Abstract
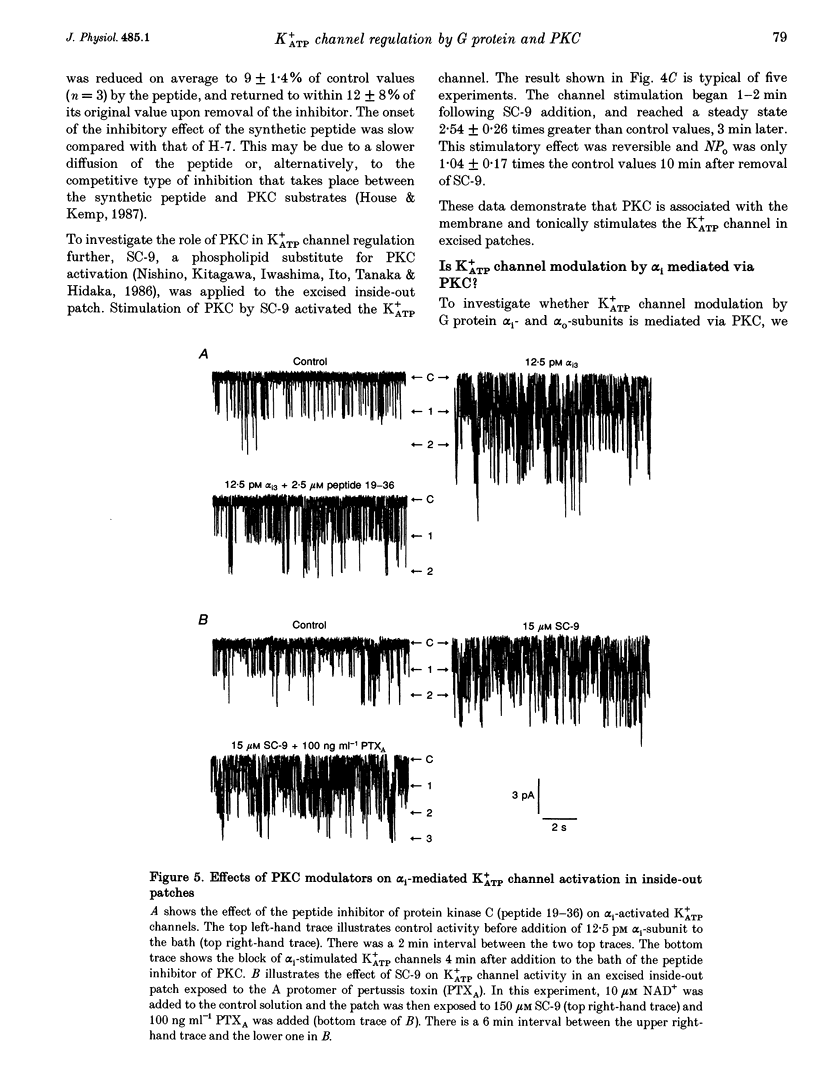
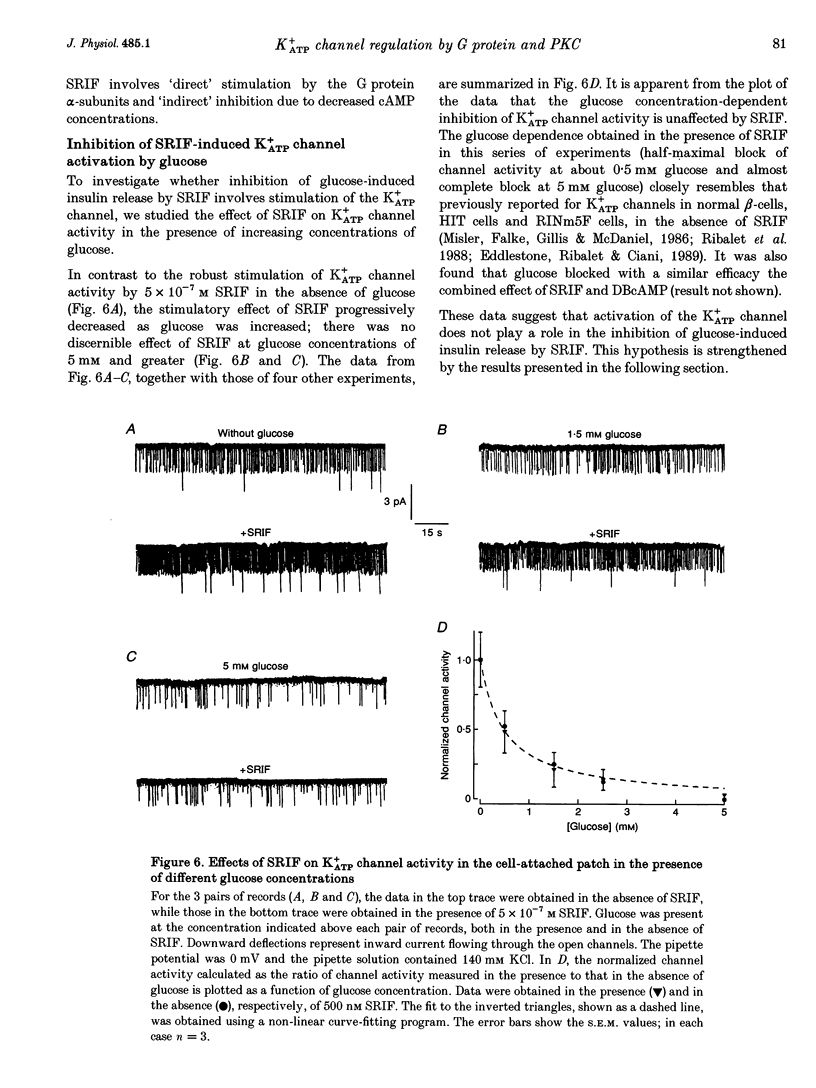
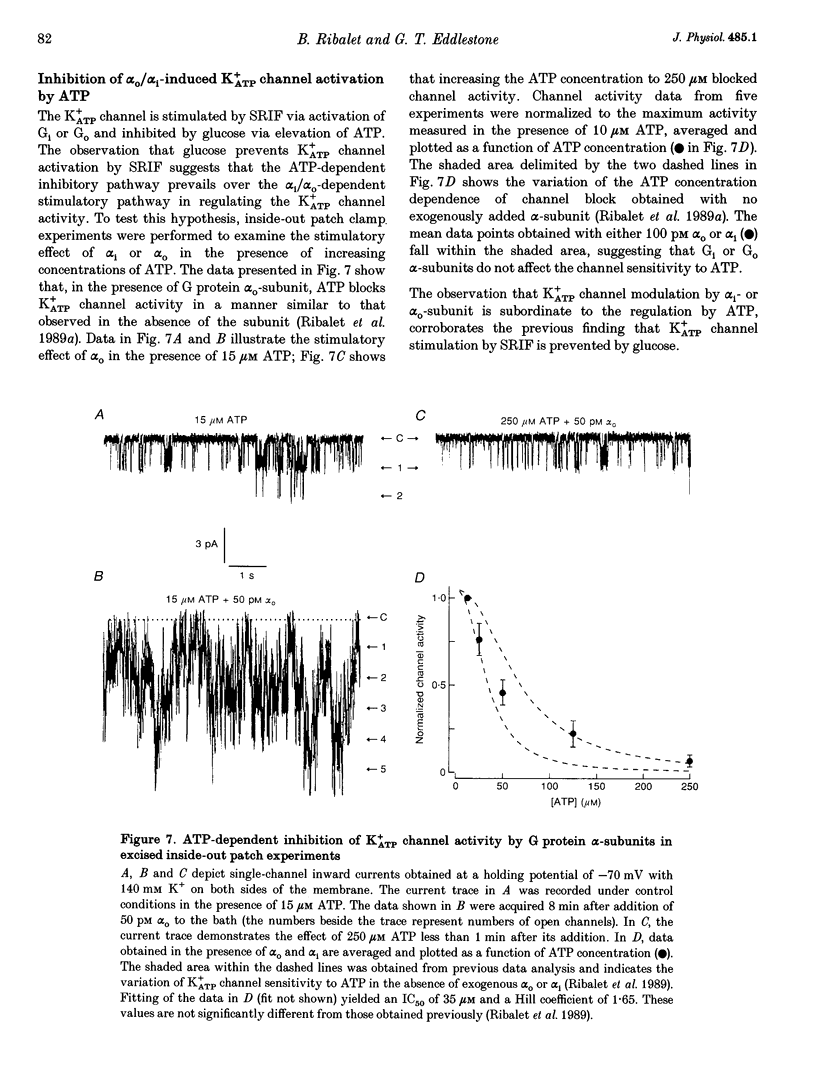
1. The G protein-mediated coupling of a somatostatin (somatotropin-releasing inhibitory factor; SRIF) receptor to the ATP-dependent K+ channel (K+ATP channel) has been studied in insulin-secreting cells using the patch clamp technique. 2. In excised outside-out patches, the concentration-dependent stimulation of the K+ATP channel by SRIF was biphasic. Stimulation reached a maximum at 15 nM (EC50 = 5.5 nM), then decayed to a minimum at 50 nM and returned to maximum stimulation at 500 nM. 3. In cell-attached patches, bath-applied SRIF caused K+ATP channel stimulation in most experiments. In a few cases, however, SRIF suppressed channel activity, a response that was reversed by addition of dibutyryl cyclic AMP (DBcAMP). Channel stimulation by SRIF or by DBcAMP did not occur in the presence of glucose. 4. In excised inside-out patches, the alpha-subunits of Gi or G(o)-type G proteins stimulated the K+ATP channel (EC50 = 29 and 42 pM, respectively). The K+ATP channel stimulation by alpha i- or alpha o-subunits had no effect on the concentration-dependent inhibition by ATP. 5. In excised inside-out patches, K+ATP channel activity was reduced by inhibitors of protein kinase C (PKC) and stimulated by a PKC activator. The stimulatory effect of PKC was unaffected by the presence of pertussis toxin, but stimulation by exogenous alpha-subunits of the G protein Gi or G(o) was prevented by PKC inhibitors. 6. From these data we deduce that SRIF can affect K+ATP channel activity directly via a membrane-delimited pathway or indirectly via a pathway requiring diffusible messengers. In the former case, alpha i/alpha o may either enhance PLC activity, stimulating PKC and thus inducing K+ATP channel phosphorylation with