–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Two types of inactivation in Shaker K+ channels: effects of alterations in the carboxy-terminal region. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Ritchie J. M. On the active form of 4-aminopyridine: block of K+ currents in rabbit Schwann cells. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:183–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehl S. J. 4-Aminopyridine causes a voltage-dependent block of the transient outward K+ current in rat melanotrophs. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:515–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A. Gating-dependent mechanism of 4-aminopyridine block in two related potassium channels. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Nov;102(5):797–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.5.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Shieh C. C., Drewe J. A., Vener D. F., Brown A. M. Segmental exchanges define 4-aminopyridine binding and the inner mouth of K+ pores. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90154-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack K., Joiner W. J., Heinemann S. H. A characterization of the activating structural rearrangements in voltage-dependent Shaker K+ channels. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R. E., Wadman W. J., Wong R. K. Outward currents of single hippocampal cells obtained from the adult guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:331–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Wagoner P. K. The inactivating K+ current in GH3 pituitary cells and its modification by chemical reagents. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:587–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig J., Heinemann S. H., Wunder F., Lorra C., Parcej D. N., Dolly J. O., Pongs O. Inactivation properties of voltage-gated K+ channels altered by presence of beta-subunit. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):289–294. doi: 10.1038/369289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):729–749. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott V. E., Rettig J., Parcej D. N., Keen J. N., Findlay J. B., Pongs O., Dolly J. O. Primary structure of a beta subunit of alpha-dendrotoxin-sensitive K+ channels from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1637–1641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Liao Y. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Presynaptic A-current based on heteromultimeric K+ channels detected in vivo. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):72–75. doi: 10.1038/365072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simurda J., Simurdová M., Christé G. Use-dependent effects of 4-aminopyridine on transient outward current in dog ventricular muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Nov;415(2):244–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00370600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. The S4-S5 loop contributes to the ion-selective pore of potassium channels. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens G. J., Garratt J. C., Robertson B., Owen D. G. On the mechanism of 4-aminopyridine action on the cloned mouse brain potassium channel mKv1.1. J Physiol. 1994 Jun 1;477(Pt 2):187–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Ruppersberg J. P., Schröter K. H., Sakmann B., Stocker M., Giese K. P., Perschke A., Baumann A., Pongs O. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3235–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglialatela M., Toro L., Stefani E. Novel voltage clamp to record small, fast currents from ion channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys J. 1992 Jan;61(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81817-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Knoth K. M., Walbridge J. A., Kroemer H., Roden D. M., Glover D. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of two voltage-gated K+ channel cDNAs from human ventricle. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):331–337. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.2001794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. Aminopyridine block of transient potassium current. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jul;80(1):1–18. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat J., Hess P. Evidence for cooperative interactions in potassium channel gating. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):420–423. doi: 10.1038/359420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht W., Wagner H. H. Block of potassium channels of the nodal membrane by 4-aminopyridine and its partial removal on depolarization. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Nov 30;367(1):77–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00583659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Kunkel D. D., Martin T. M., Schwartzkroin P. A., Tempel B. L. Heteromultimeric K+ channels in terminal and juxtaparanodal regions of neurons. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):75–79. doi: 10.1038/365075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao J. A., Tseng G. N. Modulation of 4-AP block of a mammalian A-type K channel clone by channel gating and membrane voltage. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):130–142. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80462-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Dynamics of aminopyridine block of potassium channels in squid axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Nov;68(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