consequent increase of activity, or channel phosphorylation by PKC may facilitate a direct stimulation of the channel by alpha i/alpha o. In the latter case, an alpha i/alpha o-induced fall in cAMP contributes to reduced PKA-mediated phosphorylation and suppression of channel activity.
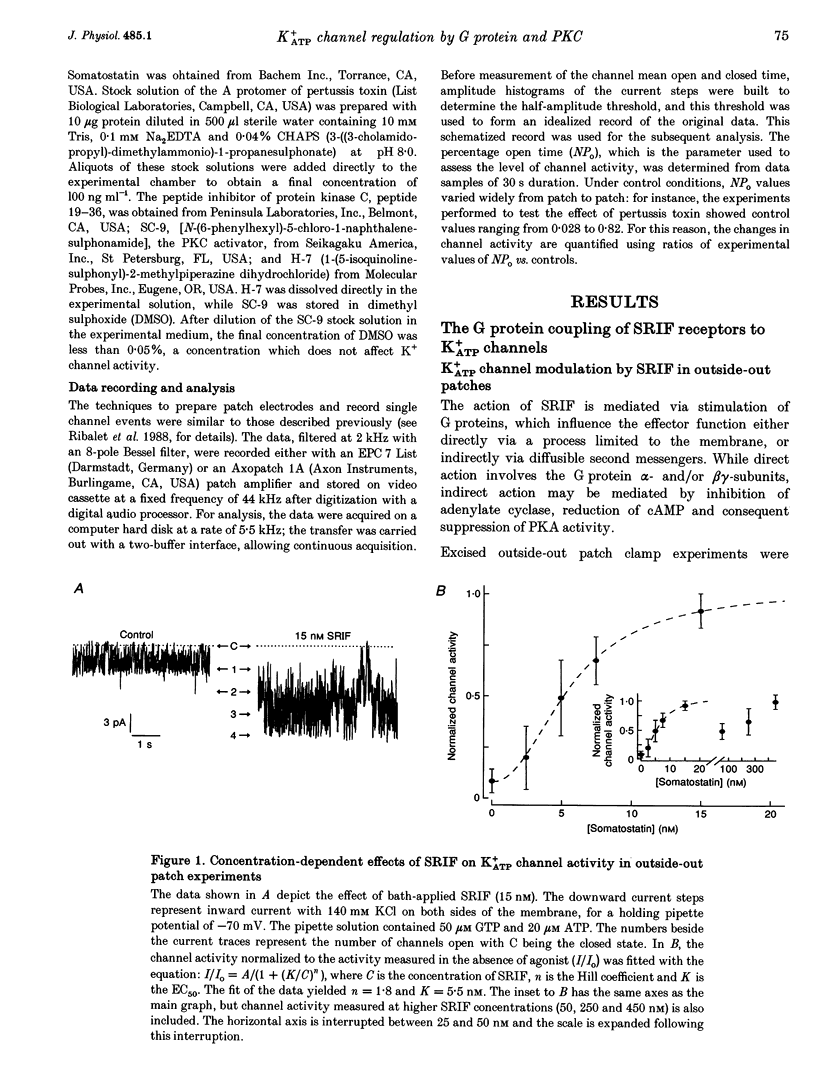
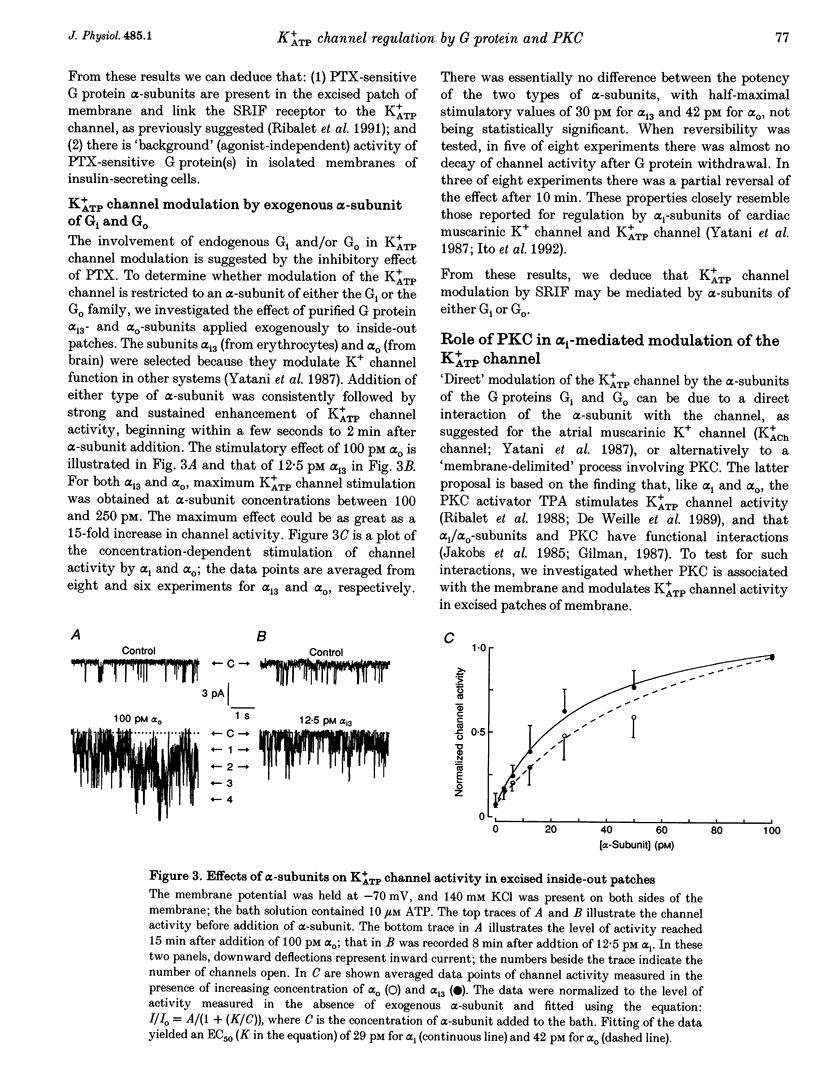
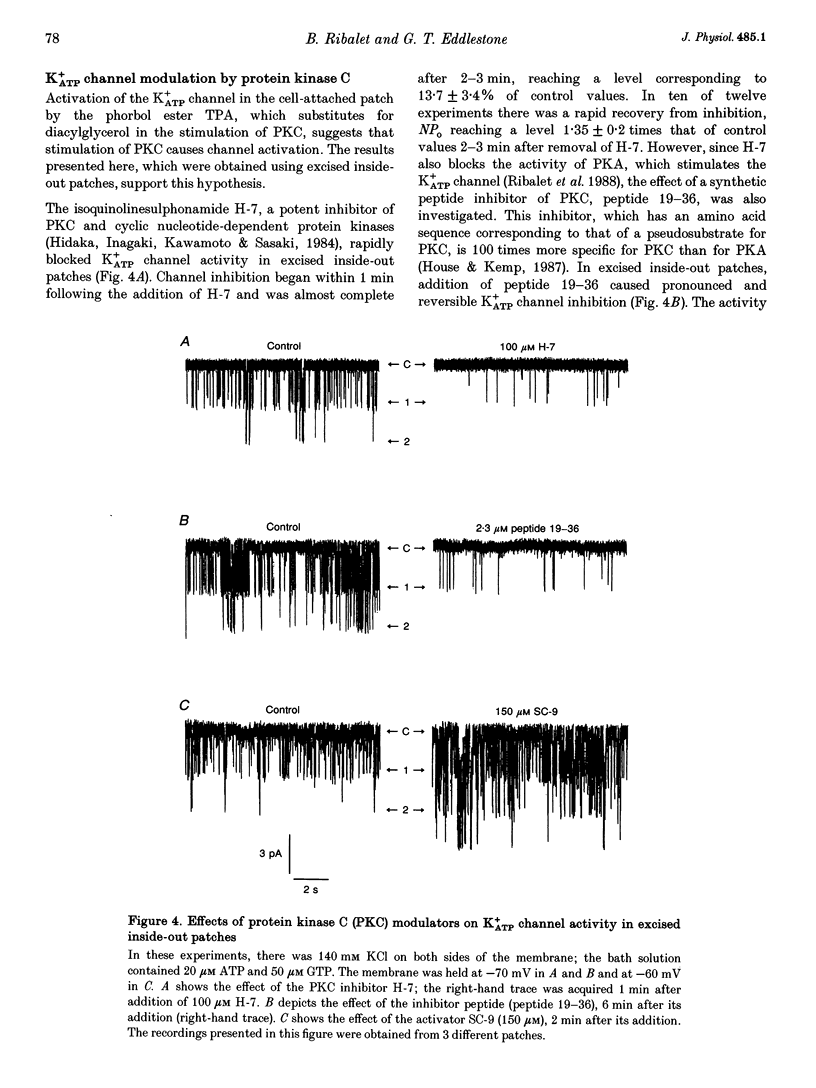
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Winslow J. W., Peralta E. G., Peterson G. L., Schimerlik M. I., Capon D. J., Ramachandran J. An M2 muscarinic receptor subtype coupled to both adenylyl cyclase and phosphoinositide turnover. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):672–675. doi: 10.1126/science.2823384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhathena S. J., Perrino P. V., Voyles N. R., Smith S. S., Wilkins S. D., Coy D. H., Schally A. V., Recant L. Reversal of somatostatin inhibition of insulin and glucagon secretion. Diabetes. 1976 Nov;25(11):1031–1040. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.11.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushfield M., Murphy G. J., Lavan B. E., Parker P. J., Hruby V. J., Milligan G., Houslay M. D. Hormonal regulation of Gi2 alpha-subunit phosphorylation in intact hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):449–457. doi: 10.1042/bj2680449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Perara E. Islet electrical pacemaker response to alpha-adrenergic stimulation. Diabetes. 1982 Nov;31(11):985–990. doi: 10.2337/diacare.31.11.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormont M., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Van Obberghen E., Spiegel A. M., Sharp G. W. Identification of G protein alpha-subunits in RINm5F cells and their selective interaction with galanin receptor. Diabetes. 1991 Sep;40(9):1170–1176. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.9.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L. Does somatostatin inhibition of insulin secretion involve two mechanisms of action? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):248–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debuyser A., Drews G., Henquin J. C. Adrenaline inhibition of insulin release: role of the repolarization of the B cell membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Sep;419(2):131–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00372998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drews G., Debuyser A., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. Galanin and epinephrine act on distinct receptors to inhibit insulin release by the same mechanisms including an increase in K+ permeability of the B-cell membrane. Endocrinology. 1990 Mar;126(3):1646–1653. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-3-1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddlestone G. T., Ribalet B., Ciani S. Comparative study of K channel behavior in beta cell lines with different secretory responses to glucose. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jul;109(2):123–134. doi: 10.1007/BF01870851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehmann H. C., Habener J. F. Insulinotropic hormone glucagon-like peptide-I(7-37) stimulation of proinsulin gene expression and proinsulin biosynthesis in insulinoma beta TC-1 cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):159–166. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1309325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. H., Xiang H. D., Rajan A. S., Kunze D. L., Boyd A. E., 3rd Somatostatin inhibits insulin secretion by a G-protein-mediated decrease in Ca2+ entry through voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the beta cell. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):837–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst R. D., Morgan N. G. Intracellular events responsible for the inhibition of insulin secretion by somatostatin. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Dec;17(6):1085–1086. doi: 10.1042/bst0171085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Tung R. T., Sugimoto T., Kobayashi I., Takahashi K., Katada T., Ui M., Kurachi Y. On the mechanism of G protein beta gamma subunit activation of the muscarinic K+ channel in guinea pig atrial cell membrane. Comparison with the ATP-sensitive K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jun;99(6):961–983. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Bauer S., Watanabe Y. Modulation of adenylate cyclase of human platelets by phorbol ester. Impairment of the hormone-sensitive inhibitory pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):425–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Two guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in rat brain serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. Interaction of the alpha-subunits with beta gamma-subunits in development of their biological activities. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8182–8191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. F., Yasuda K., Bell G. I., Reisine T. Gi alpha 3 and G(o) alpha selectively associate with the cloned somatostatin receptor subtype SSTR2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10721–10727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maletti M., Andersson M., Marie J. C., Rosselin G., Mutt V. Solubilization and partial purification of somatostatin-28 preferring receptors from hamster pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15620–15625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor F., Jr, Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Somatostatin induces translocation of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase and desensitizes somatostatin receptors in S49 lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6468–6471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino H., Kitagawa K., Iwashima A., Ito M., Tanaka T., Hidaka H. N-(6-phenylhexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide is one of a new class of activators for Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 28;889(2):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Murayama Y., Hayashi Y., Inagaki M., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. Identification of a Gs activator region of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor that is autoregulated via protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):723–730. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Tarvin J. T. Somatostatin: mechanism of action in pancreatic islet beta-cells. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):836–842. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Ciani S., Eddlestone G. T. ATP mediates both activation and inhibition of K(ATP) channel activity via cAMP-dependent protein kinase in insulin-secreting cell lines. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Oct;94(4):693–717. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Eddlestone G. T., Ciani S. Metabolic regulation of the K(ATP) and a maxi-K(V) channel in the insulin-secreting RINm5F cell. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):219–237. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Bokvist K., Ammälä C., Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O., Larsson O., Wåhlander K. Activation by adrenaline of a low-conductance G protein-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B cells. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):77–79. doi: 10.1038/349077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashima T., Katada T., Oinuma M., Inoue Y., Ui M. Endocrine cells in pancreatic islets of Langerhans are immunoreactive to antibody against guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Go) purified from rat brain. Brain Res. 1987 Aug 4;417(1):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Wollheim C. B. GTP-dependent inhibition of insulin secretion by epinephrine in permeabilized RINm5F cells. Lack of correlation between insulin secretion and cyclic AMP levels. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8615–8620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Van Dop C., Neer E. J., Snyder S. H. Go, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain resembles distribution of second messenger systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4561–4565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct activation of mammalian atrial muscarinic potassium channels by GTP regulatory protein Gk. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2432660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue D. T., Herzig S., Marban E. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of calcium channels occurs by potentiation of high-activity gating modes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):753–757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weille J. R., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Regulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in insulinoma cells: activation by somatostatin and protein kinase C and the role of cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2971–2975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]